ARM aarch64汇编学习笔记(九):使用Neon指令(一)
NEON是一种基于SIMD思想的ARM技术。 SIMD, Single Instruction Multiple Data,是一种单条指令处理多个数据的并行处理技术,相比于一条指令处理一个数据,运算速度将会大大提高。
ARMv8 有31 个64位寄存器,1个不同名字的特殊寄存器,用途取决于上下文, 因此我们可以看成 31个64位的X寄存器或者31个32位的W寄存器(X寄存器的低32位)
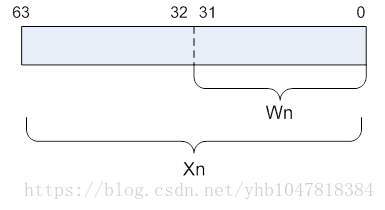
ARMv8有32个128位的V寄存器,相似的,我们同样可以看成是32个32位的S寄存器或者32个64位的D寄存器。
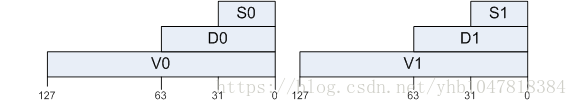
也可以用作32个64bit D0-D31或32个32bit S0-S31 或32个 16bit H0-h31 或 32个8bit B0-B31。
以一个简单的例子来说明使用Neon带来的收益。
比如, 现在有一个很简单的需求, 有2组数据, 每组数据有16 x 1024个整型数, 让它们按顺序一一相加,得到相加的和(每组数据的数不超过255,相加的和如果大于255,则返回255).
如果用C语言实现:
#include
#include
#define MAX_LEN 16 * 1024 * 1024
typedef unsigned char uint_8t;
typedef unsigned short uint_16t;
int main()
{
double start_time;
double end_time;
uint_8t *dist1 = (uint_8t *)malloc(sizeof(uint_8t) * MAX_LEN);
uint_8t *dist2 = (uint_8t *)malloc(sizeof(uint_8t) * MAX_LEN);
uint_16t *ref_out = (uint_16t *)malloc(sizeof(uint_16t) * MAX_LEN);
// 2组数据随机赋值
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_LEN; i++)
{
dist1[i] = rand() % 256;
dist2[i] = rand() % 256;
}
start_time = clock();
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_LEN; i++)
{
ref_out[i] = dist1[i] + dist2[i];
if (ref_out[i] > 255)
{
ref_out[i] = 255;
}
}
end_time = clock();
printf("C use time %f s\n", end_time - start_time);
return 0;
}
因为C语言的实现每次相加都只操作了一个寄存器,由于每一个输入和输出都不大于255, 可以用8bit的寄存器保存,对于寄存器而言造成了浪费。
如果使用Neon进行加速:
.text
.global asm_add_neon
asm_add_neon:
LOOP:
LDR Q0, [X0], #0x10
LDR Q1, [X1], #0x10
UQADD V0.16B, V0.16B, V1.16B
STR Q0, [X2], #0x10
SUBS X3, X3, #0x10
B.NE LOOP
RET
Q0代表数组A, Q1代表数组B, 每次读128bit (16个), 利用ARM vector无饱和相加指令UQADD进行计算,得到的结果存储在X2寄存器。
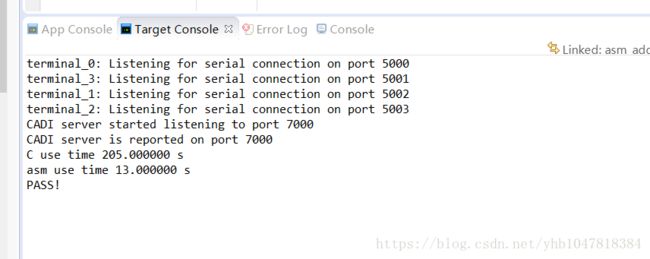
比较C语言和ARM NEON加速后实现的性能:
#include
#include
#define MAX_LEN 16 * 1024 * 1024
typedef unsigned char uint_8t;
typedef unsigned short uint_16t;
extern int asm_add_neon(uint_8t *dist1, uint_8t *dist2, uint_8t *out, int len);
int main()
{
double start_time;
double end_time;
uint_8t *dist1 = (uint_8t *)malloc(sizeof(uint_8t) * MAX_LEN);
uint_8t *dist2 = (uint_8t *)malloc(sizeof(uint_8t) * MAX_LEN);
uint_8t *out = (uint_8t *)malloc(sizeof(uint_8t) * MAX_LEN);
uint_16t *ref_out = (uint_16t *)malloc(sizeof(uint_16t) * MAX_LEN);
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_LEN; i++)
{
dist1[i] = rand() % 256;
dist2[i] = rand() % 256;
}
start_time = clock();
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_LEN; i++)
{
ref_out[i] = dist1[i] + dist2[i];
if (ref_out[i] > 255)
{
ref_out[i] = 255;
}
//printf("%d dist1[%d] dist2[%d] refout[%d] \n", i,dist1[i], dist2[i], ref_out[i]);
}
end_time = clock();
printf("C use time %f s\n", end_time - start_time);
start_time = clock();
asm_add_neon(dist1, dist2, out, MAX_LEN);
end_time = clock();
printf("asm use time %f s\n", end_time - start_time);
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_LEN; i++)
{
if (out[i] != ref_out[i])
{
printf("ERROR:%d\n", i);
return -1;
}
}
printf("PASS!\n");
return 0;
}
arm neon汇编实现的性能正好大约是纯C语言实现的16倍。