opengl 实现人体骨骼点的绘制
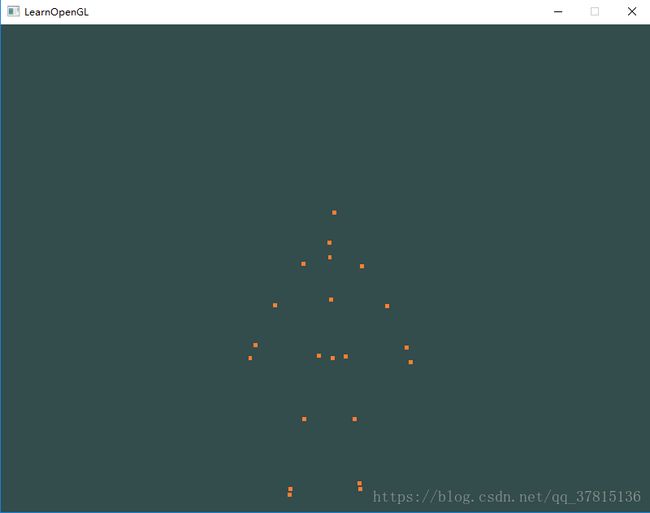
最近,想实现怎么利用opengl将Kinect扫到人体骨骼坐标点在opengl 中绘制出来,第一个想到的难点就是,在Kinect中的是世界坐标点,我怎么转换到opengl中的屏幕坐标,一开始陷入的就是觉得要改摄像机的参数,这是不对的,摄像机改变的只是你看物体的角度。所以经历一番折腾,看过网上许多有关opengl坐标系统转换的博客,我具体渲染出的人体骨骼点如下:
代码:
#include
// GLEW
#define GLEW_STATIC
#include
// GLFW
#include
#include
#include
#include
// Function prototypes
void key_callback(GLFWwindow* window, int key, int scancode, int action, int mode);
// Window dimensions
const GLuint WIDTH = 800, HEIGHT = 600;
// Shaders
const GLchar* vertexShaderSource = "#version 330 core\n"
"layout (location = 0) in vec3 position;\n"
"uniform mat4 model;\n"
"uniform mat4 view;\n"
"uniform mat4 projection;\n"
"void main()\n"
"{\n"
"gl_Position = projection * view * model * vec4(position.x, position.y, position.z, 1.0);\n"
"}\0";
const GLchar* fragmentShaderSource = "#version 330 core\n"
"out vec4 color;\n"
"void main()\n"
"{\n"
"color = vec4(1.0f, 0.5f, 0.2f, 1.0f);\n"
"}\n\0";
// The MAIN function, from here we start the application and run the game loop
int main()
{
std::cout << "Starting GLFW context, OpenGL 3.3" << std::endl;
// Init GLFW
glfwInit();
// Set all the required options for GLFW
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MAJOR, 3);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_CONTEXT_VERSION_MINOR, 3);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_OPENGL_PROFILE, GLFW_OPENGL_CORE_PROFILE);
glfwWindowHint(GLFW_RESIZABLE, GL_FALSE);
// Create a GLFWwindow object that we can use for GLFW's functions
GLFWwindow* window = glfwCreateWindow(WIDTH, HEIGHT, "LearnOpenGL", nullptr, nullptr);
glfwMakeContextCurrent(window);
// Set the required callback functions
glfwSetKeyCallback(window, key_callback);
// Set this to true so GLEW knows to use a modern approach to retrieving function pointers and extensions
glewExperimental = GL_TRUE;
// Initialize GLEW to setup the OpenGL Function pointers
glewInit();
// Define the viewport dimensions
int width, height;
glfwGetFramebufferSize(window, &width, &height);
glViewport(0, 0, width, height);
//glEnable(GL_DEPTH_TEST);
// Build and compile our shader program
// Vertex shader
GLuint vertexShader = glCreateShader(GL_VERTEX_SHADER);
glShaderSource(vertexShader, 1, &vertexShaderSource, NULL);
glCompileShader(vertexShader);
// Check for compile time errors
GLint success;
GLchar infoLog[512];
glGetShaderiv(vertexShader, GL_COMPILE_STATUS, &success);
if (!success)
{
glGetShaderInfoLog(vertexShader, 512, NULL, infoLog);
std::cout << "ERROR::SHADER::VERTEX::COMPILATION_FAILED\n" << infoLog << std::endl;
}
// Fragment shader
GLuint fragmentShader = glCreateShader(GL_FRAGMENT_SHADER);
glShaderSource(fragmentShader, 1, &fragmentShaderSource, NULL);
glCompileShader(fragmentShader);
// Check for compile time errors
