STL源码剖析——heap
Heap堆是常用的数据结构,Heap中也可以存放元素。但是STL中并没有提供Heap容器,只是提供了关于Heap操作的算法。只要支持RandomAccessIterator的容器都可以作为Heap容器。
Heap分为max heap和min heap,max heap中每次取出的结点时heap结构中值最大的结点,min heap中每次取出的结点时heap结构中值最小的结点。
Heap不允许遍历其结点,所以Heap没有迭代器。
在实际应用中,经常用vector作为heap容器,heap经常作为priority queue。
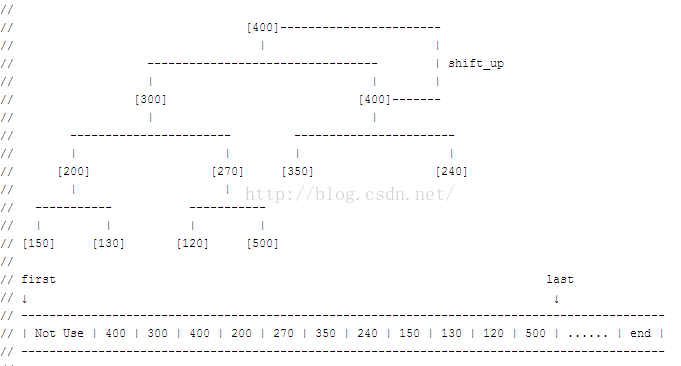
当向heap中插入元素时,插入到末尾,“向上维护”即可:指的是把插入结点与其父结点比较,如果不符合堆得要求则交换,再向上维护其父结点……
从图中可以看到算法的过程是将新加入堆的值(50),层层上挪,直到正确的位置。下面来看,摘录出来的代码。
template
inline void push_heap(RandomAccessIterator first, RandomAccessIterator last) {
// 注意,调用该函数时候,新元素位于最后一个位置(last-1)。
__push_heap_aux(first, last, distance_type(first), value_type(first));
}
template
inline void __push_heap_aux(RandomAccessIterator first,
RandomAccessIterator last, Distance*, T*) {
__push_heap(first, Distance((last - first) - 1), Distance(0),
T(*(last - 1)));
// (last-first)–1代表新元素的索引,0是堆首的索引,*(last - 1)是新加入的值
}
template
void __push_heap(RandomAccessIterator first, Distance holeIndex,
Distance topIndex, T value) {
Distance parent = (holeIndex - 1) / 2; // 找出父節點
while (holeIndex > topIndex && *(first + parent) < value) {
// 尚未到达顶端,且父节点小于新值
// 由于以上使用 operator<,可知 STL heap 是max-heap
*(first + holeIndex) = *(first + parent); // 令洞值为父值
holeIndex = parent; // percolate up:调整洞号,向上提升至父节点。
parent = (holeIndex - 1) / 2; // 新洞的父节点
} // 持续至顶端,或满足 heap 的次序特性为止。
*(first + holeIndex) = value; // 令洞值为新值。
} push_heap的用法是输入迭代器对,并且保证[first,last-1)是最大堆,*(last-1)是新加入的元素。push_heap调用辅助函数__push_heap_aux。至于为什么需要这个辅助函数了?应该是为了提取出distance_type和value_type吧,这两个内联函数的定义,可以参考stl源码剖析迭代器的那章。下面来思考真正的实现函数__push_heap。这个函数需要新加入元素位置holeIndex和堆首位置topIndex,另外还有保存好的新加入值。算法的过程很简单,就是上溯holeIndex,找到真正满足条件的位置(无法继续上回溯),然后把value放入该位置即可。
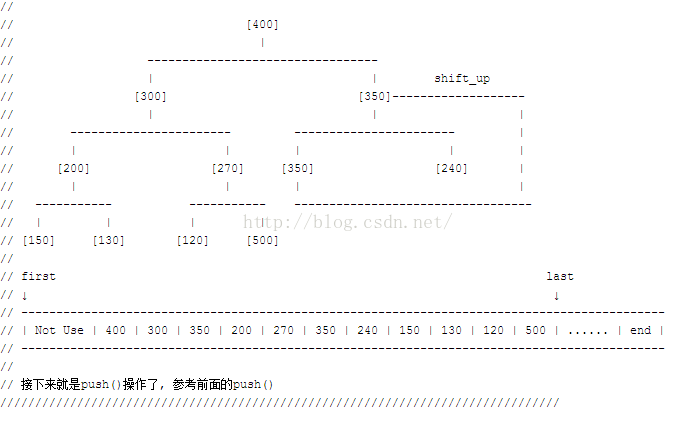
当在heap取出元素时,把末尾元素放到Heap头,"向下维护“即可:指的是父结点与孩子结点比较,如果不满足要求,与较大(较小)一个交换,再维护交换的孩子结点……
pop_heap实际上是一个相反的过程。实现思路是将堆大小加一后,再找出最后一个元素应该放入的位置holeIndex,最后再加入这个值。示意图如下:

下面看看摘录出来的代码,思想类似于push_heap,只需要求出最终的holeIndex。
template
inline void pop_heap(RandomAccessIterator first, RandomAccessIterator last) {
__pop_heap_aux(first, last, value_type(first));
}
template
