AndroidO Treble架构下Binder对象的转换过程
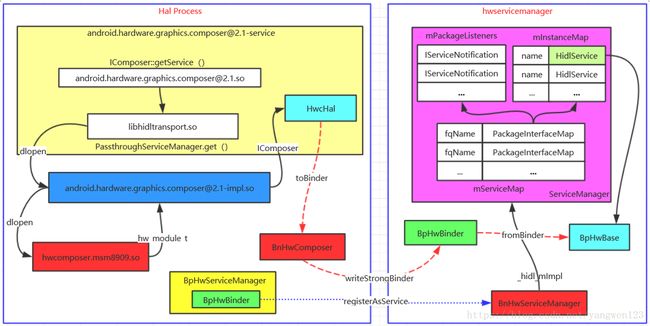
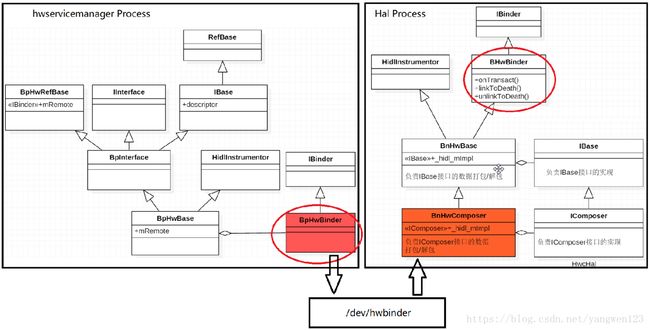
上文中详细分析了Hal的整个启动过程,这里将补充上文中没有详细分析的Binder对象转换过程,下图为hidl服务的完整注册过程:
1. HwcHal继承于IBase类,是对hw_module_t的封装,该对象位于Hal进程空间;
2. 通过hwservicemanager的binder代理将HwcHal对象注册到hwservicemanager进程空间;
3. 在IPC调用过程中,HwcHal对象的身份一直在变化,到达hwservicemanager进程后,变成BpHwBase对象,该对象封装了BpHwBinder,并保存在hwservicemanager进程中。
创建HIDL服务的本地binder对象
我们知道,binder通信可以传输的数据类型包括:
1. 普通数据类型;
2. fd句柄类型;
3. IBinder类型;
4. 经过序列化的自定义类型;
在注册HwcHal这个hidl服务对象时,由于HwcHal继承IBase类,并非binder类型,而在BpHwServiceManager::_hidl_add函数中会通过以下代码段将HwcHal这个对象发送给hwservicemanager进程,那么发送的是否是HwcHal对象本身呢?
if (service == nullptr) {
_hidl_err = _hidl_data.writeStrongBinder(nullptr);
} else {
::android::sp<::android::hardware::IBinder> _hidl_binder = ::android::hardware::toBinder<
::android::hidl::base::V1_0::IBase>(service);
if (_hidl_binder.get() != nullptr) {
_hidl_err = _hidl_data.writeStrongBinder(_hidl_binder);
} else {
_hidl_err = ::android::UNKNOWN_ERROR;
}
}::android::hardware::toBinder<::android::hidl::base::V1_0::IBase>(service)
system\libhidl\transport\include\hidl\HidlBinderSupport.h
// Construct a smallest possible binder from the given interface.
// If it is remote, then its remote() will be retrieved.
// Otherwise, the smallest possible BnChild is found where IChild is a subclass of IType
// and iface is of class IChild. BnChild will be used to wrapped the given iface.
// Return nullptr if iface is null or any failure.
template
sp toBinder(sp iface) {
IType *ifacePtr = iface.get();
if (ifacePtr == nullptr) {
return nullptr;
}
if (ifacePtr->isRemote()) {
return ::android::hardware::IInterface::asBinder(static_cast(ifacePtr));
} else {
std::string myDescriptor = details::getDescriptor(ifacePtr);
if (myDescriptor.empty()) {
// interfaceDescriptor fails
return nullptr;
}
auto func = details::gBnConstructorMap.get(myDescriptor, nullptr);
if (!func) {
return nullptr;
}
return sp(func(static_cast(ifacePtr)));
}
} 这里首先判断IComposer这个业务对象是否是BpHwComposer,如果是,那么调用asBinder来得到BpHwBinder对象。在BpHwComposer中,isRemote()默认为true,而在IComposer中,isRemote()默认为false。
struct BpHwComposer : public ::android::hardware::BpInterface, public ::android::hardware::details::HidlInstrumentor {
explicit BpHwComposer(const ::android::sp<::android::hardware::IBinder> &_hidl_impl);
typedef IComposer Pure;
virtual bool isRemote() const override { return true; } struct IComposer : public ::android::hidl::base::V1_0::IBase {
virtual bool isRemote() const override { return false; }这里注册的是HwcHal对象,他实现了IComposer接口。因此将根据接口描述符从gBnConstructorMap中找到对应的构造函数指针,然后回调构造函数:
composer\2.1\[email protected]_genc++\gen\android\hardware\graphics\composer\2.1\ComposerAll.cpp
const char* IComposer::descriptor("[email protected]::IComposer");
__attribute__((constructor))static void static_constructor() {
::android::hardware::details::gBnConstructorMap.set(IComposer::descriptor,
[](void *iIntf) -> ::android::sp<::android::hardware::IBinder> {
return new BnHwComposer(static_cast(iIntf));
});
::android::hardware::details::gBsConstructorMap.set(IComposer::descriptor,
[](void *iIntf) -> ::android::sp<::android::hidl::base::V1_0::IBase> {
return new BsComposer(static_cast(iIntf));
});
};
__attribute__((destructor))static void static_destructor() {
::android::hardware::details::gBnConstructorMap.erase(IComposer::descriptor);
::android::hardware::details::gBsConstructorMap.erase(IComposer::descriptor);
}; 这里会创建一个BnHwComposer对象,并将HwcHal保存到其变量_hidl_mImpl中:
BnHwComposer::BnHwComposer(const ::android::sp &_hidl_impl)
: ::android::hidl::base::V1_0::BnHwBase(_hidl_impl, "[email protected]", "IComposer") {
_hidl_mImpl = _hidl_impl;
auto prio = ::android::hardware::details::gServicePrioMap.get(_hidl_impl, {SCHED_NORMAL, 0});
mSchedPolicy = prio.sched_policy;
mSchedPriority = prio.prio;
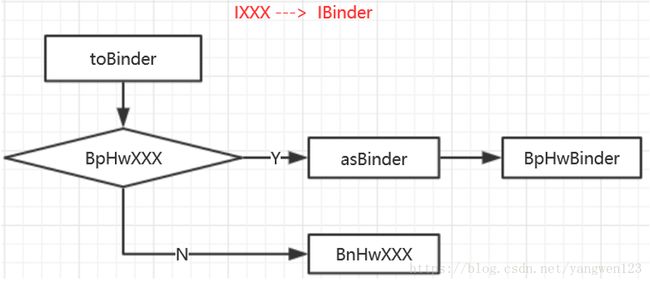
} 所以toBinder函数功能如下:
1. 如果是BpHwComposer对象,则得到BpHwComposer的成员变量BpHwBinder对象;
2. 如果是BpHwComposer对象,则创建BnHwComposer对象;
由于这里转换的是HwcHal对象,该对象实现了IComposer接口,但并不是BpHwComposer类型,因此将创建并返回一个BnHwComposer对象,接着通过_hidl_data.writeStrongBinder(_hidl_binder)将这个BnHwComposer对象传输给hwservicemanager进程,我们知道,binder驱动可以传输binder实体对象,binder驱动自动识别binder实体对象,并转化为binder代理对象,对端进程将得到binder代理对象。
system\libhwbinder\Parcel.cpp
status_t Parcel::writeStrongBinder(const sp& val)
{
return flatten_binder(ProcessState::self(), val, this);
} status_t flatten_binder(const sp& /*proc*/,
const wp& binder, Parcel* out)
{
flat_binder_object obj;
obj.flags = 0x7f | FLAT_BINDER_FLAG_ACCEPTS_FDS;
if (binder != NULL) {
sp real = binder.promote();
if (real != NULL) {
IBinder *local = real->localBinder();
if (!local) {
BpHwBinder *proxy = real->remoteBinder();
if (proxy == NULL) {
ALOGE("null proxy");
}
const int32_t handle = proxy ? proxy->handle() : 0;
obj.type = BINDER_TYPE_WEAK_HANDLE;
obj.binder = 0; /* Don't pass uninitialized stack data to a remote process */
obj.handle = handle;
obj.cookie = 0;
} else {
obj.type = BINDER_TYPE_WEAK_BINDER;
obj.binder = reinterpret_cast(binder.get_refs());
obj.cookie = reinterpret_cast(binder.unsafe_get());
}
return finish_flatten_binder(real, obj, out);
}
// XXX How to deal? In order to flatten the given binder,
// we need to probe it for information, which requires a primary
// reference... but we don't have one.
//
// The OpenBinder implementation uses a dynamic_cast<> here,
// but we can't do that with the different reference counting
// implementation we are using.
ALOGE("Unable to unflatten Binder weak reference!");
obj.type = BINDER_TYPE_BINDER;
obj.binder = 0;
obj.cookie = 0;
return finish_flatten_binder(NULL, obj, out);
} else {
obj.type = BINDER_TYPE_BINDER;
obj.binder = 0;
obj.cookie = 0;
return finish_flatten_binder(NULL, obj, out);
}
} 创建HIDL服务的binder代理对象
Hal进程将BnHwComposer对象传递给hwservicemanager后,hwservicemanager进程通过_hidl_err=_hidl_data.readNullableStrongBinder(&_hidl_service_binder);拿到client进程发送过来的BnHwComposer对象,binder实体到达目的端进程将变为binder代理对象:
system\libhwbinder\Parcel.cpp
sp Parcel::readStrongBinder() const
{
sp val;
// Note that a lot of code in Android reads binders by hand with this
// method, and that code has historically been ok with getting nullptr
// back (while ignoring error codes).
readNullableStrongBinder(&val);
return val;
} status_t Parcel::readNullableStrongBinder(sp* val) const
{
return unflatten_binder(ProcessState::self(), *this, val);
} status_t unflatten_binder(const sp& proc,
const Parcel& in, sp* out)
{
const flat_binder_object* flat = in.readObject();
if (flat) {
switch (flat->type) {
case BINDER_TYPE_BINDER:
*out = reinterpret_cast(flat->cookie);
return finish_unflatten_binder(NULL, *flat, in);
case BINDER_TYPE_HANDLE:
*out = proc->getStrongProxyForHandle(flat->handle);
return finish_unflatten_binder(
static_cast(out->get()), *flat, in);
}
}
return BAD_TYPE;
}
sp ProcessState::getStrongProxyForHandle(int32_t handle)
{
sp result;
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
handle_entry* e = lookupHandleLocked(handle);
if (e != NULL) {
// We need to create a new BpHwBinder if there isn't currently one, OR we
// are unable to acquire a weak reference on this current one. See comment
// in getWeakProxyForHandle() for more info about this.
IBinder* b = e->binder;
if (b == NULL || !e->refs->attemptIncWeak(this)) {
b = new BpHwBinder(handle);
e->binder = b;
if (b) e->refs = b->getWeakRefs();
result = b;
} else {
// This little bit of nastyness is to allow us to add a primary
// reference to the remote proxy when this team doesn't have one
// but another team is sending the handle to us.
result.force_set(b);
e->refs->decWeak(this);
}
}
return result;
} 因此hwservicemanager进程通过readStrongBinder()函数将得到BpHwBinder对象,然后通过fromBinder函数将binder代理对象转换为业务代理对象:
