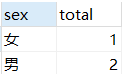MySQL单表查询语句执行顺序
一、在分析SQL查询语句执行顺序之前,我们先来认识一下 order by 、group by、having这几种子句。
1、order by:对查询结果进行排序,必须置于SQL语句的最后,语法:order by 字段名 [asc|desc]
select * from student order by age,mobile ##order by 后面可以加多个字段
select * from student order by age asc,mobile desc ## asc表示升序 desc表示降序 默认为升序排列 此语句先对age进行升序排列,对于age字段值相同的数据再进行对mobile字段的降序排列。2、distinct:去除相同的行(“相同的行”指不同行之间的相同列中的数值相同)
select DISTINCT age from student ##去掉age字段相同的行
select distinct age,mobile from student order by age,mobile desc ##去掉age,mobile字段都相同的行,并对age升序排列,然后对mobile降序排列。
注意事项:该关键字必须紧跟select关键字的后面,即如下写法是错误的: select age,distinct name from student
3、group by用于将表中数据划分为若干个组,group by后面用于指定分组的依据。
select sex,count(id) from student group by sex #将student表学生按照sex分组,然后统计每组中的人数
select name ,sex,count(sex) from student group by sex ##这样写没有意义4、where后面不能使用多行函数,只能使用单行函数和字段,having关键字弥补了这一不足:having子句用于对分组结果进行约束。
select name,count(name) from student group by name where count(name)>1 ##错的 where字句不能使用多行函数。
select name ,count(name) from student group by name having count(name)>1 查询重名的数据,并统计每条数据重复的个数5、多行函数是聚合函数,忽略null值。
select count(ifnull(name,'未知')) from student ##统计name字段数据个数(包括null)二、让我们来看下面的语句,可以帮助我们更好地理解上述子句之间的执行顺序。
create table student(
id char(1) primary key,
name varchar(8),
sex char(2) default '男' ,
age int(3) default 0
)
insert into student values ('1','王明','男',18);
insert into student values ('2','孙丽','女',17);
insert into student values ('3','王明','男',27);
insert into student (id,sex,age) values ('4','男',27);
select sex,count(sex) total from student where name like '%' group by sex order by total
##先获取符合where条件的数据,再对数据按照sex进行分组,最后对count(sex)升序排列。输出结果
三、总结
1、MySQL单表查询语句的书写顺序为: select...from...where...group by...having...order by... (having子句一般和group by子句一起使用,并且having子句必须放在group by子句之后,order by字句之前)
2、MySQL单表查询语句的执行顺序为: from...where...group by...having...select...order by...
- from:需要从哪个数据表检索数据
- where:过滤表中数据的条件
- group by:如何将上面过滤出的数据分组
- having:对上面已经分组的数据进行过滤的条件
- select:查看结果集中的哪个列,或列的计算结果
- order by :按照什么样的顺序来查看返回的数据 (desc为降序,asc为升序)