转账案例(使用ThreadLocal对象把Connection和当前线程绑定)
转账案例
【需求】:姓名为aaa的账号取出100元给姓名为bbb的账号
准备工作:
第一步:创建工程spring_day03_account
第二步:导入坐标,pom.xml
4.0.0
com.itheima
spring_day03_account
1.0-SNAPSHOT
jar
org.springframework
spring-context
5.0.2.RELEASE
org.springframework
spring-test
5.0.2.RELEASE
commons-dbutils
commons-dbutils
1.4
mysql
mysql-connector-java
5.1.6
c3p0
c3p0
0.9.1.2
junit
junit
4.12
第三步:创建com.itheima.domain
创建账号信息表
/**
* 账户的实体类
*/
public class Account implements Serializable {
private Integer id;
private String name;
private Float money;
}
第四步:创建包com.itheima.dao,
创建接口AccountDao.java
/**
* 账户的持久层接口
*/
public interface AccountDao {
/**
* 查询所有
* @return
*/
List findAllAccount();
/**
* 查询一个
* @return
*/
Account findAccountById(Integer accountId);
/**
* 保存
* @param account
*/
void saveAccount(Account account);
/**
* 更新
* @param account
*/
void updateAccount(Account account);
/**
* 删除
* @param acccountId
*/
void deleteAccount(Integer acccountId);
/**
* 根据名称查询账户
* @param accountName
* @return 如果有唯一的一个结果就返回,如果没有结果就返回null
* 如果结果集超过一个就抛异常
*/
Account findAccountByName(String accountName);
}
创建实现类AccountDaoImpl.java
/**
* 账户的持久层实现类
*/
public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao {
private QueryRunner runner;
public List findAllAccount() {
try{
return runner.query("select * from account",new BeanListHandler(Account.class));
}catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public Account findAccountById(Integer accountId) {
try{
return runner.query("select * from account where id = ? ",new BeanHandler(Account.class),accountId);
}catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public void saveAccount(Account account) {
try{
runner.update("insert into account(name,money)values(?,?)",account.getName(),account.getMoney());
}catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public void updateAccount(Account account) {
try{
runner.update("update account set name=?,money=? where id=?",account.getName(),account.getMoney(),account.getId());
}catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public void deleteAccount(Integer accountId) {
try{
runner.update("delete from account where id=?",accountId);
}catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public Account findAccountByName(String accountName) {
try{
List accounts = runner.query("select * from account where name = ? ",new BeanListHandler(Account.class),accountName);
if(accounts == null || accounts.size() == 0){
return null;
}
if(accounts.size() > 1){
throw new RuntimeException("结果集不唯一,数据有问题");
}
return accounts.get(0);
}catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
第五步:创建com.itheima.service,创建接口AccountService.java
/**
* 账户的业务层接口
*/
public interface AccountService {
/**
* 查询所有
* @return
*/
List findAllAccount();
/**
* 查询一个
* @return
*/
Account findAccountById(Integer accountId);
/**
* 保存
* @param account
*/
void saveAccount(Account account);
/**
* 更新
* @param account
*/
void updateAccount(Account account);
/**
* 删除
* @param acccountId
*/
void deleteAccount(Integer acccountId);
/**
* 转账
* @param sourceName 转出账户名称
* @param targetName 转入账户名称
* @param money 转账金额
*/
void transfer(String sourceName, String targetName, Float money);
}
创建接口的实现类,AccountServiceImpl.java
/**
* 账户的业务层实现类
*
* 事务控制应该都是在业务层
*/
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
private AccountDao accountDao;
public void setAccountDao(AccountDao accountDao) {
this.accountDao = accountDao;
}
public List findAllAccount() {
return accountDao.findAllAccount();
}
public Account findAccountById(Integer accountId) {
return accountDao.findAccountById(accountId);
}
public void saveAccount(Account account) {
accountDao.saveAccount(account);
}
public void updateAccount(Account account) {
accountDao.updateAccount(account);
}
public void deleteAccount(Integer acccountId) {
accountDao.deleteAccount(acccountId);
}
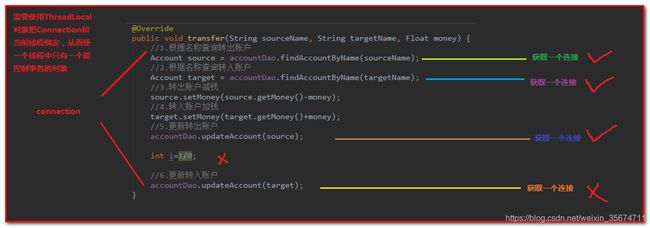
