图论09—MATLAB自带最短路函数
一、写出稀疏矩阵
- 方法一 a.起点为行,终点为列,写出行向量R和列向量C
- 方法二 a.写出权值矩阵或已知权值矩阵W
c.当G(i,j)==inf时删除,即构成最终的稀疏矩阵
二、最短路算法命令格式
view(biograph(G));
graphallshortestpath(G);
[dist path]=graphshortest(G,s,t);
[M,F,C]=graphmaxflow(G,s,t);
例:
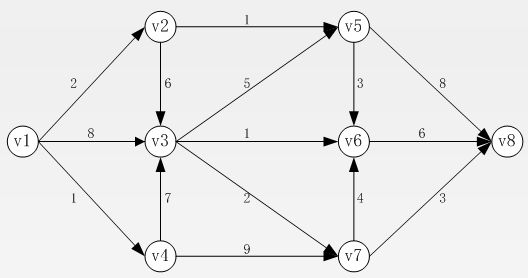
(1)构造下图的稀疏矩阵(注意方向)。
(2)使用MATLAB依据稀疏矩阵画出该图的结构图。
(3)求出各点之间的最短距离。
(4)求出点v1到点v8的最短距离和路径,并在拓扑图中用红色标记,路径加粗显示。
(5)若用边权代表通过能力(假设),求出最大流的分配方案。
解:(1)稀疏矩阵
方法一:
>> R=[1 1 2 4 1 2 3 3 5 7 3 4 5 6 7];
>> C=[2 3 3 3 4 5 5 6 6 6 7 7 8 8 8];
>>W=[2 8 6 7 1 1 5 1 3 4 2 9 8 6 3];
>> G1=sparse(R,C,W)
G1 =
(1,2) 2
(1,3) 8
(2,3) 6
(4,3) 7
(1,4) 1
(2,5) 1
(3,5) 5
(3,6) 1
(5,6) 3
(7,6) 4
(3,7) 2
(4,7) 9
(5,8) 8
(6,8) 6
(7,8) 3
即该图的稀疏矩阵为G1.
方法二:
>> W =[
0 2 8 1 Inf Inf Inf Inf
Inf 0 6 Inf 1 Inf Inf Inf
Inf Inf 0 Inf 5 1 2 Inf
Inf Inf 7 0 Inf Inf 9 Inf
Inf Inf Inf Inf 0 3 Inf 8
Inf Inf Inf Inf Inf 0 Inf 6
Inf Inf Inf Inf Inf 4 0 3
Inf Inf Inf Inf Inf Inf Inf Inf];
>> G=sparse(W);
>> for i=1:length(W)
for j=1:length(W)
if G(i,j)==inf
G(i,j)=0;
end
end
end
>> G2=G
G2 =
(1,2) 2
(1,3) 8
(2,3) 6
(4,3) 7
(1,4) 1
(2,5) 1
(3,5) 5
(3,6) 1
(5,6) 3
(7,6) 4
(3,7) 2
(4,7) 9
(5,8) 8
(6,8) 6
(7,8) 3
即稀疏矩阵为G2,显然G1=G2.
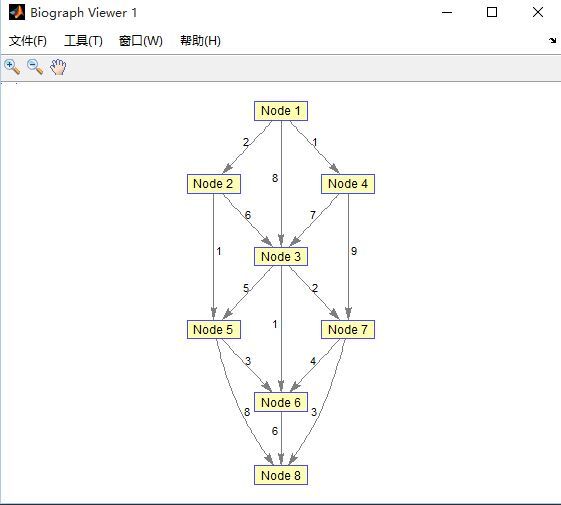
(2)结构图
>> view(biograph(G2,[],'ShowW','ON'))
(3)任意点之间的最短距离
>> graphallshortestpaths(G2)
ans =
0 2 8 1 3 6 10 11
Inf 0 6 Inf 1 4 8 9
Inf Inf 0 Inf 5 1 2 5
Inf Inf 7 0 12 8 9 12
Inf Inf Inf Inf 0 3 Inf 8
Inf Inf Inf Inf Inf 0 Inf 6
Inf Inf Inf Inf Inf 4 0 3
Inf Inf Inf Inf Inf Inf Inf 0
说明:第1行为点V1到其他点的距离,到v2为2,v3为8……v8为11。第i行为vi到其他点的距离向量。
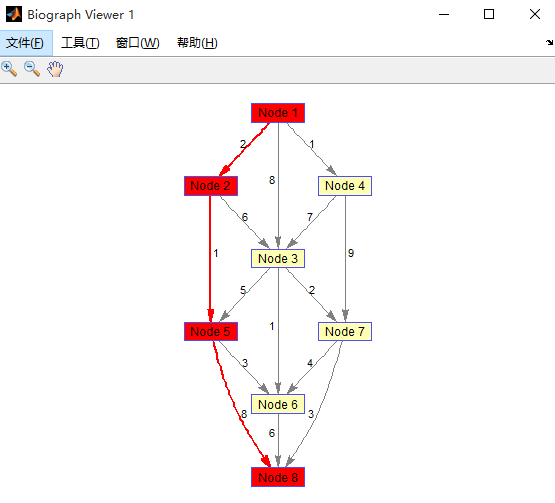
(4)求v1到v8的最短距离和路径并画图显示。
[dist path]=graphshortestpath(G2,1,8)
dist =
11
path =
1 2 5 8
即最短距离为11,路径为1->2->5->8.
>> h=view(biograph(G2,[],'showW','on'));
>> edges=getedgesbynodeid(h,get(h.Nodes(path),'ID'));
>> set(h.Nodes(path),'color',[1 0 0])
>> set(edges,'LineColor',[1 0 0])
>> set(edges,'LineWidth',1.5)
%则图片更改为:
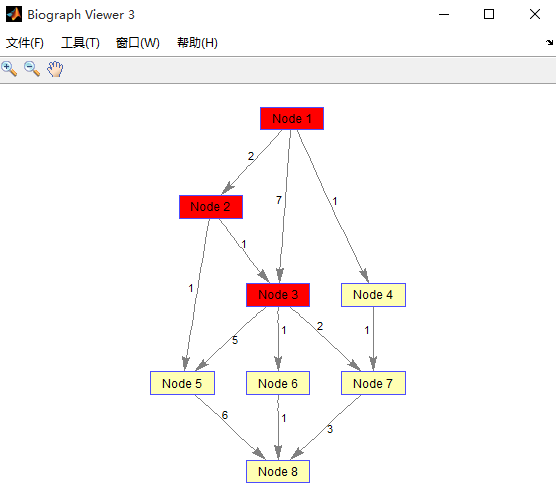
(5)最大流
>> [M,F,C]=graphmaxflow(G2,1,8)
M =
10
F =
(1,2) 2
(1,3) 7
(2,3) 1
(1,4) 1
(2,5) 1
(3,5) 5
(3,6) 1
(3,7) 2
(4,7) 1
(5,8) 6
(6,8) 1
(7,8) 3
C =
1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0
>> m=view(biograph(F,[],'showW','ON'))
即最大流为10,方案如上图。最小割为1 2 3,如下图.