文章目录
- 基于transformer 的翻译系统
- 1. 数据处理
- 1.1 英文分词
- 1.2 中文分词
- 1.3 生成字典
- 1.4 数据生成器
- 2. 构建模型
- 2.1 构造建模组件
- layer norm层
- embedding层
- multihead层
- feedforward
- label_smoothing.
- 2.2 搭建模型
- 3. 训练模型
- 3.1 参数设定
- 3.2 模型训练
- 3.3 模型推断
基于transformer 的翻译系统
论文:https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.03762
项目地址:https://github.com/audier/my_deep_project/tree/master/NLP/4.transformer
本文实现了一个基于自注意力机制的翻译系统。注意力机制是机制是这两年比较火的方向,其中去年提出的自注意力机制更是各位大神的宠儿,网上可读性较高的代码有一点点不完美的地方就是mask没有发挥作用,最近也在做翻译系统,于是整理本文分享思路。
本文代码参考网上可读性较好的项目:https://github.com/Kyubyong/transformer
但是作者在key_mask和queries_mask中有一定的失误,本文修改了对应的模型和multihead层,使该功能正常。
转载请注明出处:https://blog.csdn.net/chinatelecom08
1. 数据处理
本文使用数据:https://github.com/audier/my_deep_project/tree/master/NLP/4.transformer
with open('cmn.txt', 'r', encoding='utf8') as f:
data = f.readlines()
from tqdm import tqdm
inputs = []
outputs = []
for line in tqdm(data[:10000]):
[en, ch] = line.strip(’\n’).split(’\t’)
inputs.append(en.replace(’,’,’ ,’)[:-1].lower())
outputs.append(ch[:-1])
100%|██████████| 10000/10000 [00:00<00:00, 473991.57it/s]
print(inputs[:10])
['hi', 'hi', 'run', 'wait', 'hello', 'i try', 'i won', 'oh no', 'cheers', 'he ran']
print(outputs[:10])
['嗨', '你好', '你用跑的', '等等', '你好', '让我来', '我赢了', '不会吧', '乾杯', '他跑了']
1.1 英文分词
我们将英文用空格隔开即可,但是需要稍微修改一下,将大写字母全部用小写字母代替。在上文中使用.lower进行了替代。
for line in tqdm(data):
[en, ch] = line.strip('\n').split('\t')
inputs.append(en[:-1].lower())
outputs.append(ch[:-1])
此处我们只需要将英文用空格分开即可。
inputs = [en.split(' ') for en in inputs]
print(inputs[:10])
[['hi'], ['hi'], ['run'], ['wait'], ['hello'], ['i', 'try'], ['i', 'won'], ['oh', 'no'], ['cheers'], ['he', 'ran']]
1.2 中文分词
import jieba
outputs = [[char for char in jieba.cut(line) if char != ' '] for line in outputs]
from pyhanlp import *
outputs = [[term.word for term in HanLP.segment(line) if term.word != ' '] for line in outputs]
import jieba
jieba_outputs = [[char for char in jieba.cut(line) if char != ' '] for line in outputs[-10:]]
print(jieba_outputs)
[['你', '不應', '該', '去', '那裡', '的'], ['你', '以前', '吸煙', ',', '不是', '嗎'], ['你現', '在', '最好', '回家'], ['你', '今天', '最好', '不要', '出門'], ['你', '滑雪', '比', '我', '好'], ['你', '正在', '把', '我', '杯子', '里', '的', '东西', '喝掉'], ['你', '并', '不', '满意', ',', '对', '吧'], ['你', '病', '了', ',', '该', '休息', '了'], ['你', '很', '勇敢', ',', '不是', '嗎'], ['你', '的', '意志力', '很強']]
outputs = [[char for char in jieba.cut(line) if char != ' '] for line in tqdm(outputs)]
100%|██████████| 10000/10000 [00:00<00:00, 11981.68it/s]
1.3 生成字典
将英文和中文映射为id
def get_vocab(data, init=['']):
vocab = init
for line in tqdm(data):
for word in line:
if word not in vocab:
vocab.append(word)
return vocab
