MySQL(五)—— 数据高级操作
目录
新增数据
主键冲突
蠕虫复制
更新数据
删除数据
查询数据
Select选项
字段别名
数据源
子查询: 数据的来源是一条查询语句(查询语句的结果是二维表)
Where子句
Group by子句
Having子句
Order by子句
Limit子句
数据高级操作
数据操作: 增删改查
新增数据
基本语法
Insert into 表名 [(字段列表)] values (值列表);
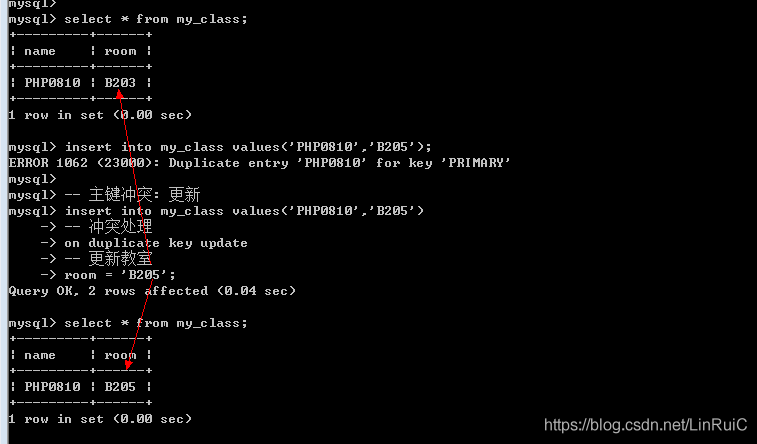
在数据插入的时候, 假设主键对应的值已经存在: 插入一定会失败!
主键冲突
当主键存在冲突的时候(Duplicate key),可以选择性的进行处理: 更新和替换
主键冲突: 更新操作
Insert into 表名[(字段列表:包含主键)] values(值列表) on duplicate key update 字段 = 新值;
-- 主键冲突: 更新
insert into my_class values('PHP0810','B205')
-- 冲突处理
on duplicate key update
-- 更新教室
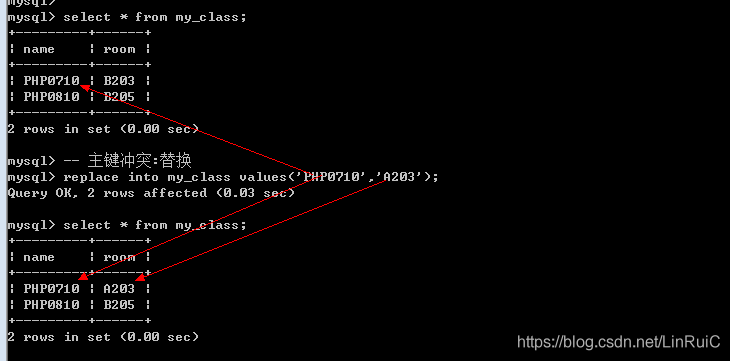
room = 'B205';主键冲突: 替换
Replace into 表名 [(字段列表:包含主键)] values(值列表);
-- 主键冲突:替换
replace into my_class values('PHP0710','A203');蠕虫复制
蠕虫复制: 从已有的数据中去获取数据,然后将数据又进行新增操作: 数据成倍的增加.
表创建高级操作: 从已有表创建新表(复制表结构)
Create table 表名 like 数据库.表名;
-- 复制创建表
create table my_copy like my_gbk;蠕虫复制: 先查出数据, 然后将查出的数据新增一遍
Insert into 表名[(字段列表)] select 字段列表/* from 数据表名;
-- 蠕虫复制
insert into my_copy select * from my_collate_bin;
-- 蠕虫复制: 先查出数据, 然后将查出的数据新增一遍
insert into my_copy select * from my_copy;
蠕虫复制的意义
- 从已有表拷贝数据到新表中
- 可以迅速的让表中的数据膨胀到一定的数量级: 测试表的压力以及效率
更新数据
基本语法
Update 表名 set 字段 = 值 [where条件];
高级新增语法
Update 表名 set 字段 = 值 [where条件] [limit 更新数量];
-- 更新部分a变成c limit:限制记录数为10
update my_copy set name = 'c' where name = 'a' limit 3;删除数据
与更新类似: 可以通过limit来限制数量
Delete from 表名 [where条件] [limit 数量];
-- 删除数据:限制记录数为10
delete from my_copy where name = 'b' limit 10;
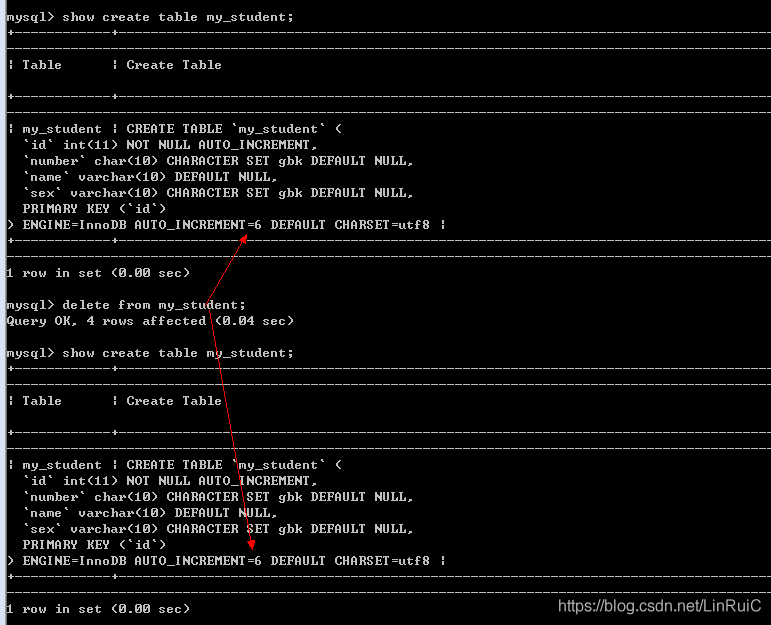
-- 删除整张表
delete from my_student;删除: 如果表中存在主键自增长,那么当删除之后, 自增长不会还原
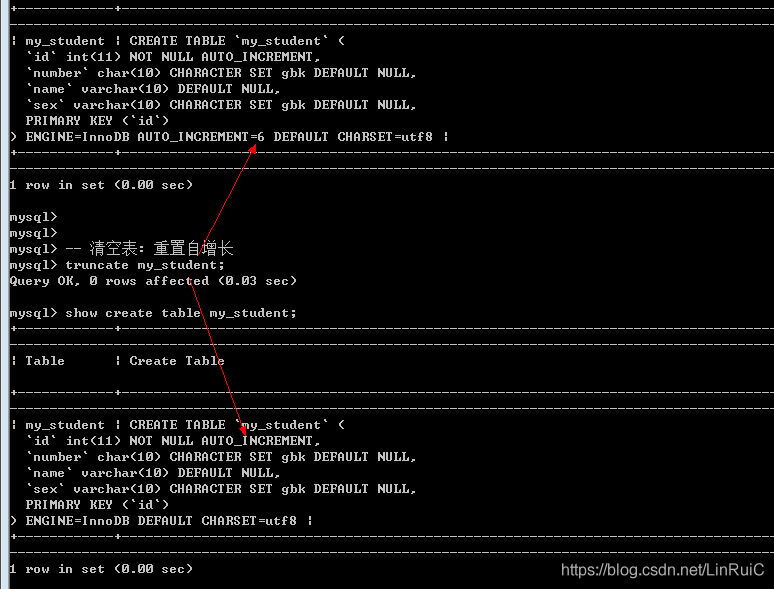
思路: 数据的删除是不会改变表结构, 只能删除表后重建表
Truncate 表名; -- 先删除改变,后新增改变
-- 清空表: 重置自增长
truncate my_student;查询数据
基本语法
Select 字段列表/* from 表名 [where条件];
完整语法
