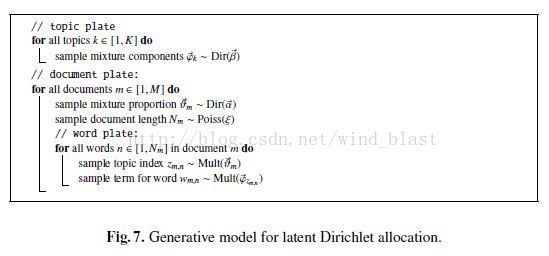
LDA(Latent dirichlet allocation)是有Blei于2003年提出的三层贝叶斯主题模型,通过无监督的学习方法发现文本中隐含的主题信息,
目的是要以无指导学习的方法从文本中发现隐含的语义维度-即“Topic”或者“Concept”。
隐性语义分析的实质是要利用文本中词项(term)的共现特征来发现文本的Topic结构,这种方法不需要任何关于文本的背景知识。
文本的隐性语义表示可以对“一词多义”和“一义多词”的语言现象进行建模,这使得搜索引擎系统得到的搜索结果与用户的query在语义层次上match,而不是仅仅只是在词汇层次上出现交集。
文档、主题以及词可以表示为下图:
LDA参数:
- K为主题个数
- M为文档总数
 是第m个文档的单词总数。
是第m个文档的单词总数。 是每个Topic下词的多项分布的Dirichlet先验参数
是每个Topic下词的多项分布的Dirichlet先验参数 是每个文档下Topic的多项分布的Dirichlet先验参数。
是每个文档下Topic的多项分布的Dirichlet先验参数。 是第m个文档中第n个词的主题
是第m个文档中第n个词的主题 是m个文档中的第n个词。
是m个文档中的第n个词。- 剩下来的两个隐含变量
 和
和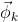 分别表示第m个文档下的Topic分布和第k个Topic下词的分布,前者是k维(k为Topic总数)向量,后者是v维向量(v为词典中term总数)
分别表示第m个文档下的Topic分布和第k个Topic下词的分布,前者是k维(k为Topic总数)向量,后者是v维向量(v为词典中term总数)
LDA生成过程:
所谓生成模型,就是说,
我们认为一篇文章的每个词都是通过“以一定概率选择了某个主题,并从这个主题中以一定概率选择某个词语”这样一个过程得到。
文档到主题服从多项式分布,主题到词服从多项式分布。
每一篇文档代表了一些主题所构成的一个概率分布,而每一个主题又代表了很多单词所构成的一个概率分布。
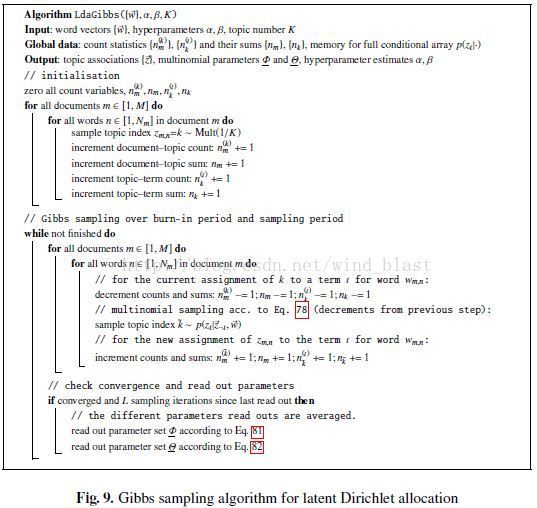
Gibbs Sampling学习LDA:
Gibbs Sampling 是Markov-Chain Monte Carlo算法的一个特例。
这个算法的运行方式是每次选取概率向量的一个维度,给定其他维度的变量值Sample当前维度的值。不断迭代,直到收敛输出待估计的参数。
- 初始时随机给文本中的每个单词分配主题
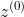
- 然后统计每个主题z下出现term t的数量以及每个文档m下出现主题z中的词的数量
- 每一轮计算,即排除当前词的主题分配,根据其他所有词的主题分配估计当前词分配各个主题的概率。
- 当得到当前词属于所有主题z的概率分布后,根据这个概率分布为该词sample一个新的主题
 。
。
然后用同样的方法不断更新下一个词的主题,直到发现每个文档下Topic分布![]() 和每个Topic下词的分布
和每个Topic下词的分布![]() 收敛,算法停止,输出待估计的参数
收敛,算法停止,输出待估计的参数![]() 和
和![]() ,最终每个单词的主题
,最终每个单词的主题![]() 也同时得出。
也同时得出。
实际应用中会设置最大迭代次数。每一次计算的公式称为Gibbs updating rule.
下面我们来推导LDA的联合分布和Gibbs updating rule。
用Gibbs Sampling 学习LDA参数的算法伪代码如下:
1 #-*- coding:utf-8 -*- 2 import logging 3 import logging.config 4 import ConfigParser 5 import numpy as np 6 import random 7 import codecs 8 import os 9 10 from collections import OrderedDict 11 #获取当前路径 12 path = os.getcwd() 13 #导入日志配置文件 14 logging.config.fileConfig("logging.conf") 15 #创建日志对象 16 logger = logging.getLogger() 17 # loggerInfo = logging.getLogger("TimeInfoLogger") 18 # Consolelogger = logging.getLogger("ConsoleLogger") 19 20 #导入配置文件 21 conf = ConfigParser.ConfigParser() 22 conf.read("setting.conf") 23 #文件路径 24 trainfile = os.path.join(path,os.path.normpath(conf.get("filepath", "trainfile"))) 25 wordidmapfile = os.path.join(path,os.path.normpath(conf.get("filepath","wordidmapfile"))) 26 thetafile = os.path.join(path,os.path.normpath(conf.get("filepath","thetafile"))) 27 phifile = os.path.join(path,os.path.normpath(conf.get("filepath","phifile"))) 28 paramfile = os.path.join(path,os.path.normpath(conf.get("filepath","paramfile"))) 29 topNfile = os.path.join(path,os.path.normpath(conf.get("filepath","topNfile"))) 30 tassginfile = os.path.join(path,os.path.normpath(conf.get("filepath","tassginfile"))) 31 #模型初始参数 32 K = int(conf.get("model_args","K")) 33 alpha = float(conf.get("model_args","alpha")) 34 beta = float(conf.get("model_args","beta")) 35 iter_times = int(conf.get("model_args","iter_times")) 36 top_words_num = int(conf.get("model_args","top_words_num")) 37 class Document(object): 38 def __init__(self): 39 self.words = [] 40 self.length = 0 41 #把整个文档及真的单词构成vocabulary(不允许重复) 42 class DataPreProcessing(object): 43 def __init__(self): 44 self.docs_count = 0 45 self.words_count = 0 46 #保存每个文档d的信息(单词序列,以及length) 47 self.docs = [] 48 #建立vocabulary表,照片文档的单词 49 self.word2id = OrderedDict() 50 def cachewordidmap(self): 51 with codecs.open(wordidmapfile, 'w','utf-8') as f: 52 for word,id in self.word2id.items(): 53 f.write(word +"\t"+str(id)+"\n") 54 class LDAModel(object): 55 def __init__(self,dpre): 56 self.dpre = dpre #获取预处理参数 57 # 58 #模型参数 59 #聚类个数K,迭代次数iter_times,每个类特征词个数top_words_num,超参数α(alpha) β(beta) 60 # 61 self.K = K 62 self.beta = beta 63 self.alpha = alpha 64 self.iter_times = iter_times 65 self.top_words_num = top_words_num 66 # 67 #文件变量 68 #分好词的文件trainfile 69 #词对应id文件wordidmapfile 70 #文章-主题分布文件thetafile 71 #词-主题分布文件phifile 72 #每个主题topN词文件topNfile 73 #最后分派结果文件tassginfile 74 #模型训练选择的参数文件paramfile 75 # 76 self.wordidmapfile = wordidmapfile 77 self.trainfile = trainfile 78 self.thetafile = thetafile 79 self.phifile = phifile 80 self.topNfile = topNfile 81 self.tassginfile = tassginfile 82 self.paramfile = paramfile 83 # p,概率向量 double类型,存储采样的临时变量 84 # nw,词word在主题topic上的分布 85 # nwsum,每各topic的词的总数 86 # nd,每个doc中各个topic的词的总数 87 # ndsum,每各doc中词的总数 88 self.p = np.zeros(self.K) 89 # nw,词word在主题topic上的分布 90 self.nw = np.zeros((self.dpre.words_count,self.K),dtype="int") 91 # nwsum,每各topic的词的总数 92 self.nwsum = np.zeros(self.K,dtype="int") 93 # nd,每个doc中各个topic的词的总数 94 self.nd = np.zeros((self.dpre.docs_count,self.K),dtype="int") 95 # ndsum,每各doc中词的总数 96 self.ndsum = np.zeros(dpre.docs_count,dtype="int") 97 self.Z = np.array([ [0 for y in xrange(dpre.docs[x].length)] for x in xrange(dpre.docs_count)]) # M*doc.size(),文档中词的主题分布 98 99 #随机先分配类型,为每个文档中的各个单词分配主题 100 for x in xrange(len(self.Z)): 101 self.ndsum[x] = self.dpre.docs[x].length 102 for y in xrange(self.dpre.docs[x].length): 103 topic = random.randint(0,self.K-1)#随机取一个主题 104 self.Z[x][y] = topic#文档中词的主题分布 105 self.nw[self.dpre.docs[x].words[y]][topic] += 1 106 self.nd[x][topic] += 1 107 self.nwsum[topic] += 1 108 109 self.theta = np.array([ [0.0 for y in xrange(self.K)] for x in xrange(self.dpre.docs_count) ]) 110 self.phi = np.array([ [ 0.0 for y in xrange(self.dpre.words_count) ] for x in xrange(self.K)]) 111 def sampling(self,i,j): 112 #换主题 113 topic = self.Z[i][j] 114 #只是单词的编号,都是从0开始word就是等于j 115 word = self.dpre.docs[i].words[j] 116 #if word==j: 117 # print 'true' 118 self.nw[word][topic] -= 1 119 self.nd[i][topic] -= 1 120 self.nwsum[topic] -= 1 121 self.ndsum[i] -= 1 122 123 Vbeta = self.dpre.words_count * self.beta 124 Kalpha = self.K * self.alpha 125 self.p = (self.nw[word] + self.beta)/(self.nwsum + Vbeta) * \ 126 (self.nd[i] + self.alpha) / (self.ndsum[i] + Kalpha) 127 128 #随机更新主题的吗 129 # for k in xrange(1,self.K): 130 # self.p[k] += self.p[k-1] 131 # u = random.uniform(0,self.p[self.K-1]) 132 # for topic in xrange(self.K): 133 # if self.p[topic]>u: 134 # break 135 136 #按这个更新主题更好理解,这个效果还不错 137 p = np.squeeze(np.asarray(self.p/np.sum(self.p))) 138 topic = np.argmax(np.random.multinomial(1, p)) 139 140 self.nw[word][topic] +=1 141 self.nwsum[topic] +=1 142 self.nd[i][topic] +=1 143 self.ndsum[i] +=1 144 return topic 145 def est(self): 146 # Consolelogger.info(u"迭代次数为%s 次" % self.iter_times) 147 for x in xrange(self.iter_times): 148 for i in xrange(self.dpre.docs_count): 149 for j in xrange(self.dpre.docs[i].length): 150 topic = self.sampling(i,j) 151 self.Z[i][j] = topic 152 logger.info(u"迭代完成。") 153 logger.debug(u"计算文章-主题分布") 154 self._theta() 155 logger.debug(u"计算词-主题分布") 156 self._phi() 157 logger.debug(u"保存模型") 158 self.save() 159 def _theta(self): 160 for i in xrange(self.dpre.docs_count):#遍历文档的个数词 161 self.theta[i] = (self.nd[i]+self.alpha)/(self.ndsum[i]+self.K * self.alpha) 162 def _phi(self): 163 for i in xrange(self.K): 164 self.phi[i] = (self.nw.T[i] + self.beta)/(self.nwsum[i]+self.dpre.words_count * self.beta) 165 def save(self): 166 # 保存theta文章-主题分布 167 logger.info(u"文章-主题分布已保存到%s" % self.thetafile) 168 with codecs.open(self.thetafile,'w') as f: 169 for x in xrange(self.dpre.docs_count): 