Ecos操作系統查看进程信息
由于最近公司用到了ecos操作系统,所以简单的了解了一下这个RTOS,其相关的社区资源较少,国内基本不用,这里结合手册整理了一部分的内容。本文章主要两部分,一是建立基本的测试进程,而是枚举所有进程并查看相关信息。
如下代码是在原来的基础上增加的进程信息获取,其中堆栈使用的查看需要在ecos系统配置时启用测量堆栈使用,实际上就是启用一个宏定义。图形化配置如下,也可以直接配置宏(不推荐)。
启用堆栈测量2:
#ifdef CYGFUN_KERNEL_THREADS_STACK_MEASUREMENT
info->stack_used = thread->measure_stack_usage();
#else
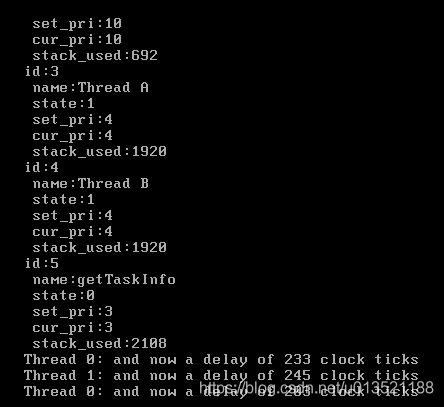
#include 使用如上的工程,重新编译后,将生成的文件扔给redboot加载即可。本人暂时没有arm芯片,使用vmware虚拟机运行ecos,可以看到打印的线程名称,当前状态,设定的优先级和线程当前的优先级以及堆栈的使用情况,当然我这里没有全部显示,所有的线程信息都在cyg_thread_info结构体中,代码和运行结果如图所示:
typedef struct
{
cyg_handle_t handle;
cyg_uint16 id;
cyg_uint32 state;
char *name;
cyg_priority_t set_pri;
cyg_priority_t cur_pri;
cyg_addrword_t stack_base;
cyg_uint32 stack_size;
cyg_uint32 stack_used;
} cyg_thread_info;
另外我会写两篇文章介绍Ecos系统的结构,主要和freertos很不相同,以及在Vmware中运行ecos操作系统,权当普及一下。
