1136785 java.lang.reflect
java.lang.reflect
本篇文章介绍
java.lang.reflect包下的类以及基本用法。为理解反射打好基础。
- Type
- GenericDeclaration
- AnnotatedElement
- AnnotatedType
- AccessibleObject&Member&Paramter
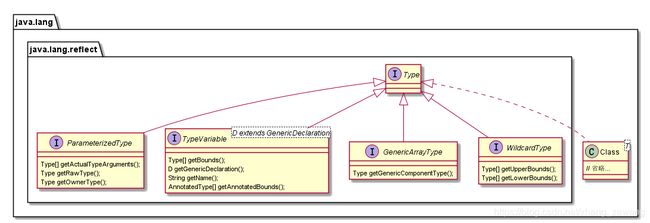
Type
package java.lang.reflect;
/**
* Type is the common superinterface for all types in the Java
* programming language. These include raw types, parameterized types,
* array types, type variables and primitive types.
*
* @since 1.5
*/
public interface Type {
/**
* Returns a string describing this type, including information
* about any type parameters.
*
* @implSpec The default implementation calls {@code toString}.
*
* @return a string describing this type
* @since 1.8
*/
default String getTypeName() {
return toString();
}
}
Type是Java中所有类型的通用超级接口。包括:
- raw types:这个raw types并不是指简单数据类型,而是指不带任何参数化的Class类型。如
String。而非诸如List等类型。 - parameterized types:参数化类型,如
List。 - array types:数组类型
- type variables:类型变量
- primitive types:简单数据类型
- other types:任何其他的,比如枚举,接口等等。
四个已有的子接口:
ParameterizedType:参数化类型TypeVariable:类型变量GenericArrayType:泛型数组类型WildcardType:通配符类型
还有一个最常用的实现:
- Class
ParameterizedType:参数化类型
是指带有参数的类型,如:Map
该类型主要的三个方法是:
Type getOwnerType();:获取该ParameterizedType类型所属的Type。比如Map.Entry的Entity就是ParameterizedType类型的,它的ownerType就是Map。Type getRawType();:获取当前ParameterizedType本身的类型。比如List返回的是List。Type[] getActualTypeArguments();:返回实际参数类型。比如Map返回String、Number
TypeVariable:类型变量
GenericDeclaration:是指可以定义类型变量的实体。目前只有
Class、Construstor、Method。
是指被定义的泛型变量。但注意和ParameterizedType不同的是,ParameterizedType是对泛型的使用,而TypeVariable是泛型的定义。
如下例子:
public <T extends Number> List<T> testTypeVariable() {
return null;
}
本例中的T就是TypeVariable类型,而List是ParameterizedType类型。
该类型主要的三个方法是:(这里暂不考虑注解)
Type[] getBounds();:返回当前类型的上边界,也就是父类或者父接口。可以有多个父接口,但只能有一个父类,且在第一的位置。D getGenericDeclaration();:获取定义该类型的元素。Class or Construstor or MethodString getName();:或许类型名称。
定义多个bounds的方式如下:
public <T extends Number & Serializable> void testBounds() {
//
}
以&连接,且Class(非接口)只能放在第一个位置,也可以全是接口。
GenericArrayType:泛型数组类型
是指由ParameterizedType或TypeVariable组成的数组类型。而普通class的数组不是GenericArrayType类型。如:
List<Stirng>[] array1; // 是GenericArrayType类型
String[] array2; // 不是GenericArrayType类型
该类型主要的一个方法是:
Type getGenericComponentType();:组成该数组的元素类型。注:无论数组有多层,该方法仅能脱最右边一层[]
WildcardType:通配符类型
指的是类似于、等类型。
注意和ParameterizedType区别是:(用例子说明)
List<? extends String> value;
- value是属于ParameterizedType类型,即
List - value的actualTypeArguments的第一个元素(当然,它本身就一个)是WildcardType类型,即
? extends String
该类型主要的两个方法是:
Type[] getUpperBounds();:得到上边界的数组Type[] getLowerBounds();:得到下边界的数组
List<? extends upper1,upper2> upperTest;
List<? super super1,super2> superTest;
对于四个子接口,jdk都有定义对应的impl,本篇文章只介绍每种type的用法,不去深究其实现。
总结
注:Class将单独讲解
通过前面的分析,可以总结出:
ParameterizedType:格式Class。T可以多个,可以是任何类型。TypeVariable:格式bounds可以是除了WildcardType之外的任何类型。GenericArrayType:格式是数组格式。但元素类型仅允许为ParameterizedType与TypeVariable。WildcardType:格式或或。只能用于ParameterizedType中。bounds可以是除了WildcardType之外的任何类型。
这四种类型中,比较特别的就是TypeVariable,因为它还继承了AnnotatedElement。这就是接下来需要讲的东西。
最后,用一个例子来总结Type
/**
* @author zhengzewang on 2018/12/29.
