第一篇:SpringBoot高级-缓存入门
JSR107
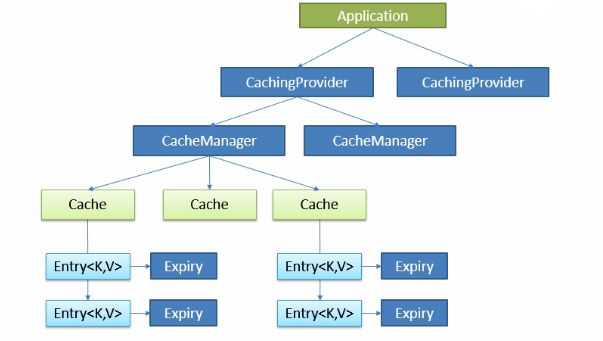
Java Caching定义了5个核心接口,分别是CachingProvider, CacheManager, Cache, Entry和Expiry。
CachingProvider定义了创建、配置、获取、管理和控制多个 CacheManager。一个应用可以在运行期访问多个CachingProvider。
CacheManager定义了创建、配置、获取、管理和控制多个唯一命名的Cache,这些Cache存在于CacheManager的上下文中。一个CacheManager仅被一个CachingProvider所拥有。
Cache是一个类似Map的数据结构并临时存储以Key为索引的值。一个Cache仅被一个CacheManager所拥有。
Entry是一个存储在Cache中的key-value对。
Expiry每一个存储在Cache中的条目有一个定义的有效期。一旦超过这个时间,条目为过期的状态。一旦过期,条目将不可访问、更新和删除。缓存有效期可以通过ExpiryPolicy设置。
使用JSR107需要导入如下包
javax.cache
cache-api
Spring缓存抽象
Spring从3.1开始定义了org.springframework.cache.Cache和org.springframework.cache.CacheManager接口来统一不同的缓存技术;并支持使用JCache(JSR-107)注解简化我们开发;
Cache接口为缓存的组件规范定义,包含缓存的各种操作集合;
Cache接口下Spring提供了各种xxxCache的实现;如RedisCache,EhCacheCache , ConcurrentMapCache等;
每次调用需要缓存功能的方法时,Spring会检查检查指定参数的指定的目标方法是否已经被调用过;如果有就直接从缓存中获取方法调用后的结果,如果没有就调用方法并缓存结果后返回给用户。下次调用直接从缓存中获取。
-
使用Spring缓存抽象时我们需要关注以下两点;
- 确定方法需要被缓存以及他们的缓存策略
- 从缓存中读取之前缓存存储的数据
重要概念和缓存注解
| Cache | 缓存接口,定义缓存操作。实现有:RedisCache、EhCacheCache、ConcurrentMapCache等 |
|---|---|
| CacheManager | 缓存管理器,管理各种缓存(Cache)组件 |
| @Cacheable | 主要针对方法配置,能够根据方法的请求参数对其结果进行缓存 |
| @CacheEvict | 清空缓存 |
| @CachePut | 保证方法被调用,又希望结果被缓存 |
| @EnableCaching | 开启基于注解的缓存 |
| keyGenerator | 缓存数据时key生成策略 |
| serialize | 缓存数据时value序列化策略 |
简要说明:
- @Cacheable注解加载方法中,那么该方法第一次会查询数据库,然后就会把数据放在缓存中,使用Cache 进行数据的读取等操作。
- @CacheEvict删除缓存,例如根据id删除用户,那么也要删除缓存中的用户信息
- @CachePut更新缓存,例如更新用户信息后,同时也要更新缓存中的用户信息
使用springboot+mybatis完成缓存初体验
一、Spring boot cache原理
第一步、自动配置类;
自动启动类:CacheAutoConfiguration
属性配置:CacheProperties
主启动类添加:@EnableCaching注解
cache POM添加:
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-cache
第二步、从缓存的配置类 中获取 多个cache
CacheConfigurationImportSelector.selectImports()方法获取
static class CacheConfigurationImportSelector implements ImportSelector {
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata) {
CacheType[] types = CacheType.values();
String[] imports = new String[types.length];
for (int i = 0; i < types.length; i++) {
imports[i] = CacheConfigurations.getConfigurationClass(types[i]);
}
return imports;
}
}
获取结果:SimpleCacheConfiguration 默认cache
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.GenericCacheConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.JCacheCacheConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.EhCacheCacheConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.HazelcastCacheConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.InfinispanCacheConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CouchbaseCacheConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CaffeineCacheConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.GuavaCacheConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.SimpleCacheConfiguration【默认】
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.NoOpCacheConfiguration
第三步:SimpleCacheConfiguration.cacheManager()
此方法中给容器中注册了一个CacheManager组件:类型为ConcurrentMapCacheManager
@Bean
public ConcurrentMapCacheManager cacheManager() {
ConcurrentMapCacheManager cacheManager = new ConcurrentMapCacheManager();
List cacheNames = this.cacheProperties.getCacheNames();
if (!cacheNames.isEmpty()) {
cacheManager.setCacheNames(cacheNames);
}
return this.customizerInvoker.customize(cacheManager);
}
第四步:查看获取缓存方法getCache()
ConcurrentMapCacheManager 类里,数据都存储到为ConcurrentMap 中
public Cache getCache(String name) {
Cache cache = this.cacheMap.get(name); //cacheMap 为ConcurrentMap 类型,获取一个cache组件
if (cache == null && this.dynamic) {
synchronized (this.cacheMap) {
cache = this.cacheMap.get(name); //cahceMap不为空获取
if (cache == null) {
//可以获取或者创建ConcurrentMapCache类型的缓存组件;他的作用将数据保存在ConcurrentMap中;
cache = createConcurrentMapCache(name);
this.cacheMap.put(name, cache); //ConcurrentMapCache.lookup();
}
}
}
return cache;
}
二、Cacheable运行流程:
@Cacheable: 1、方法运行之前,先去查询Cache(缓存组件),按照cacheNames指定的名字获取; (CacheManager先获取相应的缓存),第一次获取缓存如果没有Cache组件会自动创建。 2、去Cache中查找缓存的内容(ConcurrentMapCache.lookup()方法中去查找),使用一个key,默认就是方法的参数; key是按照某种策略生成的;默认是使用keyGenerator生成的,默认使用SimpleKeyGenerator生成key; SimpleKeyGenerator生成key的默认策略; 如果没有参数;key=new SimpleKey(); 如果有一个参数:key=参数的值 如果有多个参数:key=new SimpleKey(params);
//这个方法 SimpleKeyGenerator.generateKey() 方法生成key
public static Object generateKey(Object... params) {
if (params.length == 0) {
return SimpleKey.EMPTY;
}
if (params.length == 1) { //如果只有一个参数,直接返回这个参数为key
Object param = params[0];
if (param != null && !param.getClass().isArray()) {
return param;
}
}
return new SimpleKey(params);
}
3、没有查到缓存就调用目标方法; 4、将目标方法返回的结果,放进缓存中ConcurrentMapCache.put();
@Cacheable标注的方法执行之前先来检查缓存中有没有这个数据,默认按照参数的值作为key去查询缓存, 如果没有就运行方法并将结果放入缓存;以后再来调用就可以直接使用缓存中的数据;
核心:
- 使用CacheManager【ConcurrentMapCacheManager】按照名字得到Cache【ConcurrentMapCache】组件
- key使用keyGenerator生成的,默认是SimpleKeyGenerator
详细执行流程:ConcurrentMapCache.lookup()上断点查看,执行过程
//第一步CacheAspectSupport 中execute()
private Object execute(final CacheOperationInvoker invoker, Method method, CacheOperationContexts contexts)
//第二步 CacheAspectSupport
private Cache.ValueWrapper findCachedItem(Collection contexts) {
Object result = CacheOperationExpressionEvaluator.NO_RESULT;
for (CacheOperationContext context : contexts) {
if (isConditionPassing(context, result)) {
Object key = generateKey(context, result); //获取key
Cache.ValueWrapper cached = findInCaches(context, key);
if (cached != null) {
return cached;
}
else {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("No cache entry for key '" + key + "' in cache(s) " + context.getCacheNames());
}
}
}
}
return null;
}
//第三步:CacheAspectSupport.findInCaches()
//第四步:AbstractCacheInvoker.doGet()
//第五步:AbstractValueAdaptingCache.get();
@Override
public ValueWrapper get(Object key) {
Object value = lookup(key);
return toValueWrapper(value);
}
// 第六步:ConcurrentMapCache.lookup(); 从ConcurrentMap 中根据key获取值
@Override
protected Object lookup(Object key) {
return this.store.get(key);
}
三、Cacheable 注解的几个属性:
cacheNames/value:指定缓存组件的名字;将方法的返回结果放在哪个缓存中,是数组的方式,可以指定 多个缓存;
key:缓存数据使用的key;可以用它来指定。默认是使用方法参数的值 1-方法的返回值
编写SpEL; #i d;参数id的值 #a0 #p0 #root.args[0]
getEmp[2]keyGenerator:key的生成器;可以自己指定key的生成器的组件id
key/keyGenerator:二选一使用;cacheManager:指定缓存管理器;或者cacheResolver指定获取解析器
condition:指定符合条件的情况下才缓存;
condition = "#id>0"
condition = "#a0>1":第一个参数的值》1的时候才进行缓存unless:否定缓存;当unless指定的条件为true,方法的返回值就不会被缓存;可以获取到结果进行判断
unless = "#result == null"
unless = "#a0==2":如果第一个参数的值是2,结果不缓存;sync:是否使用异步模式;异步模式的情况下unless不支持
四、Cache使用:
1.Cacheable的使用
@Cacheable(value = {"emp"}/*,keyGenerator = "myKeyGenerator",condition = "#a0>1",unless = "#a0==2"*/)
public Employee getEmp(Integer id){
System.out.println("查询"+id+"号员工");
Employee emp = employeeMapper.getEmpById(id);
return emp;
}
2.自定义keyGenerator:
@Bean("myKeyGenerator")
public KeyGenerator keyGenerator(){
return new KeyGenerator(){
@Override
public Object generate(Object target, Method method, Object... params) {
return method.getName()+"["+ Arrays.asList(params).toString()+"]";
}
};
}
3.CachePut的使用:更新缓存
/**
* @CachePut:既调用方法,又更新缓存数据;同步更新缓存
* 修改了数据库的某个数据,同时更新缓存;
* 运行时机:
* 1、先调用目标方法
* 2、将目标方法的结果缓存起来
*
* 测试步骤:
* 1、查询1号员工;查到的结果会放在缓存中;
* key:1 value:lastName:张三
* 2、以后查询还是之前的结果
* 3、更新1号员工;【lastName:zhangsan;gender:0】
* 将方法的返回值也放进缓存了;
* key:传入的employee对象 值:返回的employee对象;
* 4、查询1号员工?
* 应该是更新后的员工;
* key = "#employee.id":使用传入的参数的员工id;
* key = "#result.id":使用返回后的id
* @Cacheable的key是不能用#result
* 为什么是没更新前的?【1号员工没有在缓存中更新】
*
*/
@CachePut(value = "emp",key = "#result.id")
public Employee updateEmp(Employee employee){
System.out.println("updateEmp:"+employee);
employeeMapper.updateEmp(employee);
return employee;
}
4.CacheEvict 缓存清除
/**
* @CacheEvict:缓存清除
* key:指定要清除的数据
* allEntries = true:指定清除这个缓存(emp缓存组件)中所有的数据
* beforeInvocation = false:缓存的清除是否在方法之前执行
* 默认代表缓存清除操作是在方法执行之后执行;如果出现异常缓存就不会清除
*
* beforeInvocation = true:
* 代表清除缓存操作是在方法运行之前执行,无论方法是否出现异常,缓存都清除
*
*
*/
@CacheEvict(value="emp",beforeInvocation = true,key = "#id")
public void deleteEmp(Integer id){
System.out.println("deleteEmp:"+id);
//employeeMapper.deleteEmpById(id);
int i = 10/0;
}
5.Caching 复杂配置
// @Caching 定义复杂的缓存规则
@Caching(
cacheable = {
@Cacheable(/*value="emp",*/key = "#lastName")
},
put = {
@CachePut(/*value="emp",*/key = "#result.id"),
@CachePut(/*value="emp",*/key = "#result.email")
}
)
public Employee getEmpByLastName(String lastName){
return employeeMapper.getEmpByLastName(lastName);
}
6.CacheConfig缓存清除
@CacheConfig(cacheNames="emp",cacheManager = "employeeCacheManager") //抽取缓存的公共配置
@Service
public class EmployeeService {