service = ::android::hardware::fromBinder<IBase,BpHwBase,BnHwBase>(_hidl_service_binder);
system\libhidl\transport\include\hidl\HidlBinderSupport.h
template
sp fromBinder(const sp& binderIface) {
using ::android::hidl::base::V1_0::IBase;
using ::android::hidl::base::V1_0::BnHwBase;
if (binderIface.get() == nullptr) {
return nullptr;
}
if (binderIface->localBinder() == nullptr) {
return new ProxyType(binderIface);
}
sp base = static_cast(binderIface.get())->getImpl();
if (details::canCastInterface(base.get(), IType::descriptor)) {
StubType* stub = static_cast(binderIface.get());
return stub->getImpl();
} else {
return nullptr;
}
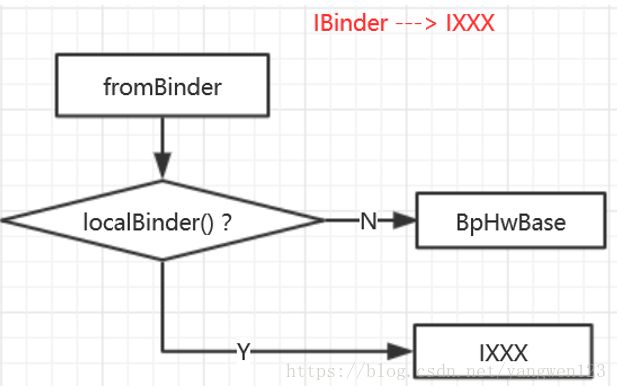
} 因此fromBinder函数功能如下:
1. 如果是binder代理,则基于binder代理创建业务代理对象;
2. 如果是binder实体,则得到业务实现类对象;
通过fromBinder函数后,这里将创建一个BpHwBase对象,并将BpHwBinder保存到其成员变量_hidl_impl中。BpHwBase::BpHwBase(const ::android::sp<::android::hardware::IBinder> &_hidl_impl)
: BpInterface(_hidl_impl),
::android::hardware::details::HidlInstrumentor("[email protected]", "IBase") {
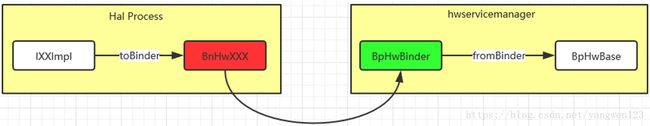
} Hal进程在向hwservicemanager进程注册IComposer接口服务时,通过服务实现类对象HwcHal经过toBinder函数将在Hal进程地址空间中创建binder实体对象BnHwComposer,然后将BnHwComposer发送给hwservicemanager进程,hwservicemanager进程将得到其binder代理对象BpHwBinder,然后经过fromBinder函数在自身进程地址空间中创建BpHwBase对象,如下图所示:
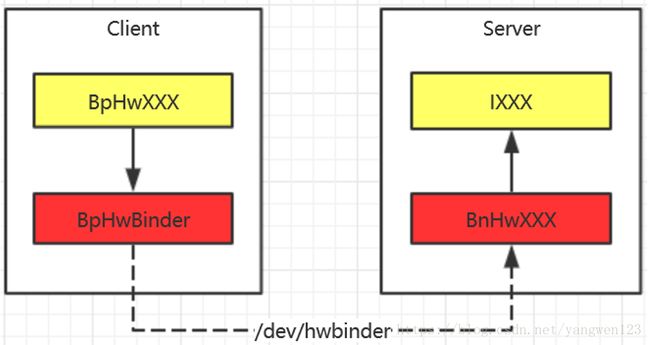
因此BnHwComposer和BpHwBinder才是真正的IBinder对象,hwservicemanager进程中的BpHwBase和Hal进程中的HwcHal就是通过BnHwComposer和BpHwBinder建立关联的,在Treble的binder架构中,无论是Client端还是Server端都是采用代理模式来实现的,这里与普通的binder通信框架有所区别,普通binder通信框架中,BpBinder和BnBinder都继承IBinder类,Client端的业务代理和Binder代理直接采用代理模式,而在Server端,业务实现在本地Binder的子类中。hwBinder下,命名有所混乱,让人很容易误以为BpHwXXX和BnHwXXX是binder通信下的代理对象和本地对象。
Treble架构下的Hal进程模型变化
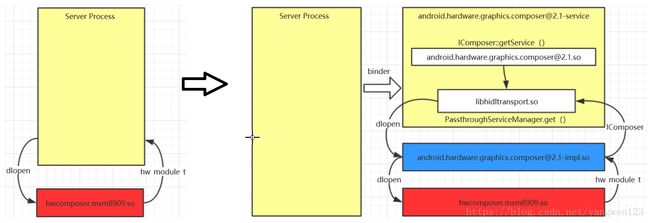
在AndroidO以前,Hal采用Legacy模式,Framework Server进程直接dlopen hal库,如下图所示:
但在AndroidO以后,所有的Hal独立运行在自己的进程空间,Framework Server进程通过binder访问Hal,为了兼容之前版本的hal实现,在hal库之上定义了一个hal实现类,用于封装hal接口,编译为[email protected],hal进程在启动时通过dlopen该so库库得到Hal接口类对象,而[email protected]中又会dlopen真正的hal实现库。
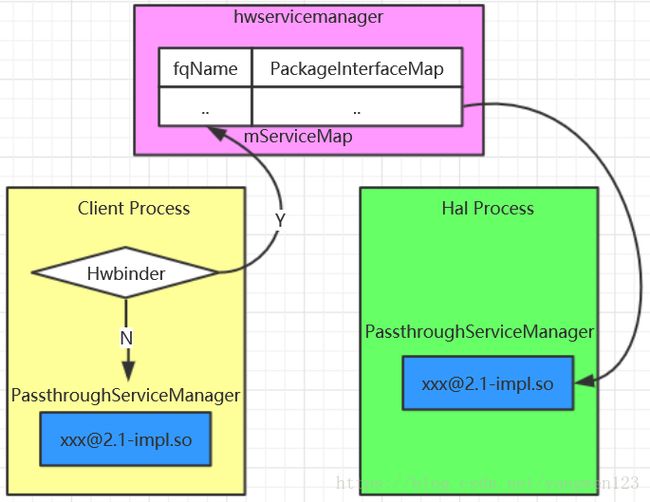
上图说明对于Hal进程来说,默认使用PassthroughServiceManager来加载[email protected]库,并得到Hidl服务接口类对象,而对于要访问Hal的Client进程,比如Framework server进程,需要根据当前访问的hidl服务的Transport类型来决定获取方式,如果当前访问的hidl服务是hwbinder,那么就从hwservicemanager中查询,如果当前方位的hidl服务是PASSTHROUGH,那么久会采用PassthroughServiceManager将[email protected]库加载到当前进程地址空间。