SpringCloud Ribbon 设计原理
Ribbon 是netflix 公司开源的基于客户端的负载均衡组件,是Spring Cloud大家庭中非常重要的一个模块;
Ribbon应该也是整个大家庭中相对而言比较复杂的模块,直接影响到服务调度的质量和性能。
全面掌握Ribbon可以帮助我们了解在分布式微服务集群工作模式下,服务调度应该考虑到的每个环节。
本文将详细地剖析Ribbon的设计原理,帮助大家对Spring Cloud 有一个更好的认知。
一. Spring集成下的Ribbon工作结构
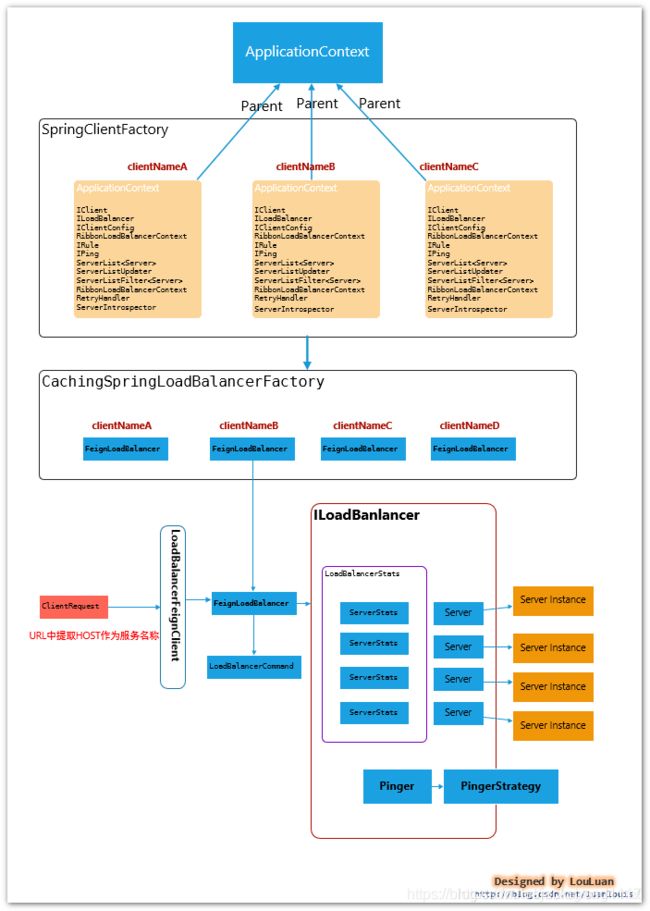
Spring Cloud集成模式下的Ribbon有以下几个特征:
- Ribbon 服务配置方式
每一个服务配置都有一个Spring ApplicationContext上下文,用于加载各自服务的实例。
比如,当前Spring Cloud 系统内,有如下几个服务:
| 服务名称 |
角色 |
依赖服务 |
| APP |
APP服务 |
Order、User |
| Order |
订单服务 |
User |
| User |
用户服务 |
无 |
App服务在实际使用中会用到order和user模块。那么在App服务的Spring上下文中,会为Order和user分别
创建一个子ApplicationContext,用于加载各自服务模块的配置,也就说客户端的配置相互独立互不影响。
2.Feign下集成模式
在使用Feign作为客户端时,最终请求会转发成 http://<服务名称>/
二. Ribbon设计原理
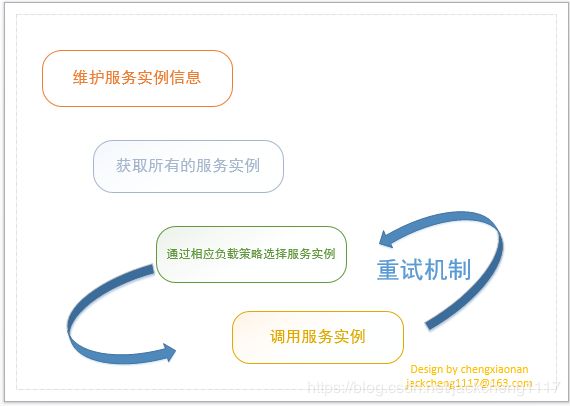
使用过SpringCloud都应该知道Ribbon组件在服务调用中起到了负载的作用。那么一个完整的负载过程有哪些步骤呢?
