RocketMQ为什么要保证订阅关系的一致性?
前段时间有个朋友向我提了一个问题,他说在搭建 RocketMQ 集群过程中遇到了关于消费订阅的问题,具体问题如下:
然后他发了报错的日志给我看:
the consumer's subscription not exist我第一时间在源码里找到了报错的位置:
org.apache.rocketmq.broker.processor.PullMessageProcessor#processRequest:
subscriptionData = consumerGroupInfo.findSubscriptionData(requestHeader.getTopic());
if (null == subscriptionData) {
log.warn("the consumer's subscription not exist, group: {}, topic:{}", requestHeader.getConsumerGroup(), requestHeader.getTopic());
response.setCode(ResponseCode.SUBSCRIPTION_NOT_EXIST);
response.setRemark("the consumer's subscription not exist" + FAQUrl.suggestTodo(FAQUrl.SAME_GROUP_DIFFERENT_TOPIC));
return response;
}此处源码是将该 Topic 的订阅信息找出来,然而这里却没找到,所以报了消费订阅不存在的错误。
朋友还跟我讲了他的消费集群中,每个消费者订阅了自己的 Topic,他的消费组中 有 c1 和 c2 消费者,c1 订阅了 topicA,而 c2 订阅了 topicB。
这时我已经知道什么原因了,我先说一下消费者的订阅信息在 broker 中是以 group 来分组的,数据结构如下:
org.apache.rocketmq.broker.client.ConsumerManager:
private final ConcurrentMap<String/* Group */, ConsumerGroupInfo> consumerTable =
new ConcurrentHashMap<String, ConsumerGroupInfo>(1024);这意味着集群中的每个消费者在向 broker 注册订阅信息的时候相互覆盖掉对方的订阅信息了,这也是为什么同一个消费组应该拥有完全一样的订阅关系的原因,而朋友在同一个消费组的每个消费者订阅关系都不一样,就出现了订阅信息相互覆盖的问题。
可是朋友这时又有疑惑了,他觉得每个消费者订阅自己的主题,貌似没问题啊,逻辑上也行的通,他不明白为什么 RocketMQ 不允许这样做,于是秉承着老司机的职业素养,下面我会从源码的角度深度分析 RocketMQ 消费订阅注册,消息拉取,消息队列负载与重新分布机制,让大家彻底弄清 RocketMQ 消费订阅机制。
消费者订阅信息注册
消费者在启动时会向所有 broker 注册订阅信息,并启动心跳机制,定时更新订阅信息,每个消费者都有一个 MQClientInstance,消费者启动时会启动这个类,启动方法中会启动一些列定时任务,其中:
org.apache.rocketmq.client.impl.factory.MQClientInstance#startScheduledTask:
this.scheduledExecutorService.scheduleAtFixedRate(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
MQClientInstance.this.cleanOfflineBroker();
MQClientInstance.this.sendHeartbeatToAllBrokerWithLock();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("ScheduledTask sendHeartbeatToAllBroker exception", e);
}
}
}, 1000, this.clientConfig.getHeartbeatBrokerInterval(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);上面是向集群内所有 broker 发送订阅心跳信息的定时任务,源码继续跟进去,发现会给集群中的每个 broker 都发送自己的 HeartbeatData,HeartbeatData 即是每个客户端的心跳数据,它包含了如下数据:
// 客户端ID
private String clientID;
// 生产者信息
private Set<ProducerData> producerDataSet = new HashSet<ProducerData>();
// 消费者信息
private Set<ConsumerData> consumerDataSet = new HashSet<ConsumerData>();其中消费者信息包含了客户端订阅的主题信息。
我们继续看看 broker 如何处理 HeartbeatData 数据,客户端发送 HeartbeatData 时的请求类型为 HEART_BEAT,我们直接找到 broker 处理 HEART_BEAT 请求类型的逻辑:
org.apache.rocketmq.broker.processor.ClientManageProcessor#heartBeat:
public RemotingCommand heartBeat(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RemotingCommand request) {
RemotingCommand response = RemotingCommand.createResponseCommand(null);
// 解码,获取 HeartbeatData
HeartbeatData heartbeatData = HeartbeatData.decode(request.getBody(), HeartbeatData.class);
ClientChannelInfo clientChannelInfo = new ClientChannelInfo(
ctx.channel(),
heartbeatData.getClientID(),
request.getLanguage(),
request.getVersion()
);
