Qt程序单元测试学习记录
7月比较忙,很少更新博客,上旬任务是给公司原来的程序做简单的单元测试。毕业这两年写过很多代码,从来没有注意过单元测试这东西,现在开始认真对待,开始看别人写的文章来学习。这里记录下最近学到的,以及自己给代码测试的方法(不见得是好的办法)。
GTest 使用 官方文档 https://github.com/google/googletest/blob/master/googletest/docs/primer.md
GMock 使用 官方文档 https://github.com/google/googletest/blob/master/googlemock/README.md
QtTest 使用 官方文档 https://doc.qt.io/qt-5/qttest-index.html
QSignalSpy 使用 官方文档 https://doc.qt.io/qt-5/qsignalspy.html
Qt程序单元测试学习记录
- 0. 前言
- 0.1 单元的定义
- 0.2 角色工作体系
- 0.3 测试任务
- 1. GTest/GMock 安装
- 1.1 GTest 下载安装(Linux)
- 1.2 GTest测试
- 1.3 GMock 安装(Linux)
- 2. GTest基本使用
- 2.1 GTest基本概念
- 2.2 GTest 断言
- 2.3 创建Test Suite
- 2.4 创建 Test Fixtures
- 2.5 调用GTest
- 2.6 编写main()
- 2.7 命令行输入测试
- 2.8 如何测试私有函数
- 3. GMock基本使用
- 3.1 什么是GMock
- 3.2 使用GMock
- 3.3 GMock案例
- 4. GTest/GMock测试框架不足
- 5.Qt信号槽相关功能测试 QSignalSpy
- 5.1 什么是QSignalSpy
- 初始化
- 常用函数
- 6.Qt UI相关功能测试 Qt Test
- 6.1 QtTest 介绍
- 6.2 QtTest 鼠标键盘模拟
- 键盘操作
- 鼠标操作
- 7.测试方法
- 7.1 组织产品代码和测试代码
- 7.2 测试工程中如何引入被测代码
- 7.3 解除类之间的依赖,何时mock
0. 前言
0.1 单元的定义
对于结构化的编程语言,程序单元指程序中定义的函数或子程序。单元测试是指对函数或子程序所进行的测试。
对于面向对象的编程语言,程序单元指特定的一个具体的类或相关的多个类。单元测试主要是指对类方法的测试。
0.2 角色工作体系
| 角色 | 职责 |
|---|---|
| 测试主管 | 审查单元测试过程,对测试结果进行评估。 |
| 测试工程师 | 对单元代码进行检查,设计单元测试用例,加载运行测试用例,记录和分析测试结果,填写单元测试Bug清单。 |
| 开发工程师 | 设计测试需要的驱动程序和桩模块,以及辅助测试工具的开发。 |
| 配置管理员 | 管理测试需要的资源,包括软硬件环境,版本管理和Bug管理。 |
0.3 测试任务
- 1 模块接口测试;
- 2 模块局部数据结构测试;
- 3 模块边界条件测试;
- 4 模块中所有独立执行通路测试;
- 5 模块的各条错误处理通路测试。
模块接口测试是单元测试的基础。只有在数据能正确流入、流出模块的前提下,其他测试才有意义。
1. GTest/GMock 安装
windos的我还没编过,有空补上。
1.1 GTest 下载安装(Linux)
git clone --recursive https://github.com/google/googletest.git
cd googletest/
mkdir bulid
cmake ..
cmake-gui ..