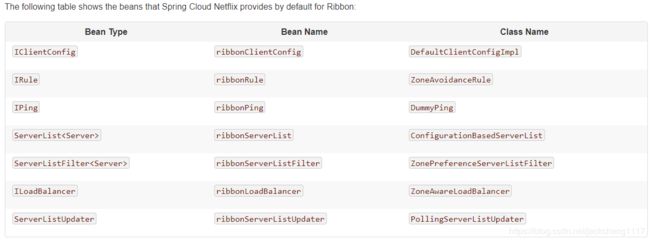
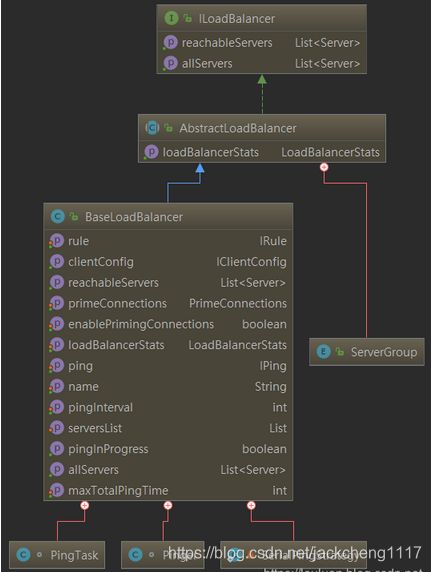
那么Ribbon也不例外,如下如图所示是Ribbon官方提供的Ribbon组件核心接口:
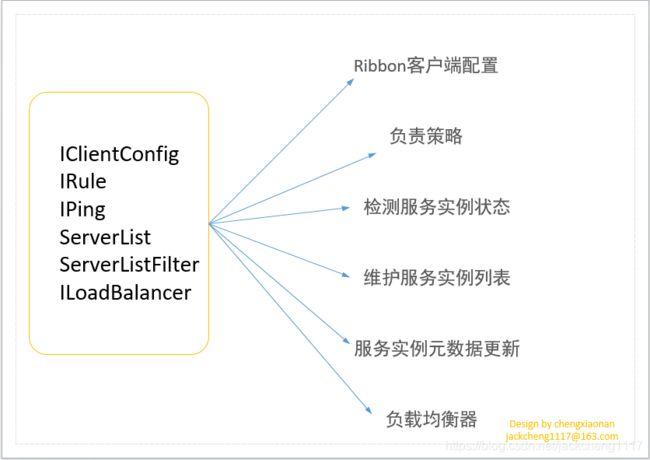
其中Ribbon最最核心的是 ILoadBalance 接口,因为该接口在其他接口的基础上最终完成了负载,那么本节将以 ILoadBalance接口为入口讲解Ribbon设计原理。
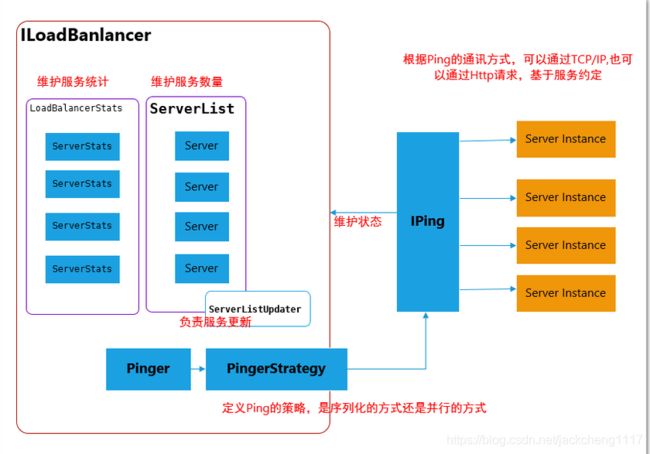
ILoadBalancer-负载均衡器核心设计
LoadBalancer 的职能主要有三个:
维护Sever列表的数量(新增、更新、删除等)
维护Server列表的状态(状态更新)
当请求Server实例时,能否返回最合适的Server实例
本节将围绕这三个职能讲解负载均衡器
先熟悉一下 ILoadBalancer实现原理图:
2.1 维护Sever列表的数量(新增、更新、删除等)
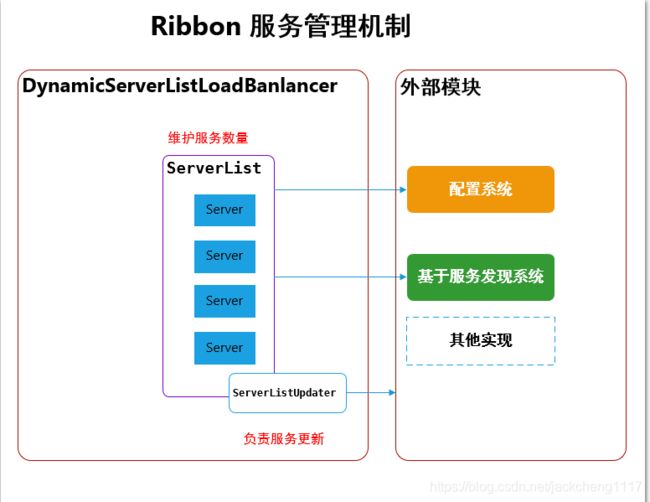
单从服务列表维护的角度上,Ribbon结构如下:
Server列表维护从实现上分为两类:
1. 基于配置的服务列表
这种方式一般是通过配置文件,静态地配置服务器列表,这种方式相对而言比较简单,
但并不是意味着在机器运行的时候就一直不变。
netflix 在做Spring cloud 套件时,使用了分布式配置框架netflix archaius ,archaius 框架有一个特点是会动态的监控配置文件的变化,
将变化刷新到各个应用上。也就是说,当我们在不关闭服务的情况下,如果修改了基于配置的服务列表时, 服务列表可以直接刷新
2. 结合服务发现组件(如Eureka)的服务注册信息动态维护服务列表
基于Spring Cloud框架下,服务注册和发现是一个分布式服务集群必不可少的一个组件,
它负责维护不同的服务实例(注册、续约、取消注册),
本文将介绍和Eureka集成模式下,如何借助Eureka的服务注册信息动态刷新ribbon 的服务列表
一般使用 SpringCloud Netflix 套件都会使用到Ribbon组件,所以将基于第二种方式讲解Server列表维护:即借助Eureka服务中心动态维护Ribbon服务列表。
如上图所示,Ribbon 是通过 ServerList 来维护Server列表的,即对应官方文档中说明的 ServerList接口。
Ribbon 通过配置项:
| 策略 | ServerList实现 |
| 基于配置 | com.netflix.loadbalancer.ConfigurationBasedServerList |
| 基于服务发现 | com.netflix.loadbalancer.DiscoveryEnabledNIWSServerList |
Server列表可能在运行的时候动态的更新,而具体的更新方式由
| 更新策略 | ServerListUpdater实现 |
| 基于定时任务的拉取服务列表 | com.netflix.loadbalancer.PollingServerListUpdater |
| 基于Eureka服务事件通知的方式更新 | com.netflix.loadbalancer.EurekaNotificationServerListUpdate |
- 基于定时任务拉取服务列表
public class PollingServerListUpdater implements ServerListUpdater {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(PollingServerListUpdater.class);
private static long LISTOFSERVERS_CACHE_UPDATE_DELAY = 1000; // msecs;
private static int LISTOFSERVERS_CACHE_REPEAT_INTERVAL = 30 * 1000; // msecs;
//基于线程池方式及钩子设置
private static class LazyHolder {
private final static String CORE_THREAD = "DynamicServerListLoadBalancer.ThreadPoolSize";
private final static DynamicIntProperty poolSizeProp = new DynamicIntProperty(CORE_THREAD, 2);
private static Thread _shutdownThread;
static ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor _serverListRefreshExecutor = null;
static {
int coreSize = poolSizeProp.get();
ThreadFactory factory = (new ThreadFactoryBuilder()).setNameFormat("PollingServerListUpdater-%d").setDaemon(true).build();
_serverListRefreshExecutor = new ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor(coreSize, factory);
poolSizeProp.addCallback(new Runnable() {@Override public void run() {
_serverListRefreshExecutor.setCorePoolSize(poolSizeProp.get());
}
});
_shutdownThread = new Thread(new Runnable() {
public void run() {
logger.info("Shutting down the Executor Pool for PollingServerListUpdater");
shutdownExecutorPool();
}
});
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(_shutdownThread);
}
private static void shutdownExecutorPool() {
if (_serverListRefreshExecutor != null) {
_serverListRefreshExecutor.shutdown();
if (_shutdownThread != null) {
try {
Runtime.getRuntime().removeShutdownHook(_shutdownThread);
} catch(IllegalStateException ise) { // NOPMD
// this can happen if we're in the middle of a real
// shutdown,
// and that's 'ok'
}
}
}
}
}
private static ScheduledThreadPoolExecutor getRefreshExecutor() {
return LazyHolder._serverListRefreshExecutor;
}
private final AtomicBoolean isActive = new AtomicBoolean(false);
private volatile long lastUpdated = System.currentTimeMillis();
private final long initialDelayMs;
private final long refreshIntervalMs;
private volatile ScheduledFuture < ?>scheduledFuture;
public PollingServerListUpdater() {
this(LISTOFSERVERS_CACHE_UPDATE_DELAY, LISTOFSERVERS_CACHE_REPEAT_INTERVAL);
}
public PollingServerListUpdater(IClientConfig clientConfig) {
this(LISTOFSERVERS_CACHE_UPDATE_DELAY, getRefreshIntervalMs(clientConfig));
}
public PollingServerListUpdater(final long initialDelayMs, final long refreshIntervalMs) {
this.initialDelayMs = initialDelayMs;
this.refreshIntervalMs = refreshIntervalMs;
}
//创建定时任务,按照特定的实行周期执行更新操作
