浅谈Attention-based Model【源码篇】
转载请标明出处:http://blog.csdn.net/wuzqchom/article/details/77918780
源码不可能每一条都详尽解释,主要在一些关键步骤上加了一些注释和些许个人理解,如有不足之处,请予指正。
计划分为三个部分:
浅谈Attention-based Model【原理篇】
浅谈Attention-based Model【源码篇】(你在这里)
浅谈Attention-based Model【实践篇】
在之前的博客:浅谈Attention-based Model【原理篇】中,介绍了注意力机制(Attention Mechanism)的原理,这篇主要通过
tf.contrib.legacy_seq2seq.embedding_attention_seq2seq()的源码来看看注意力机制的工作过程。
0. 主要函数结构
先来看看主要函数的调用过程(接下来也是按照这样的结构解释源码):
- 1.embedding_attention_seq2seq()
- 2.embedding_attention_decoder()
- 3.attention_decoder()
- attention()
- 3.attention_decoder()
- 2.embedding_attention_decoder()
其中函数attention()是实现每一个时刻的注意力机制的主要函数,即论文Grammar as a Foreign Language中的Attention Mechanism基本上都是在这个函数里面实现的
为什么说基本?这是因为 W′1hi W 1 ′ h i 是在该函数之外使用卷积操作实现的,具体详见3.attention_decoder()函数。
1. embedding_attention_seq2seq()
embedding_attention_seq2seq函数参数说明如下:
def embedding_attention_seq2seq(encoder_inputs,# 编码器的输入
decoder_inputs,# 解码器的输入
cell,# 所用的cell
num_encoder_symbols,# 编码的符号总数
num_decoder_symbols,# 解码的符号总数
embedding_size,# 向量的维度
num_heads=1,# 这个也不知道啊,默认为1,基本上可以当它不存在了
output_projection=None, # 输出投影
feed_previous=False,# 当前输入是否要考虑前一个时刻的输出,这个一般在训练的时候为False,预测的时候为True
dtype=None,
scope=None,
initial_state_attention=False):
返回值:
由(outputs,state)组成的元组
outputs的shape为[batch_size x num_decoder_symbols]
state为最后一个时刻decoder的状态,shape为[batch_size x cell.state_size]
这个函数首先为一个编码的过程:
使用EmbeddingWrapper将输入映射到embedding_size大小的向量,然后通过调用static_rnn得到了encoder的每一个时刻的输出,即为之后我们需要attention的向量。
然后再进行解码的过程:
首先使用OutputProjectionWrapper将解码器的输出映射成想要的维度
接下来执行:
if isinstance(feed_previous, bool):
return embedding_attention_decoder2. embedding_attention_decoder()
def embedding_attention_decoder(decoder_inputs,
initial_state,
attention_states,
cell,
num_symbols,
embedding_size,
num_heads=1,
output_size=None,# 输出的大小,tensorflow中为num_decoder_symbols
output_projection=None,
feed_previous=False,
update_embedding_for_previous=True,
dtype=None,
scope=None,
initial_state_attention=False):# 初始attention向量的值,默认为0
返回值:
同上
这个函数主要是通过embedding_ops.embedding_lookup()函数把decoder_inputs转换为向量的形式,之前decoder_inputs用符号的index的表示.
3. attention_decoder()
def attention_decoder(decoder_inputs,# 编码器的输入,向量形式
initial_state,# 初始状态,tensorflow照顾你为rnn编码器的最后一个时刻的state
attention_states,# 需要attention的向量,即为编码器的每一个时刻的输出
cell,
output_size=None,
num_heads=1,
loop_function=None,
dtype=None,
scope=None,
initial_state_attention=False):
终于看到核心的函数了,attention解码器参照论文
Grammar as a Foreign Language实现
为了说明方便,我把论文当中的公式放上来了:
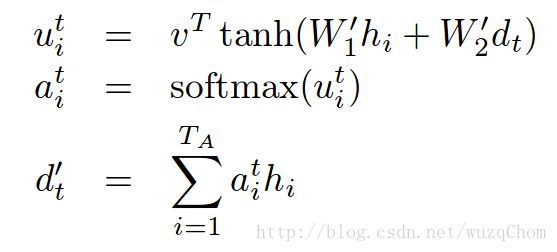
我们依次把这三个公式标号为公式(1),(2),(3)。
首先来看看 W′1hi W 1 ′ h i 的实现:
for a in xrange(num_heads):
# filter的大小,输入的通道数为输入embedding_size的大小,输出的通道为attention_vec_size,但正如前面所说,tensorflow里面这两个值是相等的
k = variable_scope.get_variable("AttnW_%d" % a,
[1, 1, attn_size, attention_vec_size])
hidden_features.append(nn_ops.conv2d(hidden, k, [1, 1, 1, 1], "SAME"))
v.append(
variable_scope.get_variable("AttnV_%d" % a, [attention_vec_size]))
如上,使用卷积核来实现相乘的操作,attn_size为attention的长度,即为编码器是输出的向量个数,attention_vec_size为attention向量的长度,tensorflow默认为embedding_size的大小,而且并没有提供参数传递,但是这个假如手动改成其它的值也没有问题。
4>
#循环,依次将解码状态的每一个时刻的是state都做一次attention,然后和该时刻的decoder_inputs值共同决定该时刻的输入
for i, inp in enumerate(decoder_inputs):
if i > 0:
variable_scope.get_variable_scope().reuse_variables()
# If loop_function is set, we use it instead of decoder_inputs.
if loop_function is not None and prev is not None:
with variable_scope.variable_scope("loop_function", reuse=True):
inp = loop_function(prev, i)
# Merge input and previous attentions into one vector of the right size.
input_size = inp.get_shape().with_rank(2)[1]
if input_size.value is None:
raise ValueError("Could not infer input size from input: %s" % inp.name)
# 和decoder_inputs该时刻的值共同决定该时刻的输入
# 这里的因为原文用的词为concat,但是这里应该是每一个维度的值相加
x = linear([inp] + attns, input_size, True)
# Run the RNN.
# 使用输入和上一个时刻的隐状态共同决定当前时刻的隐状态和解码的输出
cell_output, state = cell(x, state)
# Run the attention mechanism.
if i == 0 and initial_state_attention:
with variable_scope.variable_scope(
variable_scope.get_variable_scope(), reuse=True):
attns = attention(state)
else:
attns = attention(state)
with variable_scope.variable_scope("AttnOutputProjection"):
output = linear([cell_output] + attns, output_size, True)
if loop_function is not None:
prev = output
outputs.append(output)
最后的最后,还有最为核心的attention函数,上面是T个时刻的循环。但是每一个时刻的attention是由该函数完成的,敲黑板,即真正实现上面三个公式的地方:
def attention(query):
"""Put attention masks on hidden using hidden_features and query."""
ds = [] # Results of attention reads will be stored here.
if nest.is_sequence(query): # If the query is a tuple, flatten it.
query_list = nest.flatten(query)
for q in query_list: # Check that ndims == 2 if specified.
ndims = q.get_shape().ndims
if ndims:
assert ndims == 2
query = array_ops.concat(query_list, 1)
for a in xrange(num_heads):
with variable_scope.variable_scope("Attention_%d" % a):
# 公式(1)中的$W_2^{d_t}$
y = linear(query, attention_vec_size, True)
y = array_ops.reshape(y, [-1, 1, 1, attention_vec_size])
# Attention mask is a softmax of v^T * tanh(...).
# 公式(1)结果
s = math_ops.reduce_sum(v[a] * math_ops.tanh(hidden_features[a] + y),
[2, 3])
# 公式(2)
a = nn_ops.softmax(s)
# Now calculate the attention-weighted vector d.
# 公式(3)
d = math_ops.reduce_sum(
array_ops.reshape(a, [-1, attn_length, 1, 1]) * hidden, [1, 2])
ds.append(array_ops.reshape(d, [-1, attn_size]))
return ds