自定义View开篇,必须跨过的一道坎儿
前言
对于许多Android开发者而言,无论工作的方向是什么,自定义View是不得不跨过去的一道坎儿,相信很多伙伴有这样的感受,关于自定义View的知识都看的明白,甚至滚瓜烂熟,但是遇到自定义View实战的时候,还是感觉无从下手,其实想学好自定义View,只有一个字,'练",从今天开始我会持续开始写自定义View系列的文章,一方面巩固自己的基础,另一方面温故而知新。
自定义view的方式及异同
- 继承自View
- 继承自ViewGroup
- 继承自特定现有的View 如TextView
- 继承自特定现有的ViewGroup 如LinerLayout
我们先说继承自View和ViewGroup,这两种方式和后面两种相比 更接近于底层,可实现的view更加多样化,但是这两种方式需要处理wrap_content的情况以及padding,否则会出现显示问题。
继承自ViewGroup的控件比较复杂,需要自行处理onMeasure以及onLayout方法,margin是由父控件决定的,所以继承自View的自定义控件只需要处理padding,但是继承自ViewGroup的控件需要处理自身的padding以及子控件的margin
如何处理wrap_content问题
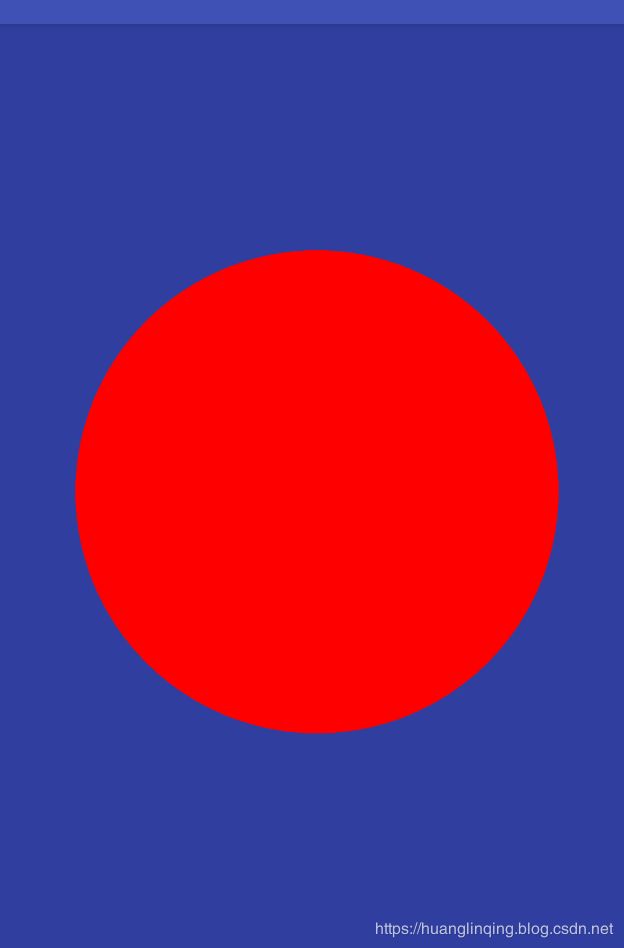
首先我们举个例子 绘制一个简单的圆形。新建CircleView类继承自View,生成三个构造方法,至于每个构造方法有什么区别我在Android自定义View之绘制圆形头像 提到过,初始化画笔等操作都是基础操作,这里就不再赘述了,在onDraw中绘制一个圆,半径为宽高中短边的一半。
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
int width = getWidth();
int height = getHeight();
int radius = Math.min(width,height) / 2;
canvas.drawCircle(width / 2,height/2,radius,paint);
}在布局中引用这个view,设置宽高为300dp,为了方便看效果 我们给这个view设置蓝色背景。运行效果图如下
接下里我们,设置宽高为wrap_content,运行效果图如下,我们可以看到效果和设置match_parent是一样的
所以针对wrap_content问题 ,最简单的方式是设置一个默认值,至于默认值设置多少,其实是随意的,那么你可能会问,那为什么TextView设置wrap_content 大小就是正好的呢,我们看一下TextView的源码:
if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
// Parent has told us how big to be. So be it.