make -j4
sudo make install
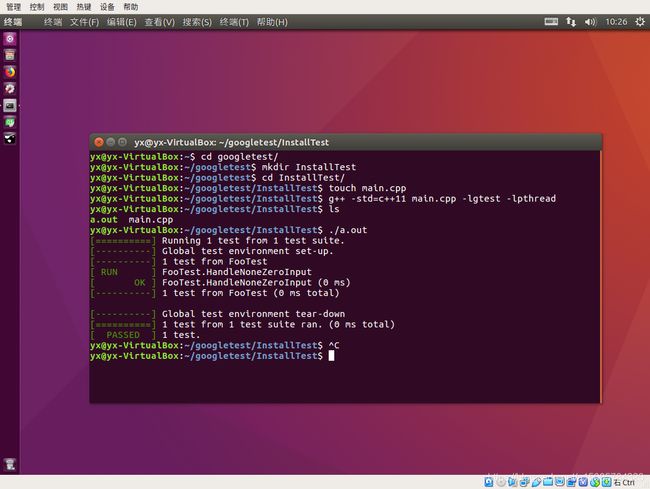
1.2 GTest测试
cd googletest/
mkdir InstallTest
cd InstallTest/
touch main.cpp
g++ -std=c++11 main.cpp -lgtest -lpthread
ls
./a.out
main.cpp 内容
#include 1.3 GMock 安装(Linux)
GMock已经集成进GTest了,编译GTest时默认就编译GMock。
2. GTest基本使用
2.1 GTest基本概念
Test Suite、Test Fixtures、Test Case
- Test Case 测试用例,验证一个函数测试是否成功。包括创建测试环境、进行测试、销毁测试环境。
- Test Suite 测试套件,一个功能可能有若干个测试用例,这些测试用例合起来叫做一个测试套件。
- Test Fixtures 测试治具,多个测试用例建测试环境和销毁测试环境相同。则建立一个测试治具,把相同配置适用于多个测试用例。
测试用例和测试名称
做UT(单元测试)时,我们把类\函数分为若干个测试用例,每个测试用例下边有若干个测试,每个测试有一个测试名称。打个比方,我有一个系统备份还原的控制类。下边有两个函数需要测试:备份和还原。我对这个类单元测试时这样命名:
- 测试用例名称 BackupManagerTest
- 测试名称1 BackupTest 备份测试(模块接口测试)
- 测试名称2 RecoveryTest 备份测试(模块接口测试)
- 测试名称3 UnZIPTest 解压压缩测试(模块局部数据结构测试)
- 测试名称4 RecoveryAlreadyBackupTest 已备份还原测试(模块中所有独立执行通路测试)
- 测试名称5 RecoveryNoBackupTest 未备份还原测试(模块的各条错误处理通路测试)
断言
对于每一个测试用例,我们需要对其行为做出断言。为真则通过测试,为假则测试失败。
2.2 GTest 断言
GTest提供了两个系列的断言宏ASSERT_ 和 EXPECT_。无论安那种断言,只要失败就意味着测试失败。
- ASSERT_ 致命断言,如果失败则跳出当前测试,进行下一个测试
- EXPECT_ 非致命断言,如果失败仅打印当前失败,接着本测试
- 关于bool值断言
| 致命断言 | 非致命断言 | 验证 |
|---|---|---|
| ASSERT_TRUE(condition); | EXPECT_TRUE(condition); | condition 是真的 |
| ASSERT_FALSE(condition); | EXPECT_FALSE(condition); | condition 是假的 |
- 关于数值型数据检查
| 致命断言 | 非致命断言 | 验证 |
|---|---|---|
| ASSERT_EQ(val1, val2); | EXPECT_EQ(val1, val2); | val1 == val2 |
| ASSERT_NE(val1, val2); | EXPECT_NE(val1, val2); | val1 != val2 |
| ASSERT_LT(val1, val2); | EXPECT_LT(val1, val2); | val1 < val2 |
| ASSERT_LE(val1, val2); | EXPECT_LE(val1, val2); | val1 <= val2 |
| ASSERT_GT(val1, val2); | EXPECT_GT(val1, val2); | val1 > val2 |
| ASSERT_GE(val1, val2); | EXPECT_GE(val1, val2); | val1 >= val2 |
- 关于字符串比较
| 致命断言 | 非致命断言 | 验证 |
|---|---|---|
| ASSERT_STREQ(str1,str2); | EXPECT_STREQ(str1,str2); | 这两个字符串具有相同的内容 |
| ASSERT_STRNE(str1,str2); | EXPECT_STRNE(str1,str2); | 两个字符串的内容不同 |
| ASSERT_STRCASEEQ(str1,str2); | EXPECT_STRCASEEQ(str1,str2); | 两个字符串的内容相同,忽略大小写 |
| ASSERT_STRCASENE(str1,str2); | EXPECT_STRCASENE(str1,str2); | 两个字符串的内容不同,忽略大小写 |
2.3 创建Test Suite
每个测试互补干扰,无法使用。
- 创建测试
使用 TEST 宏定义和命名测试功能。
TEST(TestSuiteName, TestName) {
// ... test body ...