@Override public synchronized void start(final UpdateAction updateAction) {
if (isActive.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
final Runnable wrapperRunnable = new Runnable() {@Override public void run() {
if (!isActive.get()) {
if (scheduledFuture != null) {
scheduledFuture.cancel(true);
}
return;
}
try {
执行update操作 ,更新操作定义在LoadBalancer中
updateAction.doUpdate();
lastUpdated = System.currentTimeMillis();
} catch(Exception e) {
logger.warn("Failed one update cycle", e);
}
}
};
scheduledFuture = getRefreshExecutor().scheduleWithFixedDelay(wrapperRunnable, initialDelayMs, refreshIntervalMs, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} else {
logger.info("Already active, no-op");
}
}
@Override public synchronized void stop() {
if (isActive.compareAndSet(true, false)) {
if (scheduledFuture != null) {
scheduledFuture.cancel(true);
}
} else {
logger.info("Not active, no-op");
}
}
//省略部分代码。。。
}有上述代码可以看到,ServerListUpdator只是定义了更新的方式,而具体怎么更新,则是封装成UpdateAction来操作的:
protected final ServerListUpdater.UpdateAction updateAction = new ServerListUpdater.UpdateAction() {
@Override
public void doUpdate() {
updateListOfServers();
}
};
@VisibleForTesting public void updateListOfServers() {
List < T > servers = new ArrayList < T > ();
if (serverListImpl != null) {
servers = serverListImpl.getUpdatedListOfServers();
LOGGER.debug("List of Servers for {} obtained from Discovery client: {}", getIdentifier(), servers);
if (filter != null) {
servers = filter.getFilteredListOfServers(servers);
LOGGER.debug("Filtered List of Servers for {} obtained from Discovery client: {}", getIdentifier(), servers);
}
}
updateAllServerList(servers);
}
protected void updateAllServerList(List ls) {
// other threads might be doing this - in which case, we pass
if (serverListUpdateInProgress.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
try {
for (T s : ls) {
s.setAlive(true); // set so that clients can start using these
// servers right away instead
// of having to wait out the ping cycle.