// 循环注册消费者订阅信息
for (ConsumerData data : heartbeatData.getConsumerDataSet()) {
// 按消费组获取订阅配置信息
SubscriptionGroupConfig subscriptionGroupConfig =
this.brokerController.getSubscriptionGroupManager().findSubscriptionGroupConfig(
data.getGroupName());
boolean isNotifyConsumerIdsChangedEnable = true;
if (null != subscriptionGroupConfig) {
isNotifyConsumerIdsChangedEnable = subscriptionGroupConfig.isNotifyConsumerIdsChangedEnable();
int topicSysFlag = 0;
if (data.isUnitMode()) {
topicSysFlag = TopicSysFlag.buildSysFlag(false, true);
}
String newTopic = MixAll.getRetryTopic(data.getGroupName());
this.brokerController.getTopicConfigManager().createTopicInSendMessageBackMethod(
newTopic,
subscriptionGroupConfig.getRetryQueueNums(),
PermName.PERM_WRITE | PermName.PERM_READ, topicSysFlag);
}
// 注册消费者订阅信息
boolean changed = this.brokerController.getConsumerManager().registerConsumer(
data.getGroupName(),
clientChannelInfo,
data.getConsumeType(),
data.getMessageModel(),
data.getConsumeFromWhere(),
data.getSubscriptionDataSet(),
isNotifyConsumerIdsChangedEnable
);
// ...
response.setCode(ResponseCode.SUCCESS);
response.setRemark(null);
return response;
}在这里我们可以看到,broker 收到 HEART_BEAT 请求后,将请求数据解压获取 HeartbeatData,根据 HeartbeatData 里面的消费订阅信息,循环进行注册:
org.apache.rocketmq.broker.client.ConsumerManager#registerConsumer:
public boolean registerConsumer(final String group, final ClientChannelInfo clientChannelInfo,
ConsumeType consumeType, MessageModel messageModel, ConsumeFromWhere consumeFromWhere,
final Set<SubscriptionData> subList, boolean isNotifyConsumerIdsChangedEnable) {
// 获取消费组内的消费者信息
ConsumerGroupInfo consumerGroupInfo = this.consumerTable.get(group);
// 如果消费组的消费者信息为空,则新建一个
if (null == consumerGroupInfo) {
ConsumerGroupInfo tmp = new ConsumerGroupInfo(group, consumeType, messageModel, consumeFromWhere);
ConsumerGroupInfo prev = this.consumerTable.putIfAbsent(group, tmp);
consumerGroupInfo = prev != null ? prev : tmp;
}
boolean r1 =
consumerGroupInfo.updateChannel(clientChannelInfo, consumeType, messageModel,
consumeFromWhere);
// 更新订阅信息,订阅信息是按照消费组存放的,因此这步骤就会导致同一个消费组内的各个消费者客户端的订阅信息相互被覆盖
boolean r2 = consumerGroupInfo.updateSubscription(subList);
if (r1 || r2) {
if (isNotifyConsumerIdsChangedEnable) {
this.consumerIdsChangeListener.handle(ConsumerGroupEvent.CHANGE, group, consumerGroupInfo.getAllChannel());
}
}
this.consumerIdsChangeListener.handle(ConsumerGroupEvent.REGISTER, group, subList);
return r1 || r2;
}这步骤是 broker 更新消费者订阅信息的核心方法,如果消费组的消费者信息 ConsumerGroupInfo 为空,则新建一个,从名字可知道,订阅信息是按照消费组进行存放的,因此在更新订阅信息时,订阅信息是按照消费组存放的,这步骤就会导致同一个消费组内的各个消费者客户端的订阅信息相互被覆盖。
消息拉取
在 MQClientInstance 启动时,会启动一条线程来处理消息拉取任务:
org.apache.rocketmq.client.impl.factory.MQClientInstance#start:
// Start pull service
this.pullMessageService.start();pullMessageService 继承了 ServiceThread,而 ServiceThread 实现了 Runnable 接口,它的 run 方法实现如下:
org.apache.rocketmq.client.impl.consumer.PullMessageService#run:
