HorizontalScrollView 滑动流程与在TV端使用horizontalscrollview的问题
在android TV端中实现水平滑动效果可以使用HorizontalScrollView来实现, 现在来介绍一下在TV端使用HorizontalScrollView时遇到的问题.
HorizontalScrollView 滑动流程
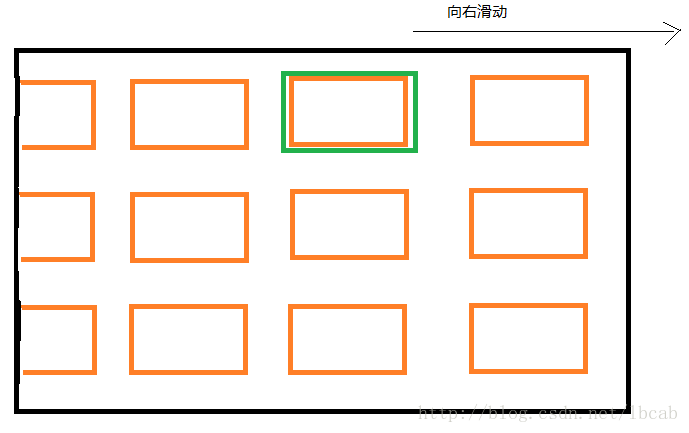
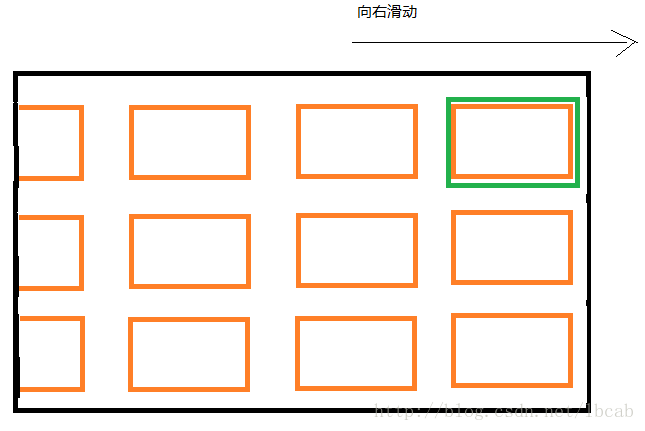
例如现在在TV端实现类似于手机launcher的功能显示所有的应用, 并使用HorizontalScrollView来实现水平滑动, 但是有这样的需求: 当应用滑动到某个子view, 这个子view并没有全部显示在屏幕上, 这个时候需要将整个应用按照你滑动的方向滑动整个屏幕的一半的距离. 如下图所示从图1到图2:
图1
原生的HorizontalScrollView只能实现当滑动到显示不全的子view上时, 只是让子view显示出来:
查看HorizontalScrollView源码分析它是怎么处理这个滑动的, 在TV端对应用的控制都是通过遥控器来进行操作, 说白了就是也就是对焦点的处理(也就是对按键消息的处理), 对于在TV端开发来说, 焦点的处理非常重要. 根据android的消息处理机制, 我们查看HorizontalScrollView的dispatchKeyEvent接口:
@Override
public boolean dispatchKeyEvent(KeyEvent event) {
// Let the focused view and/or our descendants get the key first
return super.dispatchKeyEvent(event) || executeKeyEvent(event);
}继续进入executeKeyEvent(event)方法中查看:
public boolean executeKeyEvent(KeyEvent event) {
mTempRect.setEmpty();
if (!canScroll()) {
if (isFocused()) {
View currentFocused = findFocus();
if (currentFocused == this) currentFocused = null;
View nextFocused = FocusFinder.getInstance().findNextFocus(this,
currentFocused, View.FOCUS_RIGHT);
return nextFocused != null && nextFocused != this &&
nextFocused.requestFocus(View.FOCUS_RIGHT);
}
return false;
}
boolean handled = false;
if (event.getAction() == KeyEvent.ACTION_DOWN) {
switch (event.getKeyCode()) {
case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_LEFT:
if (!event.isAltPressed()) {
handled = arrowScroll(View.FOCUS_LEFT);
} else {
handled = fullScroll(View.FOCUS_LEFT);
}
break;
case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_DPAD_RIGHT:
if (!event.isAltPressed()) {
handled = arrowScroll(View.FOCUS_RIGHT);
} else {
handled = fullScroll(View.FOCUS_RIGHT);
}
break;
case KeyEvent.KEYCODE_SPACE:
pageScroll(event.isShiftPressed() ? View.FOCUS_LEFT : View.FOCUS_RIGHT);
break;
}
}
return handled;
}通过分析executeKeyEvent的代码控制滑动的逻辑是arrowScroll(int direction), 继续查看里面的代码:
public boolean arrowScroll(int direction) {
View currentFocused = findFocus();
if (currentFocused == this) currentFocused = null;
View nextFocused = FocusFinder.getInstance().findNextFocus(this, currentFocused, direction);
final int maxJump = getMaxScrollAmount();
if (nextFocused != null && isWithinDeltaOfScreen(nextFocused, maxJump)) {
nextFocused.getDrawingRect(mTempRect);
offsetDescendantRectToMyCoords(nextFocused, mTempRect);
int scrollDelta = computeScrollDeltaToGetChildRectOnScreen(mTempRect);
doScrollX(scrollDelta);
nextFocused.requestFocus(direction);
} else {
// no new focus
int scrollDelta = maxJump;
