Dalvik虚拟机加载类的机制
作者:郭孝星
微博:郭孝星的新浪微博
邮箱:[email protected]
博客:http://blog.csdn.net/allenwells
github:https://github.com/AllenWell
在介绍Android的类加载机制之前,我们需要先了解一下Java的类加载机制。
【Java 安全技术探索之路系列:J2SE安全架构】之五:类加载器
说到Dalvik虚拟机,我们首先可能想到的是Java虚拟机,伴随着Java语言的发展,我们也一直在接触它,那么两者有什么区别呢?
- Java虚拟机基于栈,Dalvik虚拟机基于寄存器。
- Java虚拟机运行的是Java字节码,Java虚拟机运行的是Dex字节码。
由于本篇文章主要讨论的是Dalvik虚拟机的类的加载机制,所以其他区别不再展开,需要了解的可以参见我的其他文章,这里着重提一下Dalvik虚拟机和Java虚拟机加载类机制上的区别。
Dalvik虚拟机如同其他Java虚拟机一样,在运行程序时首先需要将对应的类加载到内存中。而在Java标准的虚拟机中,类加载可以从class文件中读取,也可以是其他形式的二进制流。因此,我们常常利用这一点,在程序运行时手动加载Class,从而达到代码动态加载执行的目的。
然而Dalvik虚拟机毕竟不算是标准的Java虚拟机,因此在类加载机制上,Dalvik虚拟机与Java虚拟机有许多不同之处,例如,在使用标准Java虚拟机时,我们经常自定义继承自ClassLoader的类加载器。然后通过defineClass方法来从一个二进制流中加载Class。然而,这在Dalvik虚拟机上是行不通的。
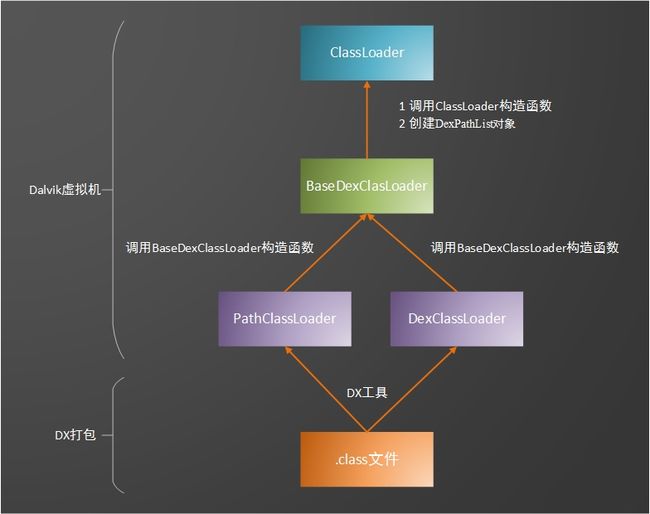
一 Dalvik虚拟机类加载结构
Dalvik虚拟机类加载流程如下图所示:
1.1 类加载器
1.1.1 系统类加载器
举例
Context.class.getClassLoader();上述代码得到的结果表明系统类的加载器是BootClassLoader。
ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader().getParent();上述代码表明系统加载器的父类加载器还是
1.1.2 应用程序加载器
举例
getClassLoader();上述代码得到的结果表明应用程序的加载器是PathClassLoader
getClassLoader().getParent();上述代码得到的结果表明应用程序的家在启动饿父类加载器是BootClassLoader。
二 Dalvik虚拟机类加载器源码分析
Android的类加载器主要有两个PathClassLoader和DexClassLoader,其中PathClassLoader是默认的类加载器,下面我们就来说说两者的区别与联系。
- PathClassLoader:支持加载DEX或者已经安装的APK(因为存在缓存的DEX)。
- DexClassLoader:支持加载APK、DEX和JAR,也可以从SD卡进行加载。
DexClassLoader和PathClassLoader都属于符合双亲委派模型的类加载器(因为它们没有重载loadClass方法)。也就是说,它们在加载一个类之前,回去检查自己以及自己以上的类加载器是否已经加载了这个类。如果已经加载过了,就会直接将之返回,而不会重复加载。
PathClassLoader还是DexClassLoader继承于BaseDexClassLoader,BaseDexClassLoader继承鱼ClassLoader,下面我们就以一个类的加载流程来分析各个加载器的源码实现,详细的源码在下方附录中给出。
要加载一个类,必须先初始化一个类加载器实例,我们拿DexClassLoader来举例,它的构造方法如下所示:
public DexClassLoader(String dexPath, String optimizedDirectory,
String libraryPath, ClassLoader parent) {
super(dexPath, new File(optimizedDirectory), libraryPath, parent);
}该函数中的参数含义如下所示:
- String dexPath:加载APK、DEX和JAR的路径。这个类可以用于Android动态加载DEX/JAR。
- String optimizedDirectory:是DEX的输出路径。
- String libraryPath:加载DEX的时候需要用到的lib库,libraryPath一般包括/vendor/lib和/system/lib。
- ClassLoader parent:DEXClassLoader指定的父类加载器
关于DexClassLoader,除了它的构造函数以外,它的源码注释里还提到以下三点:
- 这个类加载器加载的文件是.jar或者.apk文件,并且这个.jar或.apk中是包含classes.dex这个入口文件的,
主要是用来执行那些没有被安装的一些可执行文件的。 - 这个类加载器需要一个属于应用的私有的,可以的目录作为它自己的缓存优化目录,其实这个目录也就作为下面,这个构造函数的第二个参数,至于怎么实现,注释中也已经给出了答案;
- 不要把上面第二点中提到的这个缓存目录设为外部存储,因为外部存储容易收到代码注入的攻击。
通过DexClassLoader的构造函数,我们可以发现DexClassLoader的构造函数会调用父类的构造函数进行初始化,DexClassLoader的父类就是BaseDexXClassLoader,我们继续来看一下BaseDexClassLoader的构造函数:
public BaseDexClassLoader(String dexPath, File optimizedDirectory,
String libraryPath, ClassLoader parent) {
super(parent);
this.pathList = new DexPathList(this, dexPath, libraryPath, optimizedDirectory);
}我们可以发现在执行BaseDexClassLoader的构造函数时,会先调用父类ClassLoader的构造方法:
/**
* Constructs a new instance of this class with the system class loader as
* its parent.
*/
protected ClassLoader() {
this(getSystemClassLoader(), false);
}
/**
* Constructs a new instance of this class with the specified class loader
* as its parent.
*
* @param parentLoader
* The {@code ClassLoader} to use as the new class loader's
* parent.
*/
protected ClassLoader(ClassLoader parentLoader) {
this(parentLoader, false);
}
/*
* constructor for the BootClassLoader which needs parent to be null.
*/
ClassLoader(ClassLoader parentLoader, boolean nullAllowed) {
if (parentLoader == null && !nullAllowed) {
throw new NullPointerException("parentLoader == null && !nullAllowed");
}
parent = parentLoader;
}通过ClassLoader的构造函数源码可以发现,BaseDexClassLoader里的parentLoader对象经过层层传递,传递给了parent对象,parent对象是ClassLoader类里的私有变量,如下所示:
/**
* The parent ClassLoader.
*/
private ClassLoader parent;这一步做完以后,BaseDexClassLoader的构造函数紧接着就初始化了一个DexPathList对象,这是一个描述DEX文相关资源文件的条目列表。
附录
附录一:【Lollipop 5.1.1_r6】ClassLoader源码
/*
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
* contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
* this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
* The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
* (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
* the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
/*
* Copyright (C) 2008 The Android Open Source Project
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package java.lang;
import dalvik.system.PathClassLoader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.net.URL;
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.security.ProtectionDomain;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* Loads classes and resources from a repository. One or more class loaders are
* installed at runtime. These are consulted whenever the runtime system needs a
* specific class that is not yet available in-memory. Typically, class loaders
* are grouped into a tree where child class loaders delegate all requests to
* parent class loaders. Only if the parent class loader cannot satisfy the
* request, the child class loader itself tries to handle it.
*
* {@code ClassLoader} is an abstract class that implements the common
* infrastructure required by all class loaders. Android provides several
* concrete implementations of the class, with
* {@link dalvik.system.PathClassLoader} being the one typically used. Other
* applications may implement subclasses of {@code ClassLoader} to provide
* special ways for loading classes.
*
* @see Class
*/
public abstract class ClassLoader {
/**
* The 'System' ClassLoader - the one that is responsible for loading
* classes from the classpath. It is not equal to the bootstrap class loader -
* that one handles the built-in classes.
*
* Because of a potential class initialization race between ClassLoader and
* java.lang.System, reproducible when using JDWP with "suspend=y", we defer
* creation of the system class loader until first use. We use a static
* inner class to get synchronization at init time without having to sync on
* every access.
*
* @see #getSystemClassLoader()
*/
static private class SystemClassLoader {
public static ClassLoader loader = ClassLoader.createSystemClassLoader();
}
/**
* The parent ClassLoader.
*/
private ClassLoader parent;
/**
* The packages known to the class loader.