@Override
public void run() {
while (!this.isStopped()) {
try {
// 从 pullRequestQueue 中获取拉取消息请求对象
PullRequest pullRequest = this.pullRequestQueue.take();
// 执行消息拉取
this.pullMessage(pullRequest);
} catch (InterruptedException ignored) {
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("Pull Message Service Run Method exception", e);
}
}
}消费端拿到 PullRequest 对象进行拉取消息,pullRequestQueue 是一个阻塞队列,如果 pullRequest 数据为空,执行 take() 方法会一直阻塞,直到有新的 pullRequest 拉取任务进来,这里是一个很关键的步骤,你可能会想,pullRequest 什么时候被创建然后放入 pullRequestQueue?pullRequest 它是在 RebalanceImpl 中创建,它是 RocketMQ 消息队列负载与重新分布机制的实现。
消息队列负载与重新分布
从上面消息拉取源码分析可知,pullMessageService 启动时由于 pullRequestQueue 中没有 pullRequest 对象,会一直阻塞,而在 MQClientInstance 启动时,同样会启动一条线程来处理消息队列负载与重新分布任务:
org.apache.rocketmq.client.impl.factory.MQClientInstance#start:
// Start rebalance service
this.rebalanceService.start();rebalanceService 同样继承了 ServiceThread,它的 run 方法如下:
@Override
public void run() {
while (!this.isStopped()) {
this.waitForRunning(waitInterval);
this.mqClientFactory.doRebalance();
}
}继续跟进去:
org.apache.rocketmq.client.impl.consumer.RebalanceImpl#doRebalance:
public void doRebalance(final boolean isOrder) {
// 获取消费者所有订阅信息
Map<String, SubscriptionData> subTable = this.getSubscriptionInner();
if (subTable != null) {
for (final Map.Entry<String, SubscriptionData> entry : subTable.entrySet()) {
final String topic = entry.getKey();
try {
// 消息队列负载与重新分布
this.rebalanceByTopic(topic, isOrder);
} catch (Throwable e) {
if (!topic.startsWith(MixAll.RETRY_GROUP_TOPIC_PREFIX)) {
log.warn("rebalanceByTopic Exception", e);
}
}
}
}
this.truncateMessageQueueNotMyTopic();
}这里主要是获取客户端订阅的主题,并根据主题进行消息队列负载与重新分布,subTable 存储了消费者的订阅信息,消费者进行消息订阅时会填充到里面,我们接着往下:
org.apache.rocketmq.client.impl.consumer.RebalanceImpl#rebalanceByTopic:
Set<MessageQueue> mqSet = this.topicSubscribeInfoTable.get(topic);
List<String> cidAll = this.mQClientFactory.findConsumerIdList(topic, consumerGroup);rebalanceByTopic 方法是实现 Consumer 端负载均衡的核心,我们这里以集群模式的消息队列负载与重新分布,首先从 topicSubscribeInfoTable 中获取订阅主题的队列信息,接着随机从集群中的一个 broker 中获取消费组内某个 topic 的订阅客户端 ID 列表,这里需要注意的是,为什么从集群内任意一个 broker 就可以获取订阅客户端信息呢?前面的分析也说了,消费者客户端启动时会启动一个线程,向所有 broker 发送心跳包。
org.apache.rocketmq.client.impl.consumer.RebalanceImpl#rebalanceByTopic:
// 如果 主题订阅信息mqSet和主题订阅客户端不为空,就执行消息队列负载与重新分布
if (mqSet != null && cidAll != null) {
List<MessageQueue> mqAll = new ArrayList<MessageQueue>();
mqAll.addAll(mqSet);
// 排序,确保每个消息队列只分配一个消费者
Collections.sort(mqAll);
Collections.sort(cidAll);
// 消息队列分配算法
AllocateMessageQueueStrategy strategy = this.allocateMessageQueueStrategy;
// 执行算法,并得到队列重新分配后的结果对象allocateResult
List<MessageQueue> allocateResult = null;
try {
allocateResult = strategy.allocate(
this.consumerGroup,
this.mQClientFactory.getClientId(),
mqAll,
cidAll);
} catch (Throwable e) {
log.error("AllocateMessageQueueStrategy.allocate Exception. allocateMessageQueueStrategyName={}", strategy.getName(),
e);
return;
}
// ...
