4.SpringBoot学习(四)——Spring Boot Validation校验及原理
1.简介
1.1 概述
The method validation feature supported by Bean Validation 1.1 is automatically enabled as long as a JSR-303 implementation (such as Hibernate validator) is on the classpath. This lets bean methods be annotated with
javax.validationconstraints on their parameters and/or on their return value. Target classes with such annotated methods need to be annotated with the@Validatedannotation at the type level for their methods to be searched for inline constraint annotations.
只要 JSR-303 的实现(例如Hibernate验证器)在 classpath下,就会自动启用 Bean Validation 1.1 支持的方法验证功能。这使 bean 方法的参数和/或返回值可以使用 javax.validation 注解进行约束。具有此类注释方法的目标类需要在类型级别使用@Validated注释进行注释,以便在其方法中搜索内联约束注释。
2.环境
- JDK 1.8.0_201
- Spring Boot 2.2.0.RELEASE
- 构建工具(apache maven 3.6.3)
- 开发工具(IntelliJ IDEA )
- 数据库:h2
3.代码
3.1 功能说明
用户 User 类里面有 id、name、age、idCard 等字段,这些字段在处理的时候通过注解进行校验;其中 name、age 字段校验使用的是 spring boot 依赖的组件中提供的注解;而 idCard 使用自定义注解 @IdCard;这些注解都支持国际化,最终通过 jpa 保存到 h2 数据库中。
UserCommand 用来预置几条数据。
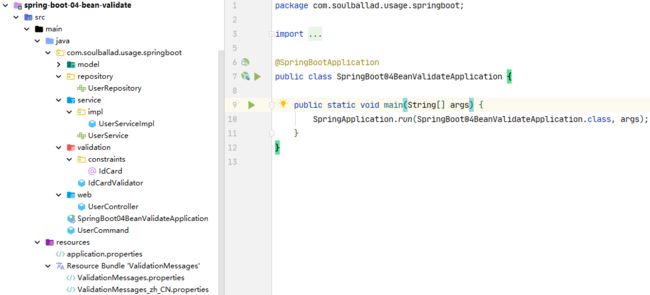
3.2 代码结构
3.3 maven 依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2databasegroupId>
<artifactId>h2artifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpaartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-validationartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-testartifactId>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
dependencies>
3.4 配置文件
application.properties
# 开启h2数据库
spring.h2.console.enabled=true
# 配置h2数据库
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:mem:user
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=org.h2.Driver
spring.datasource.username=sad
spring.datasource.password=sae
# 是否显示sql语句
spring.jpa.show-sql=true
hibernate.dialect=org.hibernate.dialect.H2Dialect
hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto=create
ValidationMessages.properties
com.soulballad.usage.model.validation.id.card.message=the id card length must be 18 and matches rule
model.user.NAME_SIZE_BETWEEN_2_AND_20=the length of name must be greater than 2 and less than 20
model.user.NAME_NOT_BLANK=name cannot be blank
model.user.AGE_MIN_1=the minimum of age is 1
model.user.AGE_MAX_200=the maximum of age is 200
model.user.AGE_NOT_NULL=age cannot be null
model.user.ID_CARD_NOT_NULL=id card cannot be null
ValidationMessages_zh_CN.properties
# 身份证号必须是符合规则的18位
com.soulballad.usage.model.validation.id.card.message=\u8eab\u4efd\u8bc1\u53f7\u5fc5\u987b\u662f\u7b26\u5408\u89c4\u5219\u768418\u4f4d
# 姓名长度必须大于2小于20
model.user.NAME_SIZE_BETWEEN_2_AND_20=\u59d3\u540d\u957f\u5ea6\u5fc5\u987b\u5927\u4e8e2\u5c0f\u4e8e20
# 姓名不能为空
model.user.NAME_NOT_BLANK=\u59d3\u540d\u4e0d\u80fd\u4e3a\u7a7a
# 年龄最小为1
model.user.AGE_MIN_1=\u5e74\u9f84\u6700\u5c0f\u4e3a1
# 年龄最大为200
model.user.AGE_MAX_200=\u5e74\u9f84\u6700\u5927\u4e3a200
# 年龄不能为空
model.user.AGE_NOT_NULL=\u5e74\u9f84\u4e0d\u80fd\u4e3a\u7a7a
# 身份证号不能为空
model.user.ID_CARD_NOT_NULL=\u8eab\u4efd\u8bc1\u53f7\u4e0d\u80fd\u4e3a\u7a7a
3.5 java代码
User.java
@Entity
@JsonIgnoreProperties(value = { "hibernateLazyInitializer", "handler" })
public class User implements Serializable {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Long id;
@Size(min = 2, max = 20, message = "{model.user.NAME_SIZE_BETWEEN_2_AND_20}")
@NotBlank(message = "{model.user.NAME_NOT_BLANK}")
private String name;
@Min(value = 1, message = "{model.user.AGE_MIN_1}")
@Max(value = 200, message = "{model.user.AGE_MAX_200}")
@NotNull(message = "{model.user.AGE_NOT_NULL}")
private Integer age;
@IdCard
@NotNull(message = "{model.user.ID_CARD_NOT_NULL}")
private String idCard;
// get&set&constructors&toString
}
UserRepository.java
@Repository
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Long> {
}
UserServiceImpl.java
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
@Override
public List<User> selectAll() {
return userRepository.findAll();
}
@Override
public User getUserById(Long id) {
return userRepository.getOne(id);
}
@Override
public User add(User user) {
return userRepository.save(user);
}
@Override
public User update(User user) {
return userRepository.save(user);
}
@Override
public User delete(Long id) {
User user = getUserById(id);
userRepository.deleteById(id);
return user;
}
}
IdCard.java
/**
* @apiNote : 自定义注解校验 {@link com.soulballad.usage.springboot.model.User} 中的idCard字段该注解中参数和 {@link NotNull} 中成员一致,不过 {@link NotNull} 中通过 {@link Repeatable} 声明了它是可复用的,
* 并通过 {@link Constraint} 注解声明注解的功能实现类
*/
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Constraint(validatedBy = {IdCardValidator.class})
public @interface IdCard {
// ValidationMessages.properties 扩展自
// org.hibernate.validator.hibernate-validator.6.0.19.Final.hibernate-validator-6.0.19.Final.jar!\org\hibernate\validator\ValidationMessages.properties
String message() default "{com.soulballad.usage.model.validation.id.card.message}";
Class<?>[] groups() default {};
Class<? extends Payload>[] payload() default {};
}
IdCardValidator.java
/**
* @apiNote : IdCard校验:注解{@link IdCard}的校验功能实现,需要实现{@link ConstraintValidator}接口, 泛型中两个参数分别为 {@link IdCard} 和 @IdCard
* 修饰的字段对应类型
*/
public class IdCardValidator implements ConstraintValidator<IdCard, String> {
@Override
public boolean isValid(String value, ConstraintValidatorContext context) {
// 校验身份证号:正规身份证号 18=2(省)+2(市)+2(区/县)+8(出生日期)+2(顺序码)+1(性别)+1(校验码)
// 这里使用正则简单校验一下
if (value.length() != 18) {
return false;
}
// 身份证号正则表达式
String regex = "^[1-9]\\d{5}(18|19|20)\\d{2}((0[1-9])|(1[0-2]))(([0-2][1-9])|10|20|30|31)\\d{3}[0-9Xx]$";
return Pattern.matches(regex, value);
}
@Override
public void initialize(IdCard constraintAnnotation) {
}
}
UserController.java
@Controller
@RequestMapping(value = "/user")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping(value = "/list", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public List<User> list() {
return userService.selectAll();
}
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping(value = "/add", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public User add(@Valid @RequestBody User user) {
return userService.add(user);
}
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping(value = "/get/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public User get(@PathVariable Long id) {
return userService.getUserById(id);