inline void __pop_heap_aux(RandomAccessIterator first,
RandomAccessIterator last, T*) {
__pop_heap(first, last - 1, last - 1, T(*(last - 1)), distance_type(first));
// pop动作的結果为底层容器的第一個元素。因此,首先设定欲调整值为尾值,然后將首值調至
// 尾节点(所以以上將迭代器result设为last-1)。然后重整 [first, last-1),
// 使之重新成一個合格的 heap。
}
template
inline void __pop_heap(RandomAccessIterator first, RandomAccessIterator last,
RandomAccessIterator result, T value, Distance*) {
*result = *first; // 設定尾值为首值,于是尾值即是結果,
// 可由调用底层容器之 pop_back() 取出尾值。
__adjust_heap(first, Distance(0), Distance(last - first), value);
// 以上欲重新調整 heap,洞号为 0,欲調整值为value。
}
template
void __adjust_heap(RandomAccessIterator first, Distance holeIndex,
Distance len, T value) {
Distance topIndex = holeIndex;
Distance secondChild = 2 * holeIndex + 2; // 洞节点之右子节点
while (secondChild < len) {
// 比较洞节点之左右兩个子值,然后以 secondChild 代表较大子节点。
if (*(first + secondChild) < *(first + (secondChild - 1)))
secondChild--;
// Percolate down:令较大大子值为洞值,再令洞号下移至较大子节点处。
*(first + holeIndex) = *(first + secondChild);
holeIndex = secondChild;
// 找出新洞节点的右子节点
secondChild = 2 * (secondChild + 1);
}
if (secondChild == len) { // 沒有右子节点,只有左子节点
// Percolate down:令左子值为洞值,再令洞号下移至左子节点处。
*(first + holeIndex) = *(first + (secondChild - 1));
holeIndex = secondChild - 1;
}
// 將欲调整值填入目前的洞号內。注意,此時肯定滿足次序特性。
// 依侯捷之见,下面直接改為 *(first + holeIndex) = value; 应该可以。
__push_heap(first, holeIndex, topIndex, value);
} 类似于push_heap,pop_heap也是调用辅助函数__pop_heap_aux。__pop_heap_aux调用__pop_heap。__pop_heap调用__adjust_heap调整holeIndex,最终在holeIndex处放入value(原最后一个的值)。关键代码是__adjust_heap中的循环。循环的主要意思是将holeIndex不断下放,直到最底层。最后的if语句的意思是,如果最底层有左子节点,而没有右子节点,那么最终位置肯定是这个左子节点。最后一句代码的意思是加入value到holeIndex,由于已经调整完毕,所以一个赋值操作也可以达到要求,参见侯捷注释。
sort_heap就比较简单了,不断将极值移动到末尾,不断pop_heap。
// 以下這個 sort_heap() 不允許指定「大小比較標準」
template
void sort_heap(RandomAccessIterator first, RandomAccessIterator last) {
// 以下,每執行一次 pop_heap(),極值(在STL heap中為極大值)即被放在尾端。
// 扣除尾端再執行一次 pop_heap(),次極值又被放在新尾端。一直下去,最後即得
// 排序結果。
while (last - first > 1)
pop_heap(first, last--); // 每執行 pop_heap() 一次,操作範圍即退縮一格。
} 最后要将的是make_heap,即将一个迭代器对里面的内容构造为最大堆。代码如下:
// 將 [first,last) 排列為一個 heap。
template
inline void make_heap(RandomAccessIterator first, RandomAccessIterator last) {
__make_heap(first, last, value_type(first), distance_type(first));
}
// 以下這組 make_heap() 不允許指定「大小比較標準」。
template
void __make_heap(RandomAccessIterator first, RandomAccessIterator last, T*,
Distance*) {
if (last - first < 2) return; // 如果長度為 0 或 1,不必重新排列。
Distance len = last - first;
// 找出第一個需要重排的子樹頭部,以 parent 標示出。由於任何葉節點都不需執行
// perlocate down,所以有以下計算。parent 命名不佳,名為 holeIndex 更好。
Distance parent = (len - 2) / 2;
while (true) {
// 重排以 parent 為首的子樹。len 是為了讓 __adjust_heap() 判斷操作範圍
__adjust_heap(first, parent, len, T(*(first + parent)));
if (parent == 0) return; // 走完根節點,就結束。
parent--; // (即將重排之子樹的)頭部向前一個節點
}
} __make_heap中代码的思路也很简单。从原序列的中间位置开始不断调整(调用__adjust_heap),每次调整的目的是以当前位置为根的构建一个子堆。至于为什么从中间位置开始就可以了?原因很简单,最底层元素的数目大致就会占了一半了。
下面是完整代码分析:
/*
*
* Copyright (c) 1994
* Hewlett-Packard Company
*
* Permission to use, copy, modify, distribute and sell this software
* and its documentation for any purpose is hereby granted without fee,
* provided that the above copyright notice appear in all copies and
* that both that copyright notice and this permission notice appear
* in supporting documentation. Hewlett-Packard Company makes no
* representations about the suitability of this software for any
* purpose. It is provided "as is" without express or implied warranty.
*
* Copyright (c) 1997
* Silicon Graphics Computer Systems, Inc.
*
* Permission to use, copy, modify, distribute and sell this software
* and its documentation for any purpose is hereby granted without fee,
* provided that the above copyright notice appear in all copies and
* that both that copyright notice and this permission notice appear
* in supporting documentation. Silicon Graphics makes no
* representations about the suitability of this software for any
* purpose. It is provided "as is" without express or implied warranty.
*/
/* NOTE: This is an internal header file, included by other STL headers.
* You should not attempt to use it directly.
*/
#ifndef __SGI_STL_INTERNAL_HEAP_H
#define __SGI_STL_INTERNAL_HEAP_H
__STL_BEGIN_NAMESPACE
#if defined(__sgi) && !defined(__GNUC__) && (_MIPS_SIM != _MIPS_SIM_ABI32)
#pragma set woff 1209
#endif

template
void __push_heap(RandomAccessIterator first, Distance holeIndex,
Distance topIndex, T value)
{
// 首先找出待处理元素的父结点
Distance parent = (holeIndex - 1) / 2;
// 判断当前待处理结点是否优先级高于其父结点, 如果是则将其父结点向下移动
// 设置当前结点为父结点位置, 继续, 直到优先级小于父结点或者已经到达heap顶端
while (holeIndex > topIndex && *(first + parent) < value) {
*(first + holeIndex) = *(first + parent);
holeIndex = parent;
parent = (holeIndex - 1) / 2;
}
// 将找到的合适的位置设置成正确值
*(first + holeIndex) = value;
}
template
inline void __push_heap_aux(RandomAccessIterator first,
RandomAccessIterator last, Distance*, T*)
{
// 因为first所指的那个元素不是heap的组成元素, 所以计算距离要减去1
__push_heap(first, Distance((last - first) - 1), Distance(0),
T(*(last - 1)));
}
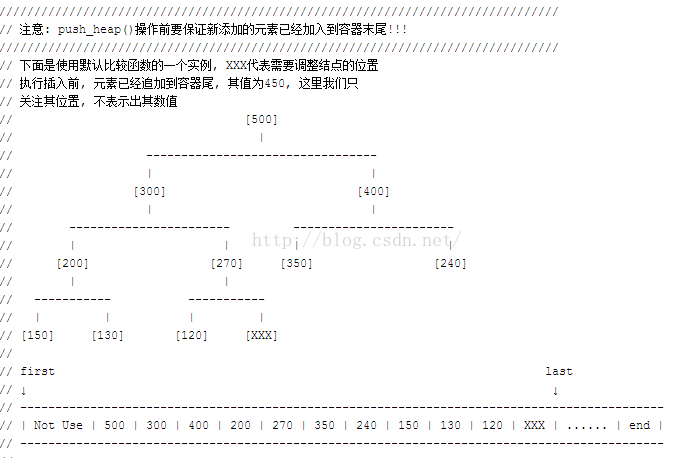
// 调用此函数前要先把待处理元素追加到容器末尾
template
inline void push_heap(RandomAccessIterator first, RandomAccessIterator last)
{
__push_heap_aux(first, last, distance_type(first), value_type(first));
}
template
void __push_heap(RandomAccessIterator first, Distance holeIndex,
Distance topIndex, T value, Compare comp)
{
Distance parent = (holeIndex - 1) / 2;
while (holeIndex > topIndex && comp(*(first + parent), value)) {
*(first + holeIndex) = *(first + parent);
holeIndex = parent;
parent = (holeIndex - 1) / 2;
}
*(first + holeIndex) = value;
}
template
inline void __push_heap_aux(RandomAccessIterator first,
RandomAccessIterator last, Compare comp,
Distance*, T*)
{
__push_heap(first, Distance((last - first) - 1), Distance(0),
T(*(last - 1)), comp);
}
// 这个除了用户自己指定优先级决策判别式外和默认的无区别
template
inline void push_heap(RandomAccessIterator first, RandomAccessIterator last,
Compare comp)
{
__push_heap_aux(first, last, comp, distance_type(first), value_type(first));
}

template
void __adjust_heap(RandomAccessIterator first, Distance holeIndex,
Distance len, T value)
{
Distance topIndex = holeIndex;
Distance secondChild = 2 * holeIndex + 2; // 弹出元素的有子孩
// 调整heap元素位置
while (secondChild < len) {
// 选择两个子孩中较大的进行操作, 使用secondChild表示其偏移
if (*(first + secondChild) < *(first + (secondChild - 1)))
secondChild--;
// 将较大元素向上填充, 并将整体偏移向下调整, 继续调整
*(first + holeIndex) = *(first + secondChild);
holeIndex = secondChild;
secondChild = 2 * (secondChild + 1);
}
if (secondChild == len) {
*(first + holeIndex) = *(first + (secondChild - 1));
holeIndex = secondChild - 1;
}
// 这里就是shift_up过程了, 将最初的heap末尾元素向上调整
// 侯捷老师对这里的理解有误, :-), 人非圣贤, 孰能无过, ^_^
__push_heap(first, holeIndex, topIndex, value);
}
template
inline void __pop_heap(RandomAccessIterator first, RandomAccessIterator last,
RandomAccessIterator result, T value, Distance*)
{
// 将弹出的元素调整到heap末尾, 这个元素需要用户手动弹出
*result = *first;
// 去掉末尾哪个弹出的元素, 调整heap
__adjust_heap(first, Distance(0), Distance(last - first), value);
}
template
inline void __pop_heap_aux(RandomAccessIterator first,
RandomAccessIterator last, T*)
{
__pop_heap(first, last - 1, last - 1, T(*(last - 1)), distance_type(first));
}
template
inline void pop_heap(RandomAccessIterator first, RandomAccessIterator last)
{
__pop_heap_aux(first, last, value_type(first));
}
template
void __adjust_heap(RandomAccessIterator first, Distance holeIndex,
Distance len, T value, Compare comp)
{
Distance topIndex = holeIndex;
Distance secondChild = 2 * holeIndex + 2;
while (secondChild < len) {
if (comp(*(first + secondChild), *(first + (secondChild - 1))))
secondChild--;
*(first + holeIndex) = *(first + secondChild);
holeIndex = secondChild;
secondChild = 2 * (secondChild + 1);
}
if (secondChild == len) {
*(first + holeIndex) = *(first + (secondChild - 1));
holeIndex = secondChild - 1;
}
__push_heap(first, holeIndex, topIndex, value, comp);
}
template
inline void __pop_heap(RandomAccessIterator first, RandomAccessIterator last,
RandomAccessIterator result, T value, Compare comp,
Distance*)
{
*result = *first;
__adjust_heap(first, Distance(0), Distance(last - first), value, comp);
}
template
inline void __pop_heap_aux(RandomAccessIterator first,
RandomAccessIterator last, T*, Compare comp)
{
__pop_heap(first, last - 1, last - 1, T(*(last - 1)), comp,
distance_type(first));
}
template
inline void pop_heap(RandomAccessIterator first, RandomAccessIterator last,
Compare comp)
{
__pop_heap_aux(first, last, value_type(first), comp);
}
// 这个没设么好说的, 参考上面的分析吧
template
void __make_heap(RandomAccessIterator first, RandomAccessIterator last, T*,
Distance*)
{
if (last - first < 2) return;
Distance len = last - first;
Distance parent = (len - 2)/2;
while (true) {
__adjust_heap(first, parent, len, T(*(first + parent)));
if (parent == 0) return;
parent--;
}
}
template
inline void make_heap(RandomAccessIterator first, RandomAccessIterator last)
{
__make_heap(first, last, value_type(first), distance_type(first));
}
template
void __make_heap(RandomAccessIterator first, RandomAccessIterator last,
Compare comp, T*, Distance*)
{
if (last - first < 2) return;
Distance len = last - first;
Distance parent = (len - 2)/2;
while (true) {
__adjust_heap(first, parent, len, T(*(first + parent)), comp);
if (parent == 0) return;
parent--;
}
}
template
inline void make_heap(RandomAccessIterator first, RandomAccessIterator last,
Compare comp)
{
__make_heap(first, last, comp, value_type(first), distance_type(first));
}
// 这个能保证heap有序, 其实个人感觉没啥必要, 这样还不如直接用平衡二叉树
template
void sort_heap(RandomAccessIterator first, RandomAccessIterator last)
{
while (last - first > 1) pop_heap(first, last--);
}
template
void sort_heap(RandomAccessIterator first, RandomAccessIterator last,
Compare comp)
{
while (last - first > 1) pop_heap(first, last--, comp);
}
#if defined(__sgi) && !defined(__GNUC__) && (_MIPS_SIM != _MIPS_SIM_ABI32)
#pragma reset woff 1209
#endif
__STL_END_NAMESPACE
#endif /* __SGI_STL_INTERNAL_HEAP_H */
// Local Variables:
// mode:C++
// End: