用户登录对接QQ、微信、微博等三方登录
1.1 三方登录介绍
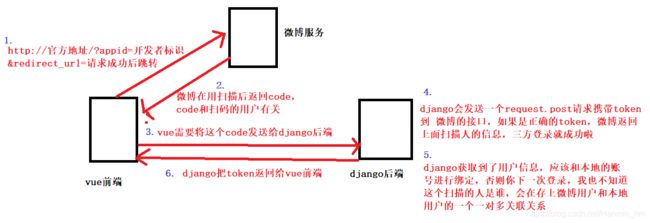
1、三方登录流程(以微博为例)
1)前端获取认证code
1. 在Vue页面加载时动态发送请求获取微博授权url
2. django收到请求的url后,通过微博应用ID(client_id)和回调地址(redirect_uri)动态生成授权url返回给Vue
3. 当用户点击上面的url进行扫码,授权成功会跳转我们的回调界面并附加code参数
4. Vue获取到微博返回的code后,会将code发送给django后端(上面的redirect_uri)
2)获取微博access_token
后端获取code后,结合client_id、client_secret、redirect_uri参数进行传递,获取微博access_token
3)获取微博用户基本信息并保存到数据库
使用获得的access_token调用获取用户基本信息的接口,获取用户第三方平台的基本信息
用户基本信息保存到数据库,然后关联本地用户,然后将用户信息返回给前端
4)生成token给Vue
django后端借助微博认证成功后,可以使用JWT生成token,返回给Vue
Vue将token存储到localStorage中,以便用户访问其他页面进行身份验证
2、oauth认证原理
1. OAuth是一个开放标准,允许用户让第三方应用访问该用户在某一网站上存储的私密的资源,而无需将用户名和密码提供给第三方应用。
2. OAuth允许用户提供一个令牌,而不是用户名和密码来访问他们存放在特定服务提供者的数据。
3. 这个code如果能出三方换取到数据就证明这个用户是三方真实的用户
3、为什么使用三方登录
1. 服务方希望用户注册, 而用户懒得填注册时的各种信息(主要是为了保证用户的唯一性,各种用户名已占用,密码格式限制).
2. 而像微信, QQ, 微博等几乎每个人都会安装的应用中用户肯定会在其中某一个应用中已经注册过,证明该用户在已经注册的应用中的唯一性.
3. 第三方登录的实质就是在授权时获得第三方应用提供的代表了用户在第三方应用中的唯一性的openid.并将openid储存在第三方服务控制的本地储存.
4、第三方登录与本地登录的关联(三种情况)
1)情况1: 本地未登录,第一次登录第三方
此时相当于注册,直接把第三方信息拉取来并注册成本地用户就可以了,并建立本地用户与第三方用户(openid)的绑定关系
2)情况2:本地未登录,再次登录第三方
此时用户已注册,获取到openid后直接找出对应的本地用户即可
3)情况3:本地登录,并绑定第三方
*这个只要将获取到的openid绑定到本地用户就可以了*
1.2 微博申请应用
微博申请应用参考
官方微博接入文档
1、前端Vue
vue init webpack webssh
npm install --save axios
- src/router/index.js 路由添加
import Vue from 'vue'
import Router from 'vue-router'
import HelloWorld from '@/components/HelloWorld'
import Login from '@/components/Login'
import WeiboCallback from '@/components/WeiboCallback'
import UserBind from '@/components/UserBind'
Vue.use(Router)
export default new Router({
mode: 'history',
routes: [
{ path: '/', name: 'HelloWorld', component: HelloWorld },
{ path: '/login', name: 'Login', component: Login }, // 登录页面
{ path: '/weibo_callback', name: 'WeiboCallback', component: WeiboCallback }, // 通过空页面发送code给后端
{ path: '/userbind', name: 'UserBind', component: UserBind }, // 将本地用户与第三方用户绑定
]
})
- src/components/Login.vue 登录页面
<template>
<div>
<a :href="weibo_url" class="weibo_login">微博</a>
</div>
</template>
<style>
</style>
<script>
import axios from "axios";
export default {
data: function(){
return {
weibo_url: '' // 动态从后端获取的微博扫码URL
}
},
mounted(){
this.get_weibo_url()
},
methods: {
get_weibo_url: function(){
// http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/weibo_url/
axios({
url: 'http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/weibo_url/',
method: 'get'
}).then(res=>{
this.weibo_url = res.data.weibo_url
})
}
}
};
</script>
- src/components/WeiboCallback.vue 通过空页面发送code给后端
<template>
<p>跳转中....</p>
</template>
<script>
import axios from 'axios'
export default {
mounted(){
this.get_code()
},
methods: {
get_code: function(){
let code = this.$route.query.code // 获取微博的验证code
console.log(code)
axios({
url:'http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/weibo_back/?code=' + code,
method: 'get'
}).then(res=>{
console.log(res)
if (res.data.code == 200) {
console.log('成功')
localStorage.username = res.data.username
localStorage.user_id = res.data.user_id
localStorage.token = res.data.token
window.location.href = '/'
}
if (res.data.code == 201) {
console.log('失败') // 如果用户未绑定,跳转到绑定页面
localStorage.access_token = res.data.response
window.location.href = '/userbind'
}
})
}
}
}
</script>
- src/components/UserBind.vue 将本地用户与第三方用户绑定
<template>
<div>
<form @submit.prevent="send_bind_info">
<p>
<label>输入账号:</label>
<input type="account" name="account" id="account" v-model="account">
</p>
<p>
<label>输入密码:</label>
<input type="password" name="pwd" id="pwd" v-model="password">
</p>
<p>
<input type="submit" value="注 册" name>
</p>
</form>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<style>
</style>
<script>
document.title = "绑定页面";
import axios from "axios";
export default {
// axios-> access_token
data: function() {
return {
password: "",
account: "",
};
},
methods: {
send_bind_info: function() {
let post_data = new FormData();
let access_token = localStorage.access_token;
post_data.append("password", this.password);
post_data.append("account", this.account);
post_data.append("access_token", access_token);
axios({
url: "http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/bind_user/",
method: "post",
data: post_data
}).then(res => {});
}
}
};
</script>
2、django后端
# requirements.txt
Django==2.0.4
djangorestframework==3.9.2
djangorestframework-jwt==1.11.0
django-cors-headers==3.0.2
- setting.py 配置使用TWT、corsheaders、rest_framework
INSTALLED_APPS = [
'rest_framework.authtoken',
'rest_framework',
'users',
'corsheaders',
]
MIDDLEWARE = [
'corsheaders.middleware.CorsMiddleware',
# 'django.middleware.common.CommonMiddleware',
]
''' 配置jwt验证 '''
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
# 身份认证
'DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES': (
'rest_framework_jwt.authentication.JSONWebTokenAuthentication',
'rest_framework.authentication.SessionAuthentication',
'rest_framework.authentication.BasicAuthentication',
),
}
import datetime
JWT_AUTH = {
'JWT_AUTH_HEADER_PREFIX': 'JWT',
'JWT_EXPIRATION_DELTA': datetime.timedelta(days=1),
'JWT_RESPONSE_PAYLOAD_HANDLER':'users.views.jwt_response_payload_handler', # 重新login登录返回函数
}
AUTH_USER_MODEL='users.User' # 指定使用users APP中的 model User进行验证
'''配置cors'''
CORS_ALLOW_CREDENTIALS = True
CORS_ORIGIN_ALLOW_ALL = True
'''微博相关配置信息'''
WEIBO_APP_KEY = '3516473472'
WEIBO_APP_SECRET = '7862ee35a0dc6f0345d0464dc34f14fc'
WEIBO_FUNC_BACK = 'http://127.0.0.1:8080/weibo_callback' # VUE的回调
- url.py 总路由
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path,include
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path('api/', include('users.urls')),
]
- users/urls.py
#! /usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from django.urls import path,re_path
from . import views
urlpatterns = [
re_path(r'register/',views.RegisterView.as_view(),name='register'),
re_path(r'weibo_url/', views.WeiboUrl.as_view(), name='weibo_url'),
re_path(r'weibo_back/',views.WeiboBack.as_view(),name='weibo_back'),
re_path(r'bind_user/',views.BindUser.as_view(),name='bind_user'),
]
- users/models.py
from django.db import models
from django.contrib.auth.models import AbstractUser
class User(AbstractUser):
username = models.CharField(max_length=64, unique=True)
password = models.CharField(max_length=255)
phone = models.CharField(max_length=64,blank=True,null=True)
class SocialUser(models.Model):
user = models.ForeignKey(User,on_delete=models.CASCADE,verbose_name='用户')
platfrom_type_choices = (
(1,'web'),
(2,'移动'),
)
platfrom_ID = models.IntegerField(choices=platfrom_type_choices,verbose_name='平台类型')
platfrom_choices = (
(1,'QQ'),
(2,'微博'),
(3,'微信'),
)
platfrom_type = models.IntegerField(choices=platfrom_choices,verbose_name='社交平台')
uid = models.CharField(max_length=100,verbose_name='用户ID')
def __str__(self):
return self.user.username
- users/serializers.py
#! /usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from rest_framework_jwt.settings import api_settings
from rest_framework import serializers
from users.models import User
from users.models import SocialUser
class UserSerializer(serializers.Serializer):
username = serializers.CharField()
password = serializers.CharField()
phone = serializers.CharField(required=False,allow_blank=True)
token = serializers.CharField(read_only=True)
def create(self, data):
user = User.objects.create(**data)
user.set_password(data.get('password'))
user.save()
# 补充生成记录登录状态的token
jwt_payload_handler = api_settings.JWT_PAYLOAD_HANDLER
jwt_encode_handler = api_settings.JWT_ENCODE_HANDLER
payload = jwt_payload_handler(user) # 创建载荷
token = jwt_encode_handler(payload) # 创建token
user.token = token
return user
class SocialUserSerializer(serializers.Serializer):
user_id = serializers.IntegerField()
platfrom_ID = serializers.IntegerField() # 平台类型(web/移动)
platfrom_type = serializers.IntegerField() # 社交平台(微博/微信/QQ)
uid = serializers.IntegerField() # 社交平台唯一ID
def create(self, validated_data):
social_user = SocialUser.objects.create(**validated_data)
return social_user
- users/views.py
from django.shortcuts import render
import json
from rest_framework.views import APIView
from rest_framework.views import Response
from rest_framework.permissions import IsAuthenticated
from rest_framework_jwt.authentication import JSONWebTokenAuthentication
from urllib.parse import urlencode
import requests
from rest_framework_jwt.settings import api_settings
from django.db import transaction
from rest_framework import serializers
from django.core.exceptions import ValidationError
from weiboLogin import settings
from users import models
from users.serializers import UserSerializer
from users.serializers import SocialUserSerializer
# 用户注册
class RegisterView(APIView):
def post(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
serializer = UserSerializer(data=request.data)
if serializer.is_valid():
serializer.save()
return Response(serializer.data, status=201)
return Response(serializer.errors, status=400)
# 重写用户登录返回函数
def jwt_response_payload_handler(token, user=None, request=None):
'''
:param token: jwt生成的token值
:param user: User对象
:param request: 请求
'''
return {
'test':'aaaa',
'token': token,
'user': user.username,
'userid': user.id
}
# 生成前端跳转到微博扫码页面的url
class WeiboUrl(APIView):
'''
生成微博的登陆页面路由地址
https://api.weibo.com/oauth2/authorize? # 微博oauth认证地址
client_id=4152203033& # 注册开发者id
response_type=code&
redirect_uri=http://127.0.0.1:8080/weibo_callback/ # 获取code后将code回调给后端地址
'''
def get(self, request):
url = 'https://api.weibo.com/oauth2/authorize?'
data = {
'client_id': settings.WEIBO_APP_KEY,
'response_type': 'code',
'redirect_uri': settings.WEIBO_FUNC_BACK,
}
weibo_url = url + urlencode(data)
# https://api.weibo.com/oauth2/authorize?client_id=4152203033&response_type=code&redirect_uri=http://127.0.0.1:8000/api/weibo_back/
return Response({'weibo_url': weibo_url})
# 微博扫码成功后携带code调用此接口,认证成功返回jwt token
class WeiboBack(APIView):
'''
通过回调连接,获取access_token
https://api.weibo.com/oauth2/access_token?
client_id=YOUR_CLIENT_ID
client_secret=YOUR_CLIENT_SECRET&
grant_type=authorization_code&
code=CODE
redirect_uri=YOUR_REGISTERED_REDIRECT_URI
'''
def get(self, request):
code = request.query_params.get('code') # code为微博微博认证的code
data = {
'client_id': settings.WEIBO_APP_KEY,
'client_secret': settings.WEIBO_APP_SECRET,
'grant_type': 'authorization_code',
'code': code,
'redirect_uri': settings.WEIBO_FUNC_BACK,
}
url = 'https://api.weibo.com/oauth2/access_token'
response = requests.post(url=url, data=data).json() # 拿取请求的返回结果
# {'access_token': '2.00jqYNTGfgNAXEbd85e6c672uTGF8E',
# 'remind_in': '157679999', 'expires_in': 157679999,
# 'uid': '5928542965', 'isRealName': 'true'}
print(response)
uid = response.get('uid') # uid是微博三方的唯一id
if not uid: # 获取不到则为微博code错误
return Response({'code': 201, 'error': '三方授权失败'})
try:
# 判断当前UID是否存在与数据库中,如果存在,代表用户可以登陆的
user = models.SocialUser.objects.get(uid=uid)
except:
# 如果不存在,代表这个用户不能登陆,先得跳转到绑定页面,将本地用户与微博用户进行绑定
return Response(
{
'code': 201,
'response': json.dumps(response)
}
)
else: # 如果获取到uid,就生成token返回给vue
jwt_payload_handler = api_settings.JWT_PAYLOAD_HANDLER
jwt_encode_handler = api_settings.JWT_ENCODE_HANDLER
payload = jwt_payload_handler(user.user) # 创建载荷
token = jwt_encode_handler(payload) # 创建token
return Response({
'code': 200,
'token': token,
'username': user.user.username,
'user_id': user.user.id,
})
# 将微博用户绑定到本地用户
class BindUser(APIView):
def post(self, request):
account = request.data.get('account') # 绑定的账号
password = request.data.get('password') # 绑定的密码
user_url = "https://api.weibo.com/2/users/show.json?access_token=%s&uid=%s"
access_token = json.loads(request.data.get('access_token'))
get_url = user_url % (access_token['access_token'], access_token['uid'])
# {'access_token': '2.00jqYNTGfgNAXEbd85e6c672uTGF8E','uid': '5928542965', 'isRealName': 'true'}
data = requests.get(url=get_url).json() # 通过token获取微博详细信息
if data.get('error'):
return Response({
'code': 201,
'token': access_token,
})
else:
try:
serializer = UserSerializer(data={'username':account,'password':password})
if serializer.is_valid():
# 创建本地用户与微博用户关联
with transaction.atomic():
save_id = transaction.savepoint() # 创建一个保存点
try:
user = serializer.save()
socialuser = SocialUserSerializer(data={
"user_id": user.id,
"platfrom_ID" : 1,
"platfrom_type": 2,
"uid" : data['id']
})
if socialuser.is_valid():
socialuser.save()
return Response({
'code': 200,
'token': user.token,
'username': user.username,
'user_id': user.id,
})
else:
transaction.savepoint_rollback(save_id) # 出现异常退回到保存点
except ValidationError:
raise
except Exception as e:
transaction.savepoint_rollback(save_id)
finally:
# 提交事务
transaction.savepoint_commit(save_id)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
return Response(status=400)