SOURCE_CODES = [’’]
TARGET_CODES = [’’, ‘’, ‘’]
encoder_vocab = get_vocab(inputs, init=SOURCE_CODES)
decoder_vocab = get_vocab(outputs, init=TARGET_CODES)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
100%|██████████| 10000/10000 [00:00<00:00, 20585.73it/s]
100%|██████████| 10000/10000 [00:01<00:00, 7808.17it/s]
print(encoder_vocab[:10])
print(decoder_vocab[:10])
['', 'hi', 'run', 'wait', 'hello', 'i', 'try', 'won', 'oh', 'no']
['', '', '', '嗨', '你好', '你', '用', '跑', '的', '等等']
1.4 数据生成器
翻译系统训练所需要的数据形式,跟谷歌gnmt输入致,gnmt的原理可以参考:https://github.com/tensorflow/nmt
大概是:
- 编码器输入:I am a student
- 解码器输入:(go) Je suis étudiant
- 解码器输出:Je suis étudiant (end)
即解码器输入起始部分有个开始符号,输出句尾有个结束符号。
encoder_inputs = [[encoder_vocab.index(word) for word in line] for line in inputs]
decoder_inputs = [[decoder_vocab.index('')] + [decoder_vocab.index(word) for word in line] for line in outputs]
decoder_targets = [[decoder_vocab.index(word) for word in line] + [decoder_vocab.index('')] for line in outputs]
print(decoder_inputs[:4])
print(decoder_targets[:4])
[[1, 3], [1, 4], [1, 5, 6, 7, 8], [1, 9]]
[[3, 2], [4, 2], [5, 6, 7, 8, 2], [9, 2]]
import numpy as np
def get_batch(encoder_inputs, decoder_inputs, decoder_targets, batch_size=4):
batch_num = len(encoder_inputs) // batch_size
for k in range(batch_num):
begin = k batch_size
end = begin + batch_size
en_input_batch = encoder_inputs[begin:end]
de_input_batch = decoder_inputs[begin:end]
de_target_batch = decoder_targets[begin:end]
max_en_len = max([len(line) for line in en_input_batch])
max_de_len = max([len(line) for line in de_input_batch])
en_input_batch = np.array([line + [0] (max_en_len-len(line)) for line in en_input_batch])
de_input_batch = np.array([line + [0] (max_de_len-len(line)) for line in de_input_batch])
de_target_batch = np.array([line + [0] (max_de_len-len(line)) for line in de_target_batch])
yield en_input_batch, de_input_batch, de_target_batch
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
batch = get_batch(encoder_inputs, decoder_inputs, decoder_targets, batch_size=4)
next(batch)
(array([[1],
[1],
[2],
[3]]), array([[1, 3, 0, 0, 0],
[1, 4, 0, 0, 0],
[1, 5, 6, 7, 8],
[1, 9, 0, 0, 0]]), array([[3, 2, 0, 0, 0],
[4, 2, 0, 0, 0],
[5, 6, 7, 8, 2],
[9, 2, 0, 0, 0]]))
2. 构建模型
模型结构如下:
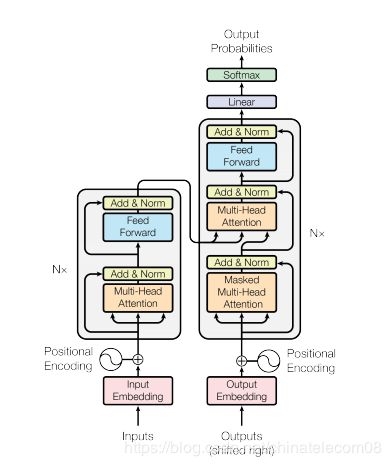
其中主要建模组件下面都会给出。
论文:https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.03762
关于论文讲解:百度即可,对着原论文代码一起看。
我个人觉得结合代码就会很好理解。
import tensorflow as tf
2.1 构造建模组件
下面代码实现了图片结构中的各个功能组件。
layer norm层
在框框的位置。
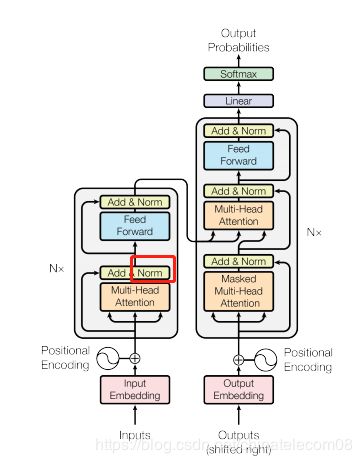
def normalize(inputs,
epsilon = 1e-8,
scope="ln",
reuse=None):
'''Applies layer normalization.