public void transfer(String sourceName, String targetName, Float money) {
System.out.println("transfer....");
//2.1根据名称查询转出账户
Account source = accountDao.findAccountByName(sourceName);
//2.2根据名称查询转入账户
Account target = accountDao.findAccountByName(targetName);
//2.3转出账户减钱
source.setMoney(source.getMoney()-money);
//2.4转入账户加钱
target.setMoney(target.getMoney()+money);
//2.5更新转出账户
accountDao.updateAccount(source);
int i=1/0;
//2.6更新转入账户
accountDao.updateAccount(target);
}
}
第六步:配置applicationContext.xml
第七步:测试
/**
* 使用Junit单元测试:测试我们的配置
*/
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(locations = "classpath:applicationContext.xml")
public class AccountServiceTest {
@Autowired
private AccountService as;
@Test
public void testTransfer(){
as.transfer("aaa","bbb",100f);
}
}
事务被自动控制了。换言之,我们使用了connection对象的setAutoCommit(true)
此方式控制事务,如果我们每次都执行一条sql语句,没有问题,但是如果业务方法一次要执行多条sql语句,这种方式就无法实现功能了。 可以在AccountServiceImpl.java中的transfer方法中添加int i = 1/0;完成测试
添加事务
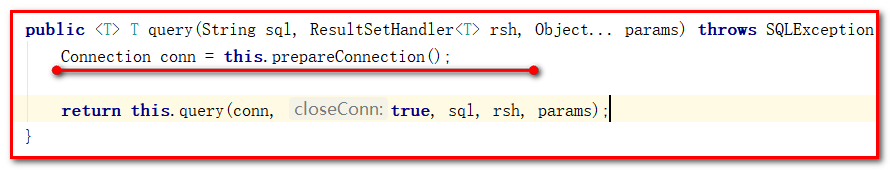
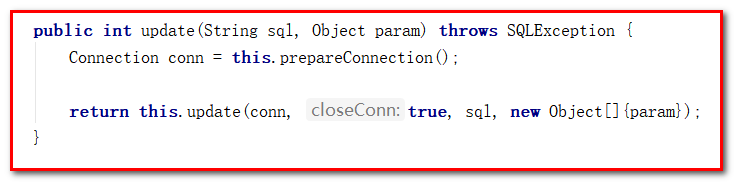
查看QueryRunner中的底层代码
query方法:
update方法:
【事务分析】
总结:
如果在AccountServiceImpl.java中的transfer方法中,抛出一个异常。此时事务不会回滚,原因是DBUtils每个操作数据都是获取一个连接,每个连接的事务都是独立的,且默认是自动提交。
解决方案:
需要使用ThreadLocal对象把Connection和当前线程绑定,从而使一个线程中只能有一个能控制事务的连接对象。
ConnectionUtils.java
第一步:创建包com.itheima.utils,编写ConnectionUtils.java
作用:连接的工具类,它用于从数据源中获取一个连接,并且实现和线程的绑定
/**
* 连接的工具类,它用于从数据源中获取一个连接,并且实现和线程的绑定
*/
public class ConnectionUtils {
private ThreadLocal tl = new ThreadLocal();
private DataSource dataSource;
public void setDataSource(DataSource dataSource) {
this.dataSource = dataSource;
}
/**
* 获取当前线程上的连接
* @return
*/
public Connection getThreadConnection() {
try{
//1.先从ThreadLocal上获取
Connection conn = tl.get();
//2.判断当前线程上是否有连接
if (conn == null) {
//3.从数据源中获取一个连接,并且存入ThreadLocal中
conn = dataSource.getConnection();
tl.set(conn);
}
//4.返回当前线程上的连接
return conn;
}catch (Exception e){
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
/**
* 把连接和线程解绑(在当前线程结束的时候执行)
*/
public void removeConnection(){
tl.remove();
}
}
TransactionManager.java
作用:和事务管理相关的工具类,它包含了,开启事务,提交事务,回滚事务和释放连接
/**
* 和事务管理相关的工具类,它包含了,开启事务,提交事务,回滚事务和释放连接
*/
public class TransactionManager {
private ConnectionUtils connectionUtils;
public void setConnectionUtils(ConnectionUtils connectionUtils) {
this.connectionUtils = connectionUtils;
}
/**
* 开启事务
*/
public void beginTransaction(){
try {
connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().setAutoCommit(false);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 提交事务
*/
public void commit(){
try {
connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().commit();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 回滚事务
*/
public void rollback(){
try {
connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().rollback();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* 释放连接
*/
public void release(){
try {
connectionUtils.getThreadConnection().close();//把连接还回连接池中
connectionUtils.removeConnection();//线程和连接解绑
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
配置AccountDaoImpl.java
作用:注入连接工具对象,使得操作数据库从同一个连接中获取
/**
* 账户的持久层实现类
*/
public class AccountDaoImpl implements AccountDao {
private QueryRunner runner;
private ConnectionUtils connectionUtils;
public void setConnectionUtils(ConnectionUtils connectionUtils) {
this.connectionUtils = connectionUtils;
}
public void setRunner(QueryRunner runner) {
this.runner = runner;
}
public List findAllAccount() {
try{
return runner.query(connectionUtils.getThreadConnection(),"select * from account",new BeanListHandler(Account.class));
}catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public Account findAccountById(Integer accountId) {
try{
return runner.query(connectionUtils.getThreadConnection(),"select * from account where id = ? ",new BeanHandler(Account.class),accountId);
}catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public void saveAccount(Account account) {
try{
runner.update(connectionUtils.getThreadConnection(),"insert into account(name,money)values(?,?)",account.getName(),account.getMoney());
}catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public void updateAccount(Account account) {
try{
runner.update(connectionUtils.getThreadConnection(),"update account set name=?,money=? where id=?",account.getName(),account.getMoney(),account.getId());
}catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public void deleteAccount(Integer accountId) {
try{
runner.update(connectionUtils.getThreadConnection(),"delete from account where id=?",accountId);
}catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public Account findAccountByName(String accountName) {
try{
List accounts = runner.query(connectionUtils.getThreadConnection(),"select * from account where name = ? ",new BeanListHandler(Account.class),accountName);
if(accounts == null || accounts.size() == 0){
return null;
}
if(accounts.size() > 1){
throw new RuntimeException("结果集不唯一,数据有问题");
}
return accounts.get(0);
}catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
配置AccountServiceImpl.java
事务操作一定需要在Service层控制。
作用:注入事务管理器对象,对每个操作都需要开启事务、提交事务、关闭事务,如果抛出异常,需要回滚事务。
/**
* 账户的业务层实现类
*
* 事务控制应该都是在业务层
*/
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
private AccountDao accountDao;
private TransactionManager txManager;
public void setTxManager(TransactionManager txManager) {
this.txManager = txManager;
}
public void setAccountDao(AccountDao accountDao) {
this.accountDao = accountDao;
}
public List findAllAccount() {
try {
//1.开启事务
txManager.beginTransaction();
//2.执行操作
List accounts = accountDao.findAllAccount();
//3.提交事务
txManager.commit();
//4.返回结果
return accounts;
}catch (Exception e){
//5.回滚操作
txManager.rollback();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
//6.释放连接
txManager.release();
}
}
public Account findAccountById(Integer accountId) {
try {
//1.开启事务
txManager.beginTransaction();
//2.执行操作
Account account = accountDao.findAccountById(accountId);
//3.提交事务
txManager.commit();
//4.返回结果
return account;
}catch (Exception e){
//5.回滚操作
txManager.rollback();
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
//6.释放连接
txManager.release();
}
}
public void saveAccount(Account account) {
try {
//1.开启事务
txManager.beginTransaction();
//2.执行操作
accountDao.saveAccount(account);
//3.提交事务
txManager.commit();
}catch (Exception e){
//4.回滚操作
txManager.rollback();
}finally {
//5.释放连接
txManager.release();
}
}
public void updateAccount(Account account) {
try {
//1.开启事务
txManager.beginTransaction();
//2.执行操作
accountDao.updateAccount(account);
//3.提交事务
txManager.commit();
}catch (Exception e){
//4.回滚操作
txManager.rollback();
}finally {
//5.释放连接
txManager.release();
}
}
public void deleteAccount(Integer acccountId) {
try {
//1.开启事务
txManager.beginTransaction();
//2.执行操作
accountDao.deleteAccount(acccountId);
//3.提交事务
txManager.commit();
}catch (Exception e){
//4.回滚操作
txManager.rollback();
}finally {
//5.释放连接
txManager.release();
}
}
public void transfer(String sourceName, String targetName, Float money) {
try {
//1.开启事务
txManager.beginTransaction();
//2.执行操作
//2.1根据名称查询转出账户
Account source = accountDao.findAccountByName(sourceName);
//2.2根据名称查询转入账户
Account target = accountDao.findAccountByName(targetName);
//2.3转出账户减钱
source.setMoney(source.getMoney()-money);
//2.4转入账户加钱
target.setMoney(target.getMoney()+money);
//2.5更新转出账户
accountDao.updateAccount(source);
int i=1/0;
//2.6更新转入账户
accountDao.updateAccount(target);
//3.提交事务
txManager.commit();
}catch (Exception e){
//4.回滚操作
txManager.rollback();
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//5.释放连接
txManager.release();
}
}
}
配置applicationContext.xml
【问题】
通过对业务层改造,已经可以实现事务控制了,但是由于我们添加了事务控制,也产生了一个新的问题:
业务层方法变得臃肿了,里面充斥着很多重复代码。并且业务层方法和事务控制方法耦合了。
试想一下,如果我们此时提交,回滚,释放资源中任何一个方法名变更,都需要修改业务层的代码,况且这还只是一个业务层实现类,而实际的项目中这种业务层实现类可能有十几个甚至几十个。
【思考】:
这个问题能不能解决呢?
答案是肯定的,使用下一小节中提到的技术。