源码分享,采用线程池,实现高性能跨平台C++多线程并行库,附测试!
由于实用需要,实现一个跨平台的多线程并行库,摆脱windows的ppl,并且兼顾效率和跨平台性,特点如下:
- 采用C++11跨平台,调度性能和windows ppl库相近;
- 使用了其他大神的 线程池代码,实现线程高效复用;
- 支持STL容器、C数组、指针多种方式传递容器目标对象做并行;
- 代码可自行完善功能;
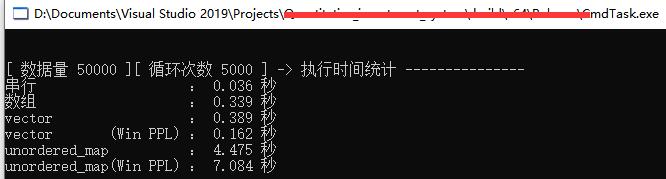
- 测试所用的执行函数体执行时间极端
{ i += 1;},目的是,测试比较多线程的调度性能; - 由于数据量不大,主执行过程短,且windows平台VC编译器对串行有优化,所有串行的速度还是很快(不过没有可比性);
- 对于连续空间排列容器(数组、vector)代码执行效率比windows PPL库略慢一些,不过调度效率尚可;
- 对于非连续空间容器(本例采用unordered_map)代码执行效率比windows PPL库快一些;
- 综合来说,若兼顾性能和考虑跨平台,代码效率还算是达标的。
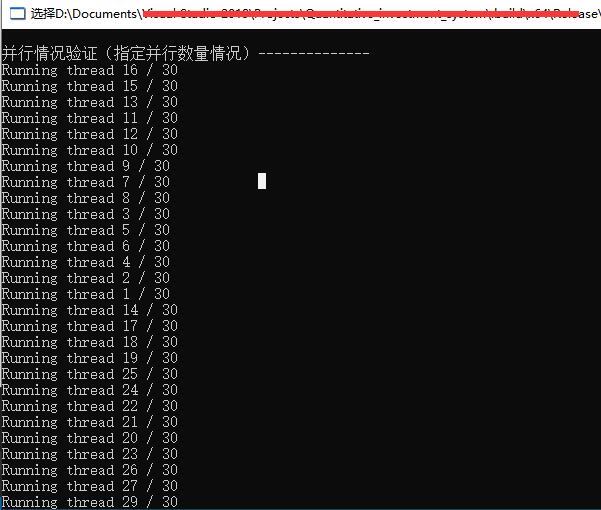
下面是并发执行效果:(指定并发30个任务,实现了并行)
(指定cpu硬件核心线程数个并发任务,也实现了并行)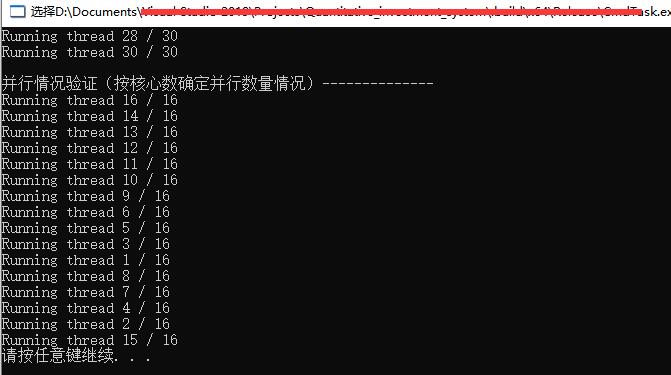
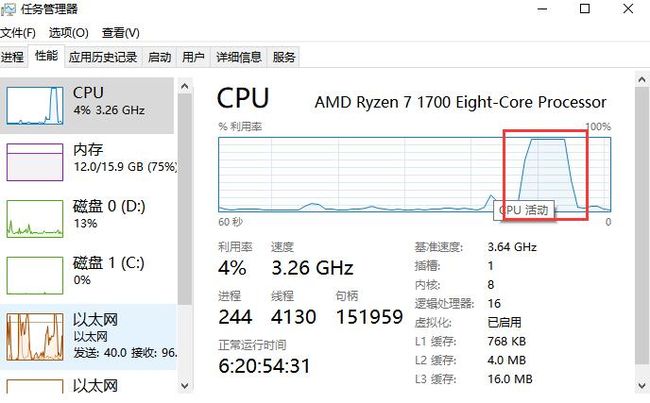
并行过程cpu出现极高峰值段(并行实现)
测试代码:
int main(){
std::mutex cs;
const int sii = 50000;
const int cycle = 5000;
int con[sii] = { 2 };
vector<int> con2(sii, 2);
unordered_map<int, int> con3;
map<int, int> con4;
for (int i = 0; i < sii; ++i)con3[i] = 2, con4[i] = 2;
auto incre = [&](int& i) {i += 1; };
auto ttt0 = clock();
for (size_t i = 0; i < cycle; i++)
for (size_t j = 0; j < sii; j++)
incre(con[j]);
auto ttt1 = (clock() - ttt0) / double(CLOCKS_PER_SEC); ttt0 = clock();
for (size_t i = 0; i < cycle; i++)
parallel(&con[0],0, sii, incre); //传首指针
auto ttt2 = (clock() - ttt0) / double(CLOCKS_PER_SEC);
ttt0 = clock();
for (size_t i = 0; i < cycle; i++)
parallel_iter(con2.begin(), con2.end(), incre);
auto ttt3 = (clock() - ttt0) / double(CLOCKS_PER_SEC); ttt0 = clock();
for (size_t i = 0; i < cycle; i++)
concurrency::parallel_for_each(con2.begin(), con2.end(), incre);
auto ttt6 = (clock() - ttt0) / double(CLOCKS_PER_SEC); ttt0 = clock();
for (size_t i = 0; i < cycle; i++)
parallel_iter(con3.begin(), con3.end(), [](pair<const int, int>& i) {i.second += 1; });
auto ttt4 = (clock() - ttt0) / double(CLOCKS_PER_SEC); ttt0 = clock();
for (size_t i = 0; i < cycle; i++)
concurrency::parallel_for_each(con3.begin(), con3.end(), [](pair<const int, int>& i) {i.second += 1; });
auto ttt5 = (clock() - ttt0) / double(CLOCKS_PER_SEC); ttt0 = clock();
for (size_t i = 0; i < cycle; i++)
parallel_iter(con4.begin(), con4.end(), [](pair<const int, int>& i) {i.second += 1; });
auto ttt7 = (clock() - ttt0) / double(CLOCKS_PER_SEC); ttt0 = clock();
for (size_t i = 0; i < cycle; i++)
concurrency::parallel_for_each(con4.begin(), con4.end(), [](pair<const int, int>& i) {i.second += 1; });
auto ttt8 = (clock() - ttt0) / double(CLOCKS_PER_SEC); ttt0 = clock();
cout << "\n[ 数据量 " << sii << " ][ 循环次数 " << cycle << " ] -> 执行时间统计 ---------------"
<< endl << "串行 : " << ttt1 << " 秒"
<< endl << "数组 : " << ttt2 << " 秒"
<< endl << "vector : " << ttt3 << " 秒"
<< endl << "vector (Win PPL) : " << ttt6 << " 秒"
<< endl << "unordered_map : " << ttt4 << " 秒"
<< endl << "unordered_map(Win PPL) : " << ttt5 << " 秒"
<< endl << "map : " << ttt7 << " 秒"
<< endl << "map (Win PPL) : " << ttt8 << " 秒";
size_t tCounts2 = 30;
auto pfun2 = [&cs, tCounts2](int i, int ni) {
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(1));
cs.lock();
cout << endl << "Running thread " << i + 1 << " / " << tCounts2;
cs.unlock();
};
auto pfun3 = [&cs](int i, int ni) {
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(1));
cs.lock();
cout << endl << "Running thread " << i + 1 << " / " << parallel_helper_hardware_concurrency();
cs.unlock();
};
cout << "\n\n并行情况验证(指定并行数量情况)--------------";
parallel_proc(tCounts2, pfun2);
cout << "\n\n并行情况验证(按核心数确定并行数量情况)--------------";
parallel_proc(pfun3);
int ci = 0;
auto ft = parallel_proc([&ci](int trdIndex, int trdIndex2)->std::string {
std::this_thread::sleep_for(std::chrono::milliseconds(1));
ci++;
char buf[40];
sprintf_s(buf, "\n%d 获得 ci 修改权 ci = %d", trdIndex, ci);
return buf;
});
for (size_t i = 0; i < ft.size(); i++)
cout << ft[i].get();
return 1;
}
头文件
CLParallel.h
#ifndef __CL_PARALLEL_H__
#define __CL_PARALLEL_H__
#include ,std::param_type<_function>>::type()
);
}
//执行与调度线程同步的nThreadsCounts个线程,并行STL容器,从容器的迭代器startedIndex至endIndex(不包含endIndex)个元素,
//回调函数传参为容器的元素类型的引用;
template<class _iter, class _function, class _task = TaskPoolStatic>
void parallel(size_t nThreadsCounts, _iter&& startedIndex, _iter&& endIndex, _function&& func, _task&& task = _task()) {
_parallel_iter(nThreadsCounts, startedIndex, endIndex, func, task
, typename std::iterator_traits<typename std::decay<_iter>::type>::iterator_category()
//, typename _get_fun_args_counts>::type()
);
}
//执行与调度线程同步的cpu核心数个线程,并行STL容器,从容器的迭代器startedIndex至endIndex(不包含endIndex)个元素,
//回调函数传参为容器的元素类型的引用;
template<class _iter, class _function, class _task = TaskPoolStatic>
void parallel_iter(_iter&& startedIndex, _iter&& endIndex, _function&& func, _task&& task = _task()) {
parallel_iter(parallel_helper_hardware_concurrency(), startedIndex, endIndex, func, task);
}
//执行与调度线程同步的cpu核心数个线程,并行STL容器,从容器的迭代器startedIndex至endIndex(不包含endIndex)个元素,
//回调函数传参为容器的元素类型的引用;
template<class _iter, class _function, class _task = TaskPoolStatic>
void parallel(_iter&& startedIndex, _iter&& endIndex, _function&& func, _task&& task = _task()) {
parallel_iter(parallel_helper_hardware_concurrency(), startedIndex, endIndex, func, task);
}
//执行与调度线程同步的nThreadsCounts个线程,并行容器con的从下标startedIndex至endIndex(不包含endIndex)个元素,
//回调函数传参为容器或数组的元素类型的引用;
template<class _contain, class _function, class _task = TaskPoolStatic>
void parallel(size_t nThreadsCounts, _contain& con, size_t startedIndex, size_t endIndex, _function&& func, _task&& task = _task()) {