Args:
inputs: A tensor with 2 or more dimensions, where the first dimension has
`batch_size`.
epsilon: A floating number. A very small number for preventing ZeroDivision Error.
scope: Optional scope for `variable_scope`.
reuse: Boolean, whether to reuse the weights of a previous layer
by the same name.
Returns:
A tensor with the same shape and data dtype as `inputs`.
'''
with tf.variable_scope(scope, reuse=reuse):
inputs_shape = inputs.get_shape()
params_shape = inputs_shape[-1:]
mean, variance = tf.nn.moments(inputs, [-1], keep_dims=True)
beta= tf.Variable(tf.zeros(params_shape))
gamma = tf.Variable(tf.ones(params_shape))
normalized = (inputs - mean) / ( (variance + epsilon) ** (.5) )
outputs = gamma * normalized + beta
return outputs
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
embedding层
这里值得一提的是本文的position encoding也是用embedding层表示,原论文中说用公式或者embedding层自己训练都可以。
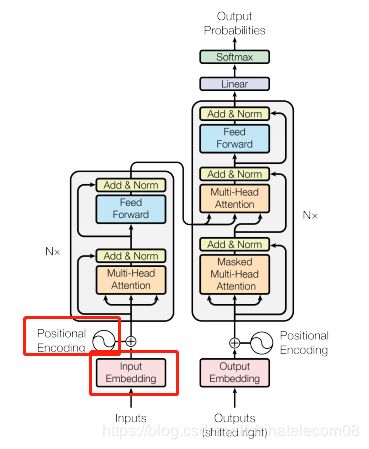
def embedding(inputs,
vocab_size,
num_units,
zero_pad=True,
scale=True,
scope="embedding",
reuse=None):
'''Embeds a given tensor.
Args:
inputs: A `Tensor` with type `int32` or `int64` containing the ids
to be looked up in `lookup table`.
vocab_size: An int. Vocabulary size.
num_units: An int. Number of embedding hidden units.
zero_pad: A boolean. If True, all the values of the fist row (id 0)
should be constant zeros.
scale: A boolean. If True. the outputs is multiplied by sqrt num_units.
scope: Optional scope for `variable_scope`.
reuse: Boolean, whether to reuse the weights of a previous layer
by the same name.
Returns:
A `Tensor` with one more rank than inputs's. The last dimensionality
should be `num_units`.
