Android 局域网内功能模块开发,教你怎么快速获取局域网内所有IP并且进行通信------ MulticastSocket
在当今的互联网时代,很多互联网公司、方案公司、智能设备公司或多或少都会接触一些局域网内的相关开发,比如某公司研发了一个app,该app需求是在局域网和网域网都可以获取自己好友的消息或信息,网域网下技术人员可以通过服务器转接信息和发送,实现交互,但是在非联网的局域网下使用部分非使用网络的功能,这就需要研究一些比较不常用的类,在通常情况下,可能大部分人首先想到的肯定是0-255的逐个去ping,这样效率超级低!而且粗暴的方式还可能导致oom,之前说到的 ping ,就是比如局域网下发射信号的主机即服务器,这里我就形象的说是路由器吧,比如路由器的ip是192.168.0.1,那连接它的其他设备的ip被分配的ip也是192.168.0.xxx,这里的xxx是一个取值范围0-255,很多时候大家为了方便就采用循环来对0-255这样的一个一个的去ping,也就是像192.168.0.2、192.168.0.3......这样一直到255,效率非常慢。。。
所以今天就给大家分享一个好东西,java.net.MulticastSocket
MulticastSocket 继承自 DatagramSocket
/*
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
* contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
* this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
* The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
* (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
* the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package java.net;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import libcore.io.IoUtils;
/**
* This class implements a multicast socket for sending and receiving IP
* multicast datagram packets.
*
* @see DatagramSocket
*/
public class MulticastSocket extends DatagramSocket {
/**
* Stores the address supplied to setInterface so we can return it from getInterface. The
* translation to an interface index is lossy because an interface can have multiple addresses.
*/
private InetAddress setAddress;
/**
* Constructs a multicast socket, bound to any available port on the
* local host.
*
* @throws IOException if an error occurs.
*/
public MulticastSocket() throws IOException {
setReuseAddress(true);
}
/**
* Constructs a multicast socket, bound to the specified {@code port} on the
* local host.
*
* @throws IOException if an error occurs.
*/
public MulticastSocket(int port) throws IOException {
super(port);
setReuseAddress(true);
}
/**
* Constructs a {@code MulticastSocket} bound to the address and port specified by
* {@code localAddress}, or an unbound {@code MulticastSocket} if {@code localAddress == null}.
*
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code localAddress} is not supported (because it's not
* an {@code InetSocketAddress}, say).
* @throws IOException if an error occurs.
*/
public MulticastSocket(SocketAddress localAddress) throws IOException {
super(localAddress);
setReuseAddress(true);
}
/**
* Returns an address of the outgoing network interface used by this socket. To avoid
* inherent unpredictability, new code should use {@link #getNetworkInterface} instead.
*
* @throws SocketException if an error occurs.
*/
public InetAddress getInterface() throws SocketException {
checkOpen();
if (setAddress != null) {
return setAddress;
}
InetAddress ipvXaddress = (InetAddress) impl.getOption(SocketOptions.IP_MULTICAST_IF);
if (ipvXaddress.isAnyLocalAddress()) {
// the address was not set at the IPv4 level so check the IPv6
// level
NetworkInterface theInterface = getNetworkInterface();
if (theInterface != null) {
Enumeration addresses = theInterface.getInetAddresses();
if (addresses != null) {
while (addresses.hasMoreElements()) {
InetAddress nextAddress = addresses.nextElement();
if (nextAddress instanceof Inet6Address) {
return nextAddress;
}
}
}
}
}
return ipvXaddress;
}
/**
* Returns the outgoing network interface used by this socket.
*
* @throws SocketException if an error occurs.
*/
public NetworkInterface getNetworkInterface() throws SocketException {
checkOpen();
int index = (Integer) impl.getOption(SocketOptions.IP_MULTICAST_IF2);
if (index != 0) {
return NetworkInterface.getByIndex(index);
}
return NetworkInterface.forUnboundMulticastSocket();
}
/**
* Returns the time-to-live (TTL) for multicast packets sent on this socket.
*
* @throws IOException if an error occurs.
*/
public int getTimeToLive() throws IOException {
checkOpen();
return impl.getTimeToLive();
}
/**
* Returns the time-to-live (TTL) for multicast packets sent on this socket.
*
* @throws IOException if an error occurs.
* @deprecated Use {@link #getTimeToLive} instead.
*/
@Deprecated
public byte getTTL() throws IOException {
checkOpen();
return impl.getTTL();
}
/**
* Adds this socket to the specified multicast group. A socket must join a
* group before data may be received. A socket may be a member of multiple
* groups but may join any group only once.
*
* @param groupAddr
* the multicast group to be joined.
* @throws IOException if an error occurs.
*/
public void joinGroup(InetAddress groupAddr) throws IOException {
checkJoinOrLeave(groupAddr);
impl.join(groupAddr);
}
/**
* Adds this socket to the specified multicast group. A socket must join a
* group before data may be received. A socket may be a member of multiple
* groups but may join any group only once.
*
* @param groupAddress
* the multicast group to be joined.
* @param netInterface
* the network interface on which the datagram packets will be
* received.
* @throws IOException
* if the specified address is not a multicast address.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException
* if no multicast group is specified.
*/
public void joinGroup(SocketAddress groupAddress, NetworkInterface netInterface) throws IOException {
checkJoinOrLeave(groupAddress, netInterface);
impl.joinGroup(groupAddress, netInterface);
}
/**
* Removes this socket from the specified multicast group.
*
* @param groupAddr
* the multicast group to be left.
* @throws NullPointerException
* if {@code groupAddr} is {@code null}.
* @throws IOException
* if the specified group address is not a multicast address.
*/
public void leaveGroup(InetAddress groupAddr) throws IOException {
checkJoinOrLeave(groupAddr);
impl.leave(groupAddr);
}
/**
* Removes this socket from the specified multicast group.
*
* @param groupAddress
* the multicast group to be left.
* @param netInterface
* the network interface on which the addresses should be
* dropped.
* @throws IOException
* if the specified group address is not a multicast address.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException
* if {@code groupAddress} is {@code null}.
*/
public void leaveGroup(SocketAddress groupAddress, NetworkInterface netInterface) throws IOException {
checkJoinOrLeave(groupAddress, netInterface);
impl.leaveGroup(groupAddress, netInterface);
}
private void checkJoinOrLeave(SocketAddress groupAddress, NetworkInterface netInterface) throws IOException {
checkOpen();
if (groupAddress == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("groupAddress == null");
}
if (netInterface != null && !netInterface.getInetAddresses().hasMoreElements()) {
throw new SocketException("No address associated with interface: " + netInterface);
}
if (!(groupAddress instanceof InetSocketAddress)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Group address not an InetSocketAddress: " +
groupAddress.getClass());
}
InetAddress groupAddr = ((InetSocketAddress) groupAddress).getAddress();
if (groupAddr == null) {
throw new SocketException("Group address has no address: " + groupAddress);
}
if (!groupAddr.isMulticastAddress()) {
throw new IOException("Not a multicast group: " + groupAddr);
}
}
private void checkJoinOrLeave(InetAddress groupAddr) throws IOException {
checkOpen();
if (groupAddr == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("groupAddress == null");
}
if (!groupAddr.isMulticastAddress()) {
throw new IOException("Not a multicast group: " + groupAddr);
}
}
/**
* Sends the given {@code packet} on this socket, using the given {@code ttl}. This method is
* deprecated because it modifies the TTL socket option for this socket twice on each call.
*
* @throws IOException if an error occurs.
* @deprecated Use {@link #setTimeToLive} instead.
*/
@Deprecated
public void send(DatagramPacket packet, byte ttl) throws IOException {
checkOpen();
InetAddress packAddr = packet.getAddress();
int currTTL = getTimeToLive();
if (packAddr.isMulticastAddress() && (byte) currTTL != ttl) {
try {
setTimeToLive(ttl & 0xff);
impl.send(packet);
} finally {
setTimeToLive(currTTL);
}
} else {
impl.send(packet);
}
}
/**
* Sets the outgoing network interface used by this socket. The interface used is the first
* interface found to have the given {@code address}. To avoid inherent unpredictability,
* new code should use {@link #getNetworkInterface} instead.
*
* @throws SocketException if an error occurs.
*/
public void setInterface(InetAddress address) throws SocketException {
checkOpen();
if (address == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("address == null");
}
NetworkInterface networkInterface = NetworkInterface.getByInetAddress(address);
if (networkInterface == null) {
throw new SocketException("Address not associated with an interface: " + address);
}
impl.setOption(SocketOptions.IP_MULTICAST_IF2, networkInterface.getIndex());
this.setAddress = address;
}
/**
* Sets the outgoing network interface used by this socket to the given
* {@code networkInterface}.
*
* @throws SocketException if an error occurs.
*/
public void setNetworkInterface(NetworkInterface networkInterface) throws SocketException {
checkOpen();
if (networkInterface == null) {
throw new SocketException("networkInterface == null");
}
impl.setOption(SocketOptions.IP_MULTICAST_IF2, networkInterface.getIndex());
this.setAddress = null;
}
/**
* Sets the time-to-live (TTL) for multicast packets sent on this socket.
* Valid TTL values are between 0 and 255 inclusive.
*
* @throws IOException if an error occurs.
*/
public void setTimeToLive(int ttl) throws IOException {
checkOpen();
if (ttl < 0 || ttl > 255) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("TimeToLive out of bounds: " + ttl);
}
impl.setTimeToLive(ttl);
}
/**
* Sets the time-to-live (TTL) for multicast packets sent on this socket.