width = widthSize;
} else {
if (mLayout != null && mEllipsize == null) {
des = desired(mLayout);
}
if (des < 0) {
boring = BoringLayout.isBoring(mTransformed, mTextPaint, mTextDir, mBoring);
if (boring != null) {
mBoring = boring;
}
} else {
fromexisting = true;
}
if (boring == null || boring == UNKNOWN_BORING) {
if (des < 0) {
des = (int) Math.ceil(Layout.getDesiredWidthWithLimit(mTransformed, 0,
mTransformed.length(), mTextPaint, mTextDir, widthLimit));
}
width = des;
} else {
width = boring.width;
}
final Drawables dr = mDrawables;
if (dr != null) {
width = Math.max(width, dr.mDrawableWidthTop);
width = Math.max(width, dr.mDrawableWidthBottom);
}
if (mHint != null) {
int hintDes = -1;
int hintWidth;
if (mHintLayout != null && mEllipsize == null) {
hintDes = desired(mHintLayout);
}
if (hintDes < 0) {
hintBoring = BoringLayout.isBoring(mHint, mTextPaint, mTextDir, mHintBoring);
if (hintBoring != null) {
mHintBoring = hintBoring;
}
}
if (hintBoring == null || hintBoring == UNKNOWN_BORING) {
if (hintDes < 0) {
hintDes = (int) Math.ceil(Layout.getDesiredWidthWithLimit(mHint, 0,
mHint.length(), mTextPaint, mTextDir, widthLimit));
}
hintWidth = hintDes;
} else {
hintWidth = hintBoring.width;
}
if (hintWidth > width) {
width = hintWidth;
}
}
width += getCompoundPaddingLeft() + getCompoundPaddingRight();
if (mMaxWidthMode == EMS) {
width = Math.min(width, mMaxWidth * getLineHeight());
} else {
width = Math.min(width, mMaxWidth);
}
if (mMinWidthMode == EMS) {
width = Math.max(width, mMinWidth * getLineHeight());
} else {
width = Math.max(width, mMinWidth);
}
// Check against our minimum width
width = Math.max(width, getSuggestedMinimumWidth());
if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) {
width = Math.min(widthSize, width);
}
}我们可以看到 ,当设置的大小是具体值的时候 宽度直接等于MeasureSpec获取的,如果测量模式是AT_MOST (设置wrap_content),就通过测量字体所占的宽度,最终取和系统测量的最小值。
对于上面的例子,我们直接设置为默认值为200即可,代码如下所示:
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
int width = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int height = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST && heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
setMeasuredDimension(200,200);
}else if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
setMeasuredDimension(200,height);
}else if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST){
setMeasuredDimension(width,200);
}
}
运行结果如下图所示,这样我们自定义的View就完成了对wrap_content的处理。
如何支持padding
首先我们将布局文件设置为match_parent,设置上下左右边距为50dp
不做特殊处理时,运行结果如下:
我们可以看到设置的padding并没有生效,我们需要在onDraw中绘制的时候考虑边距即可,代码如下
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
int width = getWidth() - getPaddingLeft() - getPaddingRight();
int height = getHeight() - getPaddingTop() - getPaddingBottom();
int radius = Math.min(width,height) / 2;
canvas.drawCircle(width / 2 + getPaddingLeft() ,height/2 + getPaddingTop(),radius,paint);
}运行效果如下图所示
从上图中可以看出padding生效了,对于自定义View继承Viewgroup时,上述两个问题的处理方式是一样的,只不过因为margin是由父控件决定的,所以测量的时候还要考虑子控件的margin,详细问题会在后面实例讲解。考虑到上面几个问题之后,一个自定义View就比较合格了,不过还缺点什么,比如 如何通过xml设置属性呢?
如何通过xml文件给自定义设置属性
上面例子中,绘制了一个红色的圆形,我们来通过xml属性配置绘制图形的颜色 以及 画笔的style吧
首先新建cycle_attr.xml文件
使用declare-styleable标签声明名字为cycleView的属性列,viewColor 表示view的颜色,format所对应的是属性值的类型reference表示资源文件 ,比如颜色值、图片等,paintStyle表示画笔的属性,这里使用枚举类,也就是说自定义属性只能是这两个值。0表示填充类型,1表示描边类型。
在自定义View中 通过TypedArray 获取自定义的属性
private void init(Context context, AttributeSet attributeSet) {
TypedArray typedArray = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attributeSet,R.styleable.cycleView);
//默认为填充类型
int style = typedArray.getInt(R.styleable.cycleView_paintStyle,0);
if (style == 1){
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
}else {
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
}
//默认为红色
int color = typedArray.getColor(R.styleable.cycleView_viewColor,Color.RED);
paint.setColor(color);
typedArray.recycle();
}
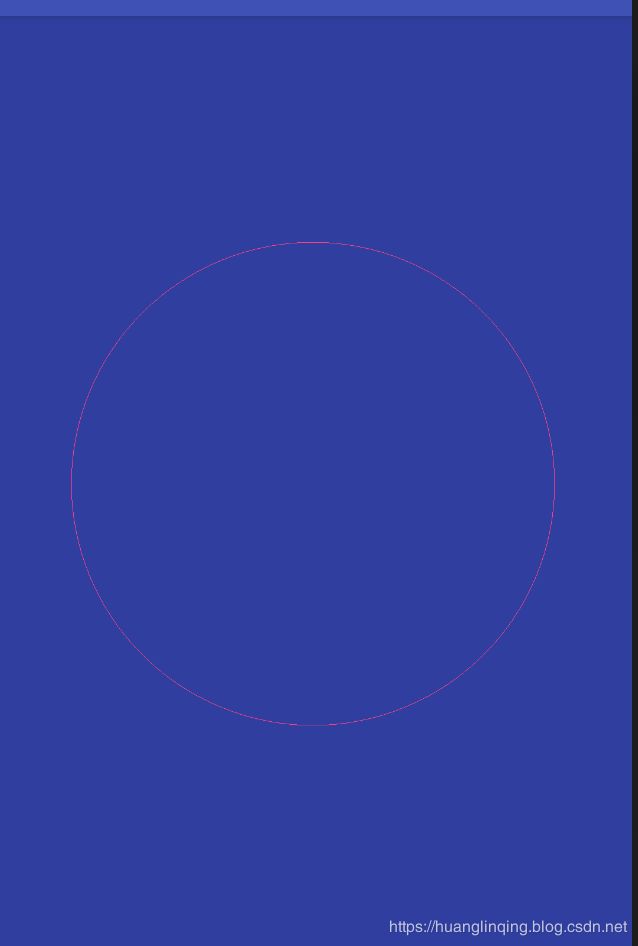
默认设置为红色,类型为填充类型,接下来我们xml中设置自定义的属性,把view颜色改为粉红色,填充类型改为描边运行结果如下图所示
如此一来,一个比较规范的自定义view就完成了。
下一篇:自定义View二篇,如何自定义一个规范的ViewGroup