Redis应用与原理(3) Redis分布式锁实现
什么是分布式锁?
分布式锁是控制分布式系统之间同步访问共享资源的一种方式。在分布式系统中,常常需要协调他们的动作。如果不同的系统或是同一个系统的不同主机之间共享了一个或一组资源,那么访问这些资源的时候,往往需要互斥来防止彼此干扰来保证一致性,在这种情况下,便需要使用到分布式锁。
实现分布式锁的几种方案:
- MySQL乐观锁
- Redis分布式锁
- ZooKeeper分布式锁
方案一实现简单,但是并发性能较差,高并发场景往往采用方案二、三。本文介绍方案二。
1. 使用redis的setnx()、get()、getset()方法,用于分布式锁
原理
这个方案的背景主要是在setnx()和expire()的方案上针对可能存在的死锁问题,做了一版优化。
那么先说明一下这三个命令,对于setnx()和get()这两个命令,相信不用再多说什么。那么getset()命令?这个命令主要有两个参数 getset(key,newValue)。该方法是原子的,对key设置newValue这个值,并且返回key原来的旧值。假设key原来是不存在的,那么多次执行这个命令,会出现下边的效果:
- getset(key, “value1”) 返回nil 此时key的值会被设置为value1
- getset(key, “value2”) 返回value1 此时key的值会被设置为value2
- 依次类推!
介绍完要使用的命令后,具体的使用步骤如下:
- setnx(lockkey, 当前时间+过期超时时间) ,如果返回1,则获取锁成功;如果返回0则没有获取到锁,转向2。
- get(lockkey)获取值oldExpireTime ,并将这个value值与当前的系统时间进行比较,如果小于当前系统时间,则认为这个锁已经超时,可以允许别的请求重新获取,转向3。
- 计算newExpireTime=当前时间+过期超时时间,然后getset(lockkey, newExpireTime) 会返回当前lockkey的值currentExpireTime。
- 判断currentExpireTime与oldExpireTime 是否相等,如果相等,说明当前getset设置成功,获取到了锁。如果不相等,说明这个锁又被别的请求获取走了,那么当前请求可以直接返回失败,或者继续重试。
- 在获取到锁之后,当前线程可以开始自己的业务处理,当处理完毕后,比较自己的处理时间和对于锁设置的超时时间,如果小于锁设置的超时时间,则直接执行delete释放锁;如果大于锁设置的超时时间,则不需要再锁进行处理。
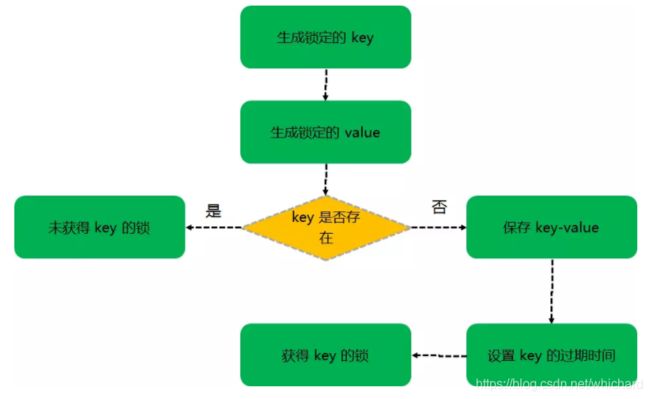
实现
public final class RedisLockUtil {
private static final int defaultExpire = 60;
private RedisLockUtil() {
//
}
/**
* 加锁
* @param key redis key
* @param expire 过期时间,单位秒
* @return true:加锁成功,false,加锁失败
*/
public static boolean lock(String key, int expire) {
RedisService redisService = SpringUtils.getBean(RedisService.class);
long status = redisService.setnx(key, "1");
if(status == 1) {
redisService.expire(key, expire);
return true;
}
return false;
}
public static boolean lock(String key) {
return lock2(key, defaultExpire);
}
/**
* 加锁
* @param key redis key
* @param expire 过期时间,单位秒
* @return true:加锁成功,false,加锁失败
*/
public static boolean lock2(String key, int expire) {
RedisService redisService = SpringUtils.getBean(RedisService.class);
long value = System.currentTimeMillis() + expire;
long status = redisService.setnx(key, String.valueOf(value));
if(status == 1) {
return true;
}
long oldExpireTime = Long.parseLong(redisService.get(key, "0"));
if(oldExpireTime < System.currentTimeMillis()) {
//超时
long newExpireTime = System.currentTimeMillis() + expire;
long currentExpireTime = Long.parseLong(redisService.getSet(key, String.valueOf(newExpireTime)));
if(currentExpireTime == oldExpireTime) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public static void unLock1(String key) {
RedisService redisService = SpringUtils.getBean(RedisService.class);
redisService.del(key);
}
public static void unLock2(String key) {
RedisService redisService = SpringUtils.getBean(RedisService.class);
long oldExpireTime = Long.parseLong(redisService.get(key, "0"));
if(oldExpireTime > System.currentTimeMillis()) {
redisService.del(key);
}
}
}
使用
public void drawRedPacket(long userId) {
String key = "draw.redpacket.userid:" + userId;
boolean lock = RedisLockUtil.lock2(key, 60);
if(lock) {
try {
//领取操作
} finally {
//释放锁
RedisLockUtil.unLock(key);
}
} else {
new RuntimeException("重复领取奖励");
}
}
可能存在的问题
问题: 在“get(lockkey)获取值oldExpireTime ”这个操作与“getset(lockkey, newExpireTime) ”这个操作之间,如果有N个线程在get操作获取到相同的oldExpireTime后,然后都去getset,假设第1个线程获取锁成功,其他锁获取失败,但是获取锁失败的线程它发起的getset命令确实执行了,这样会不会造成第一个获取锁的线程设置的锁超时时间一直在延长?