For example,
```
import tensorflow as tf
inputs = tf.to_int32(tf.reshape(tf.range(2*3), (2, 3)))
outputs = embedding(inputs, 6, 2, zero_pad=True)
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
print sess.run(outputs)
>>
[[[ 0. 0. ]
[ 0.09754146 0.67385566]
[ 0.37864095 -0.35689294]]
[[-1.01329422 -1.09939694]
[ 0.7521342 0.38203377]
[-0.04973143 -0.06210355]]]
```
```
import tensorflow as tf
inputs = tf.to_int32(tf.reshape(tf.range(2*3), (2, 3)))
outputs = embedding(inputs, 6, 2, zero_pad=False)
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
print sess.run(outputs)
>>
[[[-0.19172323 -0.39159766]
[-0.43212751 -0.66207761]
[ 1.03452027 -0.26704335]]
[[-0.11634696 -0.35983452]
[ 0.50208133 0.53509563]
[ 1.22204471 -0.96587461]]]
```
'''
with tf.variable_scope(scope, reuse=reuse):
lookup_table = tf.get_variable('lookup_table',
dtype=tf.float32,
shape=[vocab_size, num_units],
initializer=tf.contrib.layers.xavier_initializer())
if zero_pad:
lookup_table = tf.concat((tf.zeros(shape=[1, num_units]),
lookup_table[1:, :]), 0)
outputs = tf.nn.embedding_lookup(lookup_table, inputs)
if scale:
outputs = outputs * (num_units ** 0.5)
return outputs
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
multihead层
是self-attention的核心思想,务必把原理搞清楚。
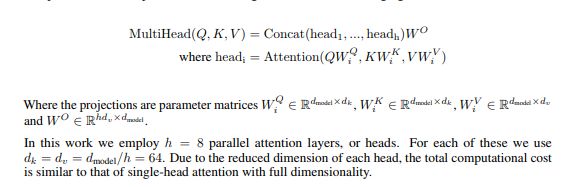
意思是自己跟自己做注意力机制,但是在这之前通过线性变换,将原来的输入映射到8个不同的空间去计算,最后再接到一起。
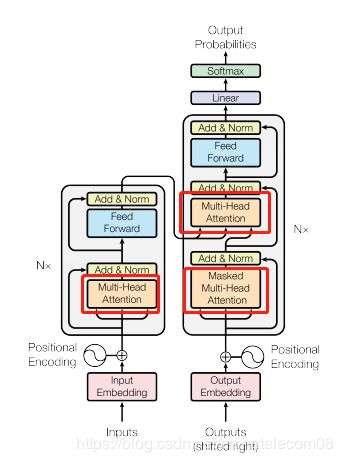
该层实现了下面功能,给谷歌鼓掌:
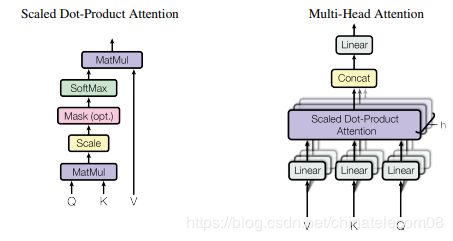
def multihead_attention(key_emb,
que_emb,
queries,
keys,
num_units=None,
num_heads=8,
dropout_rate=0,
is_training=True,
causality=False,
scope="multihead_attention",
reuse=None):
'''Applies multihead attention.
Args:
queries: A 3d tensor with shape of [N, T_q, C_q].
keys: A 3d tensor with shape of [N, T_k, C_k].
num_units: A scalar. Attention size.
dropout_rate: A floating point number.
is_training: Boolean. Controller of mechanism for dropout.
causality: Boolean. If true, units that reference the future are masked.
num_heads: An int. Number of heads.
scope: Optional scope for `variable_scope`.
reuse: Boolean, whether to reuse the weights of a previous layer
by the same name.
Returns
A 3d tensor with shape of (N, T_q, C)
'''
with tf.variable_scope(scope, reuse=reuse):
if num_units is None:
num_units = queries.get_shape().as_list[-1]
Q = tf.layers.dense(queries, num_units, activation=tf.nn.relu)
K = tf.layers.dense(keys, num_units, activation=tf.nn.relu)
V = tf.layers.dense(keys, num_units, activation=tf.nn.relu)
Q_ = tf.concat(tf.split(Q, num_heads, axis=2), axis=0)
K_ = tf.concat(tf.split(K, num_heads, axis=2), axis=0)
V_ = tf.concat(tf.split(V, num_heads, axis=2), axis=0)
outputs = tf.matmul(Q_, tf.transpose(K_, [0, 2, 1]))
outputs = outputs / (K_.get_shape().as_list()[-1] ** 0.5)
key_masks = tf.sign(tf.abs(tf.reduce_sum(key_emb, axis=-1)))
key_masks = tf.tile(key_masks, [num_heads, 1])
key_masks = tf.tile(tf.expand_dims(key_masks, 1), [1, tf.shape(queries)[1], 1])
