Python之OpenGL笔记(35):曲面物体的构建
一、目的
1、曲面物体的构建画球体;
2、棋盘纹理着色器应用;
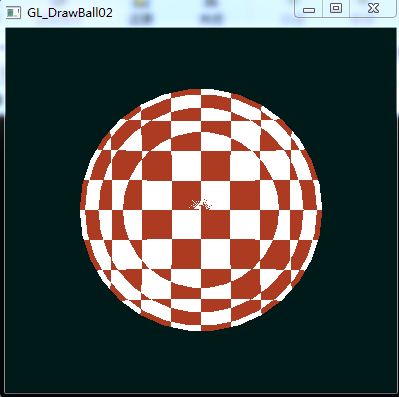
二、程序运行结果
三、曲面物体的构建基本原理
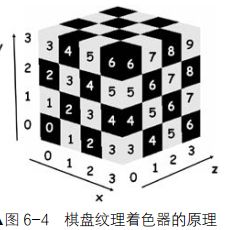
吴亚峰《OpenGL ES 3.x游戏开发》(上卷)内容
OpenGL 中任何形状的 3D 物体都是用三角形拼凑而成的,因此,构建ᴢ面物体最重要的就是找到将曲面恰当拆分成三角形的策略。最基本的策略是首先按照一定的规则将物体按行和列两个方向进行拆分,这时就可以得到很多的小四边形。然后再将每个小四边形拆分成两个三角形即可。
球面首先被按照纬度(行)和经度(列)的方向拆分成了很多的小四边形,每个小四边形又被拆分成两个小三角形。
这种拆分方式下,三角形中每个顶点的坐标都可以用解析几何的公式方便地计算出来,具体情况如下。
x = R×cosα×cosβ;
y = R×cosα×sinβ;
z = R×sinα
四、棋盘纹理着色器
具体的着色策略为,若片元位于黑色小方块中,就将该片元的颜色设置为红色;若片元位于白棋盘色小方块中,则将片元的颜色设置为白色,具体计算方法如下所列。
- 首先计算出当前片元 x、 y、 z 坐标对应的行数(x 轴)、层数(y 轴)及列数(z 轴)。
- 如果行数、层数、列数之和为奇数,则片元为红色;若和为偶数,则片元为白色。
五、源代码
"""
程序名称:GL_DrawBall02.py
编程: dalong10
功能: 球体构建、棋盘着色器应用的实现
参考资料: 《OpenGL ES 3.x游戏开发》(上卷)吴亚峰
"""
import myGL_Funcs #Common OpenGL utilities,see myGL_Funcs.py
import sys, random, math
import OpenGL
from OpenGL.GL import *
from OpenGL.GL.shaders import *
import numpy
import numpy as np
import glfw
from pyrr import Quaternion, matrix44, Vector3
strVS = """
#version 330 core
layout(location = 0) in vec3 position;
uniform mat4 uMVMatrix;
uniform mat4 uPMatrix;
uniform float Rx;
uniform float Ry;
uniform float Rz;
uniform float theta1;
out vec3 vPosition ; //用于传递给片元着色器的顶点位置
void main(){
mat4 rot3=mat4( vec4(cos(theta1)+Rx*Rx*(1-cos(theta1)), Rx*Ry*(1-cos(theta1))-Rz*sin(theta1), Rx*Rz*(1-cos(theta1))+Ry*sin(theta1), 0),
vec4(Rx*Ry*(1-cos(theta1))+Rz*sin(theta1),cos(theta1)+Ry*Ry*(1-cos(theta1)),Ry*Rz*(1-cos(theta1))-Rx*sin(theta1),0),
vec4(Rx*Rz*(1-cos(theta1))-Ry*sin(theta1),Ry*Rz*(1-cos(theta1))+Rx*sin(theta1),cos(theta1)+Rz*Rz*(1-cos(theta1)), 0.0),
vec4(0.0, 0.0,0.0, 1.0));
gl_Position=uPMatrix * uMVMatrix* rot3 *vec4(position.x, position.y, position.z, 1.0);
//将顶点的位置传给片元着色器
vPosition = position;//将原始顶点位置传递给片元着色器
}
"""
strFS = """
#version 330 core
in vec3 vPosition;//接收从顶点着色器过来的顶点位置
out vec4 fragColor;//输出的片元颜色
void main(){
vec3 color;
float n = 8.0;//外接立方体每个坐标轴方向切分的份数
float uR=1.0 ;
float span = 2.0*uR/n;//每一份的尺寸(小方块的边长)
int i = int((vPosition.x + uR)/span);//当前片元位置小方块的行数
int j = int((vPosition.y + uR)/span);//当前片元位置小方块的层数
int k = int((vPosition.z + uR)/span);//当前片元位置小方块的列数
//计算当前片元行数、层数、列数的和并对2取模
int whichColor = int(mod(float(i+j+k),2.0));
if(whichColor == 1) {//奇数时为红色
color = vec3(0.678,0.231,0.129);//红色
}
else {//偶数时为白色
color = vec3(1.0,1.0,1.0);//白色
}
//将计算出的颜色传递给管线
fragColor=vec4(color,0);
}
"""
VIEW=np.array([-0.8, 0.8, -0.8, 0.8, 1.0, 20.0]) # 视景体的left/right/bottom/top/near/far六个面
SCALE_K=np.array([1.0, 1.0, 1.0]) # 模型缩放比例
cameraPos=np.array([0.0, 0.0, 30]) # 眼睛的位置(默认z轴的正方向)