}以上是消息负载均衡的核心逻辑,RocketMQ 本身提供了 5 种负载算法,默认使用 AllocateMessageQueueAveragely 平均分配算法,它分配算法特点如下:
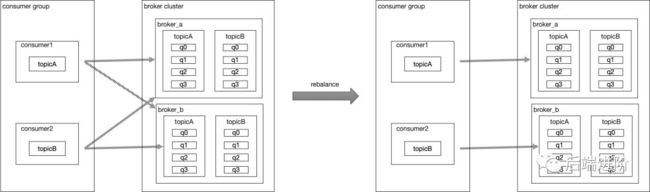
假设有消费组 g1,有消费者 c1 和 c2,c1 订阅了 topicA,c2 订阅了 topicB,集群内有 broker1 和broker2,假设 topicA 有 8 个消息队列,broker_a(q0/q1/q2/q3) 和 broker_b(q0/q1/q2/q3),前面我们知道 findConsumerIdList 方法会获取消费组内所有消费者客户端 ID,topicA 经过平均分配算法进行分配之后的消费情况如下:
c1:broker_a(q0/q1/q2/q3)
c2:broker_b(q0/q1/q2/q3)
问题就出现在这里,c2 根本没有订阅 topicA,但根据分配算法,却要加上 c2 进行分配,这样就会导致这种情况有一半的消息被分配到 c2 进行消费,被分配到 c2 的消息队列会延迟十几秒甚至更久才会被消费,topicB 同理。
下面我用图表示 topicA 和 topicB 经过 rebalance 之后的消费情况:
至于为什么会报 the consumer's subscription not exist,我们继续往下撸:
org.apache.rocketmq.client.impl.consumer.RebalanceImpl#rebalanceByTopic:
if (mqSet != null && cidAll != null) {
// ...
