Django框架(二十六:rest framework 认证)
一,基础:
1.1安装
pip install djangorestframework
二:基础知识
首先必须要知道django-rest-framework源码中到处都是基于CBV和面向对象的封装
其次是CBV:基于反射实现根据请求方式不同,执行不同的方法
三:简单实例
3.1 urls.py
path('auth/', AuthView.as_view()),
3.2 settings.py
在settings的app中添加
INSTALLED_APPS = [
‘rest_framework’,
]
3.3 model
class UserInfo(models.Model):
user_type_choices = ((1, '普通用户'), (2, 'VIP'), (3, 'SVIP'))
user_type = models.IntegerField(choices=user_type_choices)
username = models.CharField(max_length=50, unique=True)
password = models.CharField(max_length=100)
class UserToken(models.Model):
"""
保存用户token
"""
# 一个用户对应一个token。
user = models.OneToOneField(UserInfo, on_delete=True, null=True)
token = models.CharField(max_length=64, null=True)
3.4 views.py
from utils.base_authenticate import PTPermission, IPThrottle, UserThrottle
from utils.version import Version
from rest_framework.versioning import QueryParameterVersioning, URLPathVersioning
class OrderView(APIView):
authentication_classes = [Authentication] # 用于认证
def get(self, request, version):
data = {}
# 首先验证用户传递的token值和数据库中的是否一致
token = request.GET.get('token')
data = {}
if not token:
data['status'] = 0
data['message'] = 'This User Not Auth.'
return JsonResponse(data)
else:
token_obj = UserToken.objects.filter(token=token)
if not token_obj:
data['status'] = 0
data['message'] = 'This Token Is Error.'
return JsonResponse(data)
else:
data['result'] = ORDER_DETAIL # 默认的数据
return JsonResponse(data)
上面的这句代码 authentication_classes = [Authentication] 中的Authentication对象是自定义的
class Authentication(object):
"""
自定义的用户认证类
"""
def authenticate(self, request):
token = request.GET.get('token')
if not token:
raise exceptions.AuthenticationFailed('没有携带token')
else:
token_obj = UserToken.objects.filter(token=token)
if not token_obj:
raise exceptions.AuthenticationFailed('token认证失败')
else:
return (token_obj[0].user, token_obj[0].token)
def authenticate_header(self, request):
pass
四:drf源码分析
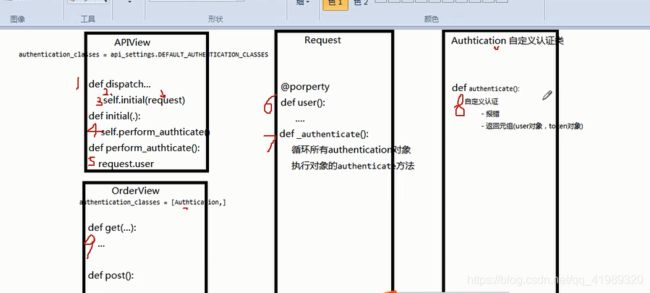
认证执行的流程
API接口的请求,从发送网络请求开始->dispatch()->self.initialize_request->构造新的Request(authenticators=[Authentication()])对象->self.initial()->self.perform_authentication(request)->Request类中的user的get方法->def _authenticate(self):->for authenticator in self.authenticators:->认证类内部的authenticate(self)方法->认证成功(user, token)->认证失败(None, None)->元组中的两个数据最终赋值给了request.user和request.auth->drf判断用户是否认证成功就是通过request.user和request.auth判断的。
找到dispatch,位置如图
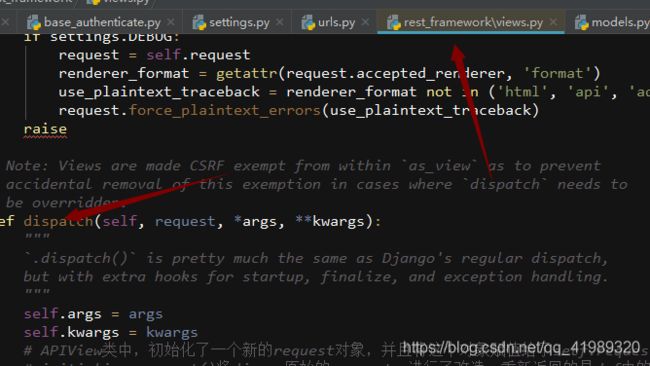
这里主要做了两件事
一:封装 对WSGI的request进行封装,丰富了原生request的功能,执行了self.initialize_request(request, *args, **kwargs)这个函数

点进这个函数,注意箭头和注释
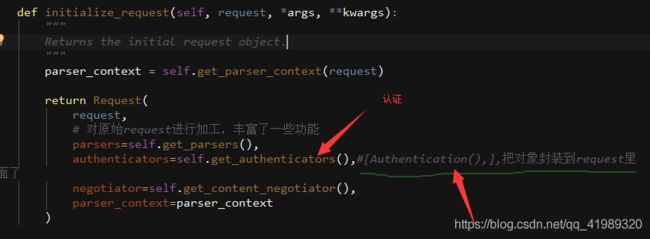
get_authenticators()
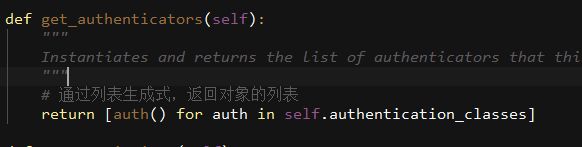
authentication_classes
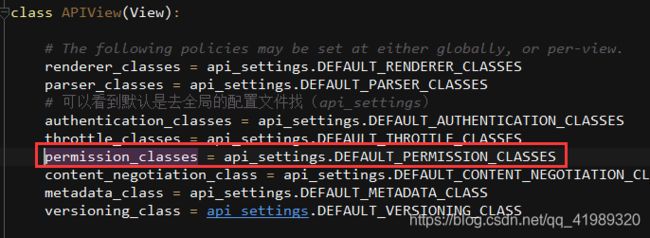
APIView里面有个 authentication_classes 字段
可以看到默认是去全局的配置文件找(api_settings)
二: 认证
initial()

perform_authentication()
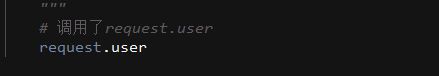
request.user

#在rest framework内部会将这两个字段赋值给request,以供后续操作使用
return (token_obj[0].user, token_obj[0].token) #例子中的return
当都没有返回值,就执行self._not_authenticated(),相当于匿名用户,没有通过认证
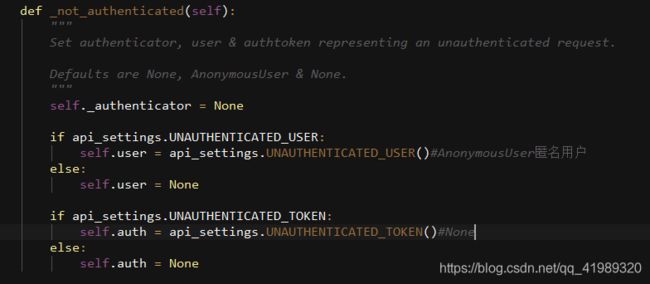
全局配置方法:
# 这个键是对接口进行全局配置的。
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
# 配置Authentication类,作为所有接口的认证类,所有接口发送请求,都要先经过这个类的认证,看是否已经登录。相当于你在每一个接口类中都设置了一个authentication_classes = [Authentication]。
"DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES": ['utils.base_authenticate.Authentication'],
}
在settings里面设置的全局认证,所有业务都需要经过认证,如果想让某个不需要认证,只需要在其中添加下面的代码:
authentication_classes = [] #里面为空,代表不需要认证
五:drf内置认证类
rest_framework里面内置了一些认证,我们自己写的认证类都要继承内置认证类 “BaseAuthentication”
4.1.BaseAuthentication源码:
class BaseAuthentication(object):
"""
All authentication classes should extend BaseAuthentication.
"""
def authenticate(self, request):
"""
Authenticate the request and return a two-tuple of (user, token).
"""
#内置的认证类,authenticate方法,如果不自己写,默认则抛出异常
raise NotImplementedError(".authenticate() must be overridden.")
def authenticate_header(self, request):
"""
Return a string to be used as the value of the `WWW-Authenticate`
header in a `401 Unauthenticated` response, or `None` if the
authentication scheme should return `403 Permission Denied` responses.
"""
#这个方法作用是当认证失败的时候,返回的响应头
pass
```
4.2.修改自己写的认证类
自己写的Authentication必须继承内置认证类BaseAuthentication
class Authentication(BaseAuthentication):
“”"
自定义的用户认证类
“”"
def authenticate(self, request):
token = request.GET.get(‘token’)
if not token:
raise exceptions.AuthenticationFailed(‘没有携带token’)
else:
token_obj = UserToken.objects.filter(token=token)
if not token_obj:
raise exceptions.AuthenticationFailed(‘token认证失败’)
else:
return (token_obj[0].user, token_obj[0].token)
def authenticate_header(self, request):
"""
Return a string to be used as the value of the `WWW-Authenticate`
header in a `401 Unauthenticated` response, or `None` if the
authentication scheme should return `403 Permission Denied` responses.
"""
pass