吴恩达机器学习第二周编程作业(Python实现)
课程作业 提取码:3szr
1、单元线性回归
ex1.py
from matplotlib.colors import LogNorm
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
from computeCost import *
from plotData import *
print('Plotting Data...')
data=np.loadtxt('./data/ex1data1.txt',delimiter=',')#加载txt格式数据集 每一行以“,”分隔
X=data[:,0]
y=data[:,1]
m=y.size
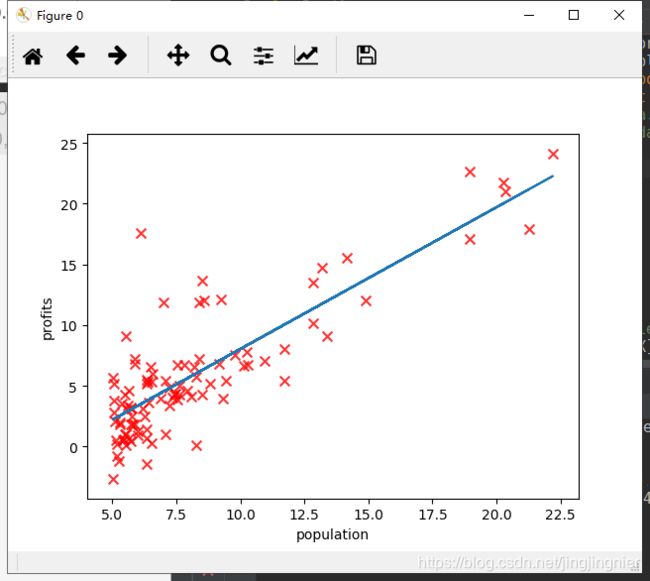
plt.figure(0)
plot_data(X,y)
# input()
print('Running Gradient Descent...')
X=np.c_[np.ones(m),X]
theta=np.zeros(2)
iterations=1500
alpha=0.01
print('Initial cost: '+str(compute_cost(X,y,theta))+'(This value should be about 32.07')
theta,J_history =gradient_descent(X,y,theta,alpha,iterations)
print('Theta found by gradient descent:'+str(theta.reshape(2)))
plt.figure(0)
line1, =plt.plot(X[:,1],np.dot(X,theta),label='Linear Regression')
plot_data(X[:,1],y)
plt.legend(handles=[line1])
input('Program paused. Press ENTER to continue')
predict1=np.dot(np.array([1,3.5]),theta)
print('For population=35,000,we predict a profit of {:0.3f}(This value should be about 4519.77)'.format(predict1*10000))
predict2=np.dot(np.array([1,7]),theta)
print('For population = 70,000, we predict a profit of {:0.3f} (This value should be about 45342.45)'.format(predict2*10000))
input('Program paused. Press ENTER to continue')
print('Visualizing J(theta_0,theta_1)...')
theta0_vals=np.linspace(-10,10,100)
theta1_vals=np.linspace(-1,4,100)
J_vals=np.zeros((theta0_vals.shape[0],theta1_vals.shape[0]))
print(theta0_vals.shape[0])
print(theta1_vals.shape[0])
for i in range(0,theta0_vals.shape[0]):
for j in range(0,theta1_vals.shape[0]):
t=np.array([theta0_vals[i],theta1_vals[j]])
J_vals[i][j]=compute_cost(X,y,t)
J_vals=np.transpose(J_vals)
fig=plt.figure(1)
ax=Axes3D(fig)
xs,ys=np.meshgrid(theta0_vals,theta1_vals)
plt.title("Visualizing J(theta_0,theta_1)")
ax.plot_surface(xs,ys,J_vals)
ax.set_xlabel('$\theta_0$',color='r')
ax.set_ylabel('$\theta_1$',color='r')
plt.show()
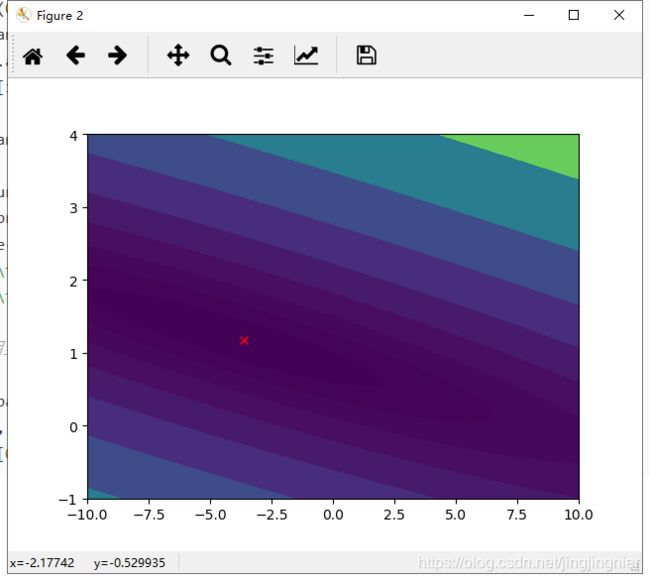
plt.figure(2)
lvls=np.logspace(-2,3,20)
plt.contourf(xs,ys,J_vals,10,levels=lvls,normal=LogNorm())
plt.plot(theta[0], theta[1], c='r', marker="x")
plt.show()plotData.py
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def plot_data(x,y):
plt.scatter(x,y,marker='x',s=50,c='r',alpha=0.8)
plt.xlabel('population')
plt.ylabel('profits')
plt.show()computeCost.py(梯度下降函数包含在内)
import numpy as np
def h(X,theta):
return X.dot(theta)
def compute_cost(X,y,theta):
m=y.size
prediction=h(X,theta)
# cost=sum(np.power(prediction-y,2))/(2*m)
cost = (prediction - y).dot(prediction - y) / (2 * m)
return cost
def gradient_descent(X,y,theta,alpha,num_iters):
m=y.size
J_history=np.zeros(num_iters)
for i in range(0,num_iters):
# theta=theta-(alpha/m)*sum((h(X,theta)-y).dot(X))
theta=theta-(alpha/m)*(h(X,theta)-y).dot(X)
J_history[i]=compute_cost(X,y,theta)
return theta,J_history