我认为这套方案确实存在这个问题的可能。但我个人认为这个微小的误差是可以忽略的,不过技术方案上存在缺陷,大家可以自行抉择哈。
问题: 这个方案必须要保证分布式服务器的时间一定要同步,否则这个锁就会出问题。
2. 基于AOP的Redis 分布式锁
在实际的使用过程中,分布式锁可以封装好后使用在方法级别,这样就不用每个地方都去获取锁和释放锁,使用起来更加方便。
- 首先定义个注解:
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Inherited;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* @author fuwei.deng
* @date 2017年6月14日 下午3:10:36
* @version 1.0.0
*/
@Target({ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
public @interface RedisLock {
/** 锁的资源,redis的key*/
String value() default "default";
/** 持锁时间,单位毫秒*/
long keepMills() default 30000;
/** 当获取失败时候动作*/
LockFailAction action() default LockFailAction.CONTINUE;
public enum LockFailAction{
/** 放弃 */
GIVEUP,
/** 继续 */
CONTINUE;
}
/** 重试的间隔时间,设置GIVEUP忽略此项*/
long sleepMills() default 200;
/** 重试次数*/
int retryTimes() default 5;
}
- 装配分布式锁的bean
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigureAfter;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnBean;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis.RedisAutoConfiguration;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import com.itopener.lock.redis.spring.boot.autoconfigure.lock.DistributedLock;
import com.itopener.lock.redis.spring.boot.autoconfigure.lock.RedisDistributedLock;
@Configuration
@AutoConfigureAfter(RedisAutoConfiguration.class)
public class DistributedLockAutoConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnBean(RedisTemplate.class)
public DistributedLock redisDistributedLock(RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate){
return new RedisDistributedLock(redisTemplate);
}
}
- 定义切面(spring boot配置方式)
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Arrays;
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfigureAfter;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnClass;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import com.itopener.lock.redis.spring.boot.autoconfigure.annotations.RedisLock;
import com.itopener.lock.redis.spring.boot.autoconfigure.annotations.RedisLock.LockFailAction;
import com.itopener.lock.redis.spring.boot.autoconfigure.lock.DistributedLock;
/**
* @author fuwei.deng
* @date 2017年6月14日 下午3:11:22
* @version 1.0.0
*/
@Aspect
@Configuration
@ConditionalOnClass(DistributedLock.class)
@AutoConfigureAfter(DistributedLockAutoConfiguration.class)
public class DistributedLockAspectConfiguration {
private final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(DistributedLockAspectConfiguration.class);
@Autowired
private DistributedLock distributedLock;
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.itopener.lock.redis.spring.boot.autoconfigure.annotations.RedisLock)")
private void lockPoint(){
}
@Around("lockPoint()")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable{
Method method = ((MethodSignature) pjp.getSignature()).getMethod();
RedisLock redisLock = method.getAnnotation(RedisLock.class);
String key = redisLock.value();
if(StringUtils.isEmpty(key)){
Object[] args = pjp.getArgs();
key = Arrays.toString(args);
}
int retryTimes = redisLock.action().equals(LockFailAction.CONTINUE) ? redisLock.retryTimes() : 0;
boolean lock = distributedLock.lock(key, redisLock.keepMills(), retryTimes, redisLock.sleepMills());
if(!lock) {
logger.debug("get lock failed : " + key);
return null;
}
//得到锁,执行方法,释放锁
logger.debug("get lock success : " + key);
try {
return pjp.proceed();
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("execute locked method occured an exception", e);
} finally {
boolean releaseResult = distributedLock.releaseLock(key);
logger.debug("release lock : " + key + (releaseResult ? " success" : " failed"));
}
return null;
}
}
- spring boot starter还需要在 resources/META-INF 中添加 spring.factories 文件
# Auto Configure
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
com.itopener.lock.redis.spring.boot.autoconfigure.DistributedLockAutoConfiguration,\
com.itopener.lock.redis.spring.boot.autoconfigure.DistributedLockAspectConfiguration
这样封装之后,使用spring boot开发的项目,直接依赖这个starter,就可以在方法上加 RedisLock 注解来实现分布式锁的功能了,当然如果需要自己控制,直接注入分布式锁的bean即可
@Autowired
private DistributedLock distributedLock;
如果需要使用其他的分布式锁实现,继承 AbstractDistributedLock 后实现获取锁和释放锁的方法即可