Select [select选项] 字段列表[字段别名]/* from 数据源 [where条件子句] [group by子句] [having子句] [order by子句] [limit 子句];
Select选项
Select选项: select对查出来的结果的处理方式
All: 默认的,保留所有的结果
-- select选项
select * from my_copy;
select all * from my_copy;Distinct: 去重, 查出来的结果,将重复给去除(所有字段都相同)
-- Distinct: 去重, 查出来的结果,将重复给去除(所有字段都相同)
select distinct * from my_copy;字段别名
字段别名: 当数据进行查询出来的时候, 有时候名字并一定就满足需求(多表查询的时候, 会有同名字段). 需要对字段名进行重命名: 别名
语法
字段名 [as] 别名;
-- 插入数据以供查询
insert into my_student values(null,'itcast0001','张三','男'),
(null,'itcast0002','李四','男'),
(null,'itcast0003','王五','女'),
(null,'itcast0004','赵六','男'),
(null,'itcast0005','小明','男');
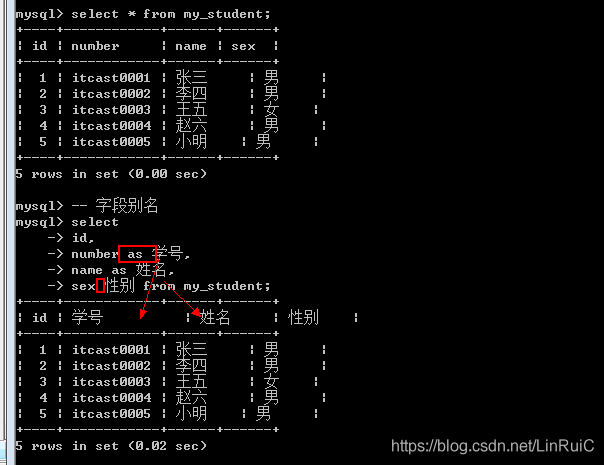
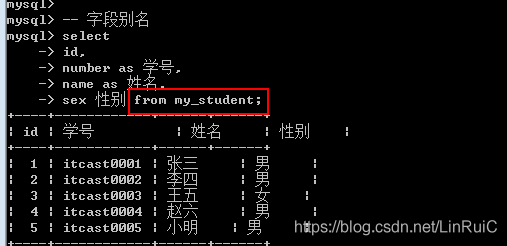
-- 字段别名
select
id,
number as 学号,
name as 姓名,
sex 性别 from my_student;数据源
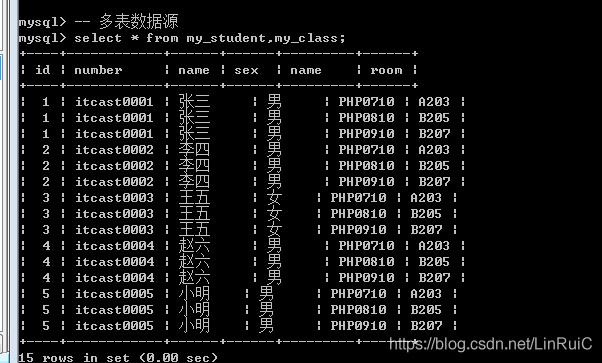
数据源: 数据的来源, 关系型数据库的来源都是数据表: 本质上只要保证数据类似二维表,最终都可以作为数据源.
数据源分为多种: 单表数据源, 多表数据源, 查询语句
单表数据源: select * from 表名;
多表数据源: select* from 表名1,表名2...;
从一张表中取出一条记录,去另外一张表中匹配所有记录,而且全部保留:(记录数和字段数),将这种结果成为: 笛卡尔积(交叉连接): 笛卡尔积没什么卵用, 所以应该尽量避免.
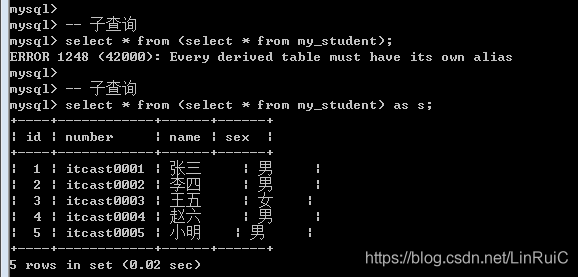
子查询: 数据的来源是一条查询语句(查询语句的结果是二维表)
Select * from (select 语句) as 表名;
-- 子查询
select * from (select * from my_student) as s;Where子句
Where子句: 用来判断数据,筛选数据.
Where子句返回结果: 0或者1, 0代表false,1代表true.
判断条件:
比较运算符: >, <, >=, <= ,!= ,<>, =, like, between and, in/not in
逻辑运算符: &&(and), ||(or), !(not)
Where原理: where是唯一一个直接从磁盘获取数据的时候就开始判断的条件: 从磁盘取出一条记录, 开始进行where判断: 判断的结果如果成立保存到内存;如果失败直接放弃.
条件查询1: 要求找出学生id为1或者3或者5的学生
-- 找学生id为1,3,5的学生
select * from my_student where id = 1 || id = 3 || id = 5; -- 逻辑判断
select * from my_student where id in(1,3,5); -- 落在集合中条件查询2: 查出区间落在180,190身高之间的学生:
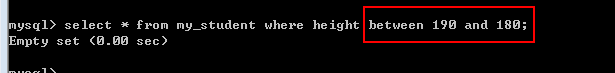
-- 找身高在180到190之间的学生
select * from my_student where height >= 180 and height <= 190;
select * from my_student where height between 180 and 190;
Between本身是闭区间; between左边的值必须小于或者等于右边的值
-- 查不到数据
select * from my_student where height between 190 and 180;
Group by子句
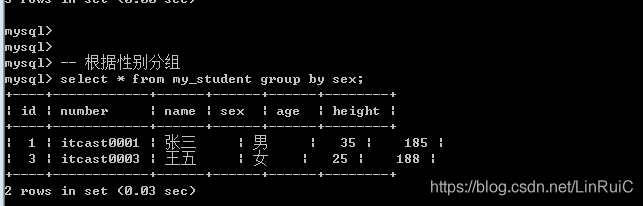
Group by:分组的意思, 根据某个字段进行分组(相同的放一组,不同的分到不同的组)
基本语法: group by 字段名;
-- 根据性别分组
select * from my_student group by sex;分组的意思: 是为了统计数据(按组统计: 按分组字段进行数据统计)
SQL提供了一系列统计函数
Count(): 统计分组后的记录数: 每一组有多少记录
Max(): 统计每组中最大的值
Min(): 统计最小值
Avg(): 统计平均值
Sum(): 统计和
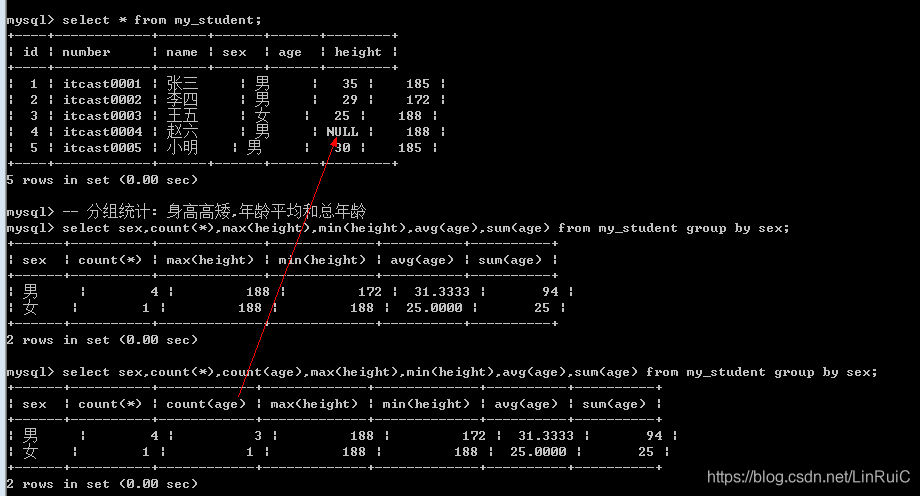
-- 分组统计: 身高高矮,年龄平均和总年龄
select sex,count(*),max(height),min(height),avg(age),sum(age) from my_student group by sex;
Count函数: 里面可以使用两种参数: *代表统计记录,字段名代表统计对应的字段(NULL不统计)
-- 分组统计: 身高高矮,年龄平均和总年龄
select sex,count(*),max(height),min(height),avg(age),sum(age) from my_student group by sex;
select sex,count(*),count(age),max(height),min(height),avg(age),sum(age) from my_student group by sex;
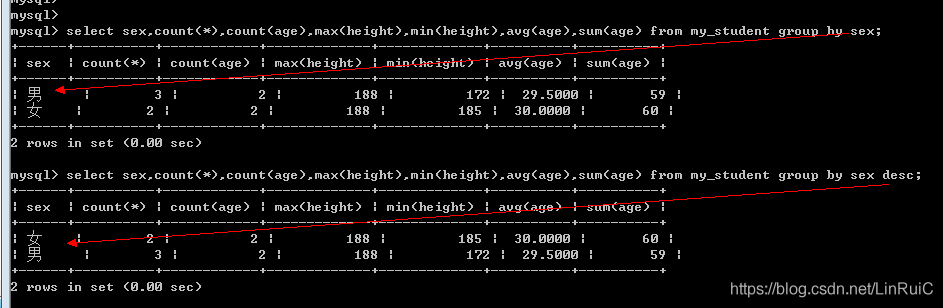
分组会自动排序: 根据分组字段:默认升序
Group by 字段 [asc|desc]; -- 对分组的结果然后合并之后的整个结果进行(升序 | 倒序)排序
select sex,count(*),count(age),max(height),min(height),avg(age),sum(age) from my_student group by sex;
select sex,count(*),count(age),max(height),min(height),avg(age),sum(age) from my_student group by sex desc;多字段分组: 先根据一个字段进行分组,然后对分组后的结果再次按照其他字段进行分组
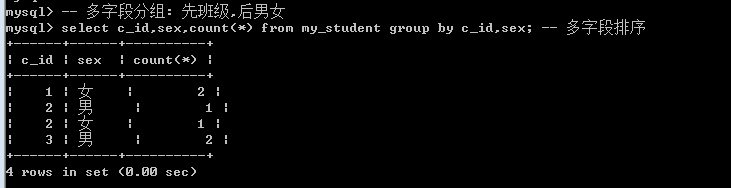
-- 多字段分组: 先班级,后男女
select c_id,sex,count(*) from my_student group by c_id,sex; -- 多字段排序
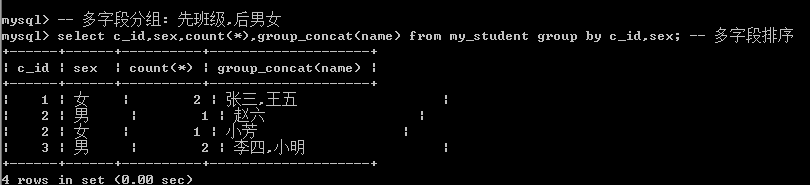
有一个函数: 可以对分组的结果中的某个字段进行字符串连接(保留该组所有的某个字段): group_concat(字段);
-- 多字段分组: 先班级,后男女
select c_id,sex,count(*),group_concat(name) from my_student group by c_id,sex; -- 多字段排序
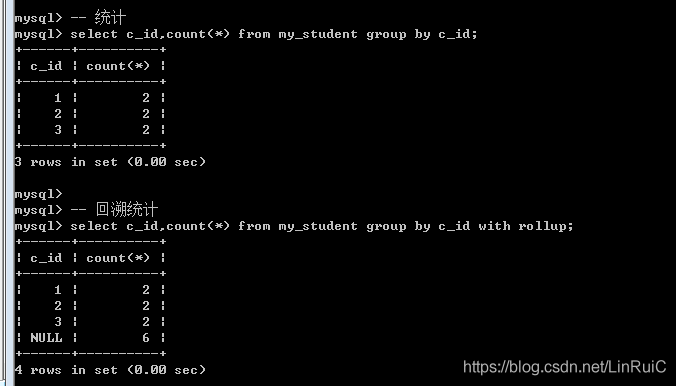
回溯统计: with rollup: 任何一个分组后都会有一个小组, 最后都需要向上级分组进行汇报统计: 根据当前分组的字段. 这就是回溯统计: 回溯统计的时候会将分组字段置空.
-- 回溯统计
select c_id,count(*) from my_student group by c_id with rollup;
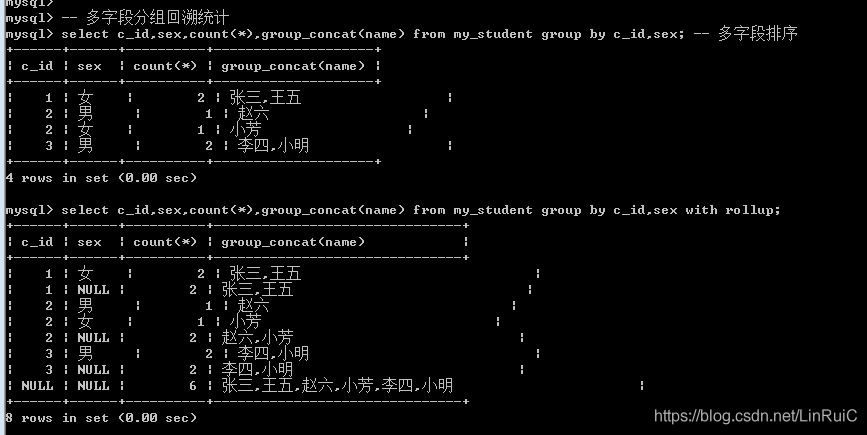
多字段回溯: 考虑第一层分组会有此回溯: 第二次分组要看第一次分组的组数, 组数是多少,回溯就是多少,然后加上第一层回溯即可.
-- 多字段分组回溯统计
select c_id,sex,count(*),group_concat(name) from my_student group by c_id,sex; -- 多字段排序
select c_id,sex,count(*),group_concat(name) from my_student group by c_id,sex with rollup;
Having子句
Having子句: 与where子句一样: 进行条件判断的.
Where是针对磁盘数据进行判断: 进入到内存之后,会进行分组操作: 分组结果就需要having来处理.
Having能做where能做的几乎所有事情, 但是where却不能做having能做的很多事情.
- 分组统计的结果或者说统计函数都只有having能够使用.
-- 求出所有班级人数大于等于2的学生人数
select c_id,count(*) from my_student group by c_id having count(*) >= 2;
-- 会报错
select c_id,count(*) from my_student where count(*) >= 2 group by c_id ;
2. Having能够使用字段别名: where不能: where是从磁盘取数据,而名字只可能是字段名: 别名是在字段进入到内存后才会产生.
-- 求出所有班级人数大于等于2的学生人数
select c_id,count(*) as total from my_student group by c_id having total >= 2;
-- 会报错
select c_id,count(*) as total from my_student where total >= 2 group by c_id ;
Order by子句
Order by: 排序, 根据某个字段进行升序或者降序排序, 依赖校对集.
使用基本语法
Order by 字段名 [asc|desc]; -- asc是升序(默认的),desc是降序
-- 排序
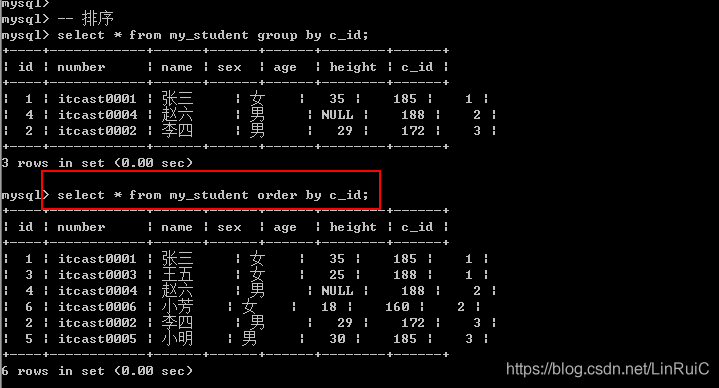
select * from my_student group by c_id;
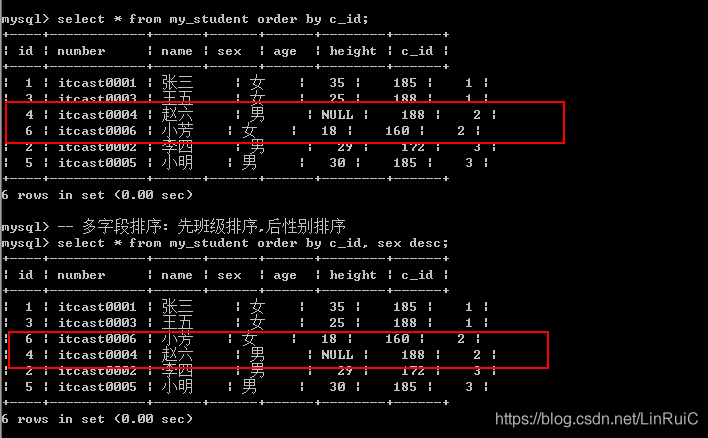
select * from my_student order by c_id;排序可以进行多字段排序: 先根据某个字段进行排序, 然后排序好的内部,再按照某个数据进行再次排序:
select * from my_student order by c_id;
-- 多字段排序: 先班级排序,后性别排序
select * from my_student order by c_id, sex desc;Limit子句
Limit子句是一种限制结果的语句: 限制数量.
Limit有两种使用方式
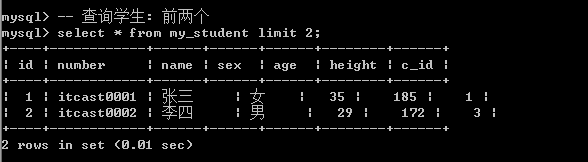
方案1: 只用来限制长度(数据量): limit 数据量;
-- 查询学生: 前两个
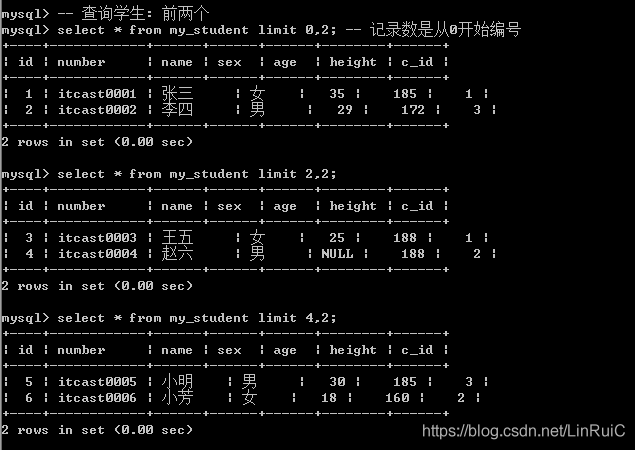
select * from my_student limit 2;方案2: 限制起始位置,限制数量: limit 起始位置,长度;
-- 查询学生: 前两个
select * from my_student limit 0,2; -- 记录数是从0开始编号
select * from my_student limit 2,2;
select * from my_student limit 4,2;Limit方案2主要用来实现数据的分页: 为用户节省时间,提交服务器的响应效率, 减少资源的浪费.
对于用户来讲: 可以点击的分页按钮: 1,2,3,4
对于服务器来讲: 根据用户选择的页码来获取不同的数据: limit offset,length;
Length: 每页显示的数据量: 基本不变
Offset: offset = (页码 - 1) * 每页显示量