}
setServersList(ls);
super.forceQuickPing();
} finally {
serverListUpdateInProgress.set(false);
}
}
} - 基于Eureka服务事件通知的方式更新
基于Eureka的更新方式则有些不同, 当Eureka注册中心发生了Server服务注册信息变更时,会将消息通知发送到EurekaNotificationServerListUpdater 上,然后此Updator触发刷新ServerList:
public class EurekaNotificationServerListUpdater implements ServerListUpdater {
//省略部分代码
@Override
public synchronized void start(final UpdateAction updateAction) {
if (isActive.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
//创建Eureka时间监听器,当Eureka发生改变后,将触发对应逻辑
this.updateListener = new EurekaEventListener() {
@Override
public void onEvent(EurekaEvent event) {
if (event instanceof CacheRefreshedEvent) {
//内部消息队列
if (!updateQueued.compareAndSet(false, true)) { // if an update is already queued
logger.info("an update action is already queued, returning as no-op");
return;
}
if (!refreshExecutor.isShutdown()) {
try {
//提交更新操作请求到消息队列中
refreshExecutor.submit(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
updateAction.doUpdate(); // 执行真正的更新操作
lastUpdated.set(System.currentTimeMillis());
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn("Failed to update serverList", e);
} finally {
updateQueued.set(false);
}
}
}); // fire and forget
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn("Error submitting update task to executor, skipping one round of updates", e);
updateQueued.set(false); // if submit fails, need to reset updateQueued to false
}
}
else {
logger.debug("stopping EurekaNotificationServerListUpdater, as refreshExecutor has been shut down");
stop();
}
}
}
};
//EurekaClient 客户端实例
if (eurekaClient == null) {
eurekaClient = eurekaClientProvider.get();
}
//基于EeurekaClient注册事件监听器
if (eurekaClient != null) {
eurekaClient.registerEventListener(updateListener);
} else {
logger.error("Failed to register an updateListener to eureka client, eureka client is null");
throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to start the updater, unable to register the update listener due to eureka client being null.");
}
} else {
logger.info("Update listener already registered, no-op");
}
}
}
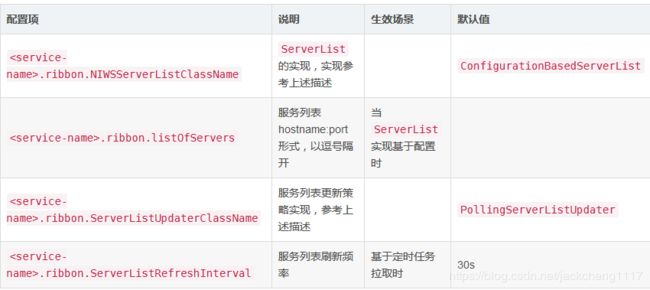
2.1.1 相关配置项
2.1.2 ribbon的默认实现
.ribbon.NIWSServerListClassName=com.netflix.loadbalancer.ConfigurationBasedServerList
.ribbon.listOfServers=,
.ribbon.ServerListUpdaterClassName=com.netflix.loadbalancer.EurekaNotificationServerListUpdater
.ribbon.ServerListRefreshInterval=30
### 更新线程池大小
DynamicServerListLoadBalancer.ThreadPoolSize=2
2.1.3 SpringCloud下集成下实现
ribbon在默认情况下,会采用如下的配置项,即,采用基于配置的服务列表维护,基于定时任务按时拉取服务列表的方式,频率为30s.
.ribbon.NIWSServerListClassName=com.netflix.loadbalancer.DiscoveryEnabledNIWSServerList
.ribbon.ServerListUpdaterClassName=com.netflix.loadbalancer.EurekaNotificationServerListUpdater
### 更新线程池大小
EurekaNotificationServerListUpdater.ThreadPoolSize=2
###通知队列接收大小
EurekaNotificationServerListUpdater.queueSize=1000
2.2 维护Server列表的状态(状态更新)
Server列表的维护是通过 IPing、Pinger、IPingStrategy 一起来维护的:
其中 Iping 接口主要用于判断服务实例是否是存活的:
| 接口实现 | 描述 |
| PingUrl | 该实现是通过ping 服务的指定url方式发送http请求判断服务是否存活 |
| PingConstant | 提供true / false 参数 指定返回服务是否存活 |
| NoOpPing | 没有执行任何逻辑,直接返回true,即服务是存活的 |
| DummyPing | Ribbon默认实现 直接返回true,即服务是存活的 |
| NIWDiscoveryPing | SpringCloud继承下默认实现 通过eurekaClient获取服务状态进而判断服务是否存活 |
IPingStrategy 接口:
SerialPingStrategy是IpingStrategy默认实现类:通过遍历 服务列表 一个一个ping服务获取服务状态
/**
* Default implementation for IPingStrategy , performs ping
* serially, which may not be desirable, if your IPing
* implementation is slow, or you have large number of servers.
