上一篇讲了基础入门 OpenGL (一) ,这一次主要学习OpenGL 纹理基本学习总结
要是做复杂的OpenGL应用程序,一定会用到纹理技术。纹理说白了就是把图片或者视频图像绘制到OpenGL空间中。
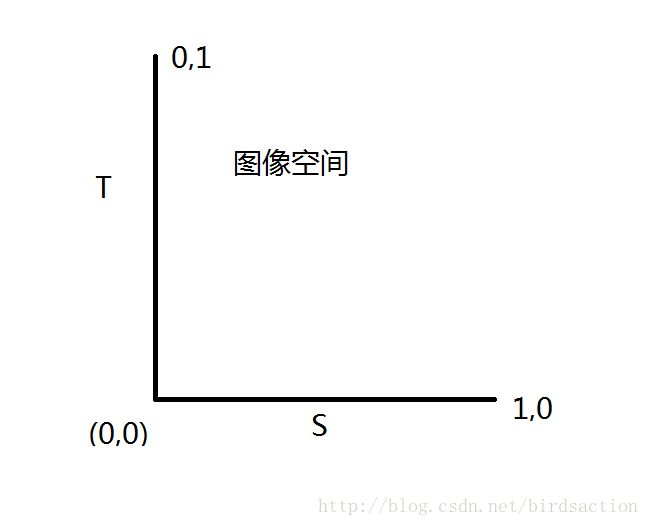
因此纹理也有坐标系,称ST坐标。或者UV
上面是纹理坐标空间。但没有固定的方向
以下演示载入一张image作为纹理贴图。
public class TextureUtils {
public static int createTexture(InputStream ins) {
int[] textures = new int[1];
GLES20.glGenTextures(1, textures, 0);//生成一个纹理
int textureId = textures[0];
GLES20.glBindTexture(GLES20.GL_TEXTURE_2D, textureId);
GLES20.glTexParameterf(GLES20.GL_TEXTURE_2D, GLES20.GL_TEXTURE_MIN_FILTER,GLES20.GL_NEAREST);
GLES20.glTexParameterf(GLES20.GL_TEXTURE_2D,GLES20.GL_TEXTURE_MAG_FILTER,GLES20.GL_LINEAR);
GLES20.glTexParameterf(GLES20.GL_TEXTURE_2D, GLES20.GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_S,GLES20.GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE);
GLES20.glTexParameterf(GLES20.GL_TEXTURE_2D, GLES20.GL_TEXTURE_WRAP_T,GLES20.GL_CLAMP_TO_EDGE);
//上面是纹理贴图的取样方式,包含拉伸方式,取临近值和线性值
Bitmap bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeStream(ins);
GLUtils.texImage2D(GLES20.GL_TEXTURE_2D, 0, bitmap, 0);//让图片和纹理关联起来。载入到OpenGl空间中
Log.d("OPENGL","bitmap:" + bitmap);
bitmap.recycle();//不须要。能够释放
return textureId;
}
}public class MyRenderer implements Renderer {
public static float[] projMatrix = new float[16];// 投影
public static float[] viewMatrix = new float[16];// 相机
public static float[] mViewPjMatrix;// 总变换矩阵
public static float[] matrixs = new float[16];
public static int textureId = -1;
Context context;
MyDrawModel drawModel;
public MyRenderer(Context context) {
this.context = context;
}
@Override
public void onDrawFrame(GL10 arg0) {
GLES20.glClear( GLES20.GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT | GLES20.GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
Log.e("", "textureId:" + textureId);
drawModel.drawFrame(textureId);
}
@Override
public void onSurfaceChanged(GL10 arg0, int w, int h) {
GLES20.glViewport(0, 0, w, h);
float ratio = (float) w / h;
Matrix.frustumM(projMatrix, 0, -ratio, ratio, -1, 1, 1, 10);//投影矩阵设置
Matrix.setLookAtM(viewMatrix, 0, 0, 0, 3, 0, 0, 0, 0.0f, 1.0f, 0.0f);//摄像机坐标设置
}
@Override
public void onSurfaceCreated(GL10 g, EGLConfig eglConfig) {
GLES20.glClearColor(0.5f,0.5f,0.5f, 1.0f);
GLES20.glEnable(GLES20.GL_DEPTH_TEST);
InputStream ins = null;
drawModel = new MyDrawModel();
drawModel.init();
try {
ins = context.getAssets().open("house.jpg");
textureId = TextureUtils.createTexture(ins);
Log.e("", "textureId:" + textureId);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
ins.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
GLES20.glDisable(GLES20.GL_CULL_FACE);
}
}
public class MyDrawModel {
private int programId;
private int mVPMatrixHandle; // 总变换矩阵引用id
private int positionHandle; // 顶点位置id
private int texCoorHandle; // 顶点纹理坐标id
private FloatBuffer vertexBuffer;
private FloatBuffer texCoorBuffer;
public MyDrawModel() {
}
public void init() {
initData();
int vertexsharder = GLHelper.compileScript(GLES20.GL_VERTEX_SHADER,
GLScript.vertex2);
int fragmentsharder = GLHelper.compileScript(GLES20.GL_FRAGMENT_SHADER,
GLScript.fragment2);
programId = GLHelper.linkAttach(vertexsharder, fragmentsharder);