cameraFront=np.array([0.0, 0.0, 0.0]) # 瞄准方向的参考点(默认在坐标原点)
cameraUp=np.array([0.0, 1.0, 0.0]) # 定义对观察者而言的上方(默认y轴的正方向)
WIN_W, WIN_H = 640, 480 # 保存窗口宽度和高度的变量
class FirstSphere:
def __init__(self, cube_verticeside ):
# load shaders
self.program = myGL_Funcs.loadShaders(strVS, strFS)
glUseProgram(self.program)
self.vertIndex = glGetAttribLocation(self.program, b"position")
self.cube_vertices = cube_verticeside
# set up vertex array object (VAO)
self.vao = glGenVertexArrays(1)
glBindVertexArray(self.vao)
# set up VBOs
vertexData = numpy.array(self.cube_vertices, numpy.float32)
self.vertexBuffer = glGenBuffers(1)
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, self.vertexBuffer)
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, 4*len(vertexData), vertexData, GL_STATIC_DRAW)
# enable arrays
glEnableVertexAttribArray(self.vertIndex)
# Position attribute
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, self.vertexBuffer)
glVertexAttribPointer(self.vertIndex, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 0,None)
# unbind VAO
glBindVertexArray(0)
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, 0)
def render(self, Rx,Ry,Rz,r1,pMatrix,mvMatrix):
# use shader
glUseProgram(self.program)
# set proj matrix
glUniformMatrix4fv(glGetUniformLocation(self.program, 'uPMatrix'),
1, GL_FALSE, pMatrix)
# set modelview matrix
glUniformMatrix4fv(glGetUniformLocation(self.program, 'uMVMatrix'),
1, GL_FALSE, mvMatrix)
glUniform1f(glGetUniformLocation(self.program, "Rx"), Rx)
glUniform1f(glGetUniformLocation(self.program, "Ry"), Ry)
glUniform1f(glGetUniformLocation(self.program, "Rz"), Rz)
theta1 = r1*PI/180.0
glUniform1f(glGetUniformLocation(self.program, "theta1"), theta1)
# bind VAO
glBindVertexArray(self.vao)
# draw
glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES,0,len(self.cube_vertices) )
# unbind VAO
glBindVertexArray(0)
def drawglobeVBO():
PI = 3.14159265358979323846264
statcky = 30 # 横向向切成多少片
stlicex = 30 # 纵向切多少片
R = 1.0 # 半径
angleHy = (2*PI)/statcky # 横向每份的角度 算出弧度值
angleZx = (2*PI)/stlicex; # 纵向每份的角度 算出弧度值
NumAngleHy = 0.0 # 当前横向角度
NumAngleZx = 0.0 # 当前纵向角度
x=0.0
y=0.0
z=0.0
c=numpy.array([], numpy.float32)
for j in range(statcky):
for i in range(stlicex):
NumAngleHy = angleHy*i #
NumAngleZx = angleZx*j # 起点都是轴指向的方向。根据右手定则决定转向,只要转向相同,那么两个就合适
x0 = R*np.cos(NumAngleHy)*np.cos(NumAngleZx)
y0 = R*np.cos(NumAngleHy)*np.sin(NumAngleZx)
z0 = R*np.sin(NumAngleHy)
x1 = R*np.cos(NumAngleHy)*np.cos(NumAngleZx+angleZx)
y1 = R*np.cos(NumAngleHy)*np.sin(NumAngleZx+angleZx)
z1 = R*np.sin(NumAngleHy)