170 for y in xrange(self.K): 171 f.write(str(self.theta[x][y]) + '\t') 172 f.write('\n') 173 # 保存phi词-主题分布 174 logger.info(u"词-主题分布已保存到%s" % self.phifile) 175 with codecs.open(self.phifile,'w') as f: 176 for x in xrange(self.K): 177 for y in xrange(self.dpre.words_count): 178 f.write(str(self.phi[x][y]) + '\t') 179 f.write('\n') 180 # 保存参数设置 181 logger.info(u"参数设置已保存到%s" % self.paramfile) 182 with codecs.open(self.paramfile,'w','utf-8') as f: 183 f.write('K=' + str(self.K) + '\n') 184 f.write('alpha=' + str(self.alpha) + '\n') 185 f.write('beta=' + str(self.beta) + '\n') 186 f.write(u'迭代次数 iter_times=' + str(self.iter_times) + '\n') 187 f.write(u'每个类的高频词显示个数 top_words_num=' + str(self.top_words_num) + '\n') 188 # 保存每个主题topic的词 189 logger.info(u"主题topN词已保存到%s" % self.topNfile) 190 191 with codecs.open(self.topNfile,'w','utf-8') as f: 192 self.top_words_num = min(self.top_words_num,self.dpre.words_count) 193 for x in xrange(self.K): 194 f.write(u'第' + str(x) + u'类:' + '\n') 195 twords = [] 196 twords = [(n,self.phi[x][n]) for n in xrange(self.dpre.words_count)] 197 twords.sort(key = lambda i:i[1], reverse= True) 198 for y in xrange(self.top_words_num): 199 word = OrderedDict({value:key for key, value in self.dpre.word2id.items()})[twords[y][0]] 200 f.write('\t'*2+ word +'\t' + str(twords[y][1])+ '\n') 201 # 保存最后退出时,文章的词分派的主题的结果 202 logger.info(u"文章-词-主题分派结果已保存到%s" % self.tassginfile) 203 with codecs.open(self.tassginfile,'w') as f: 204 for x in xrange(self.dpre.docs_count): 205 for y in xrange(self.dpre.docs[x].length): 206 f.write(str(self.dpre.docs[x].words[y])+':'+str(self.Z[x][y])+ '\t') 207 f.write('\n') 208 logger.info(u"模型训练完成。") 209 # 数据预处理,即:生成d()单词序列,以及词汇表 210 def preprocessing(): 211 logger.info(u'载入数据......') 212 with codecs.open(trainfile, 'r','utf-8') as f: 213 docs = f.readlines() 214 logger.debug(u"载入完成,准备生成字典对象和统计文本数据...") 215 # 大的文档集 216 dpre = DataPreProcessing() 217 items_idx = 0 218 for line in docs: 219 if line != "": 220 tmp = line.strip().split() 221 # 生成一个文档对象:包含单词序列(w1,w2,w3,,,,,wn)可以重复的 222 doc = Document() 223 for item in tmp: 224 if dpre.word2id.has_key(item):# 已有的话,只是当前文档追加 225 doc.words.append(dpre.word2id[item]) 226 else: # 没有的话,要更新vocabulary中的单词词典及wordidmap 227 dpre.word2id[item] = items_idx 228 doc.words.append(items_idx) 229 items_idx += 1 230 doc.length = len(tmp) 231 dpre.docs.append(doc) 232 else: 233 pass 234 dpre.docs_count = len(dpre.docs) # 文档数 235 dpre.words_count = len(dpre.word2id) # 词汇数 236 logger.info(u"共有%s个文档" % dpre.docs_count) 237 dpre.cachewordidmap() 238 logger.info(u"词与序号对应关系已保存到%s" % wordidmapfile) 239 return dpre 240 def run(): 241 # 处理文档集,及计算文档数,以及vocabulary词的总个数,以及每个文档的单词序列 242 dpre = preprocessing() 243 lda = LDAModel(dpre) 244 lda.est() 245 if __name__ == '__main__': 246 run()
本文来自于:
LDA主题模型原理解析与python实现、LDA数学八卦
谢谢博主