}
int Add(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
TEST(AddTest, HandleNoneZeroInput) {
EXPECT_EQ(7, Add(4, 3));
EXPECT_EQ(18, Add(0, 18));
}
2.4 创建 Test Fixtures
对多个测试使用相同的数据配置。
- 派生自::testing::Test,生成一个 Test Fixtures。
- 构建SetUp();为每个测试准备对象。
- 编写一个析构函数或TearDown()函数以释放您在中分配的任何资源;

- 使用 TEST 宏定义和命名测试功能。
TEST_F(TestFixtureName, TestName) {
... test body ...
}
- 官方案例
让我们为名为Queue的FIFO队列类编写测试,该类具有以下接口:
template <typename E> // E is the element type.
class Queue {
public:
Queue();
void Enqueue(const E& element);
E* Dequeue(); // Returns NULL if the queue is empty.
size_t size() const;
...
};
首先,定义一个夹具类。按照约定,您应该给它命名为FooTest,其中Foo是要测试的类。
class QueueTest : public ::testing::Test {
protected:
void SetUp() override {
q1_.Enqueue(1);
q2_.Enqueue(2);
q2_.Enqueue(3);
}
// void TearDown() override {}
Queue<int> q0_;
Queue<int> q1_;
Queue<int> q2_;
};
在这种情况下,不需要TearDown(),因为除了析构函数已经完成的工作之外,我们无需在每次测试后进行清理。我们将使用TEST_F()和此固定装置编写测试。
TEST_F(QueueTest, IsEmptyInitially) {
EXPECT_EQ(q0_.size(), 0);
}
TEST_F(QueueTest, DequeueWorks) {
int* n = q0_.Dequeue();
EXPECT_EQ(n, nullptr);
n = q1_.Dequeue();
ASSERT_NE(n, nullptr);
EXPECT_EQ(*n, 1);
EXPECT_EQ(q1_.size(), 0);
delete n;
n = q2_.Dequeue();
ASSERT_NE(n, nullptr);
EXPECT_EQ(*n, 2);
EXPECT_EQ(q2_.size(), 1);
delete n;
}
2.5 调用GTest
使用宏 RUN_ALL_TESTS()
- 保存所有googletest标志的状态。
- 为第一个测试创建Fixtures对象。
- 通过对其进行初始化Fixtures::SetUp()。
- 在Fixtures对象上运行测试。
- 通过清理Fixtures::TearDown()。
- 删除Fixtures。
- 恢复所有googletest标志的状态。
- 对下一个测试重复上述步骤,直到所有测试都已运行。
注:TEST()自动向TEST_F()隐式注册其测试。
直接看图吧,对于Test Fixtures里每个测试,
先SetUp、运行测试、清理TearDown。

class BackupManagerTest: public ::testing::Test {
public:
BackupManagerTest() {}
public:
virtual void SetUp();
virtual void TearDown();
protected:
};
void BackupManagerTest::SetUp() {
cout << "Begin SetUp ---- ";
cout << " ----End SetUp" << endl;
}
void BackupManagerTest::TearDown() {
cout << "Begin TearDown ---- ";
cout << " ----End TearDown" << endl;
}
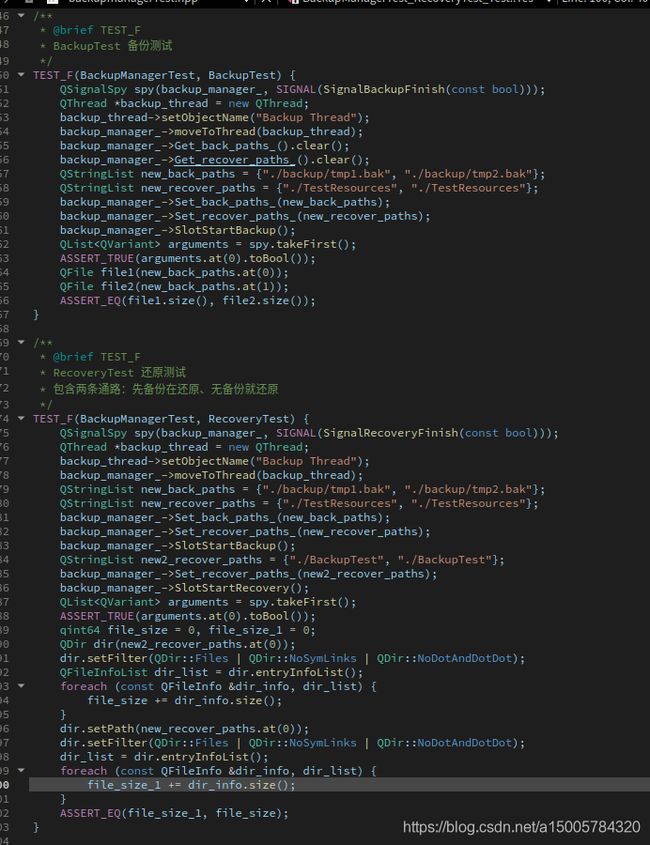
/**
* @brief TEST_F
* BackupTest 备份测试
*/
