网关 Apache APISIX 在 360 基础运维平台项目中的实践
女主宣言
今天小编为大家分享一篇关于Apache APISIX的文章,文章从开发者的角度讲述了 Apache APISIX 网关在 360 基础运维平台的落地实践,希望能对大家有所帮助。
PS:丰富的一线技术、多元化的表现形式,尽在“360云计算”,点关注哦!
Api 网关选型
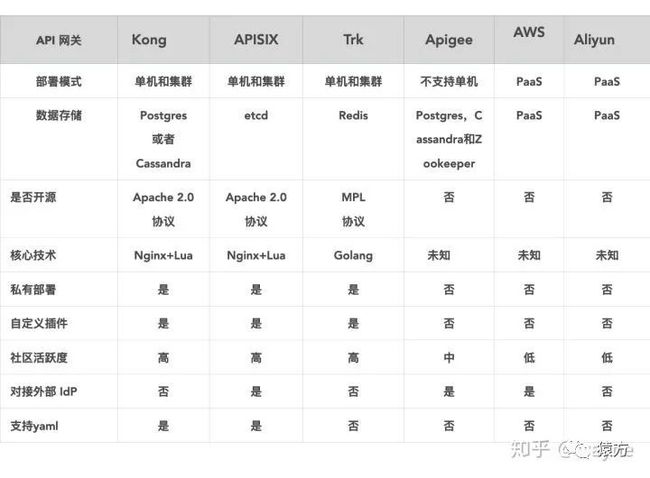
2019 年 10月,我们团队计划改造 360 基础运维平台的网关层,当时我们主要调研了社区几个比较活跃的网关,如 Kong,Orange,Apache APISIX,最终选择了 Apache APISIX 当时主要是考虑到 Apache APISIX 的存储选型 etcd 比较符合我们的使用场景。
线上运行情况
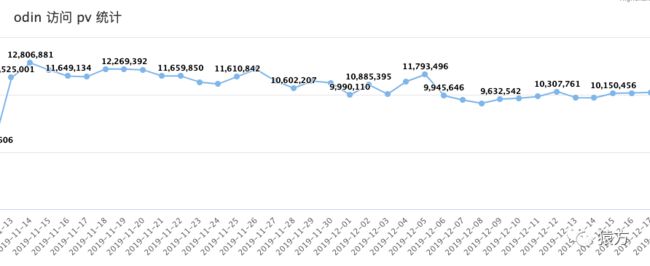
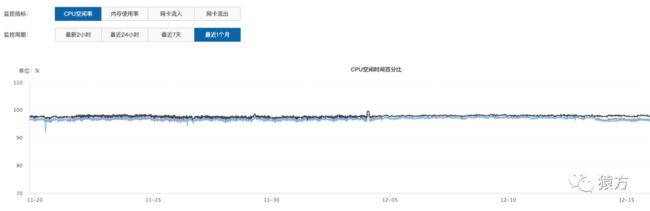
目前我们添加到网关的 API 数量接近 900 个,日均 PV 1000 万左右,从监控系统来看,网关以及我们各个微服务均运行良好。
•日均 PV
•网关 POD 监控
•微服务负载监控图
基础运维平台架构图
下图是我们运维平台项目最终的架构图,网关服务我们部署在公司的容器云上,etcd 服务我们是在 3 台虚机上部署了一套集群。
容器化开发和部署
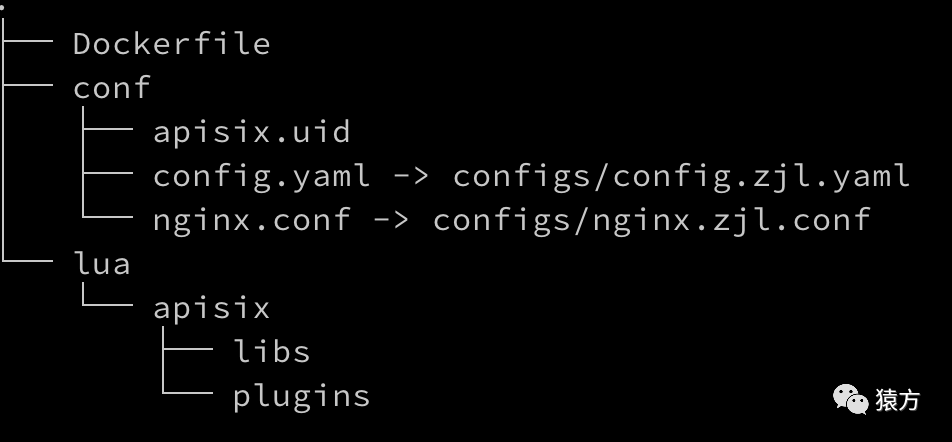
接下来我具体介绍一下我们是如何使用 Apache APISIX 搭建网关服务的,首先先给大家看下我们网关项目的代码结构
之前我给王院生(Apache APISIX PPMC 之一 )看我们的项目代码结构时,他惊讶的问我,说怎么没有看到 Apache APISIX 的 core 代码。
实际上这是我们在使用容器安装 Apache APISIX 时探索出来的一条道路。它给我们带来最大的好处是,我们业务的代码和 Apache APISIX 的核心代码完全分开,方便 Apache APISIX 升级,也方便我们的业务代码迭代。
下面我给大家分步演示一下,我们是怎么搭建一个这样的环境的。(此处假设大家都了解 docker 容器技术)
•启动 openresty 容器
我们团队基于官方的 openresty 镜像,默认安装了一些 Apache APISIX 依赖的软件如 luarocks 等,重新打包了一个新的镜像,详情可见 https://hub.docker.com/r/hulklab/openresty/dockerfile
> docker run -itd -p 9080:9080 -p9443:9443 --name myapisix hulklab/openresty:0.0.1
•进入容器
> docker exec -it myapisix bash
•安装 apisix 0.9 版本
> luarocks install apisix 0.9-0
# 安装完你会在最后看到下面这样的一行输出,我们从中可以看出 apisix 的安装目录为 /usr/local/apisix:
apisix 0.9-0 is now installed in /usr/local (license: Apache License 2.0)
•进入 Apache APISIX 安装目录
> cd /usr/local/apisix
# 进入到 apisix 的安装目录,你会发现里面只有两个目录 `conf` `logs`
> ls -l
drwxr-xr-x 3 root root 4096 Dec 18 11:52 conf
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Dec 18 11:37 logs
•启动 Apache APISIX(运行 Openresty)
> apisix start
> ps aux|grep openresty
root 1 0.0 0.0 11316 4464 pts/0 Ss+ 11:24 0:00 nginx: master process /usr/bin/openresty -g daemon off;
root 5040 0.0 0.0 87436 2588 ? Ss 11:37 0:00 nginx: master process openresty -p /usr/local/apisix -c /usr/local/apisix/conf/nginx.conf
注:如果执行
apisix start失败,是因为 Apache APISIX 依赖 etcd,你需要启动 etcd,如何启动 etcd 请参考 etcd 官方文档[1],启动 etcd 后需要修改 /usr/local/apisix/conf/config.yaml 中的 etcd.host 配置, 如:
#config.yaml:69
etcd:
host: "http://172.17.0.1:2379" # etcd address
•查看 nginx.conf
apisix 成功运行了,但是安装目录 /usr/local/apisix 里面又没有代码,那么 apisix 核心代码以及依赖代码究竟在哪里呢?
从启动的 openresty 进程看到,apisix/conf 目录下,多出了一个 nginx.conf,这个 nginx.conf 配置文件是 apisix start 命令执行时初始化出来的, 我们查看了一下 nginx.conf 中的 lua 包引用路径
> cat /usr/local/apisix/conf/nginx.conf|grep lua_package_path
lua_package_path "$prefix/deps/share/lua/5.1/?.lua;/usr/local/apisix/lua/?.lua;;/usr/local/apisix/deps/share/lua/5.1/apisix/lua/?.lua;/usr/local/apisix/deps/share/lua/5.1/?.lua;/usr/share/lua/5.1/apisix/lua/?.lua;/usr/local/share/lua/5.1/apisix/lua/?.lua;/root/.luarocks/share/lua/5.1/?.lua;/root/.luarocks/share/lua/5.1/?/init.lua;/usr/local/share/lua/5.1/?.lua;/usr/local/share/lua/5.1/?/init.lua;./?.lua;/usr/local/lib/lua/5.1/?.lua;/usr/local/lib/lua/5.1/?/init.lua;/usr/share/lua/5.1/?.lua;/usr/share/lua/5.1/?/init.lua;";
从上面的 lua_package_path 中我们挨个查看,从中发现了两个有用的信息
1.Apache APISIX 核心代码的路径:/usr/local/share/lua/5.1/apisix/lua/2.Apache APISIX 安装路径 /usr/local/apisix/lua 下的 lua 文件的加载优先级最高
于是我们做了一个尝试,仿照 Apache APISIX 的 plugins 路径,在 /usr/local/apisix 目录下创建 lua/apisix/plugins/my-plugin.lua,并在配置文件 config.yaml 中添加该插件,发现果然生效了。
•Dockerfile
贴出我们项目的 Dockerfile 文件,供大家参考。最终我们项目只有 conf 和 lua 两个目录,conf 中存放我们自己定义 config.yaml 和 nginx.conf 配置文件,lua 中存放我们自定义的插件和类库。
FROM hulklab/openresty:0.0.1
RUN luarocks install apisix 0.9-0; \
luarocks install lua-resty-cookie; \
luarocks install lua-resty-kafka; \
luarocks install lua-resty-url
WORKDIR /usr/local/apisix
RUN rm -rf conf/*; \
mkdir -p lua; \
mkdir -p logs/archive; \
install -d -m 777 /tmp/apisix_cores/
COPY conf conf
COPY lua lua
COPY logrotate /etc/logrotate.d
EXPOSE 9080 9443
ENTRYPOINT ["openresty", "-p", "/usr/local/apisix", "-c", "/usr/local/apisix/conf/nginx.conf", "-g", "daemon off;"]
插件化开发
1
项目插件介绍
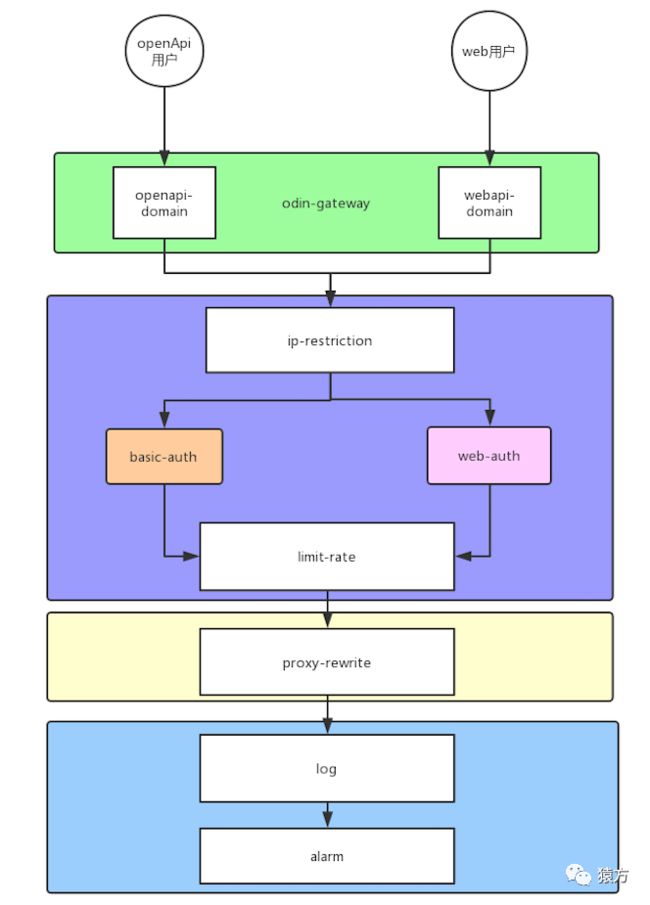
正如在上面代码结构图中所看到的,我们项目的 apisix 目录里面有两个目录,libs 和 plugins,libs 里面我们放一些常用的类库,plugins 里面存放我们自定义的业务插件,我们所有的业务都采用插件机制来开发。下图是我们项目中目前使用到的插件。
稍微解释一下,我们项目的入口域名有两个,一个是提供给 openApi 访问的,认证插件使用的是 Basic Auth,一个是提供给 web 浏览器访问的,认证插件使用的是 web auth(cookie 认证)。
对应 OpenResty 的请求处理流程,我们的插件主要集中在 access 和 log 阶段
| 插件 | 阶段 | 描述 |
| ip-restriction | access_by_lua | ip 限流,使用 apisix 原生插件 |
| basic-auth | access_by_lua | 对 openApi 请求用户鉴权,自研插件 |
| web-auth | access_by_lua | 对 webApi 请求用户鉴权,自研插件 |
| limit-rate | access_by_lua | 对请求实现用户级别和用户+请求参数级别的限流,自研插件 |
| proxy-rewrite | access_by_lua,balancer_by_lua | 对请求进行转发,设置接口级别的超时时间,自研插件 |
| log | log_by_lua | 将请求日志记录到 kafka,再通过 logstash 读到 es 中,自研插件 |
| alarm | log_by_lua | 根据响应的 statusCode 来报警,自研插件 |
2
插件开发样例
接下来以 basic-auth 插件 为例,介绍一下 Apache APISIX 插件是怎么开发的
•定义插件对象
local plugin_name = "odin-basic-auth"
local schema = {
type = "object",
properties = {
enable = { type = "boolean", default = true, enum = { true, false } },
},
}
local _M = {
version = 0.1,
priority = 2802,
name = plugin_name,
schema = schema,
}
odin-basic-auth 插件只有一个参数 enable,enable 参数表示是否使用本插件,这是由于 Apache APISIX 的插件可以绑定到 service,也可以绑定到 route,如果插件绑定到 service 之后,route 是没有办法关闭插件的,所以需要一个参数用来精细的控制某个 route 不使用 service 绑定的插件,建议官方插件都配上此参数。
•实现检测插件参数的方法
function _M.check_schema(conf)
local ok, err = core.schema.check(schema, conf)
if not ok then
return false, err
end
return true
end
check_schema 方法基本每个插件都一样
•实现插件对应阶段的方法
function _M.access(conf, ctx)
-- 0. 检测配置文件,看看是否开启了 enable
if not conf.enable then
return
end
-- 1. 获取 basic_auth 里面的 username 和 password
local headers = ngx.req.get_headers()
if not headers.Authorization then
return 401, { message = "authorization is required" }
end
local username, password, err = extract_auth_header(headers.Authorization)
if err then
return 401, { message = err }
end
-- 2. 查看 etcd 获取 username 对应的记录
local res = authorizations_etcd:get(username)
if res == nil then
return 401, { message = "failed to find authorization from etcd" }
end
-- 3. 如果没有,报认证失败
if not res.value or not res.value.id then
return 401, { message = "user is not found" }
end
local value = res.value
-- 4. 如果有,判断是否用户密码是否正确
if value.password ~= password then
return 401, { message = "password is error" }
end
end
3
Etcd 缓存对象
上面样例中的第二步,我们获取当前请求用户的实际密码以及授权路由列表时使用了 authorizations_etcd:get(username), 这里使用到了 Apache APISIX 的 etcd 缓存对象。
etcd 缓存对象的原理是利用 etcd 的 watch 功能,将数据从 etcd 缓存到内存对象中,业务使用的时候直接从内存中读取,避免网络 io 消耗,etcd 的 watch 功能又保障了数据的实时性,Apache APISIX 的这一特性,简直是让人拍案叫绝。
下面介绍一下如何使用:
•定义一个 etcd 环境对象变量
local authorizations_etcd
-- 定义 etcd 对象储存的值 scheme
local appkey_scheme = {
type = "object",
properties = {
username = {
description = "username",
type = "string",
},
password = {
type = "string",
}
},
}
•在插件的 init 阶段实例化
function _M.init()
authorizations_etcd, err = core.config.new("/authorizations", {
automatic = true,
item_schema = appkey_scheme
})
if not authorizations_etcd then
error("failed to create etcd instance for fetching authorizations: " .. err)
return
end
end
插件的 init 方法发生在 OpenResty 的 init_worker_by_lua 阶段,换句话说,每个 worker 只初始化一次。automatic 参数设置为 true,Apache APISIX 会开启 watch 功能。业务层只需要实例化 etcd 缓存对象,剩余的事情就都交给 Apache APISIX 做了。
•插件中使用 etcd 缓存对象
local res = authorizations_etcd:get(username)
4
插件 Api 的使用
上文中 etcd 缓存对象的本质还是需要从 etcd 中取数据,那么这个插件中使用到的用户相关数据是怎么添加到 etcd 呢?这不得不提到插件另一个让人尖叫的特性:Api 特性。
•定义 api
function _M.api()
return {
{
methods = { "POST", "PUT" },
uri = "/apisix/plugin/basic-auth/set",
handler = set_auth,
}
}
end
•实现 api 的 handler
local function set_auth()
local username = req.get_str("username")
local password = req.get_str("password")
local key = "/authorizations/" .. username
-- 此处存入到 etcd
local res, err = core.etcd.set(key, { username = username, password = password})
if not res then
core.response.exit(500, err)
end
core.response.exit(res.status, res.body)
end
•调用接口
> curl -i -X PUT 'http://127.0.0.1:9080/apisix/plugin/basic-auth/set' -d username=zhangsan -d password=hao123 -d user_id=3 -d action_ids=,1,2,3,
上线后遇到的问题
crontab 清理日结
由于我们网关部署在容器,运行一段时间之后,日志文件超过了默认的配额 50G,后来我们在镜像里面默认安装了 cron 和 logrotate,然后在容器 entrypoint 里面开启了 cron 用来解决这个问题。
感谢
最后特别感谢一下 Apache APISIX 的贡献者们,贴出 Apache APISIX 官网[2] 和 Apache APISIX Github 地址[3]
References
[1] etcd 官方文档: https://doczhcn.gitbook.io/etcd/index[2] Apache APISIX 官网: https://www.iresty.com/[3] Apache APISIX Github 地址: https://github.com/apache/incubator-apisix
以上就是本次分享的内容~
如果有什么建议,也可以在我们评论区留言,供大家参考学习。
360云计算
由360云平台团队打造的技术分享公众号,内容涉及数据库、大数据、微服务、容器、AIOps、IoT等众多技术领域,通过夯实的技术积累和丰富的一线实战经验,为你带来最有料的技术分享
![]()