*/
public class SimpleType<K extends Map.Entry<? extends String[][],
List<? extends String>[]> & Iterator<? super V[]>, V> {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException {
Class cls = SimpleType.class;
TypeVariable[] variables = cls.getTypeParameters();
for (TypeVariable variable : variables) {
System.out.println(getTypeInfo("", variable));
}
}
public static String getTypeInfo(String blank, Type type) {
// String bt = blank;
String result = "";
if (type instanceof ParameterizedType) {
// eg Map.Entry[]
result += print(blank, "GenericArrayType:" + type.getTypeName());
GenericArrayType genericArrayType = (GenericArrayType) type;
result += print(blank + " ", ">genericComponentType:");
result += getTypeInfo(blank + " ", genericArrayType.getGenericComponentType());
} else if (type instanceof WildcardType) {
// eg
result += print(blank, "WildcardType:" + type.getTypeName());
WildcardType wildcardType = (WildcardType) type;
result += print(blank + " ", ">upperBounds:");
Type[] upperBounds = wildcardType.getUpperBounds();
for (Type inType : upperBounds) {
result += getTypeInfo(blank + " ", inType);
}
result += print(blank + " ", ">lowerBounds:");
Type[] lowerBounds = wildcardType.getLowerBounds();
for (Type inType : lowerBounds) {
result += getTypeInfo(blank + " ", inType);
}
} else if (type instanceof Class) {
Class cls = (Class) type;
if (cls.isArray()) {
// eg String[]
result += print(blank, "Array:" + type.getTypeName());
result += print(blank + " ", ">componentType:");
result += getTypeInfo(blank + " ", cls.getComponentType());
} else {
result += print(blank, "Class:" + type.getTypeName());
}
}
return result;
}
public static String print(String blank, String info) {
return blank + info + "\n";
}
}
运行代码,将通过反射获取所有该类定义或声明的类型。结果如下:
TypeVariable:K
>genericDeclaration:
class com.zzw.java1000000.z1136785.reflect.type.SimpleType
>bounds:
ParameterizedType:java.util.Map$Entry<? extends java.lang.String[][], java.util.List<? extends java.lang.String>[]>
>rowType:
Class:java.util.Map$Entry
>ownerType:
Class:java.util.Map
>actualTypeArguments:
WildcardType:? extends java.lang.String[][]
>upperBounds:
Array:java.lang.String[][]
>componentType:
Array:java.lang.String[]
>componentType:
Class:java.lang.String
>lowerBounds:
GenericArrayType:java.util.List<? extends java.lang.String>[]
>genericComponentType:
ParameterizedType:java.util.List<? extends java.lang.String>
>rowType:
Class:java.util.List
>ownerType:
>actualTypeArguments:
WildcardType:? extends java.lang.String
>upperBounds:
Class:java.lang.String
>lowerBounds:
ParameterizedType:java.util.Iterator<? super V[]>
>rowType:
Class:java.util.Iterator
>ownerType:
>actualTypeArguments:
WildcardType:? super V[]
>upperBounds:
Class:java.lang.Object
>lowerBounds:
GenericArrayType:V[]
>genericComponentType:
TypeVariable:V
>genericDeclaration:
class com.zzw.java1000000.z1136785.reflect.type.SimpleType
>bounds:
Class:java.lang.Object
TypeVariable:V
>genericDeclaration:
class com.zzw.java1000000.z1136785.reflect.type.SimpleType
>bounds:
Class:java.lang.Object
GenericDeclaration
package java.lang.reflect;
/**
* A common interface for all entities that declare type variables.
*
* @since 1.5
*/
public interface GenericDeclaration extends AnnotatedElement {
/**
* Returns an array of {@code TypeVariable} objects that
* represent the type variables declared by the generic
* declaration represented by this {@code GenericDeclaration}
* object, in declaration order. Returns an array of length 0 if
* the underlying generic declaration declares no type variables.
*
* @return an array of {@code TypeVariable} objects that represent
* the type variables declared by this generic declaration
* @throws GenericSignatureFormatError if the generic
* signature of this generic declaration does not conform to
* the format specified in
* The Java™ Virtual Machine Specification
*/
public TypeVariable<?>[] getTypeParameters();
}
从源码可以看出,该接口的定义为:声明类型变量的所有实体的公共接口。
目前实现该接口的类只有Class、Method和Constructor。意味着只有这三类元素才可以定义类型变量,即TypeVariable。
注:因为Method和Constructor有很多相似之处,所以Java定义一个抽象父类来描述他们。
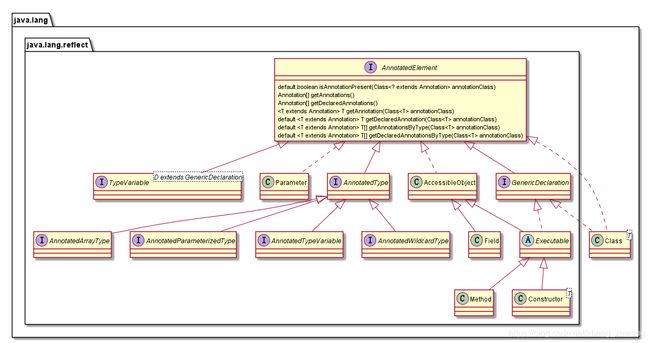
AnnotatedElement
由于源码篇幅过长,这里删除部分注解,留下主要的备注,并注明中文翻译以及简单的说明。
package java.lang.reflect;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.AnnotationFormatError;
import java.lang.annotation.Repeatable;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.function.Function;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
import sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationSupport;
import sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationType;
/**
* Represents an annotated element of the program currently running in this
* VM. This interface allows annotations to be read reflectively. All
* annotations returned by methods in this interface are immutable and
* serializable. The arrays returned by methods of this interface may be modified
* by callers without affecting the arrays returned to other callers.
*
* 表示当前在此虚拟机中运行的程序的支持带注解的元素。并且允许反射读取注释。
* 此接口中方法返回的所有注解都是不可变的和可序列化的。调用方可以修改此接口方法返回的数组,而不影响返回给其他调用方的数组。
*
* @since 1.5
* @author Josh Bloch
*/
public interface AnnotatedElement {
/**
* Returns true if an annotation for the specified type
* is present on this element, else false. This method
* is designed primarily for convenient access to marker annotations.
*
* 通俗的讲就是返回该元素是否指定类型的注解
*
* @return true if an annotation for the specified annotation
* type is present on this element, else false
* @throws NullPointerException if the given annotation class is null
* @since 1.5
*/
default boolean isAnnotationPresent(Class<? extends Annotation> annotationClass) {
return getAnnotation(annotationClass) != null;
}
/**
* Returns this element's annotation for the specified type if
* such an annotation is present, else null.
*
* 返回指定类型的注解,如果存在的话。但是它不支持@Repeatable。
* 如果不存在则查找父类,前提是当前元素是Class并且该注解是@Inherited
*
* @throws NullPointerException if the given annotation class is null
* @since 1.5
*/
<T extends Annotation> T getAnnotation(Class<T> annotationClass);
/**
* Returns annotations that are present on this element.
*
* 返回当前元素的所有注解。包括父类的注解(前提是当前元素是Class且当前元素无该注解)。
*
* @since 1.5
*/
Annotation[] getAnnotations();
/**
* Returns annotations that are associated with this element.
*
* 返回指定类型的注解。如果没有该注解,则从父类中查找。前提是当前元素是Class并且该注解是@Inherited
*
* 为什么返回值是个数组呢?是因为它支持@Repeatable。
*
* @throws NullPointerException if the given annotation class is null
* @since 1.8
*/
default <T extends Annotation> T[] getAnnotationsByType(Class<T> annotationClass) {
/*
* Definition of associated: directly or indirectly present OR
* neither directly nor indirectly present AND the element is
* a Class, the annotation type is inheritable, and the
* annotation type is associated with the superclass of the
* element.
*/
T[] result = getDeclaredAnnotationsByType(annotationClass);
if (result.length == 0 && // Neither directly nor indirectly present
this instanceof Class && // the element is a class
AnnotationType.getInstance(annotationClass).isInherited()) { // Inheritable
Class<?> superClass = ((Class<?>) this).getSuperclass();
if (superClass != null) {
// Determine if the annotation is associated with the
// superclass
result = superClass.getAnnotationsByType(annotationClass);
}
}
return result;
}
/**
* Returns this element's annotation for the specified type if
* such an annotation is directly present, else null.