x2 = R*np.cos(NumAngleHy+angleHy)*np.cos(NumAngleZx+angleZx)
y2 = R*np.cos(NumAngleHy+angleHy)*np.sin(NumAngleZx+angleZx)
z2 = R*np.sin(NumAngleHy+angleHy)
x3 = R*np.cos(NumAngleHy+angleHy)*np.cos(NumAngleZx)
y3 = R*np.cos(NumAngleHy+angleHy)*np.sin(NumAngleZx)
z3 = R*np.sin(NumAngleHy+angleHy)
c=np.hstack((c,numpy.array([x1,y1,z1], numpy.float32) ))
c=np.hstack((c,numpy.array([x3,y3,z3], numpy.float32) ))
c=np.hstack((c,numpy.array([x0,y0,z0], numpy.float32) ))
c=np.hstack((c,numpy.array([x1,y1,z1], numpy.float32) ))
c=np.hstack((c,numpy.array([x2,y2,z2], numpy.float32) ))
c=np.hstack((c,numpy.array([x3,y3,z3], numpy.float32) ))
return c
#Is called whenever a key is pressed/released via GLFW
def on_key(window, key, scancode, action, mods):
if key == glfw.KEY_ESCAPE and action == glfw.PRESS:
glfw.set_window_should_close(window,1)
if __name__ == '__main__':
import sys
import glfw
import OpenGL.GL as gl
keys=numpy.zeros(1024)
deltaTime = 0.0
lastFrame = 0.0 # Time of last frame
# Initialize the library
if not glfw.init():
sys.exit()
# Create a windowed mode window and its OpenGL context
window = glfw.create_window(640, 480, "GL_DrawBall02 ", None, None)
if not window:
glfw.terminate()
sys.exit()
# Make the window's context current
glfw.make_context_current(window)
# Install a key handler
glfw.set_key_callback(window, on_key)
PI = 3.14159265358979323846264
# 画球面
vert = drawglobeVBO()
# Loop until the user closes the window
a=0
firstSphere1 = FirstSphere(vert)
while not glfw.window_should_close(window):
currentFrame = glfw.get_time()
deltaTime = currentFrame - lastFrame
lastFrame = currentFrame
# Render here
width, height = glfw.get_framebuffer_size(window)
WIN_W, WIN_H =width, height
ratio = width / float(height)
glfw.poll_events()
gl.glViewport(0, 0, width, height)
gl.glClear(gl.GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT | gl.GL_DEPTH_BUFFER_BIT)
#glPolygonMode(GL_FRONT_AND_BACK,GL_LINE); #用于控制多边形的显示方式
gl.glMatrixMode(gl.GL_PROJECTION)
gl.glLoadIdentity()
gl.glOrtho(-ratio, ratio, -1, 1, 1, -1)
gl.glMatrixMode(gl.GL_MODELVIEW)
gl.glLoadIdentity()
gl.glClearColor(0.0,0.1,0.1,1.0)
# modelview matrix
mvMatrix = matrix44.create_look_at(cameraPos, cameraFront, cameraUp,None) # 设置视点
pMatrix = matrix44.create_perspective_projection_from_bounds(-ratio*1.0, ratio*1.0, -1, 1,20,100,None)
firstSphere1.render( 0, 1,1, a ,pMatrix, mvMatrix) #球
# Swap front and back buffers
glfw.swap_buffers(window)
# Poll for and process events
glfw.poll_events()
glfw.terminate()
六、参考资料
1、大龙10的简书:https://www.jianshu.com/p/49dec482a291
2、吴亚峰《OpenGL ES 3.x游戏开发》(上卷)