*/
private static class SerialPingStrategy implements IPingStrategy {
@Override public boolean[] pingServers(IPing ping, Server[] servers) {
int numCandidates = servers.length;
boolean[] results = new boolean[numCandidates];
logger.debug("LoadBalancer: PingTask executing [{}] servers configured", numCandidates);
for (int i = 0; i < numCandidates; i++) {
results[i] = false;
/* Default answer is DEAD. */
try {
// NOTE: IFF we were doing a real ping
// assuming we had a large set of servers (say 15)
// the logic below will run them serially
// hence taking 15 times the amount of time it takes
// to ping each server
// A better method would be to put this in an executor
// pool
// But, at the time of this writing, we dont REALLY
// use a Real Ping (its mostly in memory eureka call)
// hence we can afford to simplify this design and run
// this
// serially
if (ping != null) {
results[i] = ping.isAlive(servers[i]);
}
} catch(Exception e) {
logger.error("Exception while pinging Server: '{}'", servers[i], e);
}
}
return results;
}
}Pinger:
主要通过Timer开启 PingTask定时任务 去调用 Pinger去获取服务状态,进而进行后续状态改变通知
//开启PingTask定时任务
void setupPingTask() {
if (canSkipPing()) {
return;
}
if (lbTimer != null) {
lbTimer.cancel();
}
lbTimer = new ShutdownEnabledTimer("NFLoadBalancer-PingTimer-" + name,
true);
lbTimer.schedule(new PingTask(), 0, pingIntervalSeconds * 1000);
forceQuickPing();
}
//使用Pinger 定义定时任务
class PingTask extends TimerTask {
public void run() {
try {
new Pinger(pingStrategy).runPinger();
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("LoadBalancer [{}]: Error pinging", name, e);
}
}
}
//定义Pinger,通过持有 IPingStrategy 和 Iping 去获取服务状态
class Pinger {
private final IPingStrategy pingerStrategy;
public Pinger(IPingStrategy pingerStrategy) {
this.pingerStrategy = pingerStrategy;
}
public void runPinger() throws Exception {
if (!pingInProgress.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
return; // Ping in progress - nothing to do
}
// we are "in" - we get to Ping
Server[] allServers = null;
boolean[] results = null;
Lock allLock = null;
Lock upLock = null;
try {
/*
* The readLock should be free unless an addServer operation is
* going on...
*/
allLock = allServerLock.readLock();
allLock.lock();
allServers = allServerList.toArray(new Server[allServerList.size()]);
allLock.unlock();
int numCandidates = allServers.length;
results = pingerStrategy.pingServers(ping, allServers);
final List < Server > newUpList = new ArrayList < Server > ();
final List < Server > changedServers = new ArrayList < Server > ();
for (int i = 0; i < numCandidates; i++) {
boolean isAlive = results[i];
Server svr = allServers[i];
boolean oldIsAlive = svr.isAlive();
svr.setAlive(isAlive);
if (oldIsAlive != isAlive) {
changedServers.add(svr);
logger.debug("LoadBalancer [{}]: Server [{}] status changed to {}", name, svr.getId(), (isAlive ? "ALIVE": "DEAD"));
}
if (isAlive) {
newUpList.add(svr);
}
}
upLock = upServerLock.writeLock();
upLock.lock();
upServerList = newUpList;
upLock.unlock();
notifyServerStatusChangeListener(changedServers);
} finally {
pingInProgress.set(false);
}
}
}2.3 如何从服务列表中挑选一个合适的服务
从上面的阐述中已经知道 Ribbon是通过 ServerList维护Server列表的。但是Ribbon还提供了另外一个接口 ServerListFilter.
该接口主要是对ServerList中的服务列表进行再过滤,返回满足过滤器条件的服务实例列表。
ServerListFilter核心实现:ZoneAffinityServerListFilter
Ribbon默认采取了区域优先的过滤策略,即当Server列表中,过滤出和当前实例所在的区域(zone)一致的server列表
与此相关联的,Ribbon有两个相关得配置参数:
| 控制参数 | 说明 |
默认值 |
| 是否开启区域优先 | false | |
| 是否采取区域排他性,即只返回和当前Zone一致的服务实例 | false | |
