TensorFlow tf.nn.conv2d()介绍
一、tf.nn.conv2d()函数python版本的定义:
tf.nn.conv2d(input, filter, strides, padding, use_cudnn_on_gpu=None, name=None)需要做卷积的输入图像,是一个Tensor,shape为[batch, in_height, in_width, in_channels],含义是[训练时一个batch的图片数量, 图片高度, 图片宽度, 图像通道数]。注意这是一个4维的Tensor,数据类型为float32和float64其中之一。
2、参数 filter:
相当于CNN中的卷积核,是一个Tensor,shape为[filter_height, filter_width, in_channels, out_channels],含义是[卷积核的高度,卷积核的宽度,图像通道数,卷积核个数],要求类型与第一个参数input相同。注意,filter的第三维in_channels,就是参数input的第四维。
3、参数 strides:
做卷积时在图像每一维的步长,这是一个1维的向量,长度4。注意:一定要确保strides[0] = strides[3] = 1,因为在batch维和in_channels维不需要步长这个概念!并且,大多数情况先,在图像的水平和垂直俩方向上的步长是想同的,即strides = [1,stride,stride,1]。
4、参数padding:
string类型的量,只能是”SAME”,”VALID”其中之一,这个值决定了不同的卷积方式。
当padding = SAME时,卷积输出图像的大小(宽高)和输入图像的大小是相同的。
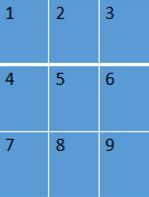
举例:加入输入图像为input = [1, 3, 3, 1],如下图:
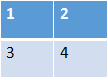
卷积核filter = [2, 2, 1, 1],如下图:
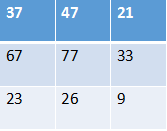
当padding = SAME时,函数会先将输入图像填充0,如下图:
然后开始卷积(每个位置加权求和),最终计算结果如下图:
可以看出,输入图像和输出图像都是3*3的图像!
当padding = VALID时,函数不会对图像进行填充0的操作,即without padding。此时,输出的图像大小会小于输入图像的大小。
5、参数use_cudnn_on_gpu:
bool类型,是否使用cudnn加速,默认为true。
6、返回值:
函数返回一个Tensor,就是我们常说的feature map!
再说strides:
是不是只要padding=’SAME’,那么卷积之后输出的尺寸就和输入相同呢?其实这还跟strides步长有关系!当步长strides = 1时对结果并没有什么影响。但不为1时,输出尺寸将不再与输入相同。
import tensorflow as tf
data=tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([64,48,48,3]),dtype=tf.float32)
weight=tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([5,5,3,64]),dtype=tf.float32)
sess=tf.InteractiveSession()
tf.global_variables_initializer().run()
conv1=tf.nn.conv2d(data,weight,strides=[1,1,1,1],padding='SAME')
conv2=tf.nn.conv2d(data,weight,strides=[1,2,2,1],padding='SAME')
conv3=tf.nn.conv2d(data,weight,strides=[1,4,4,1],padding='SAME')
print(conv1)
print(conv2)
print(conv3)Tensor("Conv2D_6:0", shape=(64, 48, 48, 64), dtype=float32)
Tensor("Conv2D_7:0", shape=(64, 24, 24, 64), dtype=float32)
Tensor("Conv2D_8:0", shape=(64, 12, 12, 64), dtype=float32)二、函数的实现过程
对于给定形状为[batch, in_height, in_width, in_channels]的tensor变量input,和形状为[filter_height, filter_width, in_channels, out_channels]的卷积核filter,函数tensorflow::ops::Conv2D(C++版本定义,和python版本为tf.nn.conv2d是对应的)大致执行如下步骤:
step1:将卷积核转换成shape为[filter_height * filter_width * in_channels, output_channels]的tensor
step2:将输入数据转换成shape为[batch, out_height, out_width, filter_height * filter_width * in_channels]的tensor
step3:按如下逻辑执行:
output[b, i, j, k] =
sum_{di, dj, q} input[b, strides[1] * i + di, strides[2] * j + dj, q] *
filter[di, dj, q, k]