* Valid TTL values are between 0 and 255 inclusive.
*
* @throws IOException if an error occurs.
* @deprecated Use {@link #setTimeToLive} instead.
*/
@Deprecated
public void setTTL(byte ttl) throws IOException {
checkOpen();
impl.setTTL(ttl);
}
@Override
synchronized void createSocket(int aPort, InetAddress addr) throws SocketException {
impl = factory != null ? factory.createDatagramSocketImpl() : new PlainDatagramSocketImpl();
impl.create();
try {
impl.setOption(SocketOptions.SO_REUSEADDR, Boolean.TRUE);
impl.bind(aPort, addr);
isBound = true;
} catch (SocketException e) {
close();
throw e;
}
}
/**
* Returns true if multicast loopback is disabled.
* See {@link SocketOptions#IP_MULTICAST_LOOP}, and note that the sense of this is the
* opposite of the underlying Unix {@code IP_MULTICAST_LOOP}.
*
* @throws SocketException if an error occurs.
*/
public boolean getLoopbackMode() throws SocketException {
checkOpen();
return !((Boolean) impl.getOption(SocketOptions.IP_MULTICAST_LOOP)).booleanValue();
}
/**
* Disables multicast loopback if {@code disable == true}.
* See {@link SocketOptions#IP_MULTICAST_LOOP}, and note that the sense of this is the
* opposite of the underlying Unix {@code IP_MULTICAST_LOOP}: true means disabled, false
* means enabled.
*
* @throws SocketException if an error occurs.
*/
public void setLoopbackMode(boolean disable) throws SocketException {
checkOpen();
impl.setOption(SocketOptions.IP_MULTICAST_LOOP, Boolean.valueOf(!disable));
}
}
了解一下该类后可以开始下面的编程,首先说一下客户端,再说服务端,最后说明使用方法
①客户端代码核心:
@Override
protected void onResume() {
super.onResume();
/**
* @author Engineer-Jsp
* 笔者在该 Activity 的 onResume()函数初始化接收的侦听
*/
onBrodacastReceiver();
} MulticastSocket multicastSocket;
/**
* @author Engineer-Jsp
* onBrodacastReceiver()
*/
private void onBrodacastReceiver() {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
// 接收数据时需要指定监听的端口号
multicastSocket = new MulticastSocket(10001);
// 创建组播ID地址
InetAddress address = InetAddress.getByName("239.0.0.1");
// 加入地址
multicastSocket.joinGroup(address);
// 包长
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
while (true) {
// 数据报
DatagramPacket datagramPacket = new DatagramPacket(buf, buf.length);
// 接收数据,同样会进入阻塞状态
multicastSocket.receive(datagramPacket);
// 从buffer中截取收到的数据
byte[] message = new byte[datagramPacket.getLength()];
// 数组拷贝
System.arraycopy(buf, 0, message, 0, datagramPacket.getLength());
// 打印来自组播里其他服务的or客户端的ip
System.out.println(datagramPacket.getAddress());
// 打印来自组播里其他服务的or客户端的消息
System.out.println(new String(message));
// 收到消息后可以进行记录然后二次确认,如果只是想获取ip,在发送方收到该消息后可关闭套接字,从而释放资源
onBrodacastSend(datagramPacket.getAddress());
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
}③ onBrodacastSend() 函数
/**
* onBrodacastSend()
* @author Engineer-Jsp
* @param address ip
*/
private void onBrodacastSend(InetAddress address) {
// 假设 239.0.0.1 已经收到了来自其他组ip段的消息,为了进行二次确认,发送 "snoop"
// 进行确认,当发送方收到该消息可以释放资源
String out = "snoop";
// 获取"snoop"的字节数组
byte[] buf = out.getBytes();
// 组报
DatagramPacket datagramPacket = new DatagramPacket(buf, buf.length);
// 设置地址,该地址来自onBrodacastReceiver()函数阻塞数据报,datagramPacket.getAddress()
datagramPacket.setAddress(address);
// 发送的端口号
datagramPacket.setPort(8082);
try {
// 开始发送
multicastSocket.send(datagramPacket);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}这是客户端的代码,下面开始上服务端的代码
①初始化
@Override
protected void onResume() {
super.onResume();
/**
* @author Engineer-Jsp
* 笔者在该 Activity 的 onResume()函数初始化接收和发送
* onBrodacastSend() 发送
* onBrodacastReceiver() 接收
*/
onBrodacastSend();
onBrodacastReceiver();
} InetAddress address;
MulticastSocket multicastSocket;
/**
* @author Engineer-Jsp
* onBrodacastSend() 发送
*/
private void onBrodacastSend() {
try {
// 侦听的端口
multicastSocket = new MulticastSocket(8082);
// 使用D类地址,该地址为发起组播的那个ip段,即侦听10001的套接字
address = InetAddress.getByName("239.0.0.1");
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
while (true) {
// 获取当前时间
String time = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss").format(new Date());
// 当前时间+标识后缀
time = time + " >>> form server onBrodacastSend()";
// 获取当前时间+标识后缀的字节数组
byte[] buf = time.getBytes();
// 组报
DatagramPacket datagramPacket = new DatagramPacket(buf, buf.length);
// 向组播ID,即接收group /239.0.0.1 端口 10001
datagramPacket.setAddress(address);
// 发送的端口号
datagramPacket.setPort(10001);
try {
// 开始发送
multicastSocket.send(datagramPacket);
// 每执行一次,线程休眠2s,然后继续下一次任务
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}).start();
} catch (UnknownHostException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}③onBrodacastReceiver()函数
/**
* @author Engineer-Jsp
* onBrodacastReceiver() 接收
*/
private void onBrodacastReceiver() {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
// 字节数组的格式,即最大大小
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
while (true) {
// 组报格式
DatagramPacket datagramPacket = new DatagramPacket(buf, buf.length);
// 接收来自group组播10001端口的二次确认,阻塞
multicastSocket.receive(datagramPacket);
// 从buf中截取收到的数据
byte[] message = new byte[datagramPacket.getLength()];
// 数组拷贝
System.arraycopy(buf, 0, message, 0, datagramPacket.getLength());
// 这里打印ip字段
System.out.println(datagramPacket.getAddress());
// 打印组播端口10001发送过来的消息
System.out.println(new String(message));
// 这里可以根据结接收到的内容进行分发处理,假如收到 10001的 "snoop"字段为关闭命令,即可在此处关闭套接字从而释放资源
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
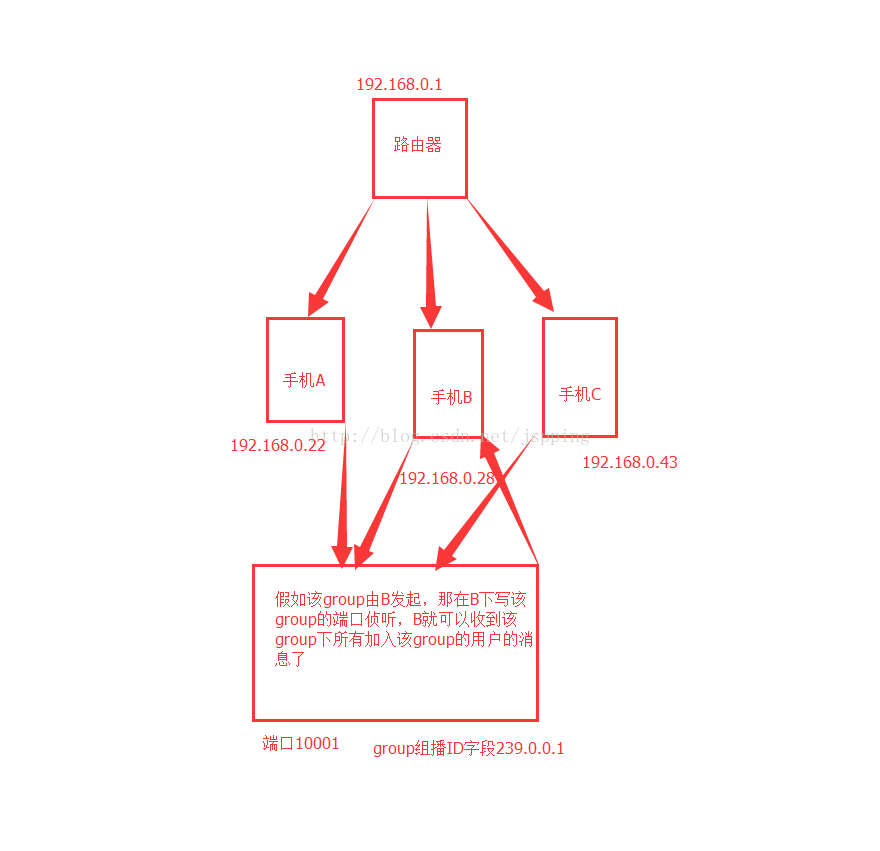
}这是服务端的代码,也分享完了,下面画一个图来大概描述一下他们的工作流程图示意:
使用方法:①首先需要在同一wifi网络下 ②需要获取所有ip的手机安装客户端,即侦听10001的那个端口 ③所有需要将信息共享并组播到 239.0.0.1:10001这个group的安装服务端 ④开启服务端与客户端开始进行数据的交互
以上是大致的描述图,帮助大家理解,谢谢观博!