paddings = tf.ones_like(outputs)*(-2**32+1)
outputs = tf.where(tf.equal(key_masks, 0), paddings, outputs)
if causality:
diag_vals = tf.ones_like(outputs[0, :, :])
tril = tf.linalg.LinearOperatorLowerTriangular(diag_vals).to_dense()
masks = tf.tile(tf.expand_dims(tril, 0), [tf.shape(outputs)[0], 1, 1])
paddings = tf.ones_like(masks)*(-2**32+1)
outputs = tf.where(tf.equal(masks, 0), paddings, outputs)
outputs = tf.nn.softmax(outputs)
query_masks = tf.sign(tf.abs(tf.reduce_sum(que_emb, axis=-1)))
query_masks = tf.tile(query_masks, [num_heads, 1])
query_masks = tf.tile(tf.expand_dims(query_masks, -1), [1, 1, tf.shape(keys)[1]])
outputs *= query_masks
outputs = tf.layers.dropout(outputs, rate=dropout_rate, training=tf.convert_to_tensor(is_training))
outputs = tf.matmul(outputs, V_)
outputs = tf.concat(tf.split(outputs, num_heads, axis=0), axis=2 )
outputs += queries
outputs = normalize(outputs)
return outputs
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
feedforward
两层全连接,用卷积模拟加速运算,也可以使用dense层。你会发现这个框架所需组件全部凑齐了,可以召唤神龙了。
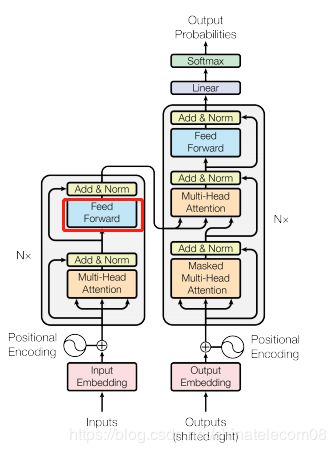
def feedforward(inputs,
num_units=[2048, 512],
scope="multihead_attention",
reuse=None):
'''Point-wise feed forward net.
Args:
inputs: A 3d tensor with shape of [N, T, C].
num_units: A list of two integers.
scope: Optional scope for `variable_scope`.
reuse: Boolean, whether to reuse the weights of a previous layer
by the same name.
Returns:
A 3d tensor with the same shape and dtype as inputs
'''
with tf.variable_scope(scope, reuse=reuse):
params = {"inputs": inputs, "filters": num_units[0], "kernel_size": 1,
"activation": tf.nn.relu, "use_bias": True}
outputs = tf.layers.conv1d(**params)
params = {"inputs": outputs, "filters": num_units[1], "kernel_size": 1,
"activation": None, "use_bias": True}
outputs = tf.layers.conv1d(**params)
outputs += inputs
outputs = normalize(outputs)
return outputs
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
label_smoothing.
对于训练有好处,将0变为接近零的小数,1变为接近1的数,下面注释很清楚。
def label_smoothing(inputs, epsilon=0.1):
'''Applies label smoothing. See https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.00567.
Args:
inputs: A 3d tensor with shape of [N, T, V], where V is the number of vocabulary.
epsilon: Smoothing rate.
For example,
```
import tensorflow as tf
inputs = tf.convert_to_tensor([[[0, 0, 1],
[0, 1, 0],
[1, 0, 0]],
[[1, 0, 0],
[1, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0]]], tf.float32)
outputs = label_smoothing(inputs)
with tf.Session() as sess:
print(sess.run([outputs]))
>>
[array([[[ 0.03333334, 0.03333334, 0.93333334],
[ 0.03333334, 0.93333334, 0.03333334],
[ 0.93333334, 0.03333334, 0.03333334]],
[[ 0.93333334, 0.03333334, 0.03333334],
[ 0.93333334, 0.03333334, 0.03333334],
[ 0.03333334, 0.93333334, 0.03333334]]], dtype=float32)]
```
'''
K = inputs.get_shape().as_list()[-1]
return ((1-epsilon) * inputs) + (epsilon / K)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
2.2 搭建模型
再看一次模型,我们发现里面的组件我们都已经构建好了。
按照这个结构搭建模型就可以啦!
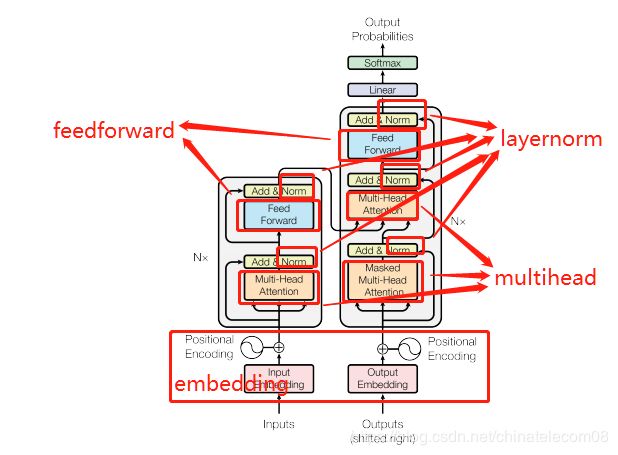
代码如下:
class Graph():
def __init__(self, is_training=True):
tf.reset_default_graph()
self.is_training = arg.is_training
self.hidden_units = arg.hidden_units
self.input_vocab_size = arg.input_vocab_size
self.label_vocab_size = arg.label_vocab_size
self.num_heads = arg.num_heads
self.num_blocks = arg.num_blocks
self.max_length = arg.max_length
self.lr = arg.lr
self.dropout_rate = arg.dropout_rate
self.x = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, shape=(None, None))
self.y = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, shape=(None, None))
self.de_inp = tf.placeholder(tf.int32, shape=(None, None))
with tf.variable_scope("encoder"):
self.en_emb = embedding(self.x, vocab_size=self.input_vocab_size, num_units=self.hidden_units, scale=True, scope="enc_embed")
self.enc = self.en_emb + embedding(tf.tile(tf.expand_dims(tf.range(tf.shape(self.x)[1]), 0), [tf.shape(self.x)[0], 1]),
vocab_size=self.max_length,num_units=self.hidden_units, zero_pad=False, scale=False,scope="enc_pe")
self.enc = tf.layers.dropout(self.enc,
rate=self.dropout_rate,
training=tf.convert_to_tensor(self.is_training))
for i in range(self.num_blocks):
with tf.variable_scope("num_blocks_{}".format(i)):
self.enc = multihead_attention(key_emb = self.en_emb,
que_emb = self.en_emb,
queries=self.enc,
keys=self.enc,
num_units=self.hidden_units,
num_heads=self.num_heads,
dropout_rate=self.dropout_rate,
is_training=self.is_training,
causality=False)
self.enc = feedforward(self.enc, num_units=[4*self.hidden_units, self.hidden_units])
with tf.variable_scope("decoder"):
self.de_emb = embedding(self.de_inp, vocab_size=self.label_vocab_size, num_units=self.hidden_units, scale=True, scope="dec_embed")
self.dec = self.de_emb + embedding(tf.tile(tf.expand_dims(tf.range(tf.shape(self.de_inp)[1]), 0), [tf.shape(self.de_inp)[0], 1]),
vocab_size=self.max_length,num_units=self.hidden_units, zero_pad=False, scale=False,scope="dec_pe")
self.dec = tf.layers.dropout(self.dec,
rate=self.dropout_rate,
training=tf.convert_to_tensor(self.is_training))
for i in range(self.num_blocks):
with tf.variable_scope("num_blocks_{}".format(i)):
self.dec = multihead_attention(key_emb = self.de_emb,
que_emb = self.de_emb,
queries=self.dec,
keys=self.dec,
num_units=self.hidden_units,
num_heads=self.num_heads,
dropout_rate=self.dropout_rate,
is_training=self.is_training,
causality=True,
scope='self_attention')
for i in range(self.num_blocks):
with tf.variable_scope("num_blocks_{}".format(i)):
self.dec = multihead_attention(key_emb = self.en_emb,
que_emb = self.de_emb,
queries=self.dec,
keys=self.enc,
num_units=self.hidden_units,
num_heads=self.num_heads,
dropout_rate=self.dropout_rate,
is_training=self.is_training,
causality=True,
scope='vanilla_attention')
self.outputs = feedforward(self.dec, num_units=[4*self.hidden_units, self.hidden_units])
self.logits = tf.layers.dense(self.outputs, self.label_vocab_size)