| 每个Server上的最大活跃请求负载数阈值 | 0.6 | |
| 最大断路过滤的百分比 | 0.8 | |
| 最少可用的服务实例阈值 | 2 |
public class ZoneAffinityServerListFilter extends
AbstractServerListFilter implements IClientConfigAware {
@Override
public List getFilteredListOfServers(List servers) {
//zone非空,并且开启了区域优先,并且服务实例数量不为空
if (zone != null && (zoneAffinity || zoneExclusive) && servers !=null && servers.size() > 0){
//基于断言过滤服务列表
List filteredServers = Lists.newArrayList(Iterables.filter(
servers, this.zoneAffinityPredicate.getServerOnlyPredicate()));
//如果允许区域优先,则返回过滤列表
if (shouldEnableZoneAffinity(filteredServers)) {
return filteredServers;
} else if (zoneAffinity) {
overrideCounter.increment();
}
}
return servers;
}
// 判断是否应该使用区域优先过滤条件
private boolean shouldEnableZoneAffinity(List filtered) {
if (!zoneAffinity && !zoneExclusive) {
return false;
}
if (zoneExclusive) {
return true;
}
// 获取统计信息
LoadBalancerStats stats = getLoadBalancerStats();
if (stats == null) {
return zoneAffinity;
} else {
logger.debug("Determining if zone affinity should be enabled with given server list: {}", filtered);
//获取区域Server快照,包含统计数据
ZoneSnapshot snapshot = stats.getZoneSnapshot(filtered);
//平均负载,此负载的意思是,当前所有的Server中,平均每台机器上的活跃请求数
double loadPerServer = snapshot.getLoadPerServer();
int instanceCount = snapshot.getInstanceCount();
int circuitBreakerTrippedCount = snapshot.getCircuitTrippedCount();
// 1. 如果Server断路的比例超过了设置的上限(默认`0.8`)
// 2. 或者当前负载超过了设置的负载上限
// 3. 如果可用的服务小于设置的服务上限`默认为2`
if (((double) circuitBreakerTrippedCount) / instanceCount >= blackOutServerPercentageThreshold.get()
|| loadPerServer >= activeReqeustsPerServerThreshold.get()
|| (instanceCount - circuitBreakerTrippedCount) < availableServersThreshold.get()) {
logger.debug("zoneAffinity is overriden. blackOutServerPercentage: {}, activeReqeustsPerServer: {}, availableServers: {}",
new Object[] {(double) circuitBreakerTrippedCount / instanceCount, loadPerServer, instanceCount - circuitBreakerTrippedCount});
return false;
} else {
return true;
}
}
}
}
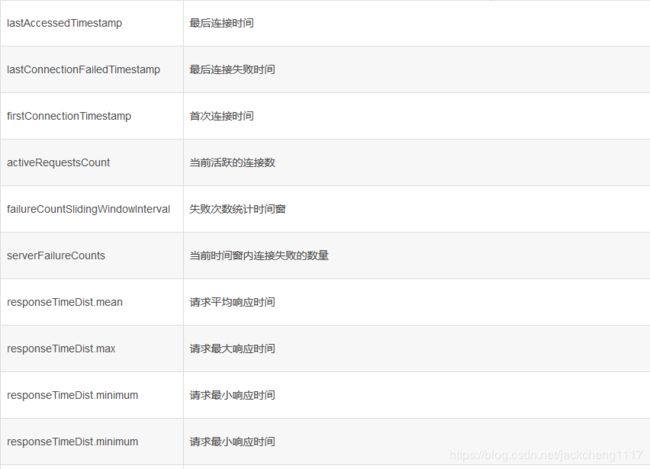
RIbbon还提供了另外一个类 ServerStats来记录每个客户端服务实例的统计信息,那么都统计了哪些信息呢?
通过 ServerLIstFilter过滤出服务列表之后,接下来就是确定服务实例了,即负载策略:
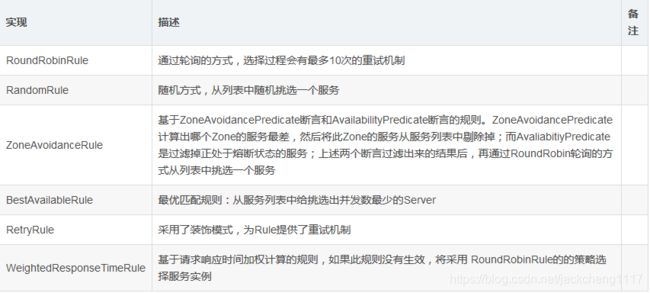
Ribbon定义了IRule 接口提供负载策略:
Ribbon定义了一些常见的规则:
RoundRobinRuel轮询策略实现:
public class RoundRobinRule extends AbstractLoadBalancerRule {
private AtomicInteger nextServerCyclicCounter;
private static final boolean AVAILABLE_ONLY_SERVERS = true;
private static final boolean ALL_SERVERS = false;
private static Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RoundRobinRule.class);
public RoundRobinRule() {
nextServerCyclicCounter = new AtomicInteger(0);
}
public RoundRobinRule(ILoadBalancer lb) {
this();
setLoadBalancer(lb);
}
public Server choose(ILoadBalancer lb, Object key) {
if (lb == null) {
log.warn("no load balancer");
return null;
}
Server server = null;
int count = 0;
//10次重试机制
while (server == null && count++ < 10) {
List reachableServers = lb.getReachableServers();
List allServers = lb.getAllServers();
int upCount = reachableServers.size();
int serverCount = allServers.size();
if ((upCount == 0) || (serverCount == 0)) {
log.warn("No up servers available from load balancer: " + lb);
return null;
}
// 生成轮询数据
int nextServerIndex = incrementAndGetModulo(serverCount);
server = allServers.get(nextServerIndex);
if (server == null) {
/* Transient. */
Thread.yield();
continue;
}
if (server.isAlive() && (server.isReadyToServe())) {
return (server);
}
// Next.