glGetShaderiv(fragmentShader, GL_COMPILE_STATUS, &success);
if (!success)
{
glGetShaderInfoLog(fragmentShader, 512, NULL, infoLog);
std::cout << "ERROR::SHADER::FRAGMENT::COMPILATION_FAILED\n" << infoLog << std::endl;
}
// Link shaders
GLuint shaderProgram = glCreateProgram();
glAttachShader(shaderProgram, vertexShader);
glAttachShader(shaderProgram, fragmentShader);
glLinkProgram(shaderProgram);
// Check for linking errors
glGetProgramiv(shaderProgram, GL_LINK_STATUS, &success);
if (!success) {
glGetProgramInfoLog(shaderProgram, 512, NULL, infoLog);
std::cout << "ERROR::SHADER::PROGRAM::LINKING_FAILED\n" << infoLog << std::endl;
}
glDeleteShader(vertexShader);
glDeleteShader(fragmentShader);
// Set up vertex data (and buffer(s)) and attribute pointers
//GLfloat vertices[] = {
// // First triangle
// 0.5f, 0.5f, // Top Right
// 0.5f, -0.5f, // Bottom Right
// -0.5f, 0.5f, // Top Left
// // Second triangle
// 0.5f, -0.5f, // Bottom Right
// -0.5f, -0.5f, // Bottom Left
// -0.5f, 0.5f // Top Left
//};
GLfloat vertices[] = {
0.01f, 0.01f, 0.0f, // Top Right
0.01f, -0.01f, 0.0f, // Bottom Right
-0.01f, -0.01f, 0.0f, // Bottom Left
-0.01f, 0.01f, 0.0f // Top Left
};
GLuint indices[] = { // Note that we start from 0!
0, 1, 3, // First Triangle
1, 2, 3 // Second Triangle
};
glm::vec3 cubePositions[] = {
glm::vec3(0.032378f, -0.442654f, 2.17715f),
glm::vec3(-0.0343935f, -0.433992f, 2.14277f),
glm::vec3(0.0983881f, -0.438157f, 2.14615f),
glm::vec3(0.0250801f, -0.155455f, 2.17354f),
glm::vec3(-0.105409f, -0.747508f, 2.14539f),
glm::vec3(0.14416f, -0.746396f, 2.15032f),
glm::vec3(-0.172575f, -1.08588f, 2.20642f),
glm::vec3(0.167421f, -1.0581f, 2.20065f),
glm::vec3(0.0200967f, 0.0561917f, 2.16359f),
glm::vec3(-0.18236f, -1.13302f, 2.08883f),
glm::vec3(0.171922f, -1.10516f, 2.08213f),
glm::vec3(0.0183976f, 0.125564f, 2.15752f),
glm::vec3(0.0436317f, 0.275752f, 2.12795f),
glm::vec3(-0.110744f, 0.021982f, 2.1629f),
glm::vec3(0.177801f, 0.00826143f, 2.16602f),
glm::vec3(-0.248465f, -0.182686f, 2.1887f),
glm::vec3(0.301957f, -0.186638f, 2.19558f),
glm::vec3(-0.345132f, -0.377335f, 2.19578f),
glm::vec3(0.397963f, -0.392711f, 2.17949f),
glm::vec3(-0.373589f, -0.442521f, 2.16485f),
glm::vec3(0.419256f, -0.465622f, 2.16209f)
/*glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f),
glm::vec3(2.0f, 5.0f, -15.0f),
glm::vec3(-1.5f, -2.2f, -2.5f),
glm::vec3(-3.8f, -2.0f, -12.3f),
glm::vec3(2.4f, -0.4f, -3.5f),
glm::vec3(-1.7f, 3.0f, -7.5f),
glm::vec3(1.3f, -2.0f, -2.5f),
glm::vec3(1.5f, 2.0f, -2.5f),
glm::vec3(1.5f, 0.2f, -1.5f),
glm::vec3(-1.3f, 1.0f, -1.5f)*/
};
GLuint VBO, VAO, EBO;
glGenVertexArrays(1, &VAO);
glGenBuffers(1, &VBO);
glGenBuffers(1, &EBO);
// Bind the Vertex Array Object first, then bind and set vertex buffer(s) and attribute pointer(s).