boolean isOK = GLHelper.checkProgram(programId);
positionHandle = GLES20.glGetAttribLocation(programId, "aPosition");
texCoorHandle = GLES20.glGetAttribLocation(programId, "aTexCoor");
mVPMatrixHandle = GLES20.glGetUniformLocation(programId, "uMVPMatrix");
Log.d("OPENGL", "positionHandle:" + positionHandle + ";texCoorHandle:"
+ texCoorHandle + ";mVPMatrixHandle:" + mVPMatrixHandle + ";"
+ isOK);
}
private void initData() {
//X,Y,Z,绘画的顶点
float vertices[] = new float[] {
0, 0, 0,
-1.8f, -1f, 0,
1.8f, -1f, 0,
1.8f, 1f, 0,
-1.8f, 1f, 0,
-1.8f, -1f, 0
};
ByteBuffer vb = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(vertices.length * 4);
vb.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder());
vertexBuffer = vb.asFloatBuffer();
vertexBuffer.put(vertices);
vertexBuffer.position(0);
//纹理空间坐标 S,T
float texCoor[] = new float[] {
0.5f, 0.5f,
0f, 1f,
1f, 1f,
1f, 0f,
0f, 0f,
0f, 1f
};
ByteBuffer cb = ByteBuffer.allocateDirect(texCoor.length * 4);
cb.order(ByteOrder.nativeOrder());
texCoorBuffer = cb.asFloatBuffer();
texCoorBuffer.put(texCoor);
texCoorBuffer.position(0);
}
public void drawFrame(int textureId) {
GLES20.glUseProgram(programId);
// // 初始化矩阵
Matrix.setRotateM(MyRenderer.matrixs, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0);
Matrix.translateM(MyRenderer.matrixs, 0, 0, 0, 1);
//矩阵转换 ,投影矩阵,摄像机矩阵。模型矩阵
MyRenderer.mViewPjMatrix = new float[16];
Matrix.multiplyMM(MyRenderer.mViewPjMatrix, 0, MyRenderer.viewMatrix,0, MyRenderer.matrixs, 0);
Matrix.multiplyMM(MyRenderer.mViewPjMatrix, 0, MyRenderer.projMatrix,0, MyRenderer.mViewPjMatrix, 0);
GLES20.glUniformMatrix4fv(mVPMatrixHandle, 1, false, MyRenderer.mViewPjMatrix, 0);
GLES20.glVertexAttribPointer(positionHandle, 3, GLES20.GL_FLOAT, false, 3 * 4, vertexBuffer);
GLES20.glVertexAttribPointer(texCoorHandle, 2, GLES20.GL_FLOAT, false, 2 * 4, texCoorBuffer);
GLES20.glEnableVertexAttribArray(positionHandle);
GLES20.glEnableVertexAttribArray(texCoorHandle);
GLES20.glActiveTexture(GLES20.GL_TEXTURE0);
GLES20.glBindTexture(GLES20.GL_TEXTURE_2D, textureId);
GLES20.glDrawArrays(GLES20.GL_TRIANGLE_FAN, 0, 6);//六个定点,绘制三角形
}
}OpenGL须要把设备的坐标归一化到[-1,-1]空间中。所以这里涉及到矩阵相乘的理论,包含世界坐标,物体坐标,摄像机坐标的转换。以后会具体介绍。
public class GLScript {
public GLScript() {
}
public static final String vertex1 = "attribute vec4 mPosition;\n" +
"void main()\n" +
"{\n" +
"gl_Position=mPosition;\n " +
"}\n";
public static final String fragment1 = "precision mediump float;\n" +
"uniform vec4 mColor;\n" +
"void main(){ gl_FragColor=mColor;\n}";
public static final String vertex2 = "uniform mat4 uMVPMatrix;\n"
+ "attribute vec3 aPosition;\n"
+ "attribute vec2 aTexCoor;\n"
+ "varying vec2 vTextureCoord;\n"
+ "void main() { \n"
+ "gl_Position = uMVPMatrix * vec4(aPosition,1);\n"
+ "vTextureCoord = aTexCoor;\n"
+ "}\n"
;
public static final String fragment2 = "precision mediump float;\n"
+ "varying vec2 vTextureCoord;\n"
+ "uniform sampler2D sTexture;\n"
+ "void main() { \n"
+ "vec2 coord = vTextureCoord;\n"
+ "coord.s = coord.s * 0.5;\n" //事实上是去图像的一半,向量缩小了
+ "gl_FragColor = texture2D(sTexture, coord); \n"
+ "}\n"
;
}
coord.s = coord.s * 0.5;其他的工具类和上一篇文章一样。
内容显示
原图: