写在前面
上篇文章介绍如何将wcf项目,修改成restful风格的接口,并在上面提供了查询的功能,上篇文章中也感谢园友在评论中的提的建议,自己也思考了下,确实是那个道理。在urltemplate中,定义的url确实不规范,虽然能实现功能,但是缺少点专业性。rest风格的请求,是通过post,delete,get,put等请求方法来区别的,而不是通过在url中取不同的名字来进行区别。这里再次感谢@~Js园友提醒。
在这篇文章中将最新的代码贴出来,方便查看。
系列文章
Restful风格wcf调用 (其中代码中的uritemplate定义不规范,建议参考本文)
代码示例
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Runtime.Serialization; using System.ServiceModel; using System.ServiceModel.Web; using System.Text; using System.Web.Script.Services; namespace Wolfy.WCFRestfuleDemo { // NOTE: You can use the "Rename" command on the "Refactor" menu to change the interface name "IService1" in both code and config file together. [ServiceContract] public interface IUserService { ////// 获得所有的用户信息 /// /// json或者xml [OperationContract] [WebGet(UriTemplate = "api/users", ResponseFormat = WebMessageFormat.Xml)] List QueryList(); /// /// 根据id查询用户信息 /// /// /// [OperationContract] [WebGet(UriTemplate = "api/users/{where}", ResponseFormat = WebMessageFormat.Json)] UserInfo Query(string where); /// /// 根据编号删除用户信息 /// /// /// [OperationContract] [WebInvoke(UriTemplate = "api/users/{id}", Method = "DELETE", ResponseFormat = WebMessageFormat.Xml)] bool Delete(string id); /// /// 添加用户信息 /// /// /// [OperationContract] [WebInvoke(UriTemplate = "api/users", Method = "POST", ResponseFormat = WebMessageFormat.Xml, RequestFormat = WebMessageFormat.Json)] bool Insert(UserInfo userInfo); /// /// 更新用户信息 /// /// /// [OperationContract] [WebInvoke(UriTemplate = "api/users", Method = "PUT", ResponseFormat = WebMessageFormat.Xml, RequestFormat = WebMessageFormat.Json)] bool Update(UserInfo userInfo); } }
修改的地方:uriTemplate,以名词组成,具体的操作通过Method谓词进行区分,另外参数中UserInfo,为其WebInvoke设置RequestFormat(请求数据类型)属性,设置为json格式的数据,这样在服务端介绍到数据后,系统内部将对齐进行反序列化为具体的实体类。还有合并按照id和name查询的接口,因为原来设置的uritemplate为api/users/{id}和api/users/{name}而且请求的方法都是get方法,无法区别到底调用哪个,所以将两个方法合并为了一个方法。
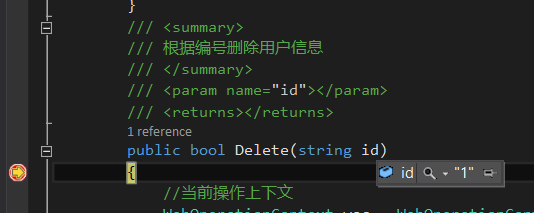
1、删除Http(delete),根据id找到用户信息,并从集合中移除。
1 ///2 /// 根据编号删除用户信息 3 /// 4 /// 5 /// 6 public bool Delete(string id) 7 { 8 //当前操作上下文 9 WebOperationContext woc = WebOperationContext.Current; 10 //状态码 11 woc.OutgoingResponse.StatusCode = System.Net.HttpStatusCode.OK; 12 try 13 { 14 if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(id)) 15 { 16 throw new ArgumentNullException("id"); 17 } 18 var users = QueryList(); 19 int iId = Convert.ToInt32(id); 20 var user = users.Where(x => x.ID == iId).FirstOrDefault(); 21 woc.OutgoingResponse.StatusCode = System.Net.HttpStatusCode.Accepted; 22 return users.Remove(user); 23 } 24 catch (Exception ex) 25 { 26 //异常 输出状态 27 woc.OutgoingResponse.StatusCode = System.Net.HttpStatusCode.ExpectationFailed; 28 woc.OutgoingResponse.StatusDescription = ex.Message; 29 return false; 30 } 31 }
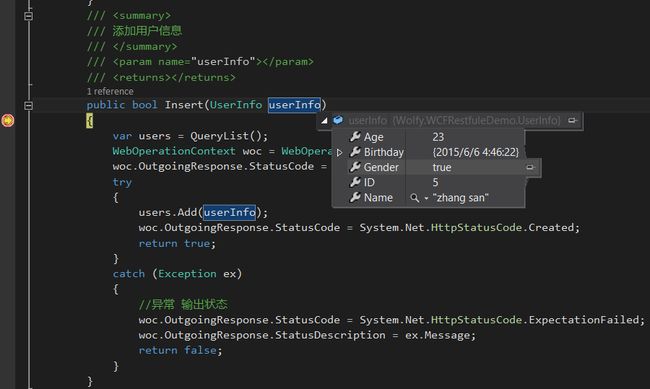
2、添加Http(post),POST里的数据格式通过RequestFormat定义为Json,WCF框架接受到Json数据的请求,会自动反序列化成UserInfo实例。
1 ///2 /// 添加用户信息 3 /// 4 /// 5 /// 6 public bool Insert(UserInfo userInfo) 7 { 8 var users = QueryList(); 9 WebOperationContext woc = WebOperationContext.Current; 10 woc.OutgoingResponse.StatusCode = System.Net.HttpStatusCode.OK; 11 try 12 { 13 users.Add(userInfo); 14 woc.OutgoingResponse.StatusCode = System.Net.HttpStatusCode.Created; 15 return true; 16 } 17 catch (Exception ex) 18 { 19 //异常 输出状态 20 woc.OutgoingResponse.StatusCode = System.Net.HttpStatusCode.ExpectationFailed; 21 woc.OutgoingResponse.StatusDescription = ex.Message; 22 return false; 23 } 24 }
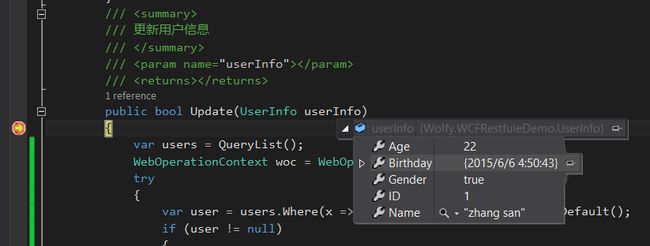
3、修改(Http/Put),根据id找到要修改的对象,对该对象重新赋值。
