react-router 的使用
文章目录
- 单页面富应用(SPA)
- 前端路由
- url 的 hash
- html5 的 history
- react-router
- 路由的基本使用
- 常见的一些 API
- BrowserRouter或HashRouter
- Link和NavLink
- Route
- Switch
- Redirect
- 路由的嵌套
- 路由传递参数
- 动态路由
- search 传递参数
- to传入对象
- react-router-config
单页面富应用(SPA)
单页面富应用:single-page application,简称SPA;
单页面富应用是指整个Web应用有一个页面,当 url 发生改变时,并不会从服务器请求新的静态资源,而是通过JavaScript监听 url 的改变,并且根据 url 的不同去渲染新的页面(组件)
前端路由
通过监听URL的改变,并且根据 url 的不同去渲染新的页面(组件),复杂这个工作的就是前端路由。
监听 url 的改变有两种方法吗,一种是 url的 hash,另一种是 html5 的 history
url 的 hash
url 的 hash 也就锚点(#),它本质上改变的是 href 属性。另外可以通过直接赋值location.hash 来改变 href
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Documenttitle>
<style>
a {
display: inline-block;
padding: 10px 20px;
color: #000000;
text-decoration: none;
border: 1px solid #eeeeee;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<a href="#/home">homea><a href="#/about">abouta>
<div id="router-view">div>
<script>
const routerView = document.getElementById('router-view');
window.addEventListener('hashchange', () => {
switch(location.hash) {
case "#/home":
routerView.innerHTML = 'home';
break;
case "#/about":
routerView.innerHTML = 'about';
break;
default:
routerView.innerHTML = '404';
}
})
script>
body>
html5 的 history
history接口是HTML5新增的, 它有l六种模式改变URL而不刷新页面:
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Documenttitle>
<style>
a {
display: inline-block;
padding: 10px 20px;
color: #000000;
text-decoration: none;
border: 1px solid #eeeeee;
}
style>
head>
<body>
<a href="/home">homea>
<a href="/about">abouta>
<div id="router-view">div>
<script>
const routerView = document.getElementById('router-view');
const aList = document.getElementsByTagName('a');
for (let item of aList) {
item.addEventListener("click", (e) => {
e.preventDefault();
const href = item.getAttribute("href");
console.log(href);
history.pushState({}, '', href)
historyChange();
})
}
function historyChange() {
switch (location.pathname) {
case "/home":
routerView.innerHTML = 'home';
break;
case "/about":
routerView.innerHTML = 'about';
break;
default:
routerView.innerHTML = '404';
}
}
script>
body>
react-router
路由的基本使用
react-router 版本从4开始,路由不再集中在一个包进行管理
- react-router是router的核心部分代码
- react-router-dom是用于浏览器的
- react-router-native是用于原生应用的
安装 reacr-router ,安装react-router-dom会自动帮助我们安装react-router的依赖
yarn add react-router-dom
传送门
常见的一些 API
BrowserRouter或HashRouter
- Router中包含了对路径改变的监听,并且会将相应的路径传递给子组件
- BrowserRouter使用history模式
- HashRouter使用hash模式
Link和NavLink
- 通常路径的跳转是使用Link组件,最终会被渲染成a元素
- NavLink是在Link基础之上增加了一些样式属性
- to属性:Link中最重要的属性,用于设置跳转到的路径
- 另外,NavLink 还有个属性 exact,是否精确匹配,Link没有这个属性
<NavLink to="/" activeStyle={{color: "red"}}>首页NavLink>
<NavLink to="/about" activeStyle={{color: "red"}}>关于NavLink>
<NavLink exact to="/" activeClassName="link-active">首页NavLink>
<NavLink to="/about" activeClassName="link-active">关于NavLink>
Route
- Route用于路径的匹配
- path属性:用于设置匹配到的路径
- component属性:设置匹配到路径后,渲染的组件
- exact:精准匹配,只有精准匹配到完全一致的路径,才会渲染对应的组件
import React, { PureComponent } from 'react';
import { BrowserRouter, Route, Link } from 'react-router-dom';
import Home from './pages/home';
import About from './pages/about';
import Profile from './pages/profile';
export default class App extends PureComponent {
render() {
return (
<BrowserRouter>
<Link to="/">首页</Link>
<Link to="/about">关于</Link>
<Link to="/profile">我的</Link>
<Route exact path="/" component={Home} />
<Route path="/about" component={About} />
<Route path="/profile" component={Profile} />
</BrowserRouter>
)
}
}
Switch
默认情况下,react-router中只要是路径被匹配到的Route对应的组件都会被渲染,比如下面这个例子
<NavLink to="/">首页NavLink>
<NavLink to="/about">关于NavLink>
<Route exact path="/" component={Home} />
<Route path="/about" component={About} />
如果点击 首页的话,那么 下面的 两个 route 都会被匹配到,如果只想选中一个的话,那么就可以使用 Switch
<Switch>
<Route exact path="/" component={Home} />
<Route path="/about" component={About} />
Switch>
Redirect
Redirect用于路由的重定向,当这个组件出现时,就会执行跳转到对应的to路径中
路由的嵌套
import React, { Component, Fragment } from "react";
import { NavLink, Route, Switch, Redirect } from "react-router-dom";
// home
class Home extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<h2>home</h2>
</div>
)
}
}
// articles
class Story extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
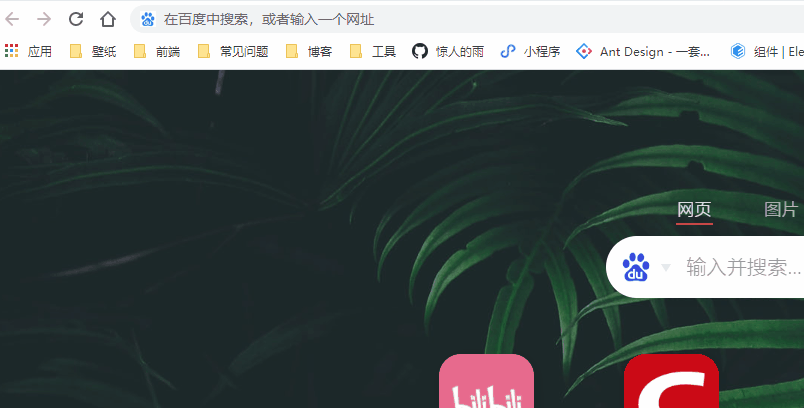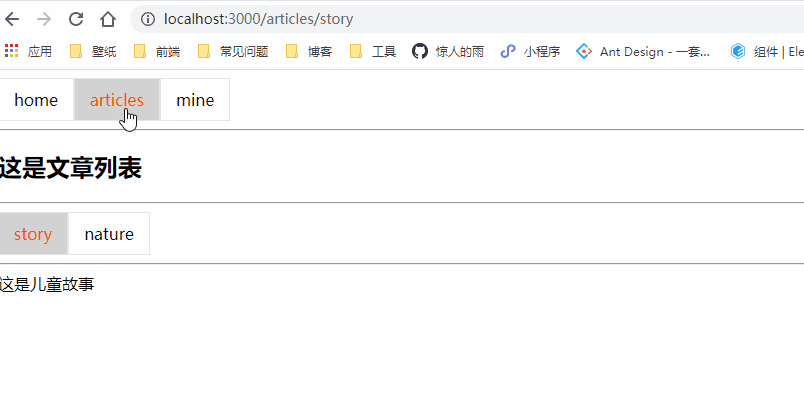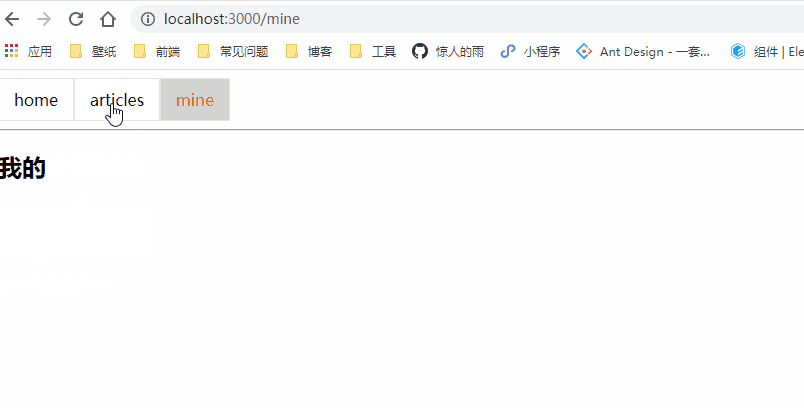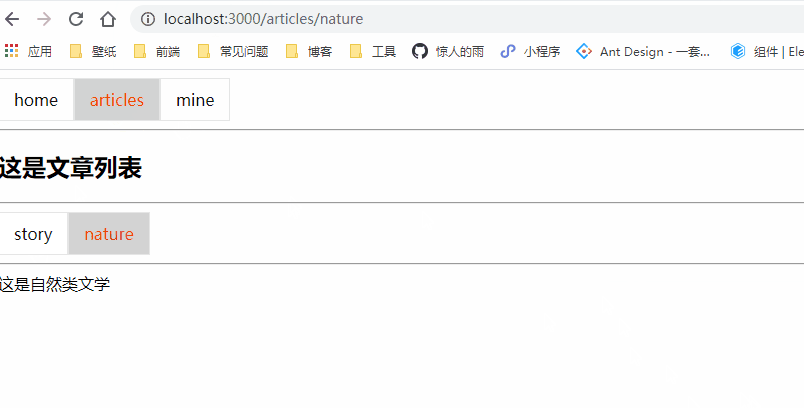
这是儿童故事
</div>
)
}
}
class Nature extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
这是自然类文学
</div>
)
}
}
class Articles extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<h2>这是文章列表</h2>
<hr/>
<NavLink to="/articles/story" activeClassName="selected">story</NavLink>
<NavLink to="/articles/nature" activeClassName="selected">nature</NavLink>
<Redirect to='/articles/story'></Redirect>
<hr />
<Switch>
<Route path="/articles/story" component={Story} exact></Route>
<Route path="/articles/nature" component={Nature}></Route>
</Switch>
</div>
)
}
}
// mine
class Mine extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<h2>我的</h2>
</div>
)
}
}
export default class componentName extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Fragment>
<NavLink to="/home" activeClassName="selected" exact>home</NavLink>
<NavLink to="/articles" activeClassName="selected">articles</NavLink>
<NavLink to="/mine" activeClassName="selected">mine</NavLink>
<Redirect to="/home"></Redirect>
<hr />
<Switch>
<Route path="/home" component={Home} exact></Route>
<Route path="/articles" component={Articles}></Route>
<Route path="/mine" component={Mine}></Route>
</Switch>
</Fragment>
);
}
}
路由传递参数
传递参数有三种方式:
- 动态路由的方式
- search传递参数
- to传入对象
动态路由
动态路由的概念指的是路由中的路径并不会固定
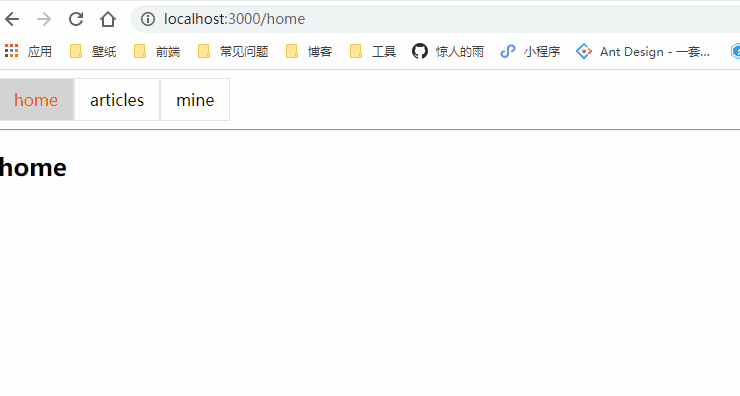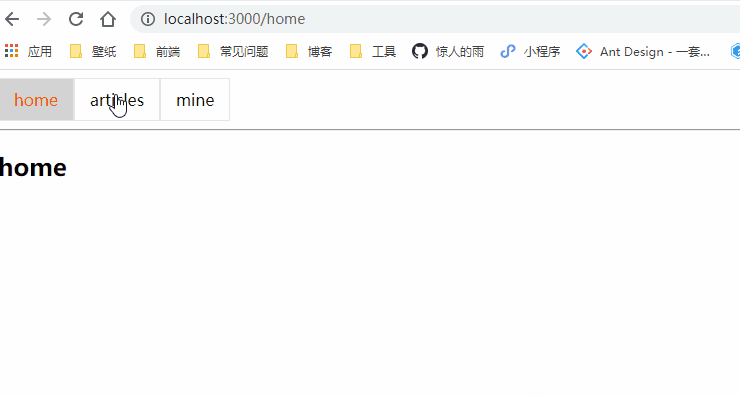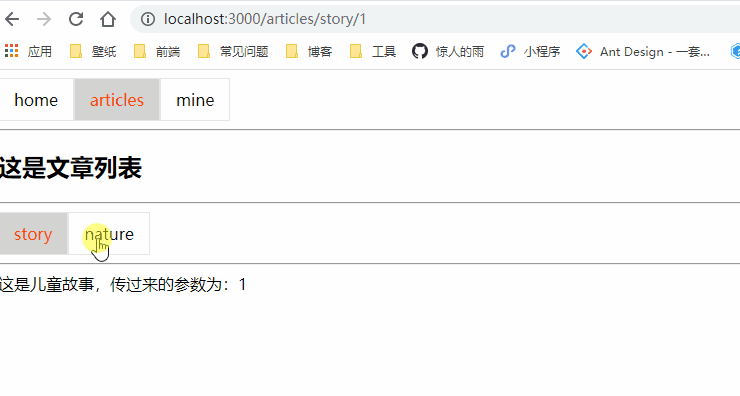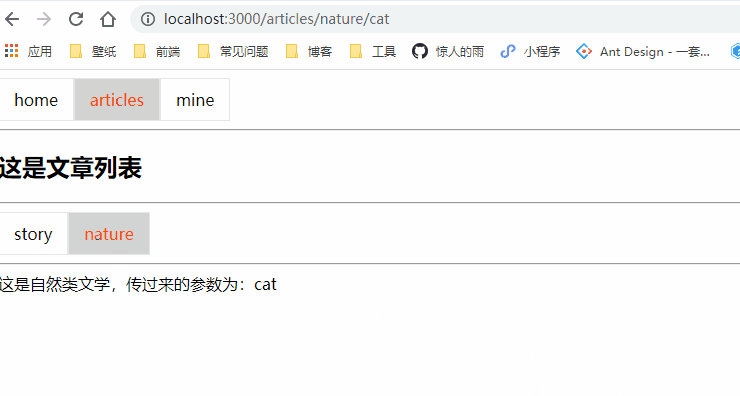
比如 /articles/story/的path对应一个组件 Story,如果我们将 path 在 Route 匹配时写成/articles/story/:id,那么/articles/story/1、/articles/story/22都可以匹配到该Route,并且进行显示
这个匹配规则,我们就称之为动态路由。
参数的获取
class Story extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
这是儿童故事,传过来的参数为:{this.props.match.params.id}
</div>
)
}
}
// 上面路由嵌套只需要修改的部分
class Story extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
这是儿童故事,传过来的参数为:{this.props.match.params.id}
</div>
)
}
}
class Nature extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
这是自然类文学,传过来的参数为:{this.props.match.params.name}
</div>
)
}
}
class Articles extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<h2>这是文章列表</h2>
<hr/>
<NavLink to="/articles/story/1" activeClassName="selected">story</NavLink>
<NavLink to="/articles/nature/cat" activeClassName="selected">nature</NavLink>
<Redirect to='/articles/story/1'></Redirect>
<hr />
<Switch>
<Route path="/articles/story/:id" component={Story} exact></Route>
<Route path="/articles/nature/:name" component={Nature}></Route>
</Switch>
</div>
)
}
}
search 传递参数
在跳转时添加一些 quert 参数即可
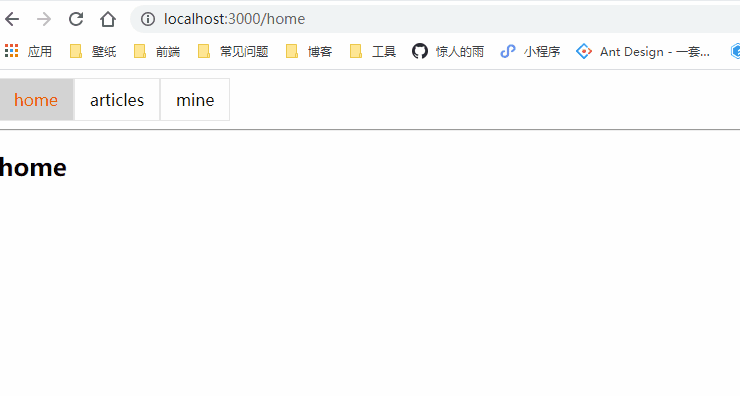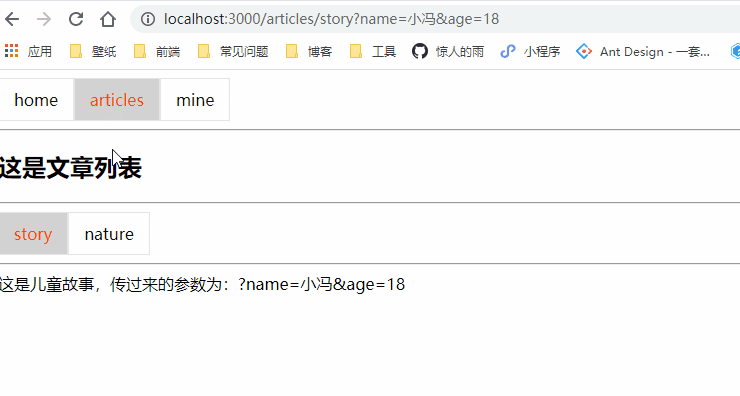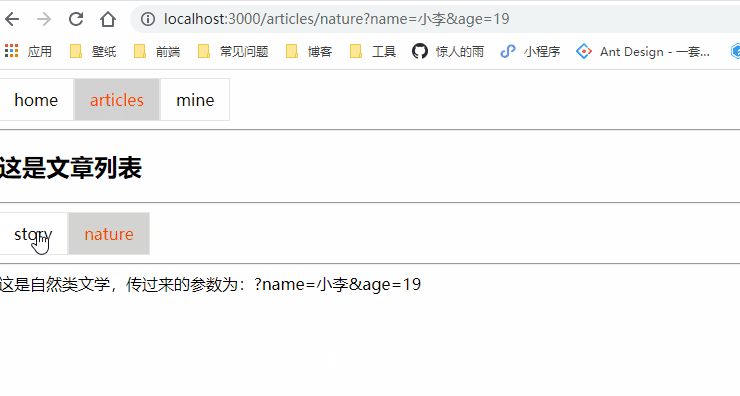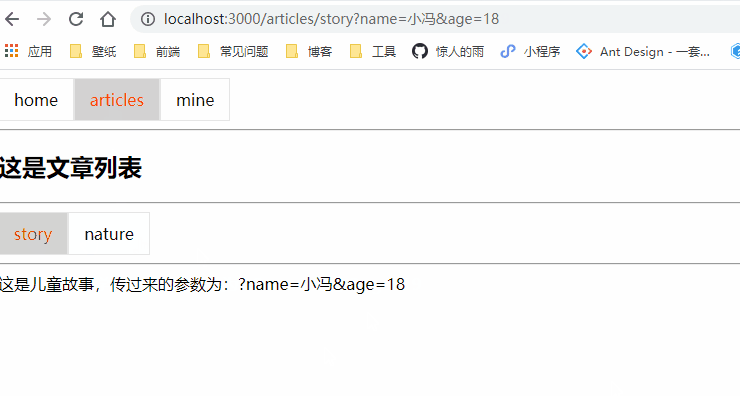
<NavLink to="/articles/story?name=小冯&age=18" activeClassName="selected">storyNavLink>
<NavLink to="/articles/nature?name=小李&age=19" activeClassName="selected">natureNavLink>
<Redirect to='/articles/story?name=小冯&age=18'>Redirect>
获取参数,获取的参数是没有经过解析的,需要自己解析
class Story extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
这是儿童故事,传过来的参数为:{this.props.location.search}
</div>
)
}
}
class Story extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
这是儿童故事,传过来的参数为:{this.props.location.search}
</div>
)
}
}
class Nature extends Component {
render() {
console.log(this.props.location.search);
return (
<div>
这是自然类文学,传过来的参数为:{this.props.location.search}
</div>
)
}
}
class Articles extends Component {
render() {
return (
<div>
<h2>这是文章列表</h2>
<hr/>
<NavLink to="/articles/story?name=小冯&age=18" activeClassName="selected">story</NavLink>
<NavLink to="/articles/nature?name=小李&age=19" activeClassName="selected">nature</NavLink>
<Redirect to='/articles/story?name=小冯&age=18'></Redirect>
<hr />
<Switch>
<Route path="/articles/story" component={Story} exact></Route>
<Route path="/articles/nature" component={Nature}></Route>
</Switch>
</div>
)
}
}
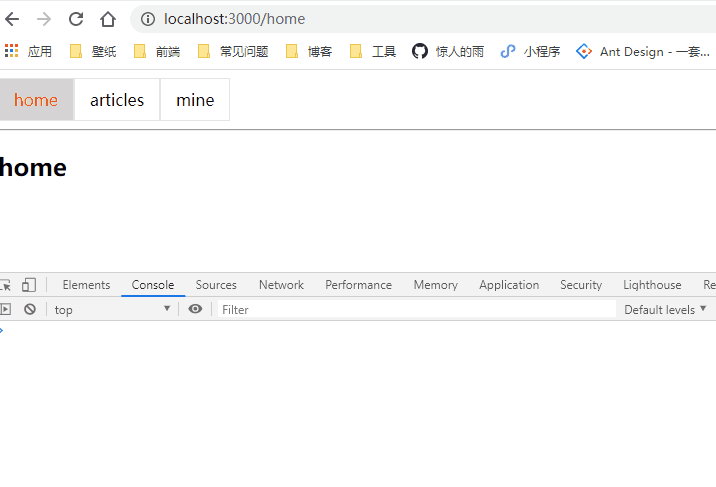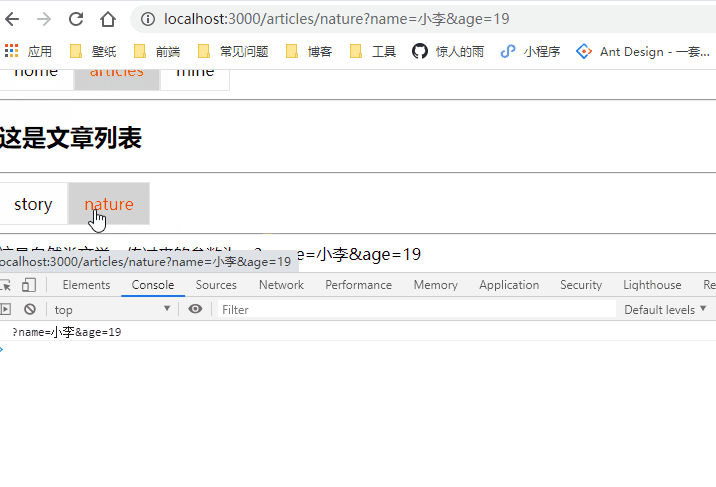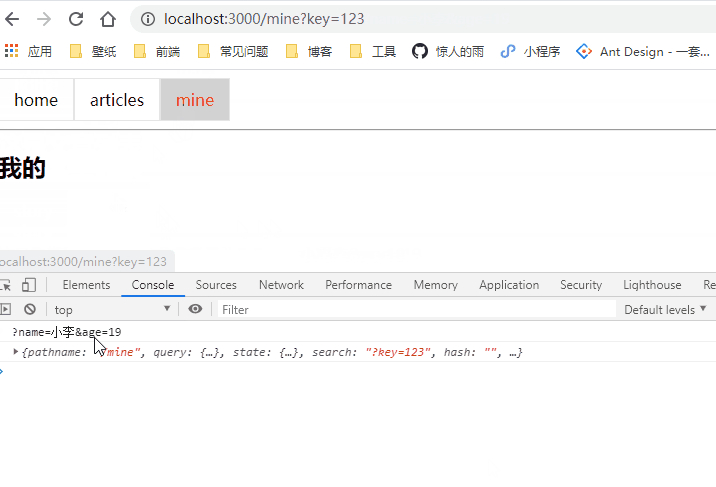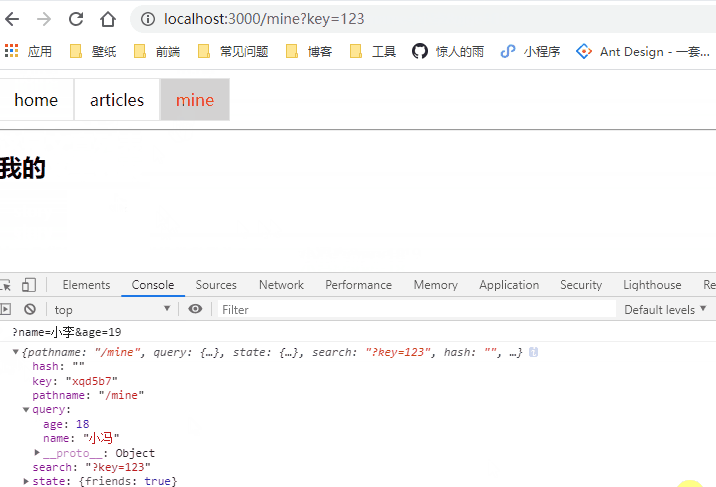
to传入对象
参数的获取:this.props.location
class Mine extends Component {
render() {
console.log(this.props.location);
return (
<div>
<h2>我的</h2>
</div>
)
}
}
// 要修改的部分
class Mine extends Component {
render() {
console.log(this.props.location);
return (
<div>
<h2>我的</h2>
</div>
)
}
}
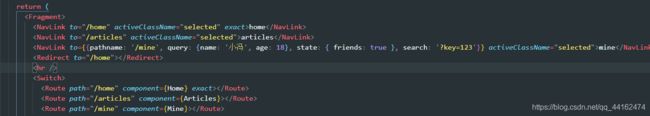
export default class componentName extends Component {
render() {
return (
<Fragment>
<NavLink to="/home" activeClassName="selected" exact>home</NavLink>
<NavLink to="/articles" activeClassName="selected">articles</NavLink>
<NavLink to={{pathname: '/mine', query: {name: '小冯', age: 18}, state: { friends: true }, search: '?key=123'}} activeClassName="selected">mine</NavLink>
<Redirect to="/home"></Redirect>
<hr />
<Switch>
<Route path="/home" component={Home} exact></Route>
<Route path="/articles" component={Articles}></Route>
<Route path="/mine" component={Mine}></Route>
</Switch>
</Fragment>
);
}
}
react-router-config
作用:类似于 vue 中路由的配置,将所有的 Route 组件 写到一个文件中
1、安装
yarn add react-router-config
2.创建 router index.js 文件
import Home from '../pages/home';
import Mine from '../pages/mine';
import Articles from '../pages/mine';
import Stroy from '../pages/mine';
import Nature from '../pages/mine';
const routes = [
{
path: '/',
component: Home
},
{
path: '/articles',
component: Article,
routes: [
{
path: '/articles/story/:id',
component: Stroy
},
{
path: '/articles/nature',
component: Nature
}
]
},
{
path: '/mine',
component: Home
}
];
module.exports = routes;
3、导入并使用 renderRoutes 函数
import { HashRouter } from 'react-router-dom';
import { renderRoutes } from "react-router-config";
import routes from './router';
class Cpn extends Comment {
render() {
return (
<HashRouter>
{renderRoutes(routes)}
</HashRouter>
)
}
}
react-router官网