server = null;
}
if (count >= 10) {
log.warn("No available alive servers after 10 tries from load balancer: "
+ lb);
}
return server;
}
/**
* Inspired by the implementation of {@link AtomicInteger#incrementAndGet()}.
*
* @param modulo The modulo to bound the value of the counter.
* @return The next value.
*/
private int incrementAndGetModulo(int modulo) {
for (;;) {
int current = nextServerCyclicCounter.get();
int next = (current + 1) % modulo;
if (nextServerCyclicCounter.compareAndSet(current, next))
return next;
}
}
@Override
public Server choose(Object key) {
return choose(getLoadBalancer(), key);
}
}
ZoneAvoidanceRule的实现:
ZoneAvoidanceRule的处理思路:
1.ZoneAvoidancePredicate 计算出哪个Zone的服务最差,然后将此Zone的服务从服务列表中剔除掉;
2.AvailabilityPredicate 将处于熔断状态的服务剔除掉;
3.将上述两步骤过滤后的服务通过RoundRobinRule挑选一个服务实例返回
ZoneAvoidancePredicate 剔除最差的Zone的过程:
public static Set getAvailableZones(
Map snapshot, double triggeringLoad,
double triggeringBlackoutPercentage) {
if (snapshot.isEmpty()) {
return null;
}
Set availableZones = new HashSet(snapshot.keySet());
if (availableZones.size() == 1) {
return availableZones;
}
Set worstZones = new HashSet();
double maxLoadPerServer = 0;
boolean limitedZoneAvailability = false;
for (Map.Entry zoneEntry : snapshot.entrySet()) {
String zone = zoneEntry.getKey();
ZoneSnapshot zoneSnapshot = zoneEntry.getValue();
int instanceCount = zoneSnapshot.getInstanceCount();
if (instanceCount == 0) {
availableZones.remove(zone);
limitedZoneAvailability = true;
} else {
double loadPerServer = zoneSnapshot.getLoadPerServer();
//如果负载超过限额,则将用可用区中剔除出去
if (((double) zoneSnapshot.getCircuitTrippedCount())
/ instanceCount >= triggeringBlackoutPercentage
|| loadPerServer < 0) {
availableZones.remove(zone);
limitedZoneAvailability = true;
} else {
//计算最差的Zone区域
if (Math.abs(loadPerServer - maxLoadPerServer) < 0.000001d) {
// they are the same considering double calculation
// round error
worstZones.add(zone);
} else if (loadPerServer > maxLoadPerServer) {
maxLoadPerServer = loadPerServer;
worstZones.clear();
worstZones.add(zone);
}
}
}
}
// 如果最大负载没有超过上限,则返回所有可用分区
if (maxLoadPerServer < triggeringLoad && !limitedZoneAvailability) {
// zone override is not needed here
return availableZones;
}
// 从最差的可用分区中随机挑选一个剔除,这么做是保证服务的高可用
String zoneToAvoid = randomChooseZone(snapshot, worstZones);
if (zoneToAvoid != null) {
availableZones.remove(zoneToAvoid);
}
return availableZones;
}
三. Ribbon的配置参数
四. 总结
Ribbon是Spring Cloud框架中相当核心的模块,负责着服务负载调用,Ribbon也可以脱离SpringCloud单独使用。
另外Ribbon是客户端的负载均衡框架,即每个客户端上,独立维护着自身的调用信息统计,相互隔离;
也就是说:Ribbon的负载均衡表现在各个机器上变现并不完全一致
Ribbon 也是整个组件框架中最复杂的一环,控制流程上为了保证服务的高可用性,
有很多比较细节的参数控制,在使用的过程中,需要深入理清每个环节的处理机制,
这样在问题定位上会高效很多。
上述内容如有不妥之处,还请读者指出,共同探讨,共同进步!
@author : [email protected]