走进tensorflow第三步——MNIST手写数字分类问题(进阶篇)
接着来吧,用卷积神经网络使结果更加精确……
上代码:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('MNIST_data',one_hot=True)
sess = tf.InteractiveSession()
def weight_variable(shape):
initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape, stddev=0.1)
return tf.Variable(initial)
def bias_variable(shape):
initial = tf.constant(0.1, shape=shape)
return tf.Variable(initial)
def conv2d(x, W):
return tf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
def max_pool_2x2(x):
return tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1],
strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
x = tf.placeholder("float", [None, 784])
W = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784,10]))
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]))
y = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(x,W) + b)
y_ = tf.placeholder("float", [None,10])
W_conv1 = weight_variable([5, 5, 1, 32])
b_conv1 = bias_variable([32])
x_image = tf.reshape(x, [-1,28,28,1])
h_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(x_image, W_conv1) + b_conv1)
h_pool1 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv1)
W_conv2 = weight_variable([5, 5, 32, 64])
b_conv2 = bias_variable([64])
h_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(h_pool1, W_conv2) + b_conv2)
h_pool2 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv2)
W_fc1 = weight_variable([7 * 7 * 64, 1024])
b_fc1 = bias_variable([1024])
h_pool2_flat = tf.reshape(h_pool2, [-1, 7*7*64])
h_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_pool2_flat, W_fc1) + b_fc1)
keep_prob = tf.placeholder("float")
h_fc1_drop = tf.nn.dropout(h_fc1, keep_prob)
W_fc2 = weight_variable([1024, 10])
b_fc2 = bias_variable([10])
y_conv=tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(h_fc1_drop, W_fc2) + b_fc2)
cross_entropy = -tf.reduce_sum(y_*tf.log(y_conv))
train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(1e-4).minimize(cross_entropy)
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y_conv,1), tf.argmax(y_,1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, "float"))
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for i in range(20000):
batch = mnist.train.next_batch(50)
if i%100 == 0:
train_accuracy = accuracy.eval(feed_dict={
x:batch[0], y_: batch[1], keep_prob: 1.0})
print("step %d, training accuracy %g"%(i, train_accuracy))
train_step.run(feed_dict={x: batch[0], y_: batch[1], keep_prob: 0.5})
print("test accuracy %g"%accuracy.eval(feed_dict={
x: mnist.test.images, y_: mnist.test.labels, keep_prob: 1.0}))关于代码细节大家可以去看上篇中提到的官方文档,有个进阶篇~~建议大家每行代码都过一遍,会有很多收获,在这里遇到一个坑,先看下错误提醒
session的问题,一定要注意,在计算之前一定要初始化变量,然后启动session,我之前调了一下,各种尝试,最后终于整对了~~~这个错误提示一般就是在初始化变量之前访问了它,那就得注意一下sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())的位置了,还有一开始的sess = tf.InteractiveSession(),这个文档里有详细的说明,真的要一条条仔细看……
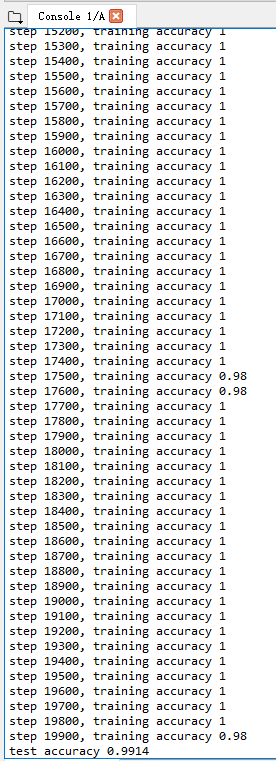
运行了20000次,tensorflow是cpu的,用的时间有点长,看效果吧:
最后的精确度为99.14%,比上篇的精确度又提升了一个档次……