if (direction == View.FOCUS_LEFT && getScrollX() < scrollDelta) {
scrollDelta = getScrollX();
} else if (direction == View.FOCUS_RIGHT && getChildCount() > 0) {
int daRight = getChildAt(0).getRight();
int screenRight = getScrollX() + getWidth();
if (daRight - screenRight < maxJump) {
scrollDelta = daRight - screenRight;
}
}
if (scrollDelta == 0) {
return false;
}
doScrollX(direction == View.FOCUS_RIGHT ? scrollDelta : -scrollDelta);
}
if (currentFocused != null && currentFocused.isFocused()
&& isOffScreen(currentFocused)) {
// previously focused item still has focus and is off screen, give
// it up (take it back to ourselves)
// (also, need to temporarily force FOCUS_BEFORE_DESCENDANTS so we are
// sure to
// get it)
final int descendantFocusability = getDescendantFocusability(); // save
setDescendantFocusability(ViewGroup.FOCUS_BEFORE_DESCENDANTS);
requestFocus();
setDescendantFocusability(descendantFocusability); // restore
}
return true;
}抛开代码细节, 只需要看最关心的地方就可以了, 最终控制滑动的方法在doScrollX(int delta)中, 在此方法中通过scrollBy来滑动, 对于scrollBy, 大家应该不陌生. 滑动距离是通过传入的delta来确定, 那么这个delta又是怎么获得的? 从arrowScroll(int direction)中可以看到delta是通过computeScrollDeltaToGetChildRectOnScreen(mTempRect)来计算出来, 那么查看一下此方法是怎么计算的:
protected int computeScrollDeltaToGetChildRectOnScreen(Rect rect) {
if (getChildCount() == 0) return 0;
int width = getWidth();
int screenLeft = getScrollX();
int screenRight = screenLeft + width;
int fadingEdge = getHorizontalFadingEdgeLength();
// leave room for left fading edge as long as rect isn't at very left
if (rect.left > 0) {
screenLeft += fadingEdge;
}
// leave room for right fading edge as long as rect isn't at very right
if (rect.right < getChildAt(0).getWidth()) {
screenRight -= fadingEdge;
}
int scrollXDelta = 0;
if (rect.right > screenRight && rect.left > screenLeft) {
// need to move right to get it in view: move right just enough so
// that the entire rectangle is in view (or at least the first
// screen size chunk).
if (rect.width() > width) {
// just enough to get screen size chunk on
scrollXDelta += (rect.left - screenLeft);
} else {
// get entire rect at right of screen
scrollXDelta += (rect.right - screenRight);
}
// make sure we aren't scrolling beyond the end of our content
int right = getChildAt(0).getRight();
int distanceToRight = right - screenRight;
scrollXDelta = Math.min(scrollXDelta, distanceToRight);
} else if (rect.left < screenLeft && rect.right < screenRight) {
// need to move right to get it in view: move right just enough so that
// entire rectangle is in view (or at least the first screen
// size chunk of it).
