从dba_hist_active_sess_history里寻找session间的等待关系
dba_hist_active_sess_history每隔10秒钟转储来自v$active_session_history的活动session信息(v$active_session_history.IS_AWR_SAMPLE=Y对应的行会被采集到到dba_hist_active_sess_history),作为AWR、ASH的重要补充,dba_hist_active_sess_history是我们drill down的有效数据来源,特别是session之间存在相互牵制的情况下尤为管用。
我们首先制造一下实验所需的数据,模拟"enq: TX - row lock contention"等待事件
###创建测试表:
create table ad.t1020_1 (id number, c2 varchar2(10)) tablespace ts_pub;
insert into ad.t1020_1 values(1,'A');
insert into ad.t1020_1 values(2,'B');
insert into ad.t1020_1 values(3,'C');
insert into ad.t1020_1 values(4,'D');
commit;
###开四个session,更新记录但不提交,模拟"enq: TX - row lock contention"等待
---session 1:
select * from v$mystat where rownum=1;
SID STATISTIC# VALUE
---------- ---------- ----------
499 0 0
exec dbms_session.set_identifier('session 1');
select module,CLIENT_IDENTIFIER from v$session where sid=499;
update ad.t1020_1 set c2='a' where id=1;
---session 2:
select * from v$mystat where rownum=1;
SID STATISTIC# VALUE
---------- ---------- ----------
2830 0 0
exec dbms_session.set_identifier('session 2');
select module,CLIENT_IDENTIFIER from v$session where sid=2830;
update ad.t1020_1 set c2='b' where id=2;
update ad.t1020_1 set c2='a-session2' where id=1;
---session 3:
select * from v$mystat where rownum=1;
SID STATISTIC# VALUE
---------- ---------- ----------
965 0 0
exec dbms_session.set_identifier('session 3');
select module,CLIENT_IDENTIFIER from v$session where sid=965;
update ad.t1020_1 set c2='c' where id=3;
update ad.t1020_1 set c2='b-session3' where id=2;
---session 4:
select * from v$mystat where rownum=1;
SID STATISTIC# VALUE
---------- ---------- ----------
2375 0 0
exec dbms_session.set_identifier('session 4');
select module,CLIENT_IDENTIFIER from v$session where sid=2375;
update ad.t1020_1 set c2='d' where id=4;
update ad.t1020_1 set c2='c-session4' where id=3;
持续约20分钟,生成一份AWR报告
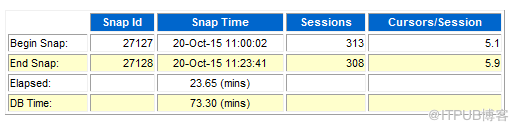
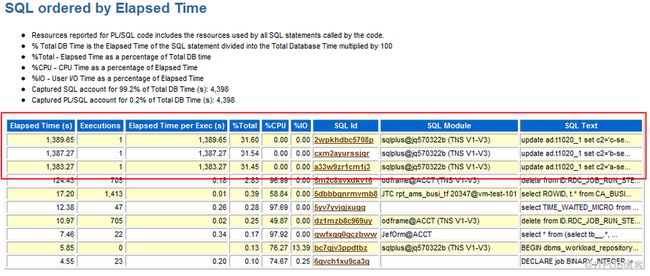

上面三张从AWR报告里摘出的图中可以看出Top 3 三条SQL耗时特别长,但CPU和IO消耗为0,初步判断这三条SQL可能在等待某些资
源,”Enqueue Activity” section里显示有较为严重的TX Transaction等待。
AWR报告提供的信息量非常有限,下钻分析还得借助于dba_hist_active_sess_history
如果v$active_session_history内容已被清理,就需要从dba_hist_active_sess_history里分析当时的详细情况,为加快检索速度,我们把热点时段的
记录保存到一张临时表
create table chh1020 as select * from dba_hist_active_sess_history where sample_time between to_date('20151020 11:00','yyyymmdd hh24:mi') and to_date('20151020 11:23','yyyymmdd hh24:mi');
使用如下语句查询chh1020表
select t.instance_number,t.sample_time,lpad('-',2*(level-1),'-')||t.client_id,t.session_id,t.BLOCKING_INST_ID,t.blocking_session,t.session_serial#,t.sql_id,t.event,t.session_state,level,connect_by_isleaf,connect_by_iscycle from chh1020 t where sample_time between to_date('20151020 11:00:00','yyyymmdd hh24:mi:ss') and to_date('20151020 11:23:00','yyyymmdd hh24:mi:ss') start with blocking_session is not null and event like 'enq: TX - row lock contention%' connect by nocycle sample_time=prior sample_time and session_id=prior blocking_session and session_serial#=prior blocking_session_serial# and instance_number=prior blocking_inst_id;
其中的"enq: TX - row lock contention"可以替换成任何你所感兴趣的event_name,
” sample_time between to_date('20151020 11:00:00','yyyymmdd hh24:mi:ss') and to_date('20151020 11:23:00','yyyymmdd hh24:mi:ss')”可以
替换成更为精确的时间段
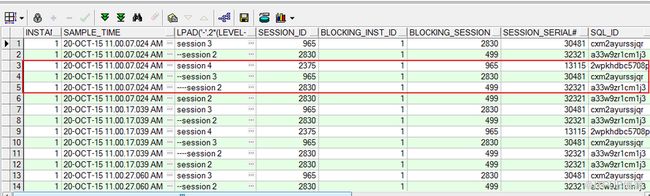
其中connect_by_isleaf=1的行所对应的blocking_session是源头session,也就是我们要重点根治的对象,因为整个row lock持续的时间较长,所以
我们只要观察某个具体的时间点里session间的等待关系,正如红色框里所标示的,session 2(sid=2830)锁住了session 3(sid=965)、session
3(sid=965)锁住了session 4(sid=2375),session 2(sid=2830)本身又被sid=499的session 锁定。
显示格式上采用了逐层缩进的方式以方便区分,缩进最深的行对应的blocking_session便是锁源session的sid。
session 4的sql_id:2wpkhdbc5708p对应的SQL语句执行时被阻塞:
select sql_text from dba_hist_sqltext where sql_id='2wpkhdbc5708p';
SQL_TEXT
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
update ad.t1020_1 set c2='c-session4' where id=3
session 3的sql_id:cxm2ayurssjqr对应的SQL语句执行时被阻塞:
select sql_text from dba_hist_sqltext where sql_id='cxm2ayurssjqr';
SQL_TEXT
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
update ad.t1020_1 set c2='b-session3' where id=2
session 2的sql_id:a33w9zr1cm1j3对应的SQL语句执行时被阻塞:
SQL> select sql_text from dba_hist_sqltext where sql_id='a33w9zr1cm1j3';
SQL_TEXT
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------
update ad.t1020_1 set c2='a-session2' where id=1
session 2的这条SQL被阻塞住了,且阻塞它的sid=499(session 1),因为session 1对应的sql语句瞬间执行完,所以在dba_hist_active_sess_history
里无法找到session 1对应的语句(如果v$active_session_history还未被清除,那么可能会从v$active_session_history里找到session 1对应的sql语
句),即便无法找到也能快速将问题定位到ad.t1020_1表的DML语句上。
通过把dba_hist_active_sess_history里的海量数据有效的关联起来帮助我们解析出当时的数据库里哪些session受到了其它session的影响,借助于
dba_hist_sqlstat、dba_hist_sqltext、dba_hist_sql_plan等视图进一步找出当时引发等待事件的源头SQL语句,为今后的优化提供了有力依据。
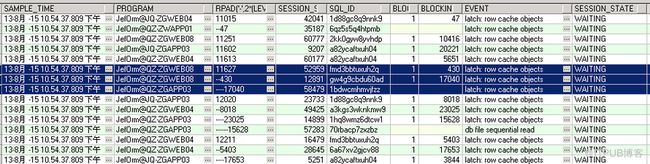
关于这个问题的详细处理过程及原因分析可以参考我的另一篇文章:
select any table权限可能引发大量latch row cache objects等待事件: http://blog.itpub.net/53956/viewspace-1783814/
虽然问题的症结不是由于某一个session所引起,但至少在大并发的情况下我们能够很容易观察到不同session对于row cache latch是串行持有的
来自 “ ITPUB博客 ” ,链接:http://blog.itpub.net/53956/viewspace-1820516/,如需转载,请注明出处,否则将追究法律责任。
转载于:http://blog.itpub.net/53956/viewspace-1820516/