opencv学习笔记(二)-对xml和yaml文件的读写操作
一.xml和yaml的简单介绍
所谓的xml,就是eXtensible Markup Language, 翻译成中文就是“可扩展标识语言“。首先XML是一种元标记语言,所谓“元标记”就是开发者可以根据自己的需要定义自己的标记,比如开发者可以定义如下标记
XML可利用于数据交换 主要是因为XML表示的信息独立于平台的,这里的平台即可以理解为不同的应用程序也可以理解为不同的操作系统;它描述了一种规范,利用它Microsoft的word文档可以和Adobe 的Acrobat交换信息,可以和数据库交换信息。
XML表示的结构化数据。
对于大型复杂的文档,xml 是一种理想语言,不仅允许指定文档中的词汇,还允许指定元素之间的关系。比如可以规定一个author元素必须有一个name子元素。可以规定企业的业务必须有包括什么子业务。
XML文档。 XML文档有DTD和XML文本组成,所谓DTD(Document Type Definition ),简单的说就是一组标记符的语法规则.,表明XML文本是怎么样组织的,比如DTD可以表示一个
和GNU一样,YAML是一个递归着说“不”的名字。不同的是,GNU对UNIX说不,YAML说不的对象是XML。YAML不是XML。
为什么不是XML呢?因为:
- YAML的可读性好。
- YAML和脚本语言的交互性好。
- YAML使用实现语言的数据类型。
- YAML有一个一致的信息模型。
- YAML易于实现。
上面5条也就是XML不足的地方。同时,YAML也有XML的下列优点:
- YAML可以基于流来处理;
- YAML表达能力强,扩展性好。
总之,YAML试图用一种比XML更敏捷的方式,来完成XML所完成的任务。
更多的内容及规范参见 http://www.yaml.org 。以及点击打开链接二.opencv中对xml 和yaml文件的读写数据结构介绍
XML\YAML文件在OpenCV中的数据结构为FileStorage,更多参考:点击打开链接
打开写操作:
FileStorage fs("test.yml", FileStorage::WRITE);打开读操作:
FileStorage fs2("test.yml", FileStorage::READ);三.对xml和yaml文件的读写操作及其示例
写操作示例只是对yaml做演示,xml的操作也一样:
示例代码:
#include "opencv2/opencv.hpp"
#include
using namespace cv;
int main(int, char** argv)
{
FileStorage fs("test.yml", FileStorage::WRITE);
fs << "frameCount" << 5;
time_t rawtime; time(&rawtime);
fs << "calibrationDate" << asctime(localtime(&rawtime));
Mat cameraMatrix = (Mat_(3,3) << 1000, 0, 320, 0, 1000, 240, 0, 0, 1);
Mat distCoeffs = (Mat_(5,1) << 0.1, 0.01, -0.001, 0, 0);
fs << "cameraMatrix" << cameraMatrix << "distCoeffs" << distCoeffs;
fs << "features" << "[";
for( int i = 0; i < 3; i++ )
{
int x = rand() % 640;
int y = rand() % 480;
uchar lbp = rand() % 256;
fs << "{:" << "x" << x << "y" << y << "lbp" << "[:";
for( int j = 0; j < 8; j++ )
fs << ((lbp >> j) & 1);
fs << "]" << "}";
}
fs << "]";
fs.release();
return 0;
} 写入的xml文档内容:
5
"Fri May 03 11:34:09 2013
"
3
3
d
1000. 0. 320. 0. 1000. 240. 0. 0. 1.
5
1
d
1.0000000000000001e-001 1.0000000000000000e-002
-1.0000000000000000e-003 0. 0.
<_>41
227
0 1 1 1 1 1 0 1
<_>260
449
0 0 1 1 0 1 1 0
<_>598
78
0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0
读操作:
FileStorage fs2("test.yml", FileStorage::READ);
// first method: use (type) operator on FileNode.
int frameCount = (int)fs2["frameCount"];
std::string date;
// second method: use FileNode::operator >>
fs2["calibrationDate"] >> date;
Mat cameraMatrix2, distCoeffs2;
fs2["cameraMatrix"] >> cameraMatrix2;
fs2["distCoeffs"] >> distCoeffs2;
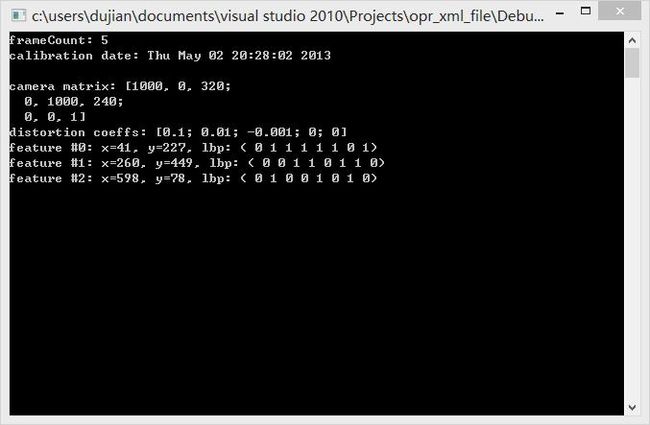
cout << "frameCount: " << frameCount << endl
<< "calibration date: " << date << endl
<< "camera matrix: " << cameraMatrix2 << endl
<< "distortion coeffs: " << distCoeffs2 << endl;
FileNode features = fs2["features"];
FileNodeIterator it = features.begin(), it_end = features.end();
int idx = 0;
std::vector lbpval;
// iterate through a sequence using FileNodeIterator
for( ; it != it_end; ++it, idx++ )
{
cout << "feature #" << idx << ": ";
cout << "x=" << (int)(*it)["x"] << ", y=" << (int)(*it)["y"] << ", lbp: (";
// you can also easily read numerical arrays using FileNode >> std::vector operator.
(*it)["lbp"] >> lbpval;
for( int i = 0; i < (int)lbpval.size(); i++ )
cout << " " << (int)lbpval[i];
cout << ")" << endl;
}
fs.release(); 读取示例:
四.结束语和参考资料
对xml的操作中,尝试了写入一幅图片,然后读取并显示出来。结果是写入成功了,但读取后显示失败,提示说没有找到用户自定义的从fileNode类型到Mat类型的转换方式,这需要自己定义吗,opencv有没有自己定义好的,可以直接调用,求大神们指教。
参考资料
http://docs.opencv.org/modules/core/doc/xml_yaml_persistence.html#filestorage