if (rect.width() > width) {
// screen size chunk
scrollXDelta -= (screenRight - rect.right);
} else {
// entire rect at left
scrollXDelta -= (screenLeft - rect.left);
}
// make sure we aren't scrolling any further than the left our content
scrollXDelta = Math.max(scrollXDelta, -getScrollX());
}
return scrollXDelta;
}从注释 “// get entire rect at right of screen” 来看, scrollXDelta += (rect.right - screenRight); 就是计算向右滑动的距离, 同理 scrollXDelta -= (screenLeft - rect.left); 是计算向左滑的距离.
分析到这我们可以得出结论: 只需要自定义CustomScrollView 继承 HorizontalScrollView, 重写computeScrollDeltaToGetChildRectOnScreen, 将计算向右向左的距离改为屏幕的一般即可实现当滑动到没有全部显示的子view时, 滑动距离为屏幕的一半:
public class CustomScrollView extends HorizontalScrollView {
public CustomScrollView(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public CustomScrollView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
public CustomScrollView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
@Override
protected int computeScrollDeltaToGetChildRectOnScreen(Rect rect) {
if (getChildCount() == 0) return 0;
int width = getWidth();
int screenLeft = getScrollX();
int screenRight = screenLeft + width;
int fadingEdge = getHorizontalFadingEdgeLength();
// leave room for left fading edge as long as rect isn't at very left
if (rect.left > 0) {
screenLeft += fadingEdge;
}
// leave room for right fading edge as long as rect isn't at very right
if (rect.right < getChildAt(0).getWidth()) {
screenRight -= fadingEdge;
}
int scrollXDelta = 0;
if (rect.right > screenRight && rect.left > screenLeft) {
// need to move right to get it in view: move right just enough so
// that the entire rectangle is in view (or at least the first
// screen size chunk).
if (rect.width() > width) {
// just enough to get screen size chunk on
scrollXDelta += (rect.left - screenLeft);
} else {
// get entire rect at right of screen
scrollXDelta += width / 2; // change here
}
// make sure we aren't scrolling beyond the end of our content
int right = getChildAt(0).getRight();
int distanceToRight = right - screenRight;
scrollXDelta = Math.min(scrollXDelta, distanceToRight);
} else if (rect.left < screenLeft && rect.right < screenRight) {
// need to move right to get it in view: move right just enough so that
// entire rectangle is in view (or at least the first screen
// size chunk of it).
if (rect.width() > width) {
scrollXDelta -= (screenRight - rect.right);
} else {
scrollXDelta -= width / 2; // chang here
}
scrollXDelta = Math.max(scrollXDelta, -getScrollX());
}
return scrollXDelta;
}
}使用HorizontalScrollView焦点乱窜或失去焦点问题
HorizontalScrollView的长度不能无限的设置, 当长度超过1万像素后会出现焦点乱窜或失去焦点的问题,
这时因为在HorizontalScrollView的滑动逻辑中使用:
FocusFinder.getInstance().findNextFocus(this, currentFocused, View.FOCUS_RIGHT);来确定下一个获得焦点的子view, 但是当HorizontalScrollView的长度超过1万像素后, 此方法返回值就不对了, 因为其内部的获得下个子view的算法中有一个方法:
/**
* Fudge-factor opportunity: how to calculate distance given major and minor
* axis distances. Warning: this fudge factor is finely tuned, be sure to
* run all focus tests if you dare tweak it.
*/
int getWeightedDistanceFor(int majorAxisDistance, int minorAxisDistance) {
return 13 * majorAxisDistance * majorAxisDistance
+ minorAxisDistance * minorAxisDistance;
}这个方法值返回类型是int, 当majorAxisDistance过大时, 根据内部的计算方法很容易超过int的最大值,所以当HorizontalScrollView的长度过大时, 此方法的返回值就会溢出, 进而导致焦点乱窜或失去焦点的问题.