*
* 同getAnnotation类似,只是不会查找父类。
*
* @throws NullPointerException if the given annotation class is null
* @since 1.8
*/
default <T extends Annotation> T getDeclaredAnnotation(Class<T> annotationClass) {
Objects.requireNonNull(annotationClass);
// Loop over all directly-present annotations looking for a matching one
for (Annotation annotation : getDeclaredAnnotations()) {
if (annotationClass.equals(annotation.annotationType())) {
// More robust to do a dynamic cast at runtime instead
// of compile-time only.
return annotationClass.cast(annotation);
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* Returns this element's annotation(s) for the specified type if
* such annotations are either directly present or
* indirectly present. This method ignores inherited
* annotations.
*
* 同getAnnotationsByType类似,只是不会查找父类。
*
* @throws NullPointerException if the given annotation class is null
* @since 1.8
*/
default <T extends Annotation> T[] getDeclaredAnnotationsByType(Class<T> annotationClass) {
Objects.requireNonNull(annotationClass);
return AnnotationSupport.
getDirectlyAndIndirectlyPresent(Arrays.stream(getDeclaredAnnotations()).
collect(Collectors.toMap(Annotation::annotationType,
Function.identity(),
((first,second) -> first),
LinkedHashMap::new)),
annotationClass);
}
/**
* Returns annotations that are directly present on this element.
* This method ignores inherited annotations.
*
* 同getAnnotations类似,只是不会查找父类的注解。
*
* @return annotations directly present on this element
* @since 1.5
*/
Annotation[] getDeclaredAnnotations();
}
AnnotatedElement表明该元素可以带有注解,并且能够被反射获取。它的主要方法有:
default boolean isAnnotationPresent(Class annotationClass):返回是否含有指定类型的注解(包括父类的)Annotation[] getAnnotations():返回当前元素所有注解(包括父类)Annotation[] getDeclaredAnnotations():返回当前元素所有注解(不包括父类)T getAnnotation(Class annotationClass) default:返回当前元素指定注解(不会查找父类),不支持@RepeatableT getDeclaredAnnotation(Class annotationClass) default:返回当前元素指定注解(如果子类不存在则查找父类),支持@RepeatableT[] getAnnotationsByType(Class annotationClass) default:返回当前元素指定注解(不会查找父类),支持@RepeatableT[] getDeclaredAnnotationsByType(Class annotationClass)
说明:
- 父类注解仅对Class元素有效。换句话说,只有Class元素能够继承父类注解,Method、Field等无法继承。继承父类注解的前提是该注解被
@Inherited注解。 - 支持
@Repeatable的含义是指定的注解类型可以是支持重复的注解,也可以是封装重复注解的注解。具体可以查看@Repeatable的用法。而不支持@Repeatable意味着参数只能是封装重复注解的注解,否则将返回null。
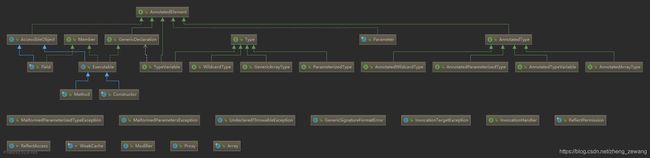
当前实现AnnotatedElement的方法结构如下:
注:Field和Executable还有一个共同实现的接口Member,但本例只讨论与AnnotatedElement有关系的结构。
AnnotatedType
前面讲到Type有四个子接口和一个实现类。因为这些type都是可以加注解的,当我们用反射去获取这些type的时候,并不会返回这些Type的注解。如果我们想要获取注解,需要调用专门的获取注解的方法。
举一个例子:
/**
* @author zhengzewang on 2019/1/7.