auto pfunc = [](bool* bKeep,size_t ni, size_t nThreadsCounts, _contain* con, size_t startedIndex, size_t endIndex, _function&& func) {
size_t is, ie;
parallel_helper_getThreadSection(endIndex - startedIndex, nThreadsCounts, ni, is, ie);
is += startedIndex;
ie += startedIndex;
ag:
try {
for (; is < ie; ++is) {
if (*bKeep)func((*con)[is]);
else break;
}
}
catch (const parallel_exception_continue & e) {
++is;
if (!strstr(e.what(), "Parallel"))
throw runtime_error(e.what());
goto ag;
}
catch (const parallel_exception_break & e) {
if (!strstr(e.what(), "Parallel"))
throw runtime_error(e.what());
}
catch (const parallel_exception_break_all & e) {
if (!strstr(e.what(), "Parallel"))
throw runtime_error(e.what());
*bKeep = false;
}
};
bool bKeep = true;
//组装完成对象序列
std::vector<std::future<void>> works(nThreadsCounts);
for (size_t i = 0; i < nThreadsCounts; i++)
works[i] = task(pfunc, &bKeep, i, nThreadsCounts, &con, startedIndex, endIndex, func);//run
//主线程同步
for (auto& i : works)i.wait();
}
//执行与调度线程同步的nThreadsCounts个线程,并行容器con的从下标startedIndex至endIndex(不包含endIndex)个元素,
//回调函数传参为容器或数组的元素类型的引用;
template<class _contain, class _function, class _task = TaskPoolStatic>
void parallel(size_t nThreadsCounts, _contain&& con, size_t startedIndex, size_t endIndex, _function&& func, _task&& task = _task()) {
parallel(nThreadsCounts, con, startedIndex, endIndex, func, task);
}
//执行与调度线程同步的cpu核心数个线程,并行容器con的从下标startedIndex至endIndex(不包含endIndex)个元素,
//回调函数传参为容器或数组的元素类型的引用;
template<class _contain, class _function, class _task = TaskPoolStatic>
void parallel(_contain&& con, size_t startedIndex, size_t endIndex, _function&& func, _task&& task = _task()) {
parallel(parallel_helper_hardware_concurrency(), con, startedIndex, endIndex, func, task);
}
//执行与调度线程同步的nThreadsCounts个线程,线程函数传参为当前线程下标i(一个0开始的索引)和总的任务线程数nThreadsCounts
//返回线程的future队列;
template<class _function,class _task = TaskPoolStatic>
auto parallel_proc(size_t nThreadsCounts, _function&& func, _task&& task = _task()) {
typedef typename result_of<_function(size_t, size_t)>::type key_type;
//组装完成对象序列
std::vector<std::future<key_type>> works(nThreadsCounts);
for (size_t i = 0; i < nThreadsCounts; i++)
works[i] = task(func, i, nThreadsCounts);//run
//主线程同步
for (auto& i : works)i.wait();
return works;
}
//执行与调度线程同步的cpu核心数个线程;
//线程函数体形式为:R(*)(T1 i,T2 nThreadsCounts);
//传参为:i为当前线程下标(一个0开始的索引)类型为T1,nThreadsCounts为总的任务线程数类型为T2,线程体返回值类型为R;
//函数返回线程的future队列;
template<class _function, class _task = TaskPoolStatic>
auto parallel_proc(_function&& func, _task&& task = _task()) {
return parallel_proc(parallel_helper_hardware_concurrency(), func, task);
}
#endif