TEST_F(BackupManagerTest, BackupTest) {
cout << "Begin BackupTest ---- ";
cout << " ----End BackupTest" << endl;
}
/**
* @brief TEST_F
* RecoveryTest 还原测试
* 包含两条通路:先备份在还原、无备份就还原
*/
TEST_F(BackupManagerTest, RecoveryTest) {
cout << "Begin RecoveryTest ---- ";
cout << " ----End RecoveryTest" << endl;
}
2.6 编写main()
#include 2.7 命令行输入测试
#ifndef COMMANDLINEMANAGERTEST_HPP
#define COMMANDLINEMANAGERTEST_HPP
#include void CommandLineManager::Initial(const QApplication &app) {
QCommandLineParser parser;
parser.addHelpOption();
parser.addVersionOption();
parser.setSingleDashWordOptionMode(QCommandLineParser::ParseAsLongOptions);
QCommandLineOption debug_option(
"debug", "Open debug mode");
QCommandLineOption test_option(
"test", "Open test dialog");
QCommandLineOption zh_option(
"zh", "Chinese language");
QCommandLineOption en_option(
"en", "English language");
QCommandLineOption phatom_option(
"phatom", "Phatom Test");
parser.addOption(debug_option);
parser.addOption(test_option);
parser.addOption(zh_option);
parser.addOption(en_option);
parser.addOption(phatom_option);
parser.process(app);
if (parser.isSet(debug_option)) {
GlobalVar::cmd_option_.debug_mode = true;
}
if (parser.isSet(test_option)) {
GlobalVar::cmd_option_.test_mode = true;
}
if (parser.isSet(zh_option)) {
GlobalVar::cmd_option_.zh_ts = true;
}
if (parser.isSet(en_option)) {
GlobalVar::cmd_option_.zh_ts = false;
}
if (parser.isSet(phatom_option)) {
GlobalVar::cmd_option_.phatom_mode = true;
}
}
2.8 如何测试私有函数
也许不是最优雅的办法,单绝对够最简单高效。直接用友元来实现私有函数的测试。对应在GTest里就是FRIEND_TEST宏。
#include
3. GMock基本使用
关于什么时候写GMock我放在第七节说个人看法。使用GMock来打桩,如果一开始在程序设计时候没有添加,后边补将会是一个很大的工作量。需要把所有调用都加一个纯虚函数接口。
3.1 什么是GMock
gMock是一个用于创建模拟类并使用它们的库。
3.2 使用GMock
- Turtle:接口类
class Turtle {
...
virtual ~Turtle() {};
virtual void PenUp() = 0;
virtual void PenDown() = 0;
virtual void Forward(int distance) = 0;
virtual void Turn(int degrees) = 0;
virtual void GoTo(int x, int y) = 0;
virtual int GetX() const = 0;
virtual int GetY() const = 0;
};
- MockTurtle:mock类
class MockTurtle : public Turtle {
public:
...
