【Linux内核实验】观察Linux行为
1. 实验目的
学习 linux 内核、进程、存储和其他资源的一些重要特性。
通过使用/proc 文件系统接口,编写一个程序检查反映机器平衡负载、进程资源利用率方面的各种内核值
学会使用/proc文件系统这种内核状态检查机制。
2. 实验内容
编写一个默认版本的程序通过检查内核状态报告 Linux 内核行为。
程序应该在stdout上打印以下值:
1) CPU 类型和型号;
2) 所使用的 Linux 内核版本;
3) 从系统最后一次启动以来已经经历了多长时间(天,小时和分钟);
4) 总共有多少 CPU 时间执行在用户态,系统态,空闲态;
5) 配置内存数量;当前可用内存数,磁盘读写请求数;
6) 内核上下文转换数。
3. 实验基础
3.1 使用w命令查看登录用户正在使用的进程信息
w命令用于显示已经登录系统的用户的名称,以及他们正在做的事。
输出的信息包括:
w
w -h
w -u
w -s3.2 使用who命令查看(登录)用户名称及所启动的进程
who命令用于列举出当前已登录系统的用户名称。
who
users3.3 使用whoami命令查看你所使用的登录名称
whoami命令用于显示登入的用户名
whoami
id -un3.4 查看系统的信息
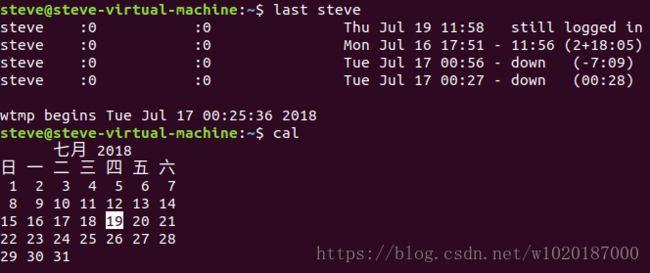
last steve
cal
find –name documentlast命令可用于显示特定用户登录系统的历史记录。
该命令的输出结果包含以下几列信息:
用户名称、tty设备号、历史登录时间日期、登出时间日期、总工作时间
3.5 /proc
cat /proc/cpuinfo //CPU的类型和型号
cat /proc/version //使用的Linux内核版本、编译器版本
cat /proc/meminfo //配置了多少内存
cat /proc/stat //有多少磁盘读写请求;从系统启动以来已经创建了多少进程 截图量过大,在此略去
注:
tty设备包括虚拟控制台,串口以及伪终端设备
idle是一个进程,其pid号为 0。其前身是系统创建的第一个进程,也是唯一一个没有通过fork()产生的进程。在smp系统中,每个处理器单元有独立的一个运行队列,而每个运行队列上又有一个idle进程,即有多少处理器单元,就有多少idle进程。系统的空闲时间,其实就是指idle进程的"运行时间"。idle进程pid==o,也就是init_task.
PID(Process Identification)指进程识别号,也就是进程标识符。操作系统里每打开一个程序都会创建一个进程ID,即PID
JCPU the CPU time used by all processes and their children on that terminal (in minutes:seconds)
PCPU the CPU time used by the currently active processes (in minutes:seconds)
4. 实验过程
编写一个默认版本的程序通过检查内核状态报告 Linux 内核行为
程序如下:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
char repTypeName[16];
char c1, c2, ch;
int interval, duration; //the gap of time and the period of time
char *lineBuf; //the buffer of line
int LB_SIZE = 255; //the maximum length
FILE *thisProcFile; //get the profile
struct timeval now;
int iteration; //record the interactive influence
lineBuf = (char *)malloc(sizeof(char) * LB_SIZE);
interval = 2; //init parameter
duration = 60;
strcpy(repTypeName,"Standard");
if(argc>1) /*the value of argc in Linux at least is 1.so make it bigger than 1,which means get over it when there is no parameter */
{
sscanf(argv[1],"%c%c",&c1,&c2);
if(c1 != '-')
{
fprintf(stderr,"usage:ksamp [-s][-l int dur]\n");
exit(1);
}
if(c2 == 's')
{
strcpy(repTypeName,"Short");
}
if(c2 == 'l')
{
strcpy(repTypeName,"Long");
interval = atoi(argv[2]);
duration = atoi(argv[3]);
}
}
//get time
gettimeofday(&now,NULL);
printf("Status report %s at %s\n", repTypeName, ctime(&(now.tv_sec)));
//correct the call of function ctime()
//get the hostname
thisProcFile = fopen("/etc/hostname","r");
memset(lineBuf, 0, LB_SIZE);
fgets(lineBuf, LB_SIZE - 1, thisProcFile);
printf("Machine host name: %s\n",lineBuf);
fclose(thisProcFile);
//get the information of version
thisProcFile = fopen("/proc/version","r");
memset(lineBuf, 0, LB_SIZE);
fgets(lineBuf, LB_SIZE - 1, thisProcFile);
printf("Machine host name: %s\n",lineBuf);
fclose(thisProcFile);
//get the information of CPU
thisProcFile = fopen("/proc/cpuinfo","r");
memset(lineBuf, 0, LB_SIZE);
fgets(lineBuf, LB_SIZE - 1, thisProcFile);
printf("The CPU: %s\n",lineBuf);
fclose(thisProcFile);
//get the current time
thisProcFile = fopen("/proc/uptime","r");
memset(lineBuf, 0, LB_SIZE);
fgets(lineBuf, LB_SIZE - 1, thisProcFile);
printf("The Runing Time: %s\n",lineBuf);
fclose(thisProcFile);
//get the information of mem
printf("The Meminfo: ");
thisProcFile = fopen("/proc/meminfo", "r");
while(!feof(thisProcFile))
{
putchar(fgetc(thisProcFile));
}
fclose(thisProcFile);
//get the current status
printf("The Meminfo: ");
thisProcFile = fopen("/proc/stat", "r");
while(!feof(thisProcFile))
{
putchar(fgetc(thisProcFile));
}
fclose(thisProcFile);
iteration = 0;
while(iteration < duration)
{
sleep(interval);
thisProcFile = fopen("/proc/loadavg" ,"r");
while(!feof(thisProcFile))
{
putchar(fgetc(thisProcFile));
}
fclose(thisProcFile);
iteration += interval;
}
return 0;
}
源代码c文件命名为test4
注:
argc是命令行总的参数个数
argv[]是argc个参数,其中第0个参数是程序的全名,以后的参数命令行后面跟的用户输入的参数,
char *argv[]是一个字符数组,其大小是int argc,主要用于命令行参数argv[],数组里每个元素代表一个参数;
fgetc是一种计算机语言中的函数。意为从文件指针stream指向的文件中读取一个字符,读取一个字节后,光标位置后移一个字节putchar函数只能用于单个字符的输出,且一次只能输出一个字符
unistd.h是unix std的意思,是POSIX标准定义的unix类系统定义符号常量的头文件,包含了许多UNIX系统服务的函数原型,例如read函数、write函数和getpid函数
time.h是c库函数,那么在具体的平台上,就就可以依靠平台而实现,所以看上去是与平台无关的,谁都可以调用,而 sys/time.h 只是在linux系统上可以调用。
5. 参考引用
https://blog.csdn.net/smallstones/article/details/42244733
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_33478897/article/details/77458775
https://blog.csdn.net/hopeneversleep/article/details/55798722
https://blog.csdn.net/mr_leehy/article/details/76419363