1 ///2 /// 更新用户信息 3 /// 4 /// 5 /// 6 public bool Update(UserInfo userInfo) 7 { 8 var users = QueryList(); 9 WebOperationContext woc = WebOperationContext.Current; 10 try 11 { 12 var user = users.Where(x => x.ID == userInfo.ID).FirstOrDefault(); 13 if (user != null) 14 { 15 user = userInfo; 16 woc.OutgoingResponse.StatusCode = System.Net.HttpStatusCode.Accepted; 17 return true; 18 } 19 else 20 { 21 woc.OutgoingResponse.StatusCode = System.Net.HttpStatusCode.NotFound; 22 return false; 23 } 24 25 } 26 catch (Exception ex) 27 { 28 //异常 输出状态 29 woc.OutgoingResponse.StatusCode = System.Net.HttpStatusCode.ExpectationFailed; 30 woc.OutgoingResponse.StatusDescription = ex.Message; 31 return false; 32 } 33 }
4、查询(http/get)
////// 获得所有的用户信息 /// /// json或者xml public List QueryList() { return new List () { new UserInfo() { ID = 1, Name = "wofly", Age = 22, Birthday = DateTime.Now, Gender = true }, new UserInfo() { ID = 2, Name = "san zhang", Age = 21, Birthday = DateTime.Now, Gender = true }, new UserInfo() { ID = 3, Name = "wukong sun", Age = 23, Birthday = DateTime.Now, Gender = false }, new UserInfo() { ID = 4, Name = "zi ma", Age = 45, Birthday = DateTime.Now, Gender = true } }; }
服务端的异常处理中通过 OutgoingResponse.StatusCode 返回不同的Code。
查询成功 —— System.Net.HttpStatusCode.OK (默认)。
创建成功 —— System.Net.HttpStatusCode.Created
更新或者删除成功 —— System.Net.HttpStatusCode.Accepted
当然,HttpStatusCode枚举不止这几个。感兴趣的可以查看这个枚举。你会发现,包揽了常见的一些状态枚举。
// Summary: // Contains the values of status codes defined for HTTP. public enum HttpStatusCode { // Summary: // Equivalent to HTTP status 100. System.Net.HttpStatusCode.Continue indicates // that the client can continue with its request. Continue = 100, // // Summary: // Equivalent to HTTP status 101. System.Net.HttpStatusCode.SwitchingProtocols // indicates that the protocol version or protocol is being changed. SwitchingProtocols = 101, // // Summary: // Equivalent to HTTP status 200. System.Net.HttpStatusCode.OK indicates that // the request succeeded and that the requested information is in the response. // This is the most common status code to receive. OK = 200, // // Summary: // Equivalent to HTTP status 201. System.Net.HttpStatusCode.Created indicates // that the request resulted in a new resource created before the response was // sent. Created = 201, // // Summary: // Equivalent to HTTP status 202. System.Net.HttpStatusCode.Accepted indicates // that the request has been accepted for further processing. Accepted = 202, // // Summary: // Equivalent to HTTP status 203. System.Net.HttpStatusCode.NonAuthoritativeInformation // indicates that the returned metainformation is from a cached copy instead // of the origin server and therefore may be incorrect. NonAuthoritativeInformation = 203, // // Summary: // Equivalent to HTTP status 204. System.Net.HttpStatusCode.NoContent indicates // that the request has been successfully processed and that the response is // intentionally blank. NoContent = 204, // // Summary: // Equivalent to HTTP status 205. System.Net.HttpStatusCode.ResetContent indicates // that the client should reset (not reload) the current resource. ResetContent = 205, // // Summary: // Equivalent to HTTP status 206. System.Net.HttpStatusCode.PartialContent indicates // that the response is a partial response as requested by a GET request that // includes a byte range. PartialContent = 206, // // Summary: // Equivalent to HTTP status 300. System.Net.HttpStatusCode.MultipleChoices // indicates that the requested information has multiple representations. The // default action is to treat this status as a redirect and follow the contents // of the Location header associated with this response. MultipleChoices = 300, // // Summary: // Equivalent to HTTP status 300. System.Net.HttpStatusCode.Ambiguous indicates // that the requested information has multiple representations. The default // action is to treat this status as a redirect and follow the contents of the // Location header associated with this response. Ambiguous = 300, // // Summary: // Equivalent to HTTP status 301. System.Net.HttpStatusCode.MovedPermanently // indicates that the requested information has been moved to the URI specified // in the Location header. The default action when this status is received is // to follow the Location header associated with the response. MovedPermanently = 301, // // Summary: // Equivalent to HTTP status 301. System.Net.HttpStatusCode.Moved indicates // that the requested information has been moved to the URI specified in the // Location header. The default action when this status is received is to follow // the Location header associated with the response. When the original request // method was POST, the redirected request will use the GET method. Moved = 301, // // Summary: // Equivalent to HTTP status 302. System.Net.HttpStatusCode.Found indicates // that the requested information is located at the URI specified in the Location // header. The default action when this status is received is to follow the // Location header associated with the response. When the original request method // was POST, the redirected request will use the GET method. Found = 302, // // Summary: // Equivalent to HTTP status 302. System.Net.HttpStatusCode.Redirect indicates // that the requested information is located at the URI specified in the Location // header. The default action when this status is received is to follow the // Location header associated with the response. When the original request method // was POST, the redirected request will use the GET method. Redirect = 302, // // Summary: // Equivalent to HTTP status 303. System.Net.HttpStatusCode.SeeOther automatically // redirects the client to the URI specified in the Location header as the result // of a POST. The request to the resource specified by the Location header will // be made with a GET. SeeOther = 303, // // Summary: // Equivalent to HTTP status 303. System.Net.HttpStatusCode.RedirectMethod automatically // redirects the client to the URI specified in the Location header as the result // of a POST. The request to the resource specified by the Location header will // be made with a GET. RedirectMethod = 303, // // Summary: // Equivalent to HTTP status 304. System.Net.HttpStatusCode.NotModified indicates // that the client's cached copy is up to date. The contents of the resource // are not transferred. NotModified = 304, // // Summary: // Equivalent to HTTP status 305. System.Net.HttpStatusCode.UseProxy indicates // that the request should use the proxy server at the URI specified in the // Location header. UseProxy = 305, // // Summary: // Equivalent to HTTP status 306. System.Net.HttpStatusCode.Unused is a proposed // extension to the HTTP/1.1 specification that is not fully specified. Unused = 306, // // Summary: // Equivalent to HTTP status 307. System.Net.HttpStatusCode.RedirectKeepVerb // indicates that the request information is located at the URI specified in // the Location header. The default action when this status is received is to // follow the Location header associated with the response. When the original // request method was POST, the redirected request will also use the POST method. RedirectKeepVerb = 307, // // Summary: // Equivalent to HTTP status 307. System.Net.HttpStatusCode.TemporaryRedirect // indicates that the request information is located at the URI specified in // the Location header. The default action when this status is received is to // follow the Location header associated with the response. When the original // request method was POST, the redirected request will also use the POST method. TemporaryRedirect = 307, // // Summary: // Equivalent to HTTP status 400. System.Net.HttpStatusCode.BadRequest indicates // that the request could not be understood by the server. System.Net.HttpStatusCode.BadRequest // is sent when no other error is applicable, or if the exact error is unknown // or does not have its own error code. BadRequest = 400, // // Summary: // Equivalent to HTTP status 401. System.Net.HttpStatusCode.Unauthorized indicates // that the requested resource requires authentication. The WWW-Authenticate // header contains the details of how to perform the authentication. Unauthorized = 401, // // Summary: // Equivalent to HTTP status 402. System.Net.HttpStatusCode.PaymentRequired // is reserved for future use. PaymentRequired = 402, // // Summary: // Equivalent to HTTP status 403. System.Net.HttpStatusCode.Forbidden indicates // that the server refuses to fulfill the request. Forbidden = 403, // // Summary: // Equivalent to HTTP status 404. System.Net.HttpStatusCode.NotFound indicates // that the requested resource does not exist on the server. NotFound = 404, // // Summary: // Equivalent to HTTP status 405. System.Net.HttpStatusCode.MethodNotAllowed // indicates that the request method (POST or GET) is not allowed on the requested // resource. MethodNotAllowed = 405, // // Summary: // Equivalent to HTTP status 406. System.Net.HttpStatusCode.NotAcceptable indicates // that the client has indicated with Accept headers that it will not accept // any of the available representations of the resource. NotAcceptable = 406, // // Summary: // Equivalent to HTTP status 407. System.Net.HttpStatusCode.ProxyAuthenticationRequired // indicates that the requested proxy requires authentication. The Proxy-authenticate // header contains the details of how to perform the authentication. ProxyAuthenticationRequired = 407, // // Summary: // Equivalent to HTTP status 408. System.Net.HttpStatusCode.RequestTimeout indicates // that the client did not send a request within the time the server was expecting // the request. RequestTimeout = 408, // // Summary: // Equivalent to HTTP status 409. System.Net.HttpStatusCode.Conflict indicates // that the request could not be carried out because of a conflict on the server. Conflict = 409, // // Summary: // Equivalent to HTTP status 410. System.Net.HttpStatusCode.Gone indicates that // the requested resource is no longer available. Gone = 410, // // Summary: // Equivalent to HTTP status 411. System.Net.HttpStatusCode.LengthRequired indicates // that the required Content-length header is missing. LengthRequired = 411, // // Summary: // Equivalent to HTTP status 412. System.Net.HttpStatusCode.PreconditionFailed // indicates that a condition set for this request failed, and the request cannot // be carried out. Conditions are set with conditional request headers like // If-Match, If-None-Match, or If-Unmodified-Since. PreconditionFailed = 412, // // Summary: // Equivalent to HTTP status 413. System.Net.HttpStatusCode.RequestEntityTooLarge // indicates that the request is too large for the server to process. RequestEntityTooLarge = 413, // // Summary: // Equivalent to HTTP status 414. System.Net.HttpStatusCode.RequestUriTooLong // indicates that the URI is too long. RequestUriTooLong = 414, // // Summary: // Equivalent to HTTP status 415. System.Net.HttpStatusCode.UnsupportedMediaType // indicates that the request is an unsupported type. UnsupportedMediaType = 415, // // Summary: // Equivalent to HTTP status 416. System.Net.HttpStatusCode.RequestedRangeNotSatisfiable // indicates that the range of data requested from the resource cannot be returned, // either because the beginning of the range is before the beginning of the // resource, or the end of the range is after the end of the resource. RequestedRangeNotSatisfiable = 416, // // Summary: // Equivalent to HTTP status 417. System.Net.HttpStatusCode.ExpectationFailed // indicates that an expectation given in an Expect header could not be met // by the server. ExpectationFailed = 417, // UpgradeRequired = 426, // // Summary: // Equivalent to HTTP status 500. System.Net.HttpStatusCode.InternalServerError // indicates that a generic error has occurred on the server. InternalServerError = 500, // // Summary: // Equivalent to HTTP status 501. System.Net.HttpStatusCode.NotImplemented indicates // that the server does not support the requested function. NotImplemented = 501, // // Summary: // Equivalent to HTTP status 502. System.Net.HttpStatusCode.BadGateway indicates // that an intermediate proxy server received a bad response from another proxy // or the origin server. BadGateway = 502, // // Summary: // Equivalent to HTTP status 503. System.Net.HttpStatusCode.ServiceUnavailable // indicates that the server is temporarily unavailable, usually due to high // load or maintenance. ServiceUnavailable = 503, // // Summary: // Equivalent to HTTP status 504. System.Net.HttpStatusCode.GatewayTimeout indicates // that an intermediate proxy server timed out while waiting for a response // from another proxy or the origin server. GatewayTimeout = 504, // // Summary: // Equivalent to HTTP status 505. System.Net.HttpStatusCode.HttpVersionNotSupported // indicates that the requested HTTP version is not supported by the server. HttpVersionNotSupported = 505, }
因为REST 是基于HTTP的, 所以对于 REST 的客户端的开发者,无法像使用传统的 WebService或者其他的WCF服务通过引用wsdl,享受“奢侈”的代码生成,而使用强类型的本地代理调用服务。开发者只能使用Http请求来进行请求,而使得客户端真正是语言无关的。
Microsoft.Http.dll 和 Microsoft.Http.Extensions.dll,它们是微软提供的REST客户端包。可以更加方便地操作 HttpRequest/Response,你可以在这里下到: http://aspnet.codeplex.com/releases/view/24644
下载:WCF REST Starter Kit Preview 2.msi
安装之后,在这里C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft WCF REST\WCF REST Starter Kit Preview 2\Assemblies(默认安装的) 你可以找到相关的程序集
代码片段
查询:HttpClient.Get方法发送get请求,返回的是HttpResponseMessage,HttpResponseMessage.Content 返回的是你在服务端设置ResponseFormat = WebMessageFormat.Xml数据,当然也可以返回json数据。
var client = new HttpClient(); var strUrl = "http://localhost:21074/userInfo/api/users"; var response = client.Get(strUrl); response.EnsureStatusIsSuccessful(); var xml = response.Content.ReadAsString(); Console.WriteLine(xml); Console.Read();
添加数据,将数据序列化成Json格式放进 HttpContent 再使用 HttpClient.Post 提交 HttpContent 数据。
HttpContent 需要指定 ContentType 是Json格式的。
var client = new HttpClient(); var strPostUrl = "http://localhost:21074/userInfo/api/users"; var postData = new { ID = 5, Name = "zhang san", Gender = true, Birthday = DateTime.Now, Age = 23 }; System.Web.Script.Serialization.JavaScriptSerializer jss = new JavaScriptSerializer(); HttpContent content = HttpContent.Create(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(jss.Serialize(postData)),"application/json"); HttpResponseMessage responseMessage = client.Post(strPostUrl, content); Console.WriteLine(responseMessage.EnsureStatusIsSuccessful().StatusCode);
客户端
![]()
更新数据:找到id为1的用户信息,并修改。
var client = new HttpClient(); var strPostUrl = "http://localhost:21074/userInfo/api/users"; var postData = new { ID = 1, Name = "zhang san", Gender = true, Birthday = DateTime.Now, Age = 22 }; System.Web.Script.Serialization.JavaScriptSerializer jss = new JavaScriptSerializer(); HttpContent content = HttpContent.Create(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(jss.Serialize(postData)), "application/json"); HttpResponseMessage responseMessage = client.Put(strPostUrl, content); Console.WriteLine(responseMessage.EnsureStatusIsSuccessful().StatusCode);
客户端
![]()
删除数据:找到id为1的,删除它
var client = new HttpClient(); var strPostUrl = "http://localhost:21074/userInfo/api/users/{0}"; HttpResponseMessage responseMessage = client.Delete(string.Format(strPostUrl,1)); Console.WriteLine(responseMessage.EnsureStatusIsSuccessful().StatusCode); Console.Read();
总结
这里将restful的增删改查操作重新修改了下,需要注意的地方是,操作的处理是以Method方法而定,而不是url,post(增加),get(查询),delete(删除),put(更改),通过上面的例子你也会发现,请求的url相同,但是不同的请求谓词(post,get,delete,put)带来的操作并不相同。另外本文也介绍了客户但HttpClient的使用。
参考文章:
http://blog.csdn.net/fangxing80/article/details/6247297