self.preds = tf.to_int32(tf.argmax(self.logits, axis=-1))
self.istarget = tf.to_float(tf.not_equal(self.y, 0))
self.acc = tf.reduce_sum(tf.to_float(tf.equal(self.preds, self.y))*self.istarget)/ (tf.reduce_sum(self.istarget))
tf.summary.scalar('acc', self.acc)
if is_training:
self.y_smoothed = label_smoothing(tf.one_hot(self.y, depth=self.label_vocab_size))
self.loss = tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits_v2(logits=self.logits, labels=self.y_smoothed)
self.mean_loss = tf.reduce_sum(self.loss*self.istarget) / (tf.reduce_sum(self.istarget))
self.global_step = tf.Variable(0, name='global_step', trainable=False)
self.optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=self.lr, beta1=0.9, beta2=0.98, epsilon=1e-8)
self.train_op = self.optimizer.minimize(self.mean_loss, global_step=self.global_step)
tf.summary.scalar('mean_loss', self.mean_loss)
self.merged = tf.summary.merge_all()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
- 45
- 46
- 47
- 48
- 49
- 50
- 51
- 52
- 53
- 54
- 55
- 56
- 57
- 58
- 59
- 60
- 61
- 62
- 63
- 64
- 65
- 66
- 67
- 68
- 69
- 70
- 71
- 72
- 73
- 74
- 75
- 76
- 77
- 78
- 79
- 80
- 81
- 82
- 83
- 84
- 85
- 86
- 87
- 88
- 89
- 90
- 91
- 92
- 93
- 94
- 95
- 96
- 97
- 98
- 99
- 100
- 101
- 102
- 103
- 104
- 105
- 106
- 107
- 108
- 109
- 110
- 111
3. 训练模型
用我们搭建好的模型,和准备好的数据进行训练!
3.1 参数设定
def create_hparams():
params = tf.contrib.training.HParams(
num_heads = 8,
num_blocks = 6,
input_vocab_size = 50,
label_vocab_size = 50,
max_length = 100,
hidden_units = 512,
dropout_rate = 0.2,
lr = 0.0003,
is_training = True)
return params
arg = create_hparams()
arg.input_vocab_size = len(encoder_vocab)
arg.label_vocab_size = len(decoder_vocab)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
3.2 模型训练
import os
epochs = 25
batch_size = 64
g = Graph(arg)
saver =tf.train.Saver()
with tf.Session() as sess:
merged = tf.summary.merge_all()
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
if os.path.exists(‘logs/model.meta’):
saver.restore(sess, ‘logs/model’)
writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(‘tensorboard/lm’, tf.get_default_graph())
for k in range(epochs):
total_loss = 0
batch_num = len(encoder_inputs) // batch_size
batch = get_batch(encoder_inputs, decoder_inputs, decoder_targets, batch_size)
for i in tqdm(range(batch_num)):
encoder_input, decoder_input, decoder_target = next(batch)
feed = {g.x: encoder_input, g.y: decoder_target, g.de_inp:decoder_input}
cost,_ = sess.run([g.mean_loss,g.train_op], feed_dict=feed)
total_loss += cost
if (k batch_num + i) % 10 == 0:
rs=sess.run(merged, feed_dict=feed)
writer.add_summary(rs, k batch_num + i)
if (k+1) % 5 == 0:
print(‘epochs’, k+1, ': average loss = ', total_loss/batch_num)
saver.save(sess, ‘logs/model’)
writer.close()
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
100%|██████████| 156/156 [00:31<00:00, 6.19it/s]
100%|██████████| 156/156 [00:24<00:00, 5.83it/s]
100%|██████████| 156/156 [00:24<00:00, 6.23it/s]
100%|██████████| 156/156 [00:24<00:00, 6.11it/s]
100%|██████████| 156/156 [00:24<00:00, 6.14it/s]
epochs 5 : average loss = 3.3463863134384155
100%|██████████| 156/156 [00:23<00:00, 6.27it/s]
100%|██████████| 156/156 [00:23<00:00, 5.86it/s]
100%|██████████| 156/156 [00:23<00:00, 6.33it/s]
100%|██████████| 156/156 [00:24<00:00, 6.08it/s]
100%|██████████| 156/156 [00:23<00:00, 6.29it/s]
epochs 10 : average loss = 2.0142565186207113
100%|██████████| 156/156 [00:24<00:00, 6.18it/s]
100%|██████████| 156/156 [00:24<00:00, 5.84it/s]
100%|██████████| 156/156 [00:24<00:00, 6.10it/s]
100%|██████████| 156/156 [00:24<00:00, 6.10it/s]
100%|██████████| 156/156 [00:23<00:00, 6.38it/s]
epochs 15 : average loss = 1.5278632457439716
100%|██████████| 156/156 [00:24<00:00, 6.15it/s]
100%|██████████| 156/156 [00:24<00:00, 5.86it/s]
100%|██████████| 156/156 [00:24<00:00, 6.23it/s]
100%|██████████| 156/156 [00:23<00:00, 6.13it/s]
100%|██████████| 156/156 [00:23<00:00, 6.32it/s]
epochs 20 : average loss = 1.4216684783116365
100%|██████████| 156/156 [00:23<00:00, 6.26it/s]
100%|██████████| 156/156 [00:23<00:00, 5.89it/s]
100%|██████████| 156/156 [00:24<00:00, 6.26it/s]
100%|██████████| 156/156 [00:24<00:00, 6.10it/s]
100%|██████████| 156/156 [00:23<00:00, 6.35it/s]
epochs 25 : average loss = 1.3833287457625072
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
- 36
- 37
- 38
- 39
- 40
- 41
- 42
- 43
- 44
3.3 模型推断
输入几条拼音测试一下效果如何:
arg.is_training = False
g = Graph(arg)
saver =tf.train.Saver()
with tf.Session() as sess:
saver.restore(sess, ‘logs/model’)
while True:
line = input(‘输入测试拼音: ‘)
if line ‘exit’: break
line = line.lower().replace(’,’, ’ ,’).strip(’\n’).split(’ ‘)
x = np.array([encoder_vocab.index(pny) for pny in line])
x = x.reshape(1, -1)
de_inp = [[decoder_vocab.index(’’)]]
while True:
y = np.array(de_inp)
preds = sess.run(g.preds, {g.x: x, g.de_inp: y})
if preds[0][-1] decoder_vocab.index(’’):
break
de_inp[0].append(preds[0][-1])
got = ‘’.join(decoder_vocab[idx] for idx in de_inp[0][1:])
print(got)
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
INFO:tensorflow:Restoring parameters from logs/model
输入测试拼音: You could be right, I suppose
我猜想你可能是对的
输入测试拼音: You don't believe Tom, do you
你不信任汤姆,对吗
输入测试拼音: Tom has lived here since 2003
汤姆自从2003年就住在这里
输入测试拼音: Tom asked if I'd found my key
湯姆問我找到我的鑰匙了吗
输入测试拼音: They have a very nice veranda
他们有一个非常漂亮的暖房
输入测试拼音: She was married to a rich man
她嫁給了一個有錢的男人
输入测试拼音: My parents sent me a postcard
我父母給我寄了一張明信片
输入测试拼音: Just put yourself in my shoes
你站在我的立場上考慮看看
输入测试拼音: It was a very stupid decision
这是一个十分愚蠢的决定
输入测试拼音: I'm really sorry to hear that
听到这样的消息我真的很难过
输入测试拼音: His wife is one of my friends
他的妻子是我的一個朋友
输入测试拼音: He thought of a good solution
他想到了一個解決的好辦法
输入测试拼音: exit
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
结果果然不错,训练速度也是比基于rnn的encoder decoder结构快很多,不得不说谷歌真棒啊。
转载请注明出处:https://blog.csdn.net/chinatelecom08
同学们喜欢的话给我项目点个星吧!
https://github.com/audier