muduo网络库源码复现笔记(十八):Reactor的关键结构
Muduo网络库简介
muduo 是一个基于 Reactor 模式的现代 C++ 网络库,作者陈硕。它采用非阻塞 IO 模型,基于事件驱动和回调,原生支持多核多线程,适合编写 Linux 服务端多线程网络应用程序。
muduo网络库的核心代码只有数千行,在网络编程技术学习的进阶阶段,muduo是一个非常值得学习的开源库。目前我也是刚刚开始学习这个网络库的源码,希望将这个学习过程记录下来。
Reactor的关键结构
Reacor的核心是事件分发机制,也就是将IO复用模型(poll/epoll)那里拿到的io事件分发给各文件描述符的事件处理函数。为了实现这个机制,我们需要编写Channel class和Poller class。下面说明一下这两个类。
1 Channel class
依据作者的介绍,Channel class的功能类似Java NIO的SelectableChannel和Selection-Key组合。Channel是为文件描述符fd服务的,它并不占有fd,亦不会在析构的时候关闭它。Channel只会属于一个EventLoop,也只属于一个IO线程。最后需要说明的是用户一般不会直接使用Channel,而回使用更上一层的封装。下面看一下Channel的代码
class Channel : boost::noncopyable
{
public:
typedef boost::function EventCallback;
typedef boost::function ReadEventCallback;
Channel(EventLoop* loop,int fd);
~Channel();
void handleEvent(Timestamp receiveTime);
void setReadCallback(const ReadEventCallback& cb)
{ readCallback_ = cb;}
void setWriteCallback(const EventCallback& cb)
{ writeCallback_ = cb;}
void setCloseCallback(const EventCallback& cb)
{ closeCallback_ = cb;}
void setErrorCallback(const EventCallback& cb)
{ errorCallback_ = cb;}
void tie(const boost::shared_ptr&);
int fd() const {return fd_;}
int events() const {return events_;}
void set_revents(int revt) {revents_ = revt;}
bool isNoneEvent() const {return events_ == kNoneEvent;}
void enableReading() {events_ |= kReadEvent; update();}
void enableWriting() {events_ |= kWriteEvent; update();}
void disableReading() {events_ &= ~kReadEvent; update();}
void disableWriting() {events_ &= ~kWriteEvent; update();}
void disableAll() {events_ &= ~kNoneEvent; update();}
bool isWriting() const {return events_ & kWriteEvent;}
//for Poller
int index() {return index_;}
void set_index(int idx) {index_ = idx;}
//for debug
string reventsToString() const;
void doNotLogHup() {logHup_ = false;}
EventLoop* ownerLoop() {return loop_;}
void remove();
private:
void update();
void handleEventWithGuard(Timestamp receiveTime);
static const int kNoneEvent;
static const int kReadEvent;
static const int kWriteEvent;
EventLoop* loop_;
const int fd_;
int events_;
int revents_;
int index_;
bool logHup_;
boost::weak_ptr tie_;
bool tied_;
bool eventHandling_;
ReadEventCallback readCallback_;
EventCallback writeCallback_;
EventCallback closeCallback_;
EventCallback errorCallback_;
};
1.1 数据成员
Channel的关键数据成员中,events_是它关心的IO事件,有用户设置。revents_是目前的活动事件,由EventLoop/Poller设置;而index_是channel所服务的fd所对应的struct pollfd数组的下标。而update函数会调用EventLoop的update函数,继而调用Poller的update函数。
1.2 handleEvent函数
这个函数由EventLoop::loop调用,它的功能是依据revents_的值分别调用不同的用户回调。
2 Poller类
Poller是一个抽象基类,这个类是IO复用模型的封装,后面会实现PollPoller(支持Poll)或者EpollPoller(支持Epoll)来继承它。看一下Poller的代码。
class Poller : boost::noncopyable
{
public:
typedef std::vector ChannelList;
Poller(EventLoop* loop);
virtual ~Poller();
virtual Timestamp poll(int timeoutMs,ChannelList* activeChannels) = 0;
//changes the intrested I/O event
virtual void updateChannel(Channel* channel) = 0;
//remove the channel
virtual void removeChannel(Channel* channel) = 0;
static Poller* newDefaultPoller(EventLoop* loop);
void assertInLoopThread()
{
ownerLoop_ -> assertInLoopThread();