glBindVertexArray(VAO);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, VBO);
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(vertices), vertices, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
glBindBuffer(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, EBO);
glBufferData(GL_ELEMENT_ARRAY_BUFFER, sizeof(indices), indices, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
glVertexAttribPointer(0, 3, GL_FLOAT, GL_FALSE, 3 * sizeof(GLfloat), (GLvoid*)0);
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, 0); // Note that this is allowed, the call to glVertexAttribPointer registered VBO as the currently bound vertex buffer object so afterwards we can safely unbind
glBindVertexArray(0); // Unbind VAO (it's always a good thing to unbind any buffer/array to prevent strange bugs), remember: do NOT unbind the EBO, keep it bound to this VAO
// Uncommenting this call will result in wireframe polygons.
//glPolygonMode(GL_FRONT_AND_BACK, GL_LINE);
// Game loop
while (!glfwWindowShouldClose(window))
{
// Check if any events have been activiated (key pressed, mouse moved etc.) and call corresponding response functions
glfwPollEvents();
// Render
// Clear the colorbuffer
glClearColor(0.2f, 0.3f, 0.3f, 1.0f);
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
// Draw our first triangle
glUseProgram(shaderProgram);
//glBindVertexArray(VAO);
//glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, 6);
//glDrawElements(GL_TRIANGLES, 6, GL_UNSIGNED_INT, 0);
glm::mat4 view;
glm::mat4 projection;
view = glm::translate(view, glm::vec3(0.0f, 0.0f, -9.0f));
projection = glm::perspective(20.0f, (GLfloat)WIDTH / (GLfloat)HEIGHT, 0.1f, 100.0f);
// Get their uniform location
GLint modelLoc = glGetUniformLocation(shaderProgram, "model");
GLint viewLoc = glGetUniformLocation(shaderProgram, "view");
GLint projLoc = glGetUniformLocation(shaderProgram, "projection");
// Pass the matrices to the shader
glUniformMatrix4fv(viewLoc, 1, GL_FALSE, glm::value_ptr(view));
// Note: currently we set the projection matrix each frame, but since the projection matrix rarely changes it's often best practice to set it outside the main loop only once.
glUniformMatrix4fv(projLoc, 1, GL_FALSE, glm::value_ptr(projection));
glBindVertexArray(VAO);
for (GLuint i = 0; i < 21; i++)
{
glm::mat4 model;
model = glm::translate(model, cubePositions[i]);
/*GLfloat angle = 20.0f * i;
model = glm::rotate(model, angle, glm::vec3(1.0f, 0.3f, 0.5f));*/
glUniformMatrix4fv(modelLoc, 1, GL_FALSE, glm::value_ptr(model));
glDrawElements(GL_TRIANGLES, 6, GL_UNSIGNED_INT, 0);
}
glBindVertexArray(0);
// Swap the screen buffers
glfwSwapBuffers(window);
}
glBindVertexArray(0);
// Properly de-allocate all resources once they've outlived their purpose
glDeleteVertexArrays(1, &VAO);
glDeleteBuffers(1, &VBO);
glDeleteBuffers(1, &EBO);
// Terminate GLFW, clearing any resources allocated by GLFW.
glfwTerminate();
return 0;
}
// Is called whenever a key is pressed/released via GLFW
void key_callback(GLFWwindow* window, int key, int scancode, int action, int mode)
{
if (key == GLFW_KEY_ESCAPE && action == GLFW_PRESS)
glfwSetWindowShouldClose(window, GL_TRUE);
}