本文参考雷神博文整理:https://blog.csdn.net/leixiaohua1020。
s : 传进去的AVFormatContext 结构体
pb:函数调用成功之后创建的AVIOContext结构体。
url:输入输出协议的地址(文件也是一种“广义”的协议,对于文件来说就是文件的路径)。
flags:打开地址的方式。可以选择只读,只写,或者读写。取值如下。
AVIO_FLAG_READ:只读。
AVIO_FLAG_WRITE:只写。
AVIO_FLAG_READ_WRITE:读写。
options:目前还没有用过。
static int io_open_default(AVFormatContext *s, AVIOContext **pb,
const char *url, int flags, AVDictionary **options)
{
int loglevel;
if (!strcmp(url, s->url) ||
s->iformat && !strcmp(s->iformat->name, "image2") ||
s->oformat && !strcmp(s->oformat->name, "image2")
) {
loglevel = AV_LOG_DEBUG;
} else
loglevel = AV_LOG_INFO;
av_log(s, loglevel, "Opening \'%s\' for %s\n", url, flags & AVIO_FLAG_WRITE ? "writing" : "reading");
#if FF_API_OLD_OPEN_CALLBACKS
FF_DISABLE_DEPRECATION_WARNINGS
if (s->open_cb)
return s->open_cb(s, pb, url, flags, &s->interrupt_callback, options);
FF_ENABLE_DEPRECATION_WARNINGS
#endif
return ffio_open_whitelist(pb, url, flags, &s->interrupt_callback, options, s->protocol_whitelist, s->protocol_blacklist);
}
此函数最主要是调用ffio_open_whitelist(),ffio_open_whitelist()的作用相当于旧版本的avio_open2(),
int ffio_open_whitelist(AVIOContext **s, const char *filename, int flags,
const AVIOInterruptCB *int_cb, AVDictionary **options,
const char *whitelist, const char *blacklist
)
{
URLContext *h;
int err;
err = ffurl_open_whitelist(&h, filename, flags, int_cb, options, whitelist, blacklist, NULL);
if (err < 0)
return err;
err = ffio_fdopen(s, h);
if (err < 0) {
ffurl_close(h);
return err;
}
return 0;
}
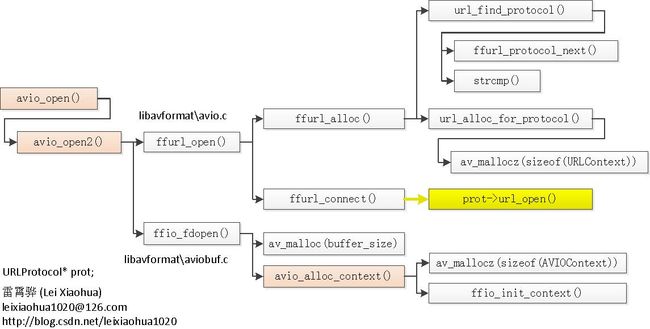
从ffio_open_whitelist()的源代码可以看出,它主要调用了2个函数:ffurl_open_whitelist()和ffio_fdopen()。其中ffurl_open_whitelist()用于初始化URLContext,ffio_fdopen()用于根据URLContext初始化AVIOContext。URLContext中包含的URLProtocol完成了具体的协议读写等工作。AVIOContext则是在URLContext的读写函数外面加上了一层“包装”(通过retry_transfer_wrapper()函数)。此函数调用结构如下:
URLProtocol和URLContext
URLContext ,URLProtocol的定义位于libavformat\url.h
typedef struct URLContext {
const AVClass *av_class; /**< information for av_log(). Set by url_open(). */
const struct URLProtocol *prot;
void *priv_data;
char *filename; /**< specified URL */
int flags;
int max_packet_size; /**< if non zero, the stream is packetized with this max packet size */
int is_streamed; /**< true if streamed (no seek possible), default = false */
int is_connected;
AVIOInterruptCB interrupt_callback;
int64_t rw_timeout; /**< maximum time to wait for (network) read/write operation completion, in mcs */
const char *protocol_whitelist;
const char *protocol_blacklist;
int min_packet_size; /**< if non zero, the stream is packetized with this min packet size */
} URLContext;
typedef struct URLProtocol {
const char *name;
int (*url_open)( URLContext *h, const char *url, int flags);
/**
* This callback is to be used by protocols which open further nested
* protocols. options are then to be passed to ffurl_open()/ffurl_connect()
* for those nested protocols.
*/
int (*url_open2)(URLContext *h, const char *url, int flags, AVDictionary **options);
int (*url_accept)(URLContext *s, URLContext **c);
int (*url_handshake)(URLContext *c);
/**
* Read data from the protocol.
* If data is immediately available (even less than size), EOF is
* reached or an error occurs (including EINTR), return immediately.
* Otherwise:
* In non-blocking mode, return AVERROR(EAGAIN) immediately.
* In blocking mode, wait for data/EOF/error with a short timeout (0.1s),
* and return AVERROR(EAGAIN) on timeout.
* Checking interrupt_callback, looping on EINTR and EAGAIN and until
* enough data has been read is left to the calling function; see
* retry_transfer_wrapper in avio.c.
*/
int (*url_read)( URLContext *h, unsigned char *buf, int size);
int (*url_write)(URLContext *h, const unsigned char *buf, int size);
int64_t (*url_seek)( URLContext *h, int64_t pos, int whence);
int (*url_close)(URLContext *h);
int (*url_read_pause)(URLContext *h, int pause);
int64_t (*url_read_seek)(URLContext *h, int stream_index,
int64_t timestamp, int flags);
int (*url_get_file_handle)(URLContext *h);
int (*url_get_multi_file_handle)(URLContext *h, int **handles,
int *numhandles);
int (*url_get_short_seek)(URLContext *h);
int (*url_shutdown)(URLContext *h, int flags);
int priv_data_size;
const AVClass *priv_data_class;
int flags;
int (*url_check)(URLContext *h, int mask);
int (*url_open_dir)(URLContext *h);
int (*url_read_dir)(URLContext *h, AVIODirEntry **next);
int (*url_close_dir)(URLContext *h);
int (*url_delete)(URLContext *h);
int (*url_move)(URLContext *h_src, URLContext *h_dst);
const char *default_whitelist;
} URLProtocol;
从URLProtocol的定义可以看出,其中包含了用于协议读写的函数指针。例如:
url_open():打开协议。
url_read():读数据。
url_write():写数据。
url_close():关闭协议。
每种具体的协议都包含了一个URLProtocol结构体,例如:
FILE协议(“文件”在FFmpeg中也被当做一种协议)的结构体ff_file_protocol的定义如下所示(位于libavformat\file.c)。
URLProtocol ff_file_protocol = {
.name = "file",
.url_open = file_open,
.url_read = file_read,
.url_write = file_write,
.url_seek = file_seek,
.url_close = file_close,
.url_get_file_handle = file_get_handle,
.url_check = file_check,
.priv_data_size = sizeof(FileContext),
.priv_data_class = &file_class,
};
在使用FILE协议进行读写的时候,调用url_open()实际上就是调用了file_open()函数,这里限于篇幅不再对file_open()的源代码进行分析。file_open()函数实际上调用了系统的打开文件函数open()。同理,调用url_read()实际上就是调用了file_read()函数;file_read()函数实际上调用了系统的读取文件函数read()。url_write(),url_seek()等函数的道理都是一样的。
从代码中可以看出,URLProtocol结构体是URLContext结构体的一个成员。由于还没有对URLContext结构体进行详细研究,有关该结构体的代码不再做过多分析。
ffurl_open_whitelist()
前文提到AVIOContext中主要调用了2个函数:ffurl_open_whitelist()和ffio_fdopen()。其中ffurl_open_whitelist()用于初始化URLContext,ffio_fdopen()用于根据URLContext初始化AVIOContext。下面首先看一下初始化URLContext的函数ffurl_open_whitelist()。
ffurl_open_whitelist()的函数定义位于libavformat\avio.c中,如下所示。
int ffurl_open_whitelist(URLContext **puc, const char *filename, int flags,
const AVIOInterruptCB *int_cb, AVDictionary **options,
const char *whitelist, const char* blacklist,
URLContext *parent)
{
AVDictionary *tmp_opts = NULL;
AVDictionaryEntry *e;
int ret = ffurl_alloc(puc, filename, flags, int_cb);
if (ret < 0)
return ret;
if (parent)
av_opt_copy(*puc, parent);
if (options &&
(ret = av_opt_set_dict(*puc, options)) < 0)
goto fail;
if (options && (*puc)->prot->priv_data_class &&
(ret = av_opt_set_dict((*puc)->priv_data, options)) < 0)
goto fail;
if (!options)
options = &tmp_opts;
av_assert0(!whitelist ||
!(e=av_dict_get(*options, "protocol_whitelist", NULL, 0)) ||
!strcmp(whitelist, e->value));
av_assert0(!blacklist ||
!(e=av_dict_get(*options, "protocol_blacklist", NULL, 0)) ||
!strcmp(blacklist, e->value));
if ((ret = av_dict_set(options, "protocol_whitelist", whitelist, 0)) < 0)
goto fail;
if ((ret = av_dict_set(options, "protocol_blacklist", blacklist, 0)) < 0)
goto fail;
if ((ret = av_opt_set_dict(*puc, options)) < 0)
goto fail;
ret = ffurl_connect(*puc, options);
if (!ret)
return 0;
fail:
ffurl_close(*puc);
*puc = NULL;
return ret;
}
从代码中可以看出,ffurl_open_whitelist()主要调用了2个函数:ffurl_alloc()和ffurl_connect()。ffurl_alloc()用于查找合适的URLProtocol,并创建一个URLContext;ffurl_connect()用于打开获得的URLProtocol。
ffurl_alloc()
int ffurl_alloc(URLContext **puc, const char *filename, int flags,
const AVIOInterruptCB *int_cb)
{
const URLProtocol *p = NULL;
p = url_find_protocol(filename);
if (p)
return url_alloc_for_protocol(puc, p, filename, flags, int_cb);
*puc = NULL;
if (av_strstart(filename, "https:", NULL) || av_strstart(filename, "tls:", NULL))
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_WARNING, "https protocol not found, recompile FFmpeg with "
"openssl, gnutls "
"or securetransport enabled.\n");
return AVERROR_PROTOCOL_NOT_FOUND;
}
从代码中可以看出,ffurl_alloc()主要调用了2个函数:url_find_protocol()根据文件路径查找合适的URLProtocol,url_alloc_for_protocol()为查找到的URLProtocol创建URLContext。
url_find_protocol()
#define URL_SCHEME_CHARS \
"abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz" \
"ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ" \
"0123456789+-."
static const struct URLProtocol *url_find_protocol(const char *filename)
{
const URLProtocol **protocols;
char proto_str[128], proto_nested[128], *ptr;
size_t proto_len = strspn(filename, URL_SCHEME_CHARS);
int i;
if (filename[proto_len] != ':' &&
(strncmp(filename, "subfile,", 8) || !strchr(filename + proto_len + 1, ':')) ||
is_dos_path(filename))
strcpy(proto_str, "file");
else
av_strlcpy(proto_str, filename,
FFMIN(proto_len + 1, sizeof(proto_str)));
av_strlcpy(proto_nested, proto_str, sizeof(proto_nested));
if ((ptr = strchr(proto_nested, '+')))
*ptr = '\0';
protocols = ffurl_get_protocols(NULL, NULL);
if (!protocols)
return NULL;
for (i = 0; protocols[i]; i++) {
const URLProtocol *up = protocols[i];
if (!strcmp(proto_str, up->name)) {
av_freep(&protocols);
return up;
}
if (up->flags & URL_PROTOCOL_FLAG_NESTED_SCHEME &&
!strcmp(proto_nested, up->name)) {
av_freep(&protocols);
return up;
}
}
av_freep(&protocols);
return NULL;
}
url_find_protocol()函数表明了FFmpeg根据文件路径猜测协议的方法。该函数首先根据strspn()函数查找字符串中第一个“非字母或数字”的字符的位置,并保存在proto_len中。一般情况下,协议URL中都是包含“:”的,比如说RTMP的URL格式是“rtmp://xxx…”,UDP的URL格式是“udp://…”,HTTP的URL格式是“http://...”。因此,一般情况下proto_len的数值就是“:”的下标(代表了“:”前面的协议名称的字符的个数,例如rtmp://的proto_len为4)。
接下来函数将filename的前proto_len个字节拷贝至proto_str字符串中。
PS:
这个地方比较纠结,源代码中av_strlcpy()函数的第3个参数size写的字符串的长度是(proto_len+1),但是查了一下av_strlcpy()的定义,发现该函数至多拷贝(size-1)个字符。这么一涨一消,最终还是拷贝了proto_len个字节。例如RTMP协议就拷贝了“rtmp”,UDP协议就拷贝了“udp”。
这里有一种例外,那就是文件路径。“文件”在FFmpeg中也是一种“协议”,并且前缀是“file”。也就是标准的文件路径应该是“file://...”格式的。但是这太不符合我们一般人的使用习惯,我们一般是不会在文件路径前面加上“file”协议名称的。所以该函数采取的方法是:一旦检测出来输入的URL是文件路径而不是网络协议,就自动向proto_str中拷贝“file”。
其中判断文件路径那里有一个很复杂的if()语句。根据我的理解,“||”前面的语句用于判断是否是相对文件路径,“||”后面的语句用于判断是否是绝对路径。判断绝对路径的时候用到了一个函数is_dos_path(),注意“&&”优先级低于“==”。如果文件路径第1个字符不为空(一般情况下是盘符)而且第2个字符为“:”,就认为它是绝对文件路径。
此外url_find_protocol()函数中还涉及到一个函数ffurl_get_protocols()。该函数用于获得下一个URLProtocol(所有的URLProtocol在FFmpeg初始化注册的时候形成一个链表结构)。ffurl_get_protocols()代码极其简单,如下所示。
const URLProtocol **ffurl_get_protocols(const char *whitelist,
const char *blacklist)
{
const URLProtocol **ret;//新建一个二级指针ret
int i, ret_idx = 0;
ret = av_mallocz_array(FF_ARRAY_ELEMS(url_protocols), sizeof(*ret));
if (!ret)
return NULL;
//从url_protocols[]按顺序找出每个URLProtocol 并放到ret中
for (i = 0; url_protocols[i]; i++) {
const URLProtocol *up = url_protocols[i];
if (whitelist && *whitelist && !av_match_name(up->name, whitelist))
continue;
if (blacklist && *blacklist && av_match_name(up->name, blacklist))
continue;
ret[ret_idx++] = up;//这里是把每个url_protocols[]按顺序放到ret
}
return ret;//返回ret
}
url_alloc_for_protocol()
static int url_alloc_for_protocol(URLContext **puc, const URLProtocol *up,
const char *filename, int flags,
const AVIOInterruptCB *int_cb)
{
URLContext *uc;
int err;
#if CONFIG_NETWORK
if (up->flags & URL_PROTOCOL_FLAG_NETWORK && !ff_network_init())
return AVERROR(EIO);
#endif
if ((flags & AVIO_FLAG_READ) && !up->url_read) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR,
"Impossible to open the '%s' protocol for reading\n", up->name);
return AVERROR(EIO);
}
if ((flags & AVIO_FLAG_WRITE) && !up->url_write) {
av_log(NULL, AV_LOG_ERROR,
"Impossible to open the '%s' protocol for writing\n", up->name);
return AVERROR(EIO);
}
uc = av_mallocz(sizeof(URLContext) + strlen(filename) + 1);
if (!uc) {
err = AVERROR(ENOMEM);
goto fail;
}
uc->av_class = &ffurl_context_class;
uc->filename = (char *)&uc[1];
strcpy(uc->filename, filename);
uc->prot = up;
uc->flags = flags;
uc->is_streamed = 0; /* default = not streamed */
uc->max_packet_size = 0; /* default: stream file */
if (up->priv_data_size) {
uc->priv_data = av_mallocz(up->priv_data_size);
if (!uc->priv_data) {
err = AVERROR(ENOMEM);
goto fail;
}
if (up->priv_data_class) {
int proto_len= strlen(up->name);
char *start = strchr(uc->filename, ',');
*(const AVClass **)uc->priv_data = up->priv_data_class;
av_opt_set_defaults(uc->priv_data);
if(!strncmp(up->name, uc->filename, proto_len) && uc->filename + proto_len == start){
int ret= 0;
char *p= start;
char sep= *++p;
char *key, *val;
p++;
if (strcmp(up->name, "subfile"))
ret = AVERROR(EINVAL);
while(ret >= 0 && (key= strchr(p, sep)) && ppriv_data, p, key+1, 0);
if (ret == AVERROR_OPTION_NOT_FOUND)
av_log(uc, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Key '%s' not found.\n", p);
*val= *key= sep;
p= val+1;
}
if(ret<0 || p!=key){
av_log(uc, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Error parsing options string %s\n", start);
av_freep(&uc->priv_data);
av_freep(&uc);
err = AVERROR(EINVAL);
goto fail;
}
memmove(start, key+1, strlen(key));
}
}
}
if (int_cb)
uc->interrupt_callback = *int_cb;
*puc = uc;
return 0;
fail:
*puc = NULL;
if (uc)
av_freep(&uc->priv_data);
av_freep(&uc);
#if CONFIG_NETWORK
if (up->flags & URL_PROTOCOL_FLAG_NETWORK)
ff_network_close();
#endif
return err;
}
url_alloc_for_protocol()完成了以下步骤:首先,检查输入的URLProtocol是否支持指定的flag。比如flag中如果指定了AVIO_FLAG_READ,则URLProtocol中必须包含url_read();如果指定了AVIO_FLAG_WRITE,则URLProtocol中必须包含url_write()。在检查无误之后,接着就可以调用av_mallocz()为即将创建的URLContext分配内存了。接下来基本上就是各种赋值工作,在这里不再详细记录。
ffurl_connect()
int ffurl_connect(URLContext *uc, AVDictionary **options)
{
int err;
AVDictionary *tmp_opts = NULL;
AVDictionaryEntry *e;
if (!options)
options = &tmp_opts;
// Check that URLContext was initialized correctly and lists are matching if set
av_assert0(!(e=av_dict_get(*options, "protocol_whitelist", NULL, 0)) ||
(uc->protocol_whitelist && !strcmp(uc->protocol_whitelist, e->value)));
av_assert0(!(e=av_dict_get(*options, "protocol_blacklist", NULL, 0)) ||
(uc->protocol_blacklist && !strcmp(uc->protocol_blacklist, e->value)));
if (uc->protocol_whitelist && av_match_list(uc->prot->name, uc->protocol_whitelist, ',') <= 0) {
av_log(uc, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Protocol '%s' not on whitelist '%s'!\n", uc->prot->name, uc->protocol_whitelist);
return AVERROR(EINVAL);
}
if (uc->protocol_blacklist && av_match_list(uc->prot->name, uc->protocol_blacklist, ',') > 0) {
av_log(uc, AV_LOG_ERROR, "Protocol '%s' on blacklist '%s'!\n", uc->prot->name, uc->protocol_blacklist);
return AVERROR(EINVAL);
}
if (!uc->protocol_whitelist && uc->prot->default_whitelist) {
av_log(uc, AV_LOG_DEBUG, "Setting default whitelist '%s'\n", uc->prot->default_whitelist);
uc->protocol_whitelist = av_strdup(uc->prot->default_whitelist);
if (!uc->protocol_whitelist) {
return AVERROR(ENOMEM);
}
} else if (!uc->protocol_whitelist)
av_log(uc, AV_LOG_DEBUG, "No default whitelist set\n"); // This should be an error once all declare a default whitelist
if ((err = av_dict_set(options, "protocol_whitelist", uc->protocol_whitelist, 0)) < 0)
return err;
if ((err = av_dict_set(options, "protocol_blacklist", uc->protocol_blacklist, 0)) < 0)
return err;
err =
uc->prot->url_open2 ? uc->prot->url_open2(uc,
uc->filename,
uc->flags,
options) :
uc->prot->url_open(uc, uc->filename, uc->flags);
av_dict_set(options, "protocol_whitelist", NULL, 0);
av_dict_set(options, "protocol_blacklist", NULL, 0);
if (err)
return err;
uc->is_connected = 1;
/* We must be careful here as ffurl_seek() could be slow,
* for example for http */
if ((uc->flags & AVIO_FLAG_WRITE) || !strcmp(uc->prot->name, "file"))
if (!uc->is_streamed && ffurl_seek(uc, 0, SEEK_SET) < 0)
uc->is_streamed = 1;
return 0;
}
该函数最重要的函数就是:URLProtocol中是否包含url_open2()?如果包含的话,就调用url_open2(),否则就调用url_open()。
url_open()本身是URLProtocol的一个函数指针,这个地方根据不同的协议调用的url_open()具体实现函数也是不一样的,例如file协议的url_open()对应的是file_open(),而file_open()最终调用了_wsopen(),_sopen()(Windows下)或者open()(Linux下,类似于fopen())这样的系统中打开文件的API函数;而libRTMP的url_open()对应的是rtmp_open(),而rtmp_open()最终调用了libRTMP的API函数RTMP_Init(),RTMP_SetupURL(),RTMP_Connect() 以及RTMP_ConnectStream()。
ffio_fdopen()
ffio_fdopen()使用已经获得的URLContext初始化AVIOContext。它的函数定义位于libavformat\aviobuf.c中,如下所示。
int ffio_fdopen(AVIOContext **s, URLContext *h)
{
AVIOInternal *internal = NULL;
uint8_t *buffer = NULL;
int buffer_size, max_packet_size;
max_packet_size = h->max_packet_size;
if (max_packet_size) {
buffer_size = max_packet_size; /* no need to bufferize more than one packet */
} else {
buffer_size = IO_BUFFER_SIZE;
}
buffer = av_malloc(buffer_size);
if (!buffer)
return AVERROR(ENOMEM);
internal = av_mallocz(sizeof(*internal));
if (!internal)
goto fail;
internal->h = h;
*s = avio_alloc_context(buffer, buffer_size, h->flags & AVIO_FLAG_WRITE,
internal, io_read_packet, io_write_packet, io_seek);
if (!*s)
goto fail;
(*s)->protocol_whitelist = av_strdup(h->protocol_whitelist);
if (!(*s)->protocol_whitelist && h->protocol_whitelist) {
avio_closep(s);
goto fail;
}
(*s)->protocol_blacklist = av_strdup(h->protocol_blacklist);
if (!(*s)->protocol_blacklist && h->protocol_blacklist) {
avio_closep(s);
goto fail;
}
(*s)->direct = h->flags & AVIO_FLAG_DIRECT;
(*s)->seekable = h->is_streamed ? 0 : AVIO_SEEKABLE_NORMAL;
(*s)->max_packet_size = max_packet_size;
(*s)->min_packet_size = h->min_packet_size;
if(h->prot) {
(*s)->read_pause = io_read_pause;
(*s)->read_seek = io_read_seek;
if (h->prot->url_read_seek)
(*s)->seekable |= AVIO_SEEKABLE_TIME;
}
(*s)->short_seek_get = io_short_seek;
(*s)->av_class = &ff_avio_class;
return 0;
fail:
av_freep(&internal);
av_freep(&buffer);
return AVERROR(ENOMEM);
}
ffio_fdopen()函数首先初始化AVIOContext中的Buffer。如果URLContext中设置了max_packet_size,则将Buffer的大小设置为max_packet_size。如果没有设置的话(似乎大部分URLContext都没有设置该值),则会分配IO_BUFFER_SIZE个字节给Buffer。IO_BUFFER_SIZE取值为32768。
ffio_fdopen()接下来会调用avio_alloc_context()初始化一个AVIOContext。avio_alloc_context()本身是一个FFmpeg的API函数。
avio_alloc_context()看上去参数很多,但实际上并不复杂。先简单解释一下它各个参数的含义:
buffer:AVIOContext中的Buffer。
buffer_size:AVIOContext中的Buffer的大小。
write_flag:设置为1则Buffer可写;否则Buffer只可读。
opaque:用户自定义数据。
read_packet():读取外部数据,填充Buffer的函数。
write_packet():向Buffer中写入数据的函数。
seek():用于Seek的函数。
该函数成功执行的话则会返回一个创建好的AVIOContext。
AVIOContext *avio_alloc_context(
unsigned char *buffer,
int buffer_size,
int write_flag,
void *opaque,
int (*read_packet)(void *opaque, uint8_t *buf, int buf_size),
int (*write_packet)(void *opaque, uint8_t *buf, int buf_size),
int64_t (*seek)(void *opaque, int64_t offset, int whence))
{
AVIOContext *s = av_malloc(sizeof(AVIOContext));
if (!s)
return NULL;
ffio_init_context(s, buffer, buffer_size, write_flag, opaque,
read_packet, write_packet, seek);
return s;
}
该函数代码很简单:首先调用av_mallocz()为AVIOContext分配一块内存空间,然后基本上将所有输入参数传递给ffio_init_context()。
ffio_init_context()这个函数的工作就是 对AVIOContext各种赋值,不算很有“技术含量”,不再详述。
ffurl_read(),ffurl_write(),ffurl_seek()
现在我们再回到ffio_fdopen(),会发现它初始化AVIOContext的结构体的时候,首先将自己分配的Buffer设置为该AVIOContext的Buffer;然后将URLContext作为用户自定义数据internal->h,最后把internal赋值给AVIOContext的opaque变量,提供给该AVIOContext;最后分别将3个函数作为该AVIOContext的读,写,跳转函数:io_read_packet, io_write_packet, io_seek分别包含对应的ffurl_read(),ffurl_write(),ffurl_seek()。下面我们选择一个ffurl_read()看看它的定义。
ffurl_read()的定义位于libavformat\avio.c,如下所示。
int ffurl_read(URLContext *h, unsigned char *buf, int size)
{
if (!(h->flags & AVIO_FLAG_READ))
return AVERROR(EIO);
return retry_transfer_wrapper(h, buf, size, 1, h->prot->url_read);
}
int ffurl_write(URLContext *h, const unsigned char *buf, int size)
{
if (!(h->flags & AVIO_FLAG_WRITE))
return AVERROR(EIO);
/* avoid sending too big packets */
if (h->max_packet_size && size > h->max_packet_size)
return AVERROR(EIO);
return retry_transfer_wrapper(h, (unsigned char *)buf, size, size,
(int (*)(struct URLContext *, uint8_t *, int))
h->prot->url_write);
}
函数先判断了一下输入的URLContext是否支持“读”或写操作,接着调用了一个函数:retry_transfer_wrapper()。
ffurl_write()的也调用了同样的一个函数retry_transfer_wrapper()。唯一的不同在于ffurl_read()调用retry_transfer_wrapper()的时候,最后一个参数是URLProtocol的url_read(),而ffurl_write()调用retry_transfer_wrapper()的时候,最后一个参数是URLProtocol的url_write()。
下面我们看一下retry_transfer_wrapper()的定义,位于libavformat\avio.c,如下所示:
static inline int retry_transfer_wrapper(URLContext *h, uint8_t *buf,
int size, int size_min,
int (*transfer_func)(URLContext *h,
uint8_t *buf,
int size))
{
int ret, len;
int fast_retries = 5;
int64_t wait_since = 0;
len = 0;
while (len < size_min) {
if (ff_check_interrupt(&h->interrupt_callback))
return AVERROR_EXIT;
ret = transfer_func(h, buf + len, size - len);
if (ret == AVERROR(EINTR))
continue;
if (h->flags & AVIO_FLAG_NONBLOCK)
return ret;
if (ret == AVERROR(EAGAIN)) {
ret = 0;
if (fast_retries) {
fast_retries--;
} else {
if (h->rw_timeout) {
if (!wait_since)
wait_since = av_gettime_relative();
else if (av_gettime_relative() > wait_since + h->rw_timeout)
return AVERROR(EIO);
}
av_usleep(1000);
}
} else if (ret == AVERROR_EOF)
return (len > 0) ? len : AVERROR_EOF;
else if (ret < 0)
return ret;
if (ret) {
fast_retries = FFMAX(fast_retries, 2);
wait_since = 0;
}
len += ret;
}
return len;
}
从代码中可以看出,它的核心实际上是调用了一个名称为transfer_func()的函数。而该函数就是retry_transfer_wrapper()的第四个参数。该函数实际上是对URLProtocol的读写操作中的错误进行了一些“容错”处理,可以让数据的读写更加的稳定。
avio_alloc_context()执行完毕后,ffio_fdopen()函数的工作就基本完成了,ffio_open_whitelist()的工作(就是io_open_default)也就做完了。