*
* java 1.8之前获取type和注解的方法
*/
public class AnnotatedTypeOrigin<@TypeParameterAnnotation K extends Map<String, @TypeUseAnnotation List<String>[]>>
extends @TypeUseAnnotation ArrayList<@TypeUseAnnotation String> {
public void doit(@ParameterAnnotation String str, String str2) {
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException {
Class cls = AnnotatedTypeOrigin.class;
Method method = cls.getMethod("doit", String.class, String.class);
// 1.8之前
Type[] types = method.getGenericParameterTypes();
Annotation[][] annotations = method.getParameterAnnotations();
}
}
对
TypeVariable和对父类等加注解是1.8才开始支持的功能,所以本例暂时忽略@TypeParameterAnnotation和@TypeUseAnnotation。以method为例。
从代码可以看出,(1.8之前)如果想要获取参数的类型以及注解,需要分别调用两个方法。两个方法都是有序的,且数组的长度一定等于参数的长度。如果某个参数没有注解,则对应的第二层数组的长度则为0。两个方法通过顺序保持一致来实现合作。
但这种方式始终感觉很别扭,于是java从1.8开始支持用一个方法同时获取type和annotation。以method为例:
AnnotatedType[] annotatedTypes = method.getAnnotatedParameterTypes();
先看看AnnotatedType的结构:
/**
* {@code AnnotatedType} represents the potentially annotated use of a type in
* the program currently running in this VM. The use may be of any type in the
* Java programming language, including an array type, a parameterized type, a
* type variable, or a wildcard type.
*
* @since 1.8
*/
public interface AnnotatedType extends AnnotatedElement {
/**
* Returns the underlying type that this annotated type represents.
*
* @return the type this annotated type represents
*/
public Type getType();
}
于是,对于Type和Anotation:
- Type:通过方法
getType()获取。 - Annotation:继承了
AnnotatedElement,具体见 AnnotatedElement。
到这里,又引出另外一个问题。对于参数化类型,嵌套的Type(比如ParameterizedType的getActualTypeArguments())也是可以加注解的。如果想要获取嵌套Type的注解,那就必须得获得AnnotatedType。也就是说,在1.8之前,是无法实现这个功能。当然,1.8之前,也不支持在嵌套的Type里添加注解。
想要一探究竟,就需要知道AnnotatedType的结构。
到这里,想必我们的疑惑都已经全部解开了,不需要再多做说明。(用兴趣的读者可以将前面的例子补充,通过反射获取所有的AnnotatedType)
需要注意的是,结合前面的Type总结两点:
- Type的种类应理解为五种,而不是四种。即最普通的Class(包括普通Class的数组,接口,枚举等)以及Type的四个子接口(可以理解为可嵌套Type的Type)。
- 同样,对于
AnnotatedType也是一样,也是五种。除了它的四个子接口外,还有它本身。四个子接口负责描述对应的四种Type,而AnnotatedType则负责描述最普通的Class。
通过查看源码,可以得到上诉结论的验证:
- Class类为最普通类型的实现,Type的四个子接口jdk均分别有对应的实现。
AnnotatedType的实现类均在sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotatedTypeFactory中定义。除了有其四个子接口的实现外,还有AnnotatedTypeBaseImpl直接实现AnnotatedType。
AccessibleObject&Member&Paramter
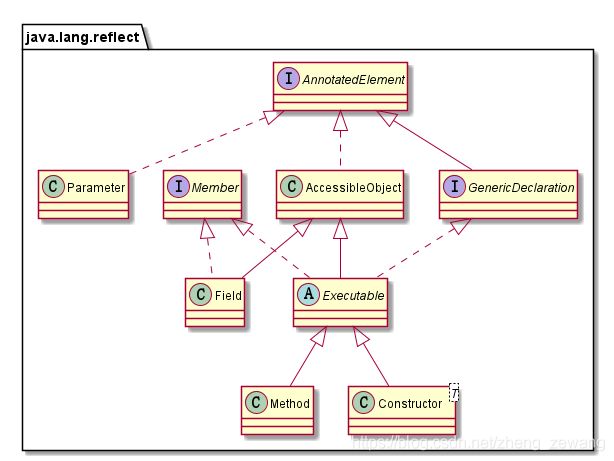
了解这部分内容之前先回顾一下 AnnotatedElement。尤其是它的结构图。
现在我们将AccessibleObject&Member&Paramter关系结构图再剥离出来:
Member&AccessibleObject
Member&AccessibleObject均是用来描述类的成员信息,包括Field、Method、Controller。但他们略有不同:
- Member:单个成员(字段或方法)或构造函数的标识信息的接口。
- AccessibleObject:主要提供了标记反射对象的能力,以在使用时抑制默认Java语言访问控制检查。
Paramter
有关方法参数的信息。
有关Class成员信息的具体实现及用法,这里不多做讲解。有兴趣可以查看我的另一篇专门讲Class的文章,本篇文章的目的仅仅是介绍reflect以及它的结构。更多的使用场景需要在实际运用多多总结。
参考文档
Java中的Type类型详解
Java源码解析之GenericDeclaration详解
thanks! 顶部 底部 **