}
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping(value = "/delete/{id}", method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
public User delete(@PathVariable Long id) {
return userService.delete(id);
}
@ResponseBody
@RequestMapping(value = "/update", method = RequestMethod.PUT)
public User update(@Valid @RequestBody User user) {
return userService.update(user);
}
}
UserCommand.java
@Component
public class UserCommand implements CommandLineRunner {
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
// 身份证号由 http://sfz.uzuzuz.com/ 在线生成
User user1 = new User("zhangsan", 23, "110101200303072399");
User user2 = new User("lisi", 34, "110113198708074275");
User user3 = new User("wangwu", 45, "110113197308182272");
userRepository.saveAll(Arrays.asList(user1, user2, user3));
userRepository.deleteById(3L);
}
}
3.6 git 地址
spring-boot/spring-boot-04-bean-validate
4.结果
启动 SpringBoot04BeanValidateApplication.main 方法,在 spring-boot-04-bean-validate.http 访问下列地址,观察输出信息是否符合预期。
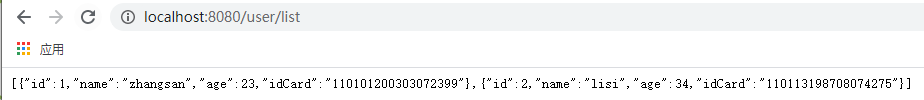
### GET /user/list
GET http://localhost:8080/user/list
Accept: application/json
### GET /user/get/{id}
GET http://localhost:8080/user/get/1
Accept: application/json
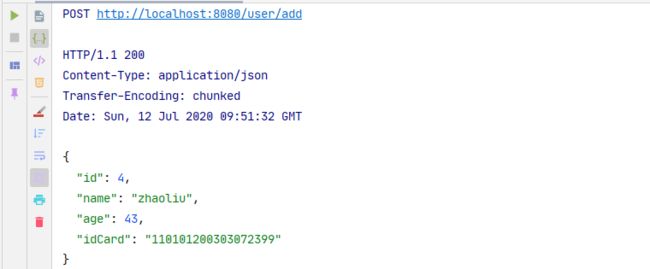
### POST /user/add success
POST http://localhost:8080/user/add
Content-Type: application/json
Accept: */*
Cache-Control: no-cache
{
"name": "zhaoliu",
"age": 43,
"idCard": "110101200303072399"
}
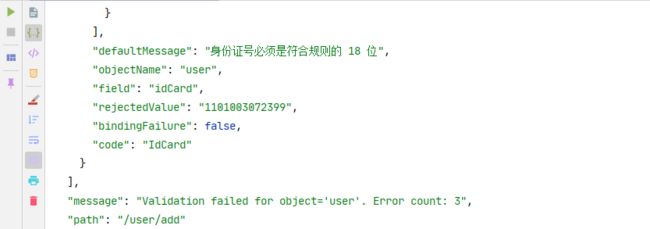
### POST /user/add idCard&name&age illegal
POST http://localhost:8080/user/add
Content-Type: application/json
Accept: */*
# Accept-Language: en_US 使用此配置可选择中、英文错误提示
{
"name": "s",
"age": 243,
"idCard": "1101003072399"
}
### PUT /user/update success
PUT http://localhost:8080/user/update
Content-Type: application/json
Accept: */*
{
"id": 2,
"name": "sunqi",
"age": 43,
"idCard": "110101200303072399"
}
### DELETE /user/delete/{id} success
DELETE http://localhost:8080/user/delete/1
Content-Type: application/json
Accept: */*
5.源码分析
5.1 注解校验如何生效的?
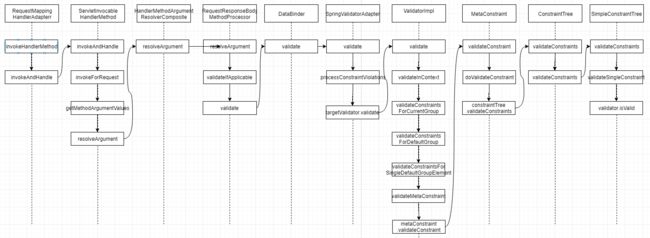
在 UserController#add 方法上有使用 @Valid 注解,标明这个方法需要校验,同时也可以使用 @Validated 注解标明要校验的位置。那么 @Valid 是如何生效的呢?
在 SpringBoot学习(三)——WebMVC及其工作原理 中,有跟踪 Spring MVC 的运行原理,@Valid 的注解校验就在
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter#invokeHandlerMethod 方法中
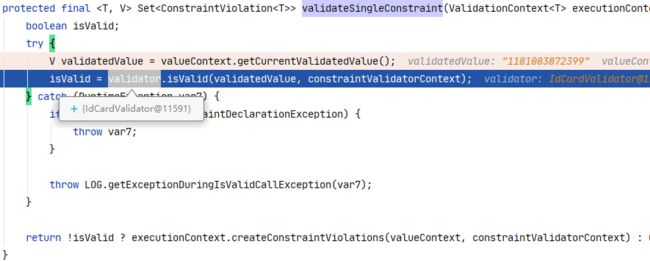
在 ConstraintTree#validateSingleConstraint 中使用具体的 Validator 对参数进行校验
protected final <T, V> Set<ConstraintViolation<T>> validateSingleConstraint(ValidationContext<T> executionContext, ValueContext<?, ?> valueContext, ConstraintValidatorContextImpl constraintValidatorContext, ConstraintValidator<A, V> validator) {
boolean isValid;
try {
V validatedValue = valueContext.getCurrentValidatedValue();
isValid = validator.isValid(validatedValue, constraintValidatorContext);
} catch (RuntimeException var7) {
if (var7 instanceof ConstraintDeclarationException) {
throw var7;
}
throw LOG.getExceptionDuringIsValidCallException(var7);
}
return !isValid ? executionContext.createConstraintViolations(valueContext, constraintValidatorContext) : Collections.emptySet();
}