苹果采购问题(DP)
Suppose you drive a pickup truck from apple market 1 to apple market n. Along the high way,
you will go through apple markets, 2, 3, …, n-1. At each market, you can buy or sell apples.
From a customer point of view, the buying price B[i] and selling price S[i] (dollar per pound)
at market i are known, 1 £ i £ n. In addition, we assume the following:
(1) You should never drive backward.
(2) Initially, the truck is empty.
(3) You should fully load the truck each time you buy apples and should sell all apples entirely
each time you sell apples.
(4) You can sell apples at most once in each market. That is, at a market, you can
(3.1) buy apples only
(3.2) sell apples only
(3.3) buy apples and then sell them at the same market
(3.4) sell apples and then buy apples at the same market
(3.5) buy apples, sell them, and buy again at the same market, but no sell the second time
(3.6) do nothing.
(5) You can sell apples a multiple number of times but at different markets.
Now, we wish to find an optimal sequence of trades in the order they are made such that
the total profit will be maximized. Here each trade is represented by a pair of (buying market,
selling market). The following figure shows an example.
If we do the following sequence of trades: (1, 1), (1, 3), (4, 5), (5, 6), then the total profit will
be (4-3)+(7-3)+(9-2)+(8-7) = 13 dollars for each pound of truck capacity.
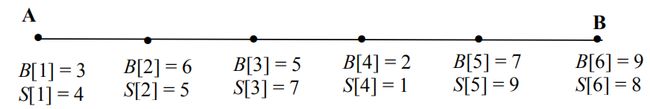
(a) Please design a dynamic programming algorithm to determine an optimal trade sequence
such that the total profit is maximized. You need to define the sub-problems, find inductive
formula, and initial conditions. Pseudo code is not required.
(b) Apply your algorithm to the following example.

题目大意
从A到B共有n个市场,你可以在每个市场中选择购买或出售苹果,B[i]表示购入价格,S[i]表示售价,问如何选择购买出售序列使得盈利最多。
ps:
1.不能回头
2.每次购买或出售苹果必须以整卡车为单位(那我们可以假设卡车上最多放一个苹果)
3.每个市场最多买一次苹果,但可以多次出售。
设计动态规划子问题
同样对于动态规划问题,我们先考虑其子问题
我们可以知道,在这个问题中在每个市场采取何种买入策略还需知道上一次购入苹果是在哪个市场,又由于是从第一个市场往后依次经过,我们可以设置子问题为从第一个市场到第i个市场的利润为M[i](假设第i个市场已经是最后一个市场了)(若在第i个市场卖苹果则其收入也算入)
写出递推公式
(写到M[i]时是默认前面的i-1个子问题的解都已经知道了)
M[i]=max(k=1~i-1){M[k]+max{S[i]-B[k],S[i]-B[i],0}};
<解出问题:如果我在这个市场想卖,那上一个选择购入的市场是哪一个时使得我的利润最大>
(在找到了上一个可能购买点k后,在i个市场进行的操作有三种可能1.在k点购入,i点卖出 2.在i点买入,在i点卖出 3.在k~i未进行任何购买)
(又因为我们不知道到第i个点时上一个可能购买点k的位置,故用枚举法来计算出最大的)
实现细节
关于记录每一组购入市场和销售市场的问题
可以设置一个数组PAIR[i]=k表示若在市场i出售,则其购入苹果的市场为k,若未购入则令k=0;
关于初始化的问题
我们采用自底向上需要设置最底层的值
M[1]=max{S[1]-B[1],0}(要嘛在1号市场买了再卖出,要嘛就不买)
PAIR[1] = 1 if (S[1] – B[1]) > 0
PAIR[1] = 0 if (S[1] – B[1]) < 0
伪代码
MAX_Profit(B[n+1],S[n+1],PAIR[n+1],M[n+1])
{
//先赋初值
if(S[1]>B[1])
{
PAIR[1]=1;
M[1]=S[1]-B[1];
}
else
{
PAIR[1]=0;
M[1]=0;
}
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++)
{
//自底向上求第一个市场到每个市场的情况
M[i]=0;//直接用这个值代表最大值可以省去中间记录最大值的中间变量
for(int k=1;k<i;k++)
{
//计算M[i]
if(M[i]<M[k]+max(S[i]-B[k],S[i]-S[i],0);
M[i]=M[k]+max(S[i]-B[k],S[i]-S[i],0);
//计算PAIR[i]
if(max(S[i]-B[k],S[i]-S[i],0)==0)
PAIR[i]=0;
else if(max(S[i]-B[k],S[i]-S[i],0)==S[i]-B[k])
PAIR[i]=k;
else if(max(S[i]-B[k],S[i]-S[i],0)==S[i]-S[i])
PAIR[i]=i;
}
}
}
可知算法的时间复杂度为O(n^2),因为其中有2个for循环
(b)对上述样例应用该算法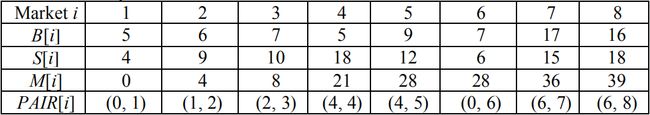
可知最大收益是39,而购买顺序为
(1,2), (2, 3), (4, 4), (4,5), (6, 8).