Set<MessageQueue> allocateResultSet = new HashSet<MessageQueue>();
if (allocateResult != null) {
allocateResultSet.addAll(allocateResult);
}
// 用户重新分配后的结果allocateResult来更新当前消费者负载的消息队列缓存表processQueueTable,并生成 pullRequestList 放入 pullRequestQueue 阻塞队列中
boolean changed = this.updateProcessQueueTableInRebalance(topic, allocateResultSet, isOrder);
if (changed) {
log.info(
"rebalanced result changed. allocateMessageQueueStrategyName={}, group={}, topic={}, clientId={}, mqAllSize={}, cidAllSize={}, rebalanceResultSize={}, rebalanceResultSet={}",
strategy.getName(), consumerGroup, topic, this.mQClientFactory.getClientId(), mqSet.size(), cidAll.size(),
allocateResultSet.size(), allocateResultSet);
this.messageQueueChanged(topic, mqSet, allocateResultSet);
}
}以上代码逻辑主要是拿 mqSet 和 cidAll 进行消息队列负载与重新分布,得到结果 allocateResult,它是一个 MessageQueue 列表,接着用 allocateResult 更新消费者负载的消息队列缓存表 processQueueTable,生成 pullRequestList 放入 pullRequestQueue 阻塞队列中:
org.apache.rocketmq.client.impl.consumer.RebalanceImpl#updateProcessQueueTableInRebalance:
List<PullRequest> pullRequestList = new ArrayList<PullRequest>();
// 循环执行,将mqSet订阅数据封装成PullRequest对象,并添加到pullRequestList中
for (MessageQueue mq : mqSet) {
// 如果缓存列表不存在该订阅信息,说明这次消息队列重新分配后新增加的消息队列
if (!this.processQueueTable.containsKey(mq)) {
if (isOrder && !this.lock(mq)) {
log.warn("doRebalance, {}, add a new mq failed, {}, because lock failed", consumerGroup, mq);
continue;
}
this.removeDirtyOffset(mq);
ProcessQueue pq = new ProcessQueue();
long nextOffset = this.computePullFromWhere(mq);
if (nextOffset >= 0) {
ProcessQueue pre = this.processQueueTable.putIfAbsent(mq, pq);
if (pre != null) {
log.info("doRebalance, {}, mq already exists, {}", consumerGroup, mq);
} else {
log.info("doRebalance, {}, add a new mq, {}", consumerGroup, mq);
PullRequest pullRequest = new PullRequest();
pullRequest.setConsumerGroup(consumerGroup);
pullRequest.setNextOffset(nextOffset);
pullRequest.setMessageQueue(mq);
pullRequest.setProcessQueue(pq);
pullRequestList.add(pullRequest);
changed = true;
}
} else {
log.warn("doRebalance, {}, add new mq failed, {}", consumerGroup, mq);
}
}
}
// 将pullRequestList添加到PullMessageService中的pullRequestQueue阻塞队列中,以唤醒PullMessageService线程执行消息拉取
this.dispatchPullRequest(pullRequestList);前面我们讲到消息拉取是从 pullRequestQueue 阻塞队列中拿 pullRequest 执行拉取的,以上方法就是创建 pullRequest 的地方。
源码分析到这里,就可以弄清楚为什么会报 the consumer's subscription not exist 这个错误了:
假设有消费者组 g1,g1下有消费者 c1 和消费者 c2,c1 订阅了 topicA,c2 订阅了 topicB,此时c2 先启动,将 g1 的订阅信息更新为 topicB,c1 随后启动,将 g1 的订阅信息覆盖为 topicA,c1 的 Rebalance 负载将 topicA 的 pullRequest 添加到 pullRequestQueue 中,而恰好此时 c2 心跳包又将 g1 的订阅信息更新为 topicB,那么此时 c1 的 PullMessageService 线程拿到 pullRequestQueue 中 topicA 的 pullRequest 进行消息拉取,然而在 broker 端找不到消费者组 g1 下 topicA 的订阅信息(因为此时恰好被 c2 心跳包给覆盖了),就会报消费者订阅信息不存在的错误了。
近期热文
RocketMQ消息发送的高可用设计
关于RocketMQ Topic的创建机制,我还有一些细节上的思考
深度解析RocketMQ Topic的创建机制
RocketMQ源码分析之路由中心
RocketMQ的消费模式
分布式事务中间件Seata的设计原理
我对支付平台架构设计的一些思考
Mybatis-spring源码分析之注册Mapper Bean
mybatis-plus源码分析之sql注入器
基于Jenkins Pipeline自动化部署
Dubbo服务暴露之注册地址和端口
Dubbo全链路追踪日志的实现
![]()
长按可以订阅
如果你也有 RocketMQ 方面的问题
欢迎留言,另外
点个在看,欧气满满![]()