ubuntu下C语言打开bmp图像文件并读取数据
相关http://bbs.csdn.net/topics/60230428
http://www.cnblogs.com/lidabo/p/3701882.html
http://zhidao.baidu.com/link?url=z2RD6QN2hd0NsZ7nxFfrA0IFwYxgtKFiAgfatUa3OpJ7_TjUe_vifslk-JIQNrGe5a4I-WyQ2_-jL5WXOoPquoxuWVB9dTBr40D1-5rO_Ky
程序如下:
///
/// 程序功能:1.实现读取bmp图像2.根据图像点的坐标输出该坐标下的rgb颜色值。
/// 系统Ubuntu 15.10,编程语言C,最新整理时间 2016.8.25。
/// 该程序是在实现纯高斯的C语言版本,遇到bmp图像的读取问题而来的
///
#include
#include
#include
//自定义数据类型
typedef unsigned long DWORD;
typedef int BOOL;
typedef unsigned char BYTE;
typedef unsigned short WORD;
//位图信息头结构体定义
typedef struct tagBITMAPINFOHEADER
{
DWORD biSize;
long biWidth;
long biHeight;
WORD biPlanes;
WORD biBitCount;
DWORD biCompression;
DWORD biSizeImage;
long biXPelsPerMeter;
long biYPelsPerMeter;
DWORD biClrUsed;
DWORD biClrImportant;
} BITMAPINFOHEADER;
//读取bmp图像函数
int ReadBmp(const char* szFileName);
//给定(x,y)输出该点的rgb颜色值函数
int GetDIBColor(int X, int Y, BYTE *r, BYTE *g, BYTE *b);
//定义一个位图信息头结构体对象
BITMAPINFOHEADER bih;
BYTE *Buffer = NULL;
long LineByteWidth;
int main(void)
{
int x, y; //坐标
BYTE r, g, b;//rgb颜色值
int n;
char szfilename[255] = "input.bmp"; //输入的图像路径
if (ReadBmp(szfilename) == 0)
{
printf("failure to read file %s", szfilename);
return 1;
}
printf("Width: %ld\n", bih.biWidth);
printf("Height: %ld\n", bih.biHeight);
printf("BitCount: %d\n\n", (int)bih.biBitCount);
while(1)
{
printf("input the X:");
scanf("%d", &x);
if (x < 0)
break;
printf("input the Y:");
scanf("%d", &y);
if (GetDIBColor(x, y, &r, &g, &b) == 1)
printf("(%d, %d): r:%d, g:%d, b:%d\n", x, y, (int)r, (int)g, (int)b);
else
printf("input error.\n");
}
free(Buffer);
return 0;
}
///
/// 函数功能实现读取bmp图像
///
/// 图像文件的路径
int ReadBmp(const char* szFileName)
{
//文件状态变量
FILE *file;
//定义大小为7的数组,用于后面的存储
WORD bfh[7];
long dpixeladd;
//读取图像文件失败,返回0
if (NULL == (file = fopen(szFileName, "rb")))
{
return 0;
}
//读取成功后,输出图像路径
printf("%s\n", szFileName);
//读取7个WORD的数据到数组中
fread(&bfh, sizeof(WORD), 7, file);
//判断数组中的第一个元素是不是BM,详见说明文档
if (bfh[0] != (WORD)(((WORD)'B')|('M'<<8)))
{
fclose(file);
return 0;
}
//如果前面确定是bmp图像,则读取位图信息头数据
fread(&bih, sizeof(BITMAPINFOHEADER), 1, file);
//如果不是24位的bmp图像则退出
if (bih.biBitCount < 24)
{
fclose(file);
return 0;
}
//几个通道?一般bih.biBitCount = 24,该值为3
dpixeladd = bih.biBitCount / 8;
//一行的跨度
LineByteWidth = bih.biWidth * (dpixeladd);
//使该宽度值能被4整出
if ((LineByteWidth % 4) != 0)
LineByteWidth += 4 - (LineByteWidth % 4);
//开辟新的内存,存储颜色值
if ((Buffer = (BYTE*)malloc(sizeof(BYTE)* LineByteWidth * bih.biHeight)) != NULL)
{
fread(Buffer, LineByteWidth * bih.biHeight, 1, file);
fclose(file);
return 1;
}
//关闭文件
fclose(file);
return 0;
}
///
/// 函数功能:根据图像点的坐标输出该坐标下的rgb颜色值。
///
/// 图像中点横坐标
/// 图像中点纵坐标
/// 该坐标下点的r分量值
/// 该坐标下点的g分量值
/// 该坐标下点的b分量值
int GetDIBColor(int X, int Y, BYTE *r, BYTE *g, BYTE *b)
{
int dpixeladd;
BYTE *ptr;
//如果坐标值越界,直接返回
if (X < 0 || X >= bih.biWidth || Y < 0 || Y >= bih.biHeight)
{
return 0;
}
dpixeladd = bih.biBitCount / 8;
//(x,y)像素点的存储地址
ptr = Buffer + X * dpixeladd + (bih.biHeight - 1 - Y) * LineByteWidth;
*b = *ptr;
*g = *(ptr + 1);
*r = *(ptr + 2);
return 1;
} 程序中细节解释;
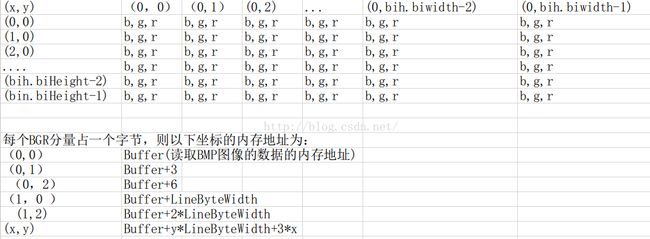
如果是自左往右,自上往下的方式则:
运行结果: