ANR源码分析之Service Timeout
在前面的一篇文章中,分析了Broadcast Timeout的流程,接下来继续分析Service Timeout的流程。Service默认不会运行在子线程中,它也不会运行在一个独立的进程中,它同样执行在UI线程中,因此也不能在Service中执行耗时操作,否则也会产生的ANR。
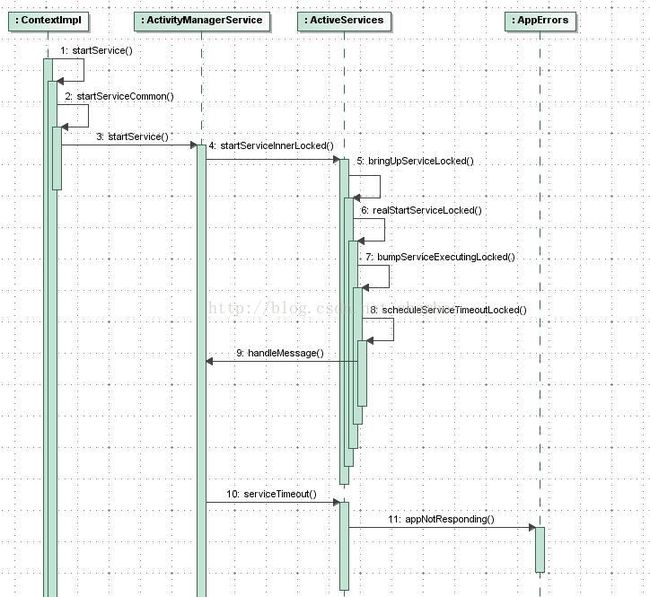
Service Timeout整体流程如下图所示:
1.startService(ContextImpl.java)
/*
* 启动服务
*/
public ComponentName startService(Intent service) {
warnIfCallingFromSystemProcess();
return startServiceCommon(service, mUser);
}
private ComponentName startServiceCommon(Intent service, UserHandle user) {
try {
validateServiceIntent(service);//验证Service的Intent
service.prepareToLeaveProcess(this);
ComponentName cn = ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().startService(
mMainThread.getApplicationThread(), service, service.resolveTypeIfNeeded(
getContentResolver()), getOpPackageName(), user.getIdentifier());//调用AMS的start方法
........
return cn;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}在ActivityManagerService.java类中
public ComponentName startService(IApplicationThread caller, Intent service,
String resolvedType, String callingPackage, int userId)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
enforceNotIsolatedCaller("startService");
......
synchronized(this) {
final int callingPid = Binder.getCallingPid();
final int callingUid = Binder.getCallingUid();
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
ComponentName res = mServices.startServiceLocked(caller, service,
resolvedType, callingPid, callingUid, callingPackage, userId);//调用ActiveServices的startServiceLocked方法
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
return res;
}
}在ActiveServices.java类中
ComponentName startServiceLocked(IApplicationThread caller, Intent service, String resolvedType,
int callingPid, int callingUid, String callingPackage, final int userId)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
final boolean callerFg;
if (caller != null) {
final ProcessRecord callerApp = mAm.getRecordForAppLocked(caller);
.........
//调用者不是处于后台线程组中
callerFg = callerApp.setSchedGroup != ProcessList.SCHED_GROUP_BACKGROUND;
} else {
callerFg = true;
}
.......
ServiceRecord r = res.record;
......
//准备startService参数
r.lastActivity = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
r.startRequested = true;
r.delayedStop = false;
r.pendingStarts.add(new ServiceRecord.StartItem(r, false, r.makeNextStartId(),
service, neededGrants));
......
return startServiceInnerLocked(smap, service, r, callerFg, addToStarting);
}
ComponentName startServiceInnerLocked(ServiceMap smap, Intent service, ServiceRecord r,
boolean callerFg, boolean addToStarting) throws TransactionTooLargeException {
ServiceState stracker = r.getTracker();
if (stracker != null) {
stracker.setStarted(true, mAm.mProcessStats.getMemFactorLocked(), r.lastActivity);
}
r.callStart = false;
synchronized (r.stats.getBatteryStats()) {
r.stats.startRunningLocked();
}
//调用bringUpServiceLocked方法将服务调起
String error = bringUpServiceLocked(r, service.getFlags(), callerFg, false, false);
.......
return r.name;
}
private String bringUpServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r, int intentFlags, boolean execInFg,
boolean whileRestarting, boolean permissionsReviewRequired)
throws TransactionTooLargeException {
......
final boolean isolated = (r.serviceInfo.flags&ServiceInfo.FLAG_ISOLATED_PROCESS) != 0;
......
if (!isolated) {
app = mAm.getProcessRecordLocked(procName, r.appInfo.uid, false);
if (DEBUG_MU) Slog.v(TAG_MU, "bringUpServiceLocked: appInfo.uid=" + r.appInfo.uid
+ " app=" + app);
if (app != null && app.thread != null) {
try {
app.addPackage(r.appInfo.packageName, r.appInfo.versionCode, mAm.mProcessStats);
//调用realStartServiceLocked方法启动服务
realStartServiceLocked(r, app, execInFg);
return null;
} catch (TransactionTooLargeException e) {
throw e;
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Exception when starting service " + r.shortName, e);
}
}
} else {
........
}
........
}
private final void realStartServiceLocked(ServiceRecord r,
ProcessRecord app, boolean execInFg) throws RemoteException {
.......
r.app = app;
r.restartTime = r.lastActivity = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
final boolean newService = app.services.add(r);
//开始监控onCreate方法执行时长
bumpServiceExecutingLocked(r, execInFg, "create");
mAm.updateLruProcessLocked(app, false, null);
mAm.updateOomAdjLocked();
boolean created = false;
try {
......
mAm.notifyPackageUse(r.serviceInfo.packageName,
PackageManager.NOTIFY_PACKAGE_USE_SERVICE);
app.forceProcessStateUpTo(ActivityManager.PROCESS_STATE_SERVICE);
//开始Service的onCreate流程
app.thread.scheduleCreateService(r, r.serviceInfo,
mAm.compatibilityInfoForPackageLocked(r.serviceInfo.applicationInfo),
app.repProcState);
r.postNotification();
created = true;
} catch (DeadObjectException e) {
......
} finally {
......
}
......
//开始Service的onBind流程
requestServiceBindingsLocked(r, execInFg);
......
//开始Service的onStart流程
sendServiceArgsLocked(r, execInFg, true);
......
} /*
* 记录服务方法执行开始时间,并开始监控服务方法执行是否超时
*/
private final void bumpServiceExecutingLocked(ServiceRecord r, boolean fg, String why) {
......
long now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();//记录当前方法执行的开始时间
if (r.executeNesting == 0) {
r.executeFg = fg;
ServiceState stracker = r.getTracker();
if (stracker != null) {
stracker.setExecuting(true, mAm.mProcessStats.getMemFactorLocked(), now);
}
if (r.app != null) {
r.app.executingServices.add(r);
r.app.execServicesFg |= fg;
if (r.app.executingServices.size() == 1) {
//服务方法首次执行时,调用该方法
scheduleServiceTimeoutLocked(r.app);
}
}
} else if (r.app != null && fg && !r.app.execServicesFg) {
r.app.execServicesFg = true;
//服务方法非首次执行时,调用该方法
scheduleServiceTimeoutLocked(r.app);
}
r.executeFg |= fg;//记录服务是否在前台执行
r.executeNesting++;//记录服务执行方法的次数
r.executingStart = now;//记录服务方法执行的开始时间
} void scheduleServiceTimeoutLocked(ProcessRecord proc) {
......
long now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
Message msg = mAm.mHandler.obtainMessage(
ActivityManagerService.SERVICE_TIMEOUT_MSG);
msg.obj = proc;
//发送消息到AMS中,并添加延迟时间,如果是前台服务,则超时时间为20s,如果是后台服务,则超时时间为200s
mAm.mHandler.sendMessageAtTime(msg,
proc.execServicesFg ? (now+SERVICE_TIMEOUT) : (now+ SERVICE_BACKGROUND_TIMEOUT));
}
//服务超时时间为20s
static final int SERVICE_TIMEOUT = 20*1000;
//在后台线程组中服务超时时间为200s
static final int SERVICE_BACKGROUND_TIMEOUT = SERVICE_TIMEOUT * 10;ActivityManagerService接收到scheduleServiceTimeoutLocked方法发送过来的SERVICE_TIMEOUT_MSG消息后,调用ActiveServices的serviceTimeout方法发送ANR消息
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
case SERVICE_TIMEOUT_MSG: {
......
mServices.serviceTimeout((ProcessRecord)msg.obj);//调用ActiveServices的serviceTimeOut()方法
} break;
}void serviceTimeout(ProcessRecord proc) {
String anrMessage = null;
synchronized(mAm) {
......
final long now = SystemClock.uptimeMillis();
//计算当前时间减去服务超时时间
final long maxTime = now -
(proc.execServicesFg ? SERVICE_TIMEOUT : SERVICE_BACKGROUND_TIMEOUT);
ServiceRecord timeout = null;
long nextTime = 0;
//遍历服务执行方法列表,如果有方法执行时间超过服务执行超时最大时间,则发送ANR消息
for (int i=proc.executingServices.size()-1; i>=0; i--) {
ServiceRecord sr = proc.executingServices.valueAt(i);
//服务执行开始时间小于maxTime,则说明服务已经超时了
if (sr.executingStart < maxTime) {
timeout = sr;
break;
}
if (sr.executingStart > nextTime) {
nextTime = sr.executingStart;//更新服务执行下一次开始时间
}
}
if (timeout != null && mAm.mLruProcesses.contains(proc)) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Timeout executing service: " + timeout);
......
anrMessage = "executing service " + timeout.shortName;//记录服务执行超时的一些信息
} else {
//服务没有超时,则监控下一个服务方法执行是否超时
Message msg = mAm.mHandler.obtainMessage(
ActivityManagerService.SERVICE_TIMEOUT_MSG);
msg.obj = proc;
mAm.mHandler.sendMessageAtTime(msg, proc.execServicesFg
? (nextTime+SERVICE_TIMEOUT) : (nextTime + SERVICE_BACKGROUND_TIMEOUT));
}
}
//服务超时,发送ANR消息给AppErrors给用户显示
if (anrMessage != null) {
mAm.mAppErrors.appNotResponding(proc, null, null, false, anrMessage);
}
} 在服务方法执行完成后,将取消服务超时监控。在realStartServiceLocked方法中,执行完bumpServiceExecutingLocked方法后,接着执行ActivityThread的scheduleCreateService方法。
1.scheduleCreateService方法(ActivityThread.java)
/*
* createService方法来创建服务
*/
public final void scheduleCreateService(IBinder token,
ServiceInfo info, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, int processState) {
updateProcessState(processState, false);
CreateServiceData s = new CreateServiceData();
s.token = token;
s.info = info;
s.compatInfo = compatInfo;
sendMessage(H.CREATE_SERVICE, s);
}
public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
case CREATE_SERVICE:
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, ("serviceCreate: " + String.valueOf(msg.obj)));
handleCreateService((CreateServiceData)msg.obj);
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
break;
}
private void handleCreateService(CreateServiceData data) {
.....
// 获取服务的package信息
LoadedApk packageInfo = getPackageInfoNoCheck(
data.info.applicationInfo, data.compatInfo);
Service service = null;
try {
// 通过反射创建服务类
java.lang.ClassLoader cl = packageInfo.getClassLoader();
service = (Service) cl.loadClass(data.info.name).newInstance();
} catch (Exception e) {
......
}
try {
if (localLOGV) Slog.v(TAG, "Creating service " + data.info.name);
ContextImpl context = ContextImpl.createAppContext(this, packageInfo);
context.setOuterContext(service);
Application app = packageInfo.makeApplication(false, mInstrumentation);
service.attach(context, this, data.info.name, data.token, app,
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault());
//回调服务的onCreate方法
service.onCreate();
mServices.put(data.token, service);
try {
ActivityManagerNative.getDefault().serviceDoneExecuting(
data.token, SERVICE_DONE_EXECUTING_ANON, 0, 0);//调用AMS的serviceDoneExecuting方法
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
......
}
}public void serviceDoneExecuting(IBinder token, int type, int startId, int res) {
synchronized(this) {
if (!(token instanceof ServiceRecord)) {
Slog.e(TAG, "serviceDoneExecuting: Invalid service token=" + token);
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid service token");
}
mServices.serviceDoneExecutingLocked((ServiceRecord)token, type, startId, res);
}
}void serviceDoneExecutingLocked(ServiceRecord r, int type, int startId, int res) {
boolean inDestroying = mDestroyingServices.contains(r);
if (r != null) {
.......
final long origId = Binder.clearCallingIdentity();
serviceDoneExecutingLocked(r, inDestroying, inDestroying);
Binder.restoreCallingIdentity(origId);
} else {
........
}
}
private void serviceDoneExecutingLocked(ServiceRecord r, boolean inDestroying,
boolean finishing) {
......
r.executeNesting--;
if (r.executeNesting <= 0) {
if (r.app != null) {
.....
r.app.execServicesFg = false;
r.app.executingServices.remove(r);
if (r.app.executingServices.size() == 0) {
if (DEBUG_SERVICE || DEBUG_SERVICE_EXECUTING) Slog.v(TAG_SERVICE_EXECUTING,
"No more executingServices of " + r.shortName);
//移除SERVICE_TIMEOUT_MSG消息,取消对服务方法执行时间的监控
mAm.mHandler.removeMessages(ActivityManagerService.SERVICE_TIMEOUT_MSG, r.app);
} else if (r.executeFg) {
......
}
.......
}
r.executeFg = false;
.......
}
}至此,完整的介绍了在执行服务方法的时候,设置监听服务超时的过程以及移除监听服务超时的过程。默认情况下,服务执行的超时时间为20s,在后台线程组中服务执行超时时间为200s。