MOCK_METHOD(void, PenUp, (), (override));
MOCK_METHOD(void, PenDown, (), (override));
MOCK_METHOD(void, Forward, (int distance), (override));
MOCK_METHOD(void, Turn, (int degrees), (override));
MOCK_METHOD(void, GoTo, (int x, int y), (override));
MOCK_METHOD(int, GetX, (), (const, override));
MOCK_METHOD(int, GetY, (), (const, override));
};
- 使用它
MockTurtle turtle;
EXPECT_CALL(turtle, PenDown())
.Times(AtLeast(1));
3.3 GMock案例
#ifndef USERDAO_H
#define USERDAO_H
#include #ifndef MOCKUSEDSESSIONDAO
#define MOCKUSEDSESSIONDAO
#include "dao/userdao.h"
#include MockUserDao *mock_dao = new MockUserDao;
EXPECT_CALL(*mock_dao,
SelectUserList(_)).WillRepeatedly(DoAll(
SetArgReferee<0>(QList<UserInfo>({user_list})), Return(1)));
qDebug() << mock_dao->SelectUserList(user_list);
4. GTest/GMock测试框架不足
一般情况下GTest就够了,为什么要了解Qt Test
Qt Test优点:
- 用于对 (Qt)UI 组件进行单元测试的唯一框架,如果要模拟测试**(Qt)UI**,必须使用 Qt Test。
- QSignalSpy:验证发射的信号(仅对Qt有用),可以与其他测试框架一起很好的使用
- 集成在Qt内部,无需第三方库
Qt Test缺点:
- 中文资料较少,官方文档介绍仅仅是基本使用,跟实际情况相差很多。使用Qt Test测试软件少,很难借鉴。
- 默认不支持 Test Fixtures (测试治具),必须自己手动创建
- QCOMPARE无法比较不同类型的值。
- 对Mock 支持很差
- 没有测试断言的测试
- 测试结构很奇怪
- Vs里比较麻烦
也许不是最好的办法,但很多人方法和建议是使用GTest模板,配合QSignalSpy和 (Qt)UI模拟 来做测试。
可以看看
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/1524390/what-unit-testing-framework-should-i-use-for-qt
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/4879628/comparing-qtest-with-other-frameworks
5.Qt信号槽相关功能测试 QSignalSpy
5.1 什么是QSignalSpy
QSignalSpy可以连接到任何对象的任何信号并记录其发射。 QSignalSpy本身是QVariant列表的列表。信号的每次发射都将在列表后面添加一个项目,其中包含信号的参数。
初始化
QSignalSpy spy(myPushButton, &QPushButton::clicked);
QSignalSpy spy(myPushButton, SIGNAL(clicked(bool)));
常用函数
| 函数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| QByteArray QSignalSpy::signal() const | 返回当前监听类型 |
| bool QSignalSpy::wait(int timeout = 5000) | 启动事件循环,直到接收到给定信号为止。超时返回false |
| bool QSignalSpy::isValid() const | 收到有效信号返回真 |
比如:
/**
* @brief TEST_F
* DataBackupTest 备份数据测试
*/
TEST_F(ManageViewTest, DataBackupTest) {
m_widget_->show();
m_widget_->backup_manager_->Set_back_paths_({"./"});
QSignalSpy spy(m_widget_, SIGNAL(SignalStartBackup()));
ASSERT_EQ(0, spy.count());
QTimer::singleShot(100, m_widget_, [ = ] {
m_widget_->yes_button->click();
});
QTest::mouseClick(m_widget_->ui->backup_button, Qt::LeftButton);
ASSERT_EQ(1, spy.count());
}
QSignalSpy spy(myCustomObject, SIGNAL(mySignal(int,QString,double)));
myCustomObject->doSomething(); // trigger emission of the signal
QList<QVariant> arguments = spy.takeFirst();
QVERIFY(arguments.at(0).type() == QVariant::Int);
QVERIFY(arguments.at(1).type() == QVariant::String);
QVERIFY(arguments.at(2).type() == QVariant::double);
6.Qt UI相关功能测试 Qt Test
6.1 QtTest 介绍
QtTest类似GtTest,提供了一系列接口和宏用来做单元/集成测试。提供了几个初始化和析构函数,也有提供了自己的全局测试参数、各种断言以及跟cmaketest (CTest)对接的很多宏。
![]()
不过不用研究那么多测试框架,大家都大同小异。无非就是利用友元的特性创建测试函数。c++的测试框架GTest算是比较完善和资料很多的,QtTest虽然也不错但中文资料很少,官网说明也仅仅是使用介绍和基本例子。去github上下载小型开源软件的代码基本都是使用GTest,参考和借鉴别人思路更方便。
当然,QtTest还是要了解的。界面相关测试肯定要模拟鼠标键盘,QtTest就提供了一系列模拟接口方便做界面测试。CTest和QtTest一起用,无疑大大提升开发效率。
6.2 QtTest 鼠标键盘模拟
QtTest模拟键盘鼠标基本思路是:
- 确认需要模拟的Widget(比如按钮、输入栏)
- 确认位置(鼠标),默认情况在输入Widget的中间
- 确认键盘修饰(alt、shift等),默认无
- 确认模拟操作(移动、按下、松开、点击、双击、连续多次点击)
- 确认每次操作等待时间,默认0
- 使用 QTest命名空间下的鼠标键盘模拟操作
键盘操作
| 函数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| QTest::keyPress | 按下按键 |
| QTest::keyRelease | 释放按键 |
| QTest::keyClick | 点击键盘(按下并释放)。 |
| QTest::keyClicks | 连续点击键盘(按下并释放多次)。 |
| QTest::keySequence | 连续输入,相当于keyClicks。 |
| QTest::Shortcut | 快捷键(如果快捷键一个按键,就相当于keyClick。快捷键是组合键就相当于keyClicks)。 |
鼠标操作
| 函数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| QTest::MousePress | 按下鼠标按钮。 |
| QTest::MouseRelease | 释放鼠标按钮。 |
| QTest::MouseClick | 单击鼠标按钮(按下并释放)。 |
| QTest::MouseDClick | 双击鼠标按钮(按下并释放两次)。 |
| QTest::MouseMove | 移动鼠标。 |
比如:
/**
* @brief TEST_F
* 增加用户测试
* 可以增加用户
* 两次密码错误
* 两次密码正确
*/
TEST_F(UserEditViewTest, AddUserTest) {
QString use_name = "add";
QSignalSpy spy(m_widget_, SIGNAL(SignalEditUserInfo(
const QString, const QString,
const EditType)));
m_widget_->show();
m_widget_->SetDialog(UserEditView::ADD, use_name);
ASSERT_EQ("", m_widget_->ui->username_edit->text());
// username_edit 可以输入
QTest::keyPress(m_widget_->ui->username_edit, Qt::Key_A);
QTest::keyPress(m_widget_->ui->username_edit, Qt::Key_D);
QTest::keyPress(m_widget_->ui->username_edit, Qt::Key_D);
ASSERT_EQ(use_name, m_widget_->ui->username_edit->text());
// 输入错误密码
QTest::keyPress(m_widget_->ui->password_edit_1, Qt::Key_1);
QTest::keyPress(m_widget_->ui->password_edit_2, Qt::Key_2);
QTest::mouseClick(m_widget_->ui->confirm_button, Qt::LeftButton);
ASSERT_EQ(0, spy.count());
// 输入正确密码
QTest::keyPress(m_widget_->ui->password_edit_2, Qt::Key_Backspace);
QTest::keyPress(m_widget_->ui->password_edit_2, Qt::Key_1);
QTest::mouseClick(m_widget_->ui->confirm_button, Qt::LeftButton);
ASSERT_EQ(1, spy.count());
QList<QVariant> arguments = spy.takeFirst();
ASSERT_EQ(arguments.at(0).toString(), use_name);
ASSERT_EQ(arguments.at(1).toString(), "1");
ASSERT_EQ(arguments.at(2).value<UserEditView::EditType>(), 1);
}
- 使用 QTestEventList封装一系列鼠标键盘操作
这个方法跟直接使用QTest命名空间下的鼠标键盘模拟操作区别就是可以把一系列模拟操作融合成一个操作合集,这个合集可以保存成数据,也可以在多个不同的widget操作。
可以理解成填充QTest命名空间下的鼠标键盘模拟操作。AddXXX用来填充操作、addDelay用来填充延时、simulate用来执行模拟。
比如:
/**
* @brief TEST_F
* MouseClick 鼠标点击验证
*/
TEST_F(FoldControlViewTest, MouseClick) {
m_widget_->show();
QSignalSpy spy(m_widget_, SIGNAL(SignalsHiddenButtonClicked()));
QTestEventList events;
events.addMouseClick(Qt::LeftButton);
events.addDelay(200);
events.simulate(m_widget_->ui->pushButton);
events.simulate(m_widget_->ui->pushButton);
events.simulate(m_widget_->ui->pushButton);
ASSERT_EQ(spy.count(), 3);
}
7.测试方法
7.1 组织产品代码和测试代码
我在github上拉一些完整的带测试工程的软件代码。
- 软件比较大的话,一般在根目录会有一个文件夹放测试数据,单元/集成测试代码在源码下对应文件夹下本别有该文件夹内文件测试工程测试工程。
└── usr
├── 源码
│ │ └── 模块/功能/分类 A
│ │ │ │ └── A 相关源码
│ │ │ │ │ │ └── A 测试代码
│ │ └── 模块/功能/分类 B
│ │ │ │ └── B 相关源码
│ │ │ │ │ │ └── B 测试代码
│ │ └── 模块/功能/分类 C
│ │ │ │ └── C 相关源码
│ │ │ │ │ │ └── C 测试代码
├── 测试数据
│ │ │ │ └── ABC 测试数据
│ │ │ │ └── ABC 测试通用框架
- 小型软件则是把所有测试工程和测试数据放在单独一个文件夹。
└── usr
├── 源码
│ │ └── 模块/功能/分类 A
│ │ │ │ └── A 相关源码
│ │ └── 模块/功能/分类 B
│ │ │ │ └── B 相关源码
│ │ └── 模块/功能/分类 C
│ │ │ │ └── C 相关源码
├── 测试数据
│ │ │ │ └── ABC 测试数据
│ │ │ │ └── ABC 测试通用框架
│ │ │ │ └── ABC 测试代码
│ │ │ │ │ │ └── A 测试代码
│ │ │ │ │ │ └── B 测试代码
│ │ │ │ │ │ └── C 测试代码
7.2 测试工程中如何引入被测代码
一般有下边两种方法:
- 将被测代码单独测试并且不包含其他任何产品代码。被测代码依赖的所有ThirdService、ThirdLibrary、软件内其他Class全部Mock掉。
- 基本需要把所有用的第三方库、自己内部所有代码全部mock一遍
- 适合依赖相对少
- 测试覆盖面广,代码可测性强
- 适合代码质量要求高,并且开发时间充裕的项目
- 把产品代码编译成库,测试代码调用
- 大大减少Mock,缩短测试开发时间
- public函数测试时 :产品代码不会包含任何的测试代码
- private函数测试需要使用FRIEND_TEST,产品代码.h文件需要包含测试代码
- 测试代码可以调用整个程序资源,缩短测试开发时间
- 可以通过makefile来控制产品代码和测试代码(cmkae 的 enable_testing )
7.3 解除类之间的依赖,何时mock
用过 gmock会发现当你使用ThirdService、ThirdLibrary时。由于gmock采用的是继承的方式,你需要自己重新实现一个ThirdService。
当你真正想把被测代码隔离开了的时候,才进行Mock。