}
private:
EventLoop* ownerLoop_; //the eventloop poller belongs to
};
Poller的虚函数poll完成Poller的核心功能:获取当前活动的IO事件,然后将其加入activeChannels。updateChannel和removeChannel分别用于将一个Channel对应的fd从struct pollfd数组中加入或去除。
2.1 PollPoller类
PollPoller类继承了Poller,使用poll函数实现IO复用。当前我们就使用PollPoller,后续会补充EpollPoller。PollPoller类的fillActiveChannels是找出有事件的fd,填入activeChannels。ChannelMap是文件描述符和Channel指针的一个map。
class PollPoller : public Poller
{
public:
PollPoller(EventLoop* loop);
virtual ~PollPoller();
virtual Timestamp poll(int timeoutMs,ChannelList* activeChannels);
virtual void updateChannel(Channel* channel);
virtual void removeChannel(Channel* channel);
private:
void fillActiveChannels(int numEvents,ChannelList* activeChannels) const;
typedef std::vector PollFdList;
typedef std::map ChannelMap; //key:fd,value:pointer of Channel
PollFdList pollfds_;
ChannelMap channels_;
};
2.1.1updateChannel函数
这个函数的作用维护和更新pollfd_数组。它可以为数组增加文件描述符,也可以暂时忽略某文件描述符的事件或者重新关注它。注意在忽略文件描述符时,采用的方式时将它的文件描述符取反减一,可以帮助remove。(减1是为了文件描述符可能为0)。
void PollPoller::updateChannel(Channel* channel)
{
Poller::assertInLoopThread();
LOG_TRACE << "fd = " << channel -> fd() << " events = " << channel -> events();
if(channel -> index() < 0)
{
//new channel,add to pollfds
assert(channels_.find(channel ->fd()) == channels_.end());
struct pollfd pfd;
pfd.fd = channel -> fd();
pfd.events = static_cast(channel -> events());
pfd.revents = 0;
pollfds_.push_back(pfd);
int idx = static_cast(pollfds_.size()) - 1;
channel -> set_index(idx);
channels_[pfd.fd] = channel;
}
else
{
//update exsiting one
assert(channels_.find(channel -> fd()) != channels_.end());
assert(channels_[channel -> fd()] == channel);
int idx = channel -> index();
assert(0 <= idx && idx < static_cast(pollfds_.size()));
struct pollfd& pfd = pollfds_[idx];
assert(pfd.fd == channel -> fd() || pfd.fd == -channel -> fd() - 1);
pfd.events = static_cast(channel -> events());
pfd.revents = 0;
if(channel -> isNoneEvent())
{
pfd.fd = -channel->fd() - 1;
}
}
}
2.1.2removeChannel函数
removeChannel函数复杂度为O(1),它采用的方法是交换需要删除的Channel和数组中最后一位Channel,然后pop_back。
void PollPoller::removeChannel(Channel* channel)
{
Poller::assertInLoopThread();
LOG_TRACE << "fd = " << channel -> fd();
assert(channels_.find(channel -> fd()) != channels_.end());
assert(channels_[channel->fd()] == channel);
assert(channel -> isNoneEvent());
int idx = channel -> index();
assert(0 <= idx && idx < static_cast(pollfds_.size()));
const struct pollfd& pfd = pollfds_[idx]; (void) pfd;
assert(pfd.fd == -channel -> fd() - 1 && pfd.events == channel -> events());
size_t n = channels_.erase(channel -> fd());
assert(n == 1);(void) n;
if(implicit_cast(idx) == pollfds_.size() - 1)
{
pollfds_.pop_back();
}
else
{
int channelAtEnd = pollfds_.back().fd;
iter_swap(pollfds_.begin() + idx,pollfds_.end() - 1);
if(channelAtEnd < 0)
{
channelAtEnd = -channelAtEnd - 1;
}
channels_[channelAtEnd] -> set_index(idx);
pollfds_.pop_back();
}
}
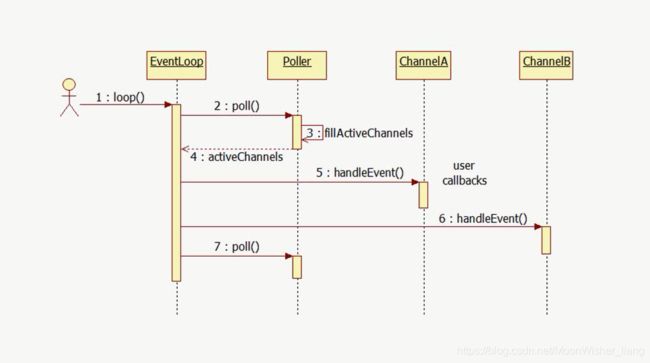
小结
在我们完成上述两个类之后,Reactor的核心内容构造完毕。在EventLoop的loop函数中,我们利用Poller可以得到活跃的Channel,然后便可以分别处理这些活跃的Channel,如此循环。时序图如下: