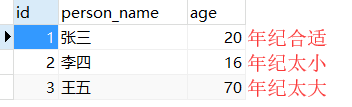基于SpringBoot+Mybatis开发的简单异常处理器(ExceptionHandle)
需求:
按照一个人的ID确认他的年龄,如果小于18岁则太年轻,大于65岁则年纪太大。
构思:
一个Person类,按照id查找Person的age属性,并对查找出来的age进行判断。
1.如果年纪小于18,则出现异常“你太年轻”;
2.如果年纪大于65,则出现异常“你年纪太大”。
3.查询结果要求返回一个Result的Json对象,要求Result中包含:- 错误代码(-1为其他错误,0为age<18,1为查找成功,2为age>65)
- 提示信息(“”后台错误”,“你太年轻”,“查询成功”,“你年纪太大”)
- 对象数据(查询成功则输出查找出的对象,否则输出为null)
开发流程:
对象
涉及到两个对象,“Result”和“Person”,其中Person对象与数据库中person表对应,而Result类则用于输出JSON信息到前台。
Person类
public class Person {
private Integer id;//id
private String personName;//姓名
private Integer age;//年龄
public Integer getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Integer id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getPersonName() {
return personName;
}
public void setPersonName(String personName) {
this.personName = personName;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
Result类
public class Result {
//错误代码
private Integer code;
//提示信息
private String message;
//对象数据
private Object object;
public Result() {
}
public Result(Integer code, String message, Object object) {
this.code = code;
this.message = message;
this.object = object;
}
}
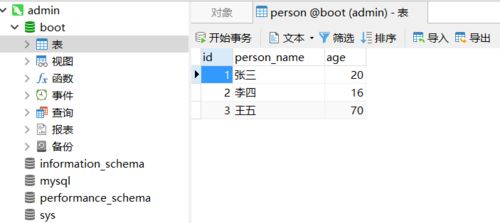
同时,在数据库中建表:
实现:
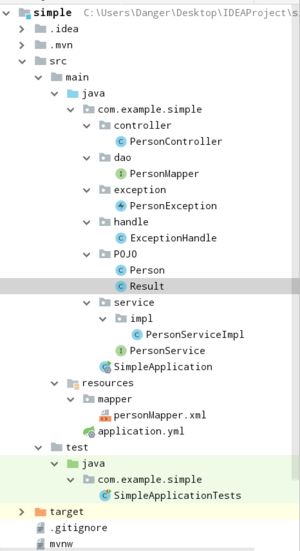
我们首先可以看到项目包的基本结构:
1.配置application.yml文件:
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/boot?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8&allowMultiQueries=true&useSSL=false
username: root
password: admin
server:
port: 8080
mybatis:
#mapper文件路径
mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/*.xml
2.配置personMapper.xml
由于本次需求较为简单,我们只需要开发一个方法findOne即可:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<mapper namespace="com.example.simple.dao.PersonMapper">
<!--根据id查找person-->
<select id="findOne" resultType="com.example.simple.POJO.Person">
SELECT id, person_name AS personName, age FROM person
WHERE id = #{id}
</select>
</mapper>
3. DAO层:
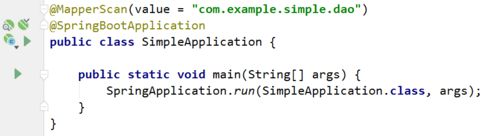
注意:区别于SSM,我们不需要再在DAO层加@Repository注解,应为我们在主类SimpleApplication中已经配置了Mapper的自动扫描如图:
package com.example.simple.dao;
import com.example.simple.POJO.Person;
public interface PersonMapper {
//根据id查找一个person
public Person findOne(Integer id);
}
4. service
在这一层我们要对年龄是否符合我们的要求做判断,所以会令其抛出异常并对其进行相应的处理。我们前面已经要求对于不合格的年纪要记录错误代码,还有提示信息以及相关数据,所以我们接着来自定义PersonException:
//自定义异常类
public class PersonException extends RuntimeException {
//错误代码
private Integer code;
public PersonException(Integer code,String message) {
//用来输出错误信息
super(message);
this.code = code;
}
public Integer getCode() {
return code;
}
public void setCode(Integer code) {
this.code = code;
}
}
那么PersonServiceImpl中的代码就有:
@Service
public class PersonServiceImpl implements PersonService {
//在IDEA环境下,定义的personMapper会报错,
//但其实并没有错,因为我们已经设置了@MapperScan注解
@Autowired
private PersonMapper personMapper;
@Override
public Result findAgeById(Integer id) {
Person person = personMapper.findOne(id);
//判断年龄
if (person.getAge() < 18){
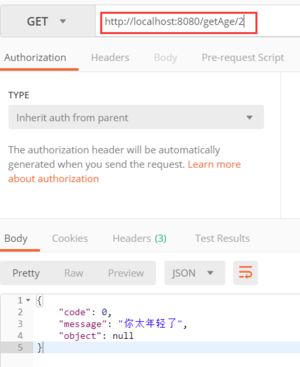
throw new PersonException(0,"你太年轻了");
}else if (person.getAge() > 65){
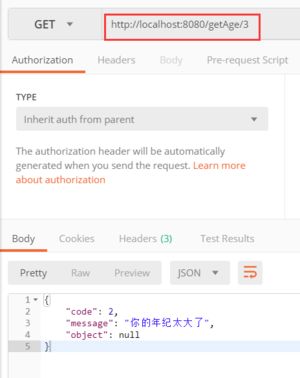
throw new PersonException(2,"你的年纪太大了");
}
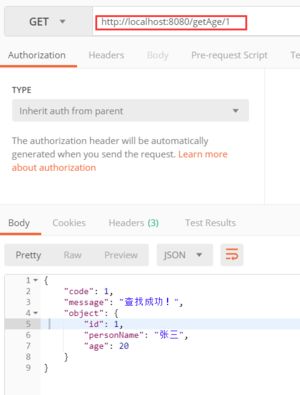
return new Result(1,"查找成功!",person);
}
}
我们前面已经说过,还要把这个错误代码和错误信息赋给Result类,再通过它输出到界面上,所以我们就需要有一个:
5.ExceptionHandle(异常处理器)处理抛出的异常信息:
@ControllerAdvice
public class ExceptionHandle {
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
@ResponseBody
public Result handle(Exception e) {
if (e instanceof PersonException) {
PersonException personException = (PersonException) e;
return new Result(personException.getCode(), personException.getMessage(), null);
}else {
e.printStackTrace();
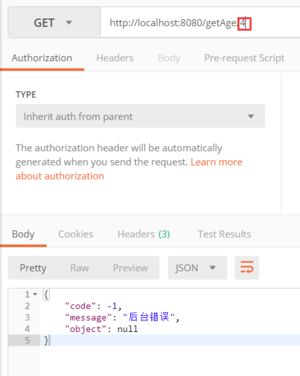
return new Result(-1,"后台错误",null);
}
}
}
6. 最后是contrller层
@RestController
public class PersonController {
@Autowired
private PersonService personService;
@GetMapping(value = "/getAge/{id}")
public Result getAgeById(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) {
return personService.findAgeById(id);
}
}
7.Postman测试
首先再次摆出数据库中信息:
最后我们通过Postman测试数据:
这样,我们就将Result的JSON数据传递到了前台,而前台就会根据错误代码和提示及信息进行相应处理。