*/
private Map packages = new HashMap();
/**
* To avoid unloading individual classes, {@link java.lang.reflect.Proxy}
* only generates one class for each set of interfaces. This maps sets of
* interfaces to the proxy class that implements all of them. It is declared
* here so that these generated classes can be unloaded with their class
* loader.
*
* @hide
*/
public final Map>, Class> proxyCache =
new HashMap>, Class>();
/**
* Create the system class loader. Note this is NOT the bootstrap class
* loader (which is managed by the VM). We use a null value for the parent
* to indicate that the bootstrap loader is our parent.
*/
private static ClassLoader createSystemClassLoader() {
String classPath = System.getProperty("java.class.path", ".");
// String[] paths = classPath.split(":");
// URL[] urls = new URL[paths.length];
// for (int i = 0; i < paths.length; i++) {
// try {
// urls[i] = new URL("file://" + paths[i]);
// }
// catch (Exception ex) {
// ex.printStackTrace();
// }
// }
//
// return new java.net.URLClassLoader(urls, null);
// TODO Make this a java.net.URLClassLoader once we have those?
return new PathClassLoader(classPath, BootClassLoader.getInstance());
}
/**
* Returns the system class loader. This is the parent for new
* {@code ClassLoader} instances and is typically the class loader used to
* start the application.
*/
public static ClassLoader getSystemClassLoader() {
return SystemClassLoader.loader;
}
/**
* Finds the URL of the resource with the specified name. The system class
* loader's resource lookup algorithm is used to find the resource.
*
* @return the {@code URL} object for the requested resource or {@code null}
* if the resource can not be found.
* @param resName
* the name of the resource to find.
* @see Class#getResource
*/
public static URL getSystemResource(String resName) {
return SystemClassLoader.loader.getResource(resName);
}
/**
* Returns an enumeration of URLs for the resource with the specified name.
* The system class loader's resource lookup algorithm is used to find the
* resource.
*
* @return an enumeration of {@code URL} objects containing the requested
* resources.
* @param resName
* the name of the resource to find.
* @throws IOException
* if an I/O error occurs.
*/
public static Enumeration getSystemResources(String resName) throws IOException {
return SystemClassLoader.loader.getResources(resName);
}
/**
* Returns a stream for the resource with the specified name. The system
* class loader's resource lookup algorithm is used to find the resource.
* Basically, the contents of the java.class.path are searched in order,
* looking for a path which matches the specified resource.
*
* @return a stream for the resource or {@code null}.
* @param resName
* the name of the resource to find.
* @see Class#getResourceAsStream
*/
public static InputStream getSystemResourceAsStream(String resName) {
return SystemClassLoader.loader.getResourceAsStream(resName);
}
/**
* Constructs a new instance of this class with the system class loader as
* its parent.
*/
protected ClassLoader() {
this(getSystemClassLoader(), false);
}
/**
* Constructs a new instance of this class with the specified class loader
* as its parent.
*
* @param parentLoader
* The {@code ClassLoader} to use as the new class loader's
* parent.
*/
protected ClassLoader(ClassLoader parentLoader) {
this(parentLoader, false);
}
/*
* constructor for the BootClassLoader which needs parent to be null.
*/
ClassLoader(ClassLoader parentLoader, boolean nullAllowed) {
if (parentLoader == null && !nullAllowed) {
throw new NullPointerException("parentLoader == null && !nullAllowed");
}
parent = parentLoader;
}
/**
* Constructs a new class from an array of bytes containing a class
* definition in class file format.
*
* @param classRep
* the memory image of a class file.
* @param offset
* the offset into {@code classRep}.
* @param length
* the length of the class file.
* @return the {@code Class} object created from the specified subset of
* data in {@code classRep}.
* @throws ClassFormatError
* if {@code classRep} does not contain a valid class.
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException
* if {@code offset < 0}, {@code length < 0} or if
* {@code offset + length} is greater than the length of
* {@code classRep}.
* @deprecated Use {@link #defineClass(String, byte[], int, int)}
*/
@Deprecated
protected final Class defineClass(byte[] classRep, int offset, int length)
throws ClassFormatError {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("can't load this type of class file");
}
/**
* Constructs a new class from an array of bytes containing a class
* definition in class file format.
*
* @param className
* the expected name of the new class, may be {@code null} if not
* known.
* @param classRep
* the memory image of a class file.
* @param offset
* the offset into {@code classRep}.
* @param length
* the length of the class file.
* @return the {@code Class} object created from the specified subset of
* data in {@code classRep}.
* @throws ClassFormatError
* if {@code classRep} does not contain a valid class.
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException
* if {@code offset < 0}, {@code length < 0} or if
* {@code offset + length} is greater than the length of
* {@code classRep}.
*/
protected final Class defineClass(String className, byte[] classRep, int offset, int length)
throws ClassFormatError {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("can't load this type of class file");
}
/**
* Constructs a new class from an array of bytes containing a class
* definition in class file format and assigns the specified protection
* domain to the new class. If the provided protection domain is
* {@code null} then a default protection domain is assigned to the class.
*
* @param className
* the expected name of the new class, may be {@code null} if not
* known.
* @param classRep
* the memory image of a class file.
* @param offset
* the offset into {@code classRep}.
* @param length
* the length of the class file.
* @param protectionDomain
* the protection domain to assign to the loaded class, may be
* {@code null}.
* @return the {@code Class} object created from the specified subset of
* data in {@code classRep}.
* @throws ClassFormatError
* if {@code classRep} does not contain a valid class.
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException
* if {@code offset < 0}, {@code length < 0} or if
* {@code offset + length} is greater than the length of
* {@code classRep}.
* @throws NoClassDefFoundError
* if {@code className} is not equal to the name of the class
* contained in {@code classRep}.
*/
protected final Class defineClass(String className, byte[] classRep, int offset, int length,
ProtectionDomain protectionDomain) throws java.lang.ClassFormatError {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("can't load this type of class file");
}
/**
* Defines a new class with the specified name, byte code from the byte
* buffer and the optional protection domain. If the provided protection
* domain is {@code null} then a default protection domain is assigned to
* the class.
*
* @param name
* the expected name of the new class, may be {@code null} if not
* known.
* @param b
* the byte buffer containing the byte code of the new class.
* @param protectionDomain
* the protection domain to assign to the loaded class, may be
* {@code null}.
* @return the {@code Class} object created from the data in {@code b}.
* @throws ClassFormatError
* if {@code b} does not contain a valid class.
* @throws NoClassDefFoundError
* if {@code className} is not equal to the name of the class
* contained in {@code b}.
*/
protected final Class defineClass(String name, ByteBuffer b,
ProtectionDomain protectionDomain) throws ClassFormatError {
byte[] temp = new byte[b.remaining()];
b.get(temp);
return defineClass(name, temp, 0, temp.length, protectionDomain);
}
/**
* Overridden by subclasses, throws a {@code ClassNotFoundException} by
* default. This method is called by {@code loadClass} after the parent
* {@code ClassLoader} has failed to find a loaded class of the same name.
*
* @param className
* the name of the class to look for.
* @return the {@code Class} object that is found.
* @throws ClassNotFoundException
* if the class cannot be found.
*/
protected Class findClass(String className) throws ClassNotFoundException {
throw new ClassNotFoundException(className);
}
/**
* Returns the class with the specified name if it has already been loaded
* by the VM or {@code null} if it has not yet been loaded.
*
* @param className
* the name of the class to look for.
* @return the {@code Class} object or {@code null} if the requested class
* has not been loaded.
*/
protected final Class findLoadedClass(String className) {
ClassLoader loader;
if (this == BootClassLoader.getInstance())
loader = null;
else
loader = this;
return VMClassLoader.findLoadedClass(loader, className);
}
/**
* Finds the class with the specified name, loading it using the system
* class loader if necessary.
*
* @param className
* the name of the class to look for.
* @return the {@code Class} object with the requested {@code className}.
* @throws ClassNotFoundException
* if the class can not be found.
*/
protected final Class findSystemClass(String className) throws ClassNotFoundException {
return Class.forName(className, false, getSystemClassLoader());
}
/**
* Returns this class loader's parent.
*
* @return this class loader's parent or {@code null}.
*/
public final ClassLoader getParent() {
return parent;
}
/**
* Returns the URL of the resource with the specified name. This
* implementation first tries to use the parent class loader to find the
* resource; if this fails then {@link #findResource(String)} is called to
* find the requested resource.
*
* @param resName
* the name of the resource to find.
* @return the {@code URL} object for the requested resource or {@code null}
* if the resource can not be found
* @see Class#getResource
*/
public URL getResource(String resName) {
URL resource = parent.getResource(resName);
if (resource == null) {
resource = findResource(resName);
}
return resource;
}
/**
* Returns an enumeration of URLs for the resource with the specified name.
* This implementation first uses this class loader's parent to find the
* resource, then it calls {@link #findResources(String)} to get additional
* URLs. The returned enumeration contains the {@code URL} objects of both
* find operations.
*
* @return an enumeration of {@code URL} objects for the requested resource.
* @param resName
* the name of the resource to find.
* @throws IOException
* if an I/O error occurs.
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public Enumeration getResources(String resName) throws IOException {
Enumeration first = parent.getResources(resName);
Enumeration second = findResources(resName);
return new TwoEnumerationsInOne(first, second);
}
/**
* Returns a stream for the resource with the specified name. See
* {@link #getResource(String)} for a description of the lookup algorithm
* used to find the resource.
*
* @return a stream for the resource or {@code null} if the resource can not be found
* @param resName
* the name of the resource to find.
* @see Class#getResourceAsStream
*/
public InputStream getResourceAsStream(String resName) {
try {
URL url = getResource(resName);
if (url != null) {
return url.openStream();
}
} catch (IOException ex) {
// Don't want to see the exception.
}
return null;
}
/**
* Loads the class with the specified name. Invoking this method is
* equivalent to calling {@code loadClass(className, false)}.
*
* Note: In the Android reference implementation, the
* second parameter of {@link #loadClass(String, boolean)} is ignored
* anyway.
*
*
* @return the {@code Class} object.
* @param className
* the name of the class to look for.
* @throws ClassNotFoundException
* if the class can not be found.
*/
public Class loadClass(String className) throws ClassNotFoundException {
return loadClass(className, false);
}
/**
* Loads the class with the specified name, optionally linking it after
* loading. The following steps are performed:
*
* - Call {@link #findLoadedClass(String)} to determine if the requested
* class has already been loaded.
* - If the class has not yet been loaded: Invoke this method on the
* parent class loader.
* - If the class has still not been loaded: Call
* {@link #findClass(String)} to find the class.
*
*
* Note: In the Android reference implementation, the
* {@code resolve} parameter is ignored; classes are never linked.
*
*
* @return the {@code Class} object.
* @param className
* the name of the class to look for.
* @param resolve
* Indicates if the class should be resolved after loading. This
* parameter is ignored on the Android reference implementation;
* classes are not resolved.
* @throws ClassNotFoundException
* if the class can not be found.
*/
protected Class loadClass(String className, boolean resolve) throws ClassNotFoundException {
Class clazz = findLoadedClass(className);
if (clazz == null) {
ClassNotFoundException suppressed = null;
try {
clazz = parent.loadClass(className, false);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
suppressed = e;
}
if (clazz == null) {
try {
clazz = findClass(className);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.addSuppressed(suppressed);
throw e;
}
}
}
return clazz;
}
/**
* Forces a class to be linked (initialized). If the class has already been
* linked this operation has no effect.
*
* Note: In the Android reference implementation, this
* method has no effect.
*
*
* @param clazz
* the class to link.
*/
protected final void resolveClass(Class clazz) {
// no-op, doesn't make sense on android.
}
/**
* Finds the URL of the resource with the specified name. This
* implementation just returns {@code null}; it should be overridden in
* subclasses.
*
* @param resName
* the name of the resource to find.
* @return the {@code URL} object for the requested resource.
*/
protected URL findResource(String resName) {
return null;
}
/**
* Finds an enumeration of URLs for the resource with the specified name.
* This implementation just returns an empty {@code Enumeration}; it should
* be overridden in subclasses.
*
* @param resName
* the name of the resource to find.
* @return an enumeration of {@code URL} objects for the requested resource.
* @throws IOException
* if an I/O error occurs.
*/
@SuppressWarnings( {
"unchecked", "unused"
})
protected Enumeration findResources(String resName) throws IOException {
return Collections.emptyEnumeration();
}
/**
* Returns the absolute path of the native library with the specified name,
* or {@code null}. If this method returns {@code null} then the virtual
* machine searches the directories specified by the system property
* "java.library.path".
*
* This implementation always returns {@code null}.
*
*
* @param libName
* the name of the library to find.
* @return the absolute path of the library.
*/
protected String findLibrary(String libName) {
return null;
}
/**
* Returns the package with the specified name. Package information is
* searched in this class loader.
*
* @param name
* the name of the package to find.
* @return the package with the requested name; {@code null} if the package
* can not be found.
*/
protected Package getPackage(String name) {
synchronized (packages) {
return packages.get(name);
}
}
/**
* Returns all the packages known to this class loader.
*
* @return an array with all packages known to this class loader.
*/
protected Package[] getPackages() {
synchronized (packages) {
Collection col = packages.values();
Package[] result = new Package[col.size()];
col.toArray(result);
return result;
}
}
/**
* Defines and returns a new {@code Package} using the specified
* information. If {@code sealBase} is {@code null}, the package is left
* unsealed. Otherwise, the package is sealed using this URL.
*
* @param name
* the name of the package.
* @param specTitle
* the title of the specification.
* @param specVersion
* the version of the specification.
* @param specVendor
* the vendor of the specification.
* @param implTitle
* the implementation title.
* @param implVersion
* the implementation version.
* @param implVendor
* the specification vendor.
* @param sealBase
* the URL used to seal this package or {@code null} to leave the
* package unsealed.
* @return the {@code Package} object that has been created.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException
* if a package with the specified name already exists.
*/
protected Package definePackage(String name, String specTitle, String specVersion,
String specVendor, String implTitle, String implVersion, String implVendor, URL sealBase)
throws IllegalArgumentException {
synchronized (packages) {
if (packages.containsKey(name)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Package " + name + " already defined");
}
Package newPackage = new Package(name, specTitle, specVersion, specVendor, implTitle,
implVersion, implVendor, sealBase);
packages.put(name, newPackage);
return newPackage;
}
}
/**
* Sets the signers of the specified class. This implementation does
* nothing.
*
* @param c
* the {@code Class} object for which to set the signers.
* @param signers
* the signers for {@code c}.
*/
protected final void setSigners(Class c, Object[] signers) {
}
/**
* Sets the assertion status of the class with the specified name.
*
* Note: This method does nothing in the Android reference
* implementation.
*
*
* @param cname
* the name of the class for which to set the assertion status.
* @param enable
* the new assertion status.
*/
public void setClassAssertionStatus(String cname, boolean enable) {
}
/**
* Sets the assertion status of the package with the specified name.
*
* Note: This method does nothing in the Android reference
* implementation.
*
*
* @param pname
* the name of the package for which to set the assertion status.
* @param enable
* the new assertion status.
*/
public void setPackageAssertionStatus(String pname, boolean enable) {
}
/**
* Sets the default assertion status for this class loader.
*
* Note: This method does nothing in the Android reference
* implementation.
*
*
* @param enable
* the new assertion status.
*/
public void setDefaultAssertionStatus(boolean enable) {
}
/**
* Sets the default assertion status for this class loader to {@code false}
* and removes any package default and class assertion status settings.
*
* Note: This method does nothing in the Android reference
* implementation.
*
*/
public void clearAssertionStatus() {
}
}
/*
* Provides a helper class that combines two existing URL enumerations into one.
* It is required for the getResources() methods. Items are fetched from the
* first enumeration until it's empty, then from the second one.
*/
class TwoEnumerationsInOne implements Enumeration {
private final Enumeration first;
private final Enumeration second;
public TwoEnumerationsInOne(Enumeration first, Enumeration second) {
this.first = first;
this.second = second;
}
@Override
public boolean hasMoreElements() {
return first.hasMoreElements() || second.hasMoreElements();
}
@Override
public URL nextElement() {
if (first.hasMoreElements()) {
return first.nextElement();
} else {
return second.nextElement();
}
}
}
/**
* Provides an explicit representation of the boot class loader. It sits at the
* head of the class loader chain and delegates requests to the VM's internal
* class loading mechanism.
*/
class BootClassLoader extends ClassLoader {
private static BootClassLoader instance;
@FindBugsSuppressWarnings("DP_CREATE_CLASSLOADER_INSIDE_DO_PRIVILEGED")
public static synchronized BootClassLoader getInstance() {
if (instance == null) {
instance = new BootClassLoader();
}
return instance;
}
public BootClassLoader() {
super(null, true);
}
@Override
protected Class findClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException {
return Class.classForName(name, false, null);
}
@Override
protected URL findResource(String name) {
return VMClassLoader.getResource(name);
}
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
@Override
protected Enumeration findResources(String resName) throws IOException {
return Collections.enumeration(VMClassLoader.getResources(resName));
}
/**
* Returns package information for the given package. Unfortunately, the
* Android BootClassLoader doesn't really have this information, and as a
* non-secure ClassLoader, it isn't even required to, according to the spec.
* Yet, we want to provide it, in order to make all those hopeful callers of
* {@code myClass.getPackage().getName()} happy. Thus we construct a Package
* object the first time it is being requested and fill most of the fields
* with dummy values. The Package object is then put into the ClassLoader's
* Package cache, so we see the same one next time. We don't create Package
* objects for null arguments or for the default package.
*
* There a limited chance that we end up with multiple Package objects
* representing the same package: It can happen when when a package is
* scattered across different JAR files being loaded by different
* ClassLoaders. Rather unlikely, and given that this whole thing is more or
* less a workaround, probably not worth the effort.
*/
@Override
protected Package getPackage(String name) {
if (name != null && !name.isEmpty()) {
synchronized (this) {
Package pack = super.getPackage(name);
if (pack == null) {
pack = definePackage(name, "Unknown", "0.0", "Unknown", "Unknown", "0.0",
"Unknown", null);
}
return pack;
}
}
return null;
}
@Override
public URL getResource(String resName) {
return findResource(resName);
}
@Override
protected Class loadClass(String className, boolean resolve)
throws ClassNotFoundException {
Class clazz = findLoadedClass(className);
if (clazz == null) {
clazz = findClass(className);
}
return clazz;
}
@Override
public Enumeration getResources(String resName) throws IOException {
return findResources(resName);
}
}
/**
* TODO Open issues - Missing / empty methods - Signer stuff - Protection
* domains - Assertions
*/
附录二:【Lollipop 5.1.1_r6】BaseDexClassLoader源码
/*
* Copyright (C) 2011 The Android Open Source Project
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package dalvik.system;
import java.io.File;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.List;
/**
* Base class for common functionality between various dex-based
* {@link ClassLoader} implementations.
*/
public class BaseDexClassLoader extends ClassLoader {
private final DexPathList pathList;
/**
* Constructs an instance.
*
* @param dexPath the list of jar/apk files containing classes and
* resources, delimited by {@code File.pathSeparator}, which
* defaults to {@code ":"} on Android
* @param optimizedDirectory directory where optimized dex files
* should be written; may be {@code null}
* @param libraryPath the list of directories containing native
* libraries, delimited by {@code File.pathSeparator}; may be
* {@code null}
* @param parent the parent class loader
*/
public BaseDexClassLoader(String dexPath, File optimizedDirectory,
String libraryPath, ClassLoader parent) {
super(parent);
this.pathList = new DexPathList(this, dexPath, libraryPath, optimizedDirectory);
}
@Override
protected Class findClass(String name) throws ClassNotFoundException {
List suppressedExceptions = new ArrayList();
Class c = pathList.findClass(name, suppressedExceptions);
if (c == null) {
ClassNotFoundException cnfe = new ClassNotFoundException("Didn't find class \"" + name + "\" on path: " + pathList);
for (Throwable t : suppressedExceptions) {
cnfe.addSuppressed(t);
}
throw cnfe;
}
return c;
}
@Override
protected URL findResource(String name) {
return pathList.findResource(name);
}
@Override
protected Enumeration findResources(String name) {
return pathList.findResources(name);
}
@Override
public String findLibrary(String name) {
return pathList.findLibrary(name);
}
/**
* Returns package information for the given package.
* Unfortunately, instances of this class don't really have this
* information, and as a non-secure {@code ClassLoader}, it isn't
* even required to, according to the spec. Yet, we want to
* provide it, in order to make all those hopeful callers of
* {@code myClass.getPackage().getName()} happy. Thus we construct
* a {@code Package} object the first time it is being requested
* and fill most of the fields with dummy values. The {@code
* Package} object is then put into the {@code ClassLoader}'s
* package cache, so we see the same one next time. We don't
* create {@code Package} objects for {@code null} arguments or
* for the default package.
*
* There is a limited chance that we end up with multiple
* {@code Package} objects representing the same package: It can
* happen when when a package is scattered across different JAR
* files which were loaded by different {@code ClassLoader}
* instances. This is rather unlikely, and given that this whole
* thing is more or less a workaround, probably not worth the
* effort to address.
*
* @param name the name of the class
* @return the package information for the class, or {@code null}
* if there is no package information available for it
*/
@Override
protected synchronized Package getPackage(String name) {
if (name != null && !name.isEmpty()) {
Package pack = super.getPackage(name);
if (pack == null) {
pack = definePackage(name, "Unknown", "0.0", "Unknown",
"Unknown", "0.0", "Unknown", null);
}
return pack;
}
return null;
}
/**
* @hide
*/
public String getLdLibraryPath() {
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
for (File directory : pathList.getNativeLibraryDirectories()) {
if (result.length() > 0) {
result.append(':');
}
result.append(directory);
}
return result.toString();
}
@Override public String toString() {
return getClass().getName() + "[" + pathList + "]";
}
}
附录三:【Lollipop 5.1.1_r6】PathClassLoader源码
/*
* Copyright (C) 2007 The Android Open Source Project
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package dalvik.system;
/**
* Provides a simple {@link ClassLoader} implementation that operates on a list
* of files and directories in the local file system, but does not attempt to
* load classes from the network. Android uses this class for its system class
* loader and for its application class loader(s).
*/
public class PathClassLoader extends BaseDexClassLoader {
/**
* Creates a {@code PathClassLoader} that operates on a given list of files
* and directories. This method is equivalent to calling
* {@link #PathClassLoader(String, String, ClassLoader)} with a
* {@code null} value for the second argument (see description there).
*
* @param dexPath the list of jar/apk files containing classes and
* resources, delimited by {@code File.pathSeparator}, which
* defaults to {@code ":"} on Android
* @param parent the parent class loader
*/
public PathClassLoader(String dexPath, ClassLoader parent) {
super(dexPath, null, null, parent);
}
/**
* Creates a {@code PathClassLoader} that operates on two given
* lists of files and directories. The entries of the first list
* should be one of the following:
*
*
* - JAR/ZIP/APK files, possibly containing a "classes.dex" file as
* well as arbitrary resources.
*
- Raw ".dex" files (not inside a zip file).
*
*
* The entries of the second list should be directories containing
* native library files.
*
* @param dexPath the list of jar/apk files containing classes and
* resources, delimited by {@code File.pathSeparator}, which
* defaults to {@code ":"} on Android
* @param libraryPath the list of directories containing native
* libraries, delimited by {@code File.pathSeparator}; may be
* {@code null}
* @param parent the parent class loader
*/
public PathClassLoader(String dexPath, String libraryPath,
ClassLoader parent) {
super(dexPath, null, libraryPath, parent);
}
}
附录四:【Lollipop 5.1.1_r6】DexClassLoader源码
/*
* Copyright (C) 2008 The Android Open Source Project
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package dalvik.system;
import java.io.File;
/**
* A class loader that loads classes from {@code .jar} and {@code .apk} files
* containing a {@code classes.dex} entry. This can be used to execute code not
* installed as part of an application.
*
* This class loader requires an application-private, writable directory to
* cache optimized classes. Use {@code Context.getCodeCacheDir()} to create
* such a directory:
{@code
* File dexOutputDir = context.getCodeCacheDir();
* }
*
* Do not cache optimized classes on external storage.
* External storage does not provide access controls necessary to protect your
* application from code injection attacks.
*/
public class DexClassLoader extends BaseDexClassLoader {
/**
* Creates a {@code DexClassLoader} that finds interpreted and native
* code. Interpreted classes are found in a set of DEX files contained
* in Jar or APK files.
*
*
The path lists are separated using the character specified by the
* {@code path.separator} system property, which defaults to {@code :}.
*
* @param dexPath the list of jar/apk files containing classes and
* resources, delimited by {@code File.pathSeparator}, which
* defaults to {@code ":"} on Android
* @param optimizedDirectory directory where optimized dex files
* should be written; must not be {@code null}
* @param libraryPath the list of directories containing native
* libraries, delimited by {@code File.pathSeparator}; may be
* {@code null}
* @param parent the parent class loader
*/
public DexClassLoader(String dexPath, String optimizedDirectory,
String libraryPath, ClassLoader parent) {
super(dexPath, new File(optimizedDirectory), libraryPath, parent);
}
}
附录五:【Lollipop 5.1.1_r6】DexFile源码
/*
* Copyright (C) 2007 The Android Open Source Project
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package dalvik.system;
import android.system.ErrnoException;
import android.system.StructStat;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.List;
import libcore.io.Libcore;
/**
* Manipulates DEX files. The class is similar in principle to
* {@link java.util.zip.ZipFile}. It is used primarily by class loaders.
*
* Note we don't directly open and read the DEX file here. They're memory-mapped
* read-only by the VM.
*/
public final class DexFile {
private long mCookie;
private final String mFileName;
private final CloseGuard guard = CloseGuard.get();
/**
* Opens a DEX file from a given File object. This will usually be a ZIP/JAR
* file with a "classes.dex" inside.
*
* The VM will generate the name of the corresponding file in
* /data/dalvik-cache and open it, possibly creating or updating
* it first if system permissions allow. Don't pass in the name of
* a file in /data/dalvik-cache, as the named file is expected to be
* in its original (pre-dexopt) state.
*
* @param file
* the File object referencing the actual DEX file
*
* @throws IOException
* if an I/O error occurs, such as the file not being found or
* access rights missing for opening it
*/
public DexFile(File file) throws IOException {
this(file.getPath());
}
/**
* Opens a DEX file from a given filename. This will usually be a ZIP/JAR
* file with a "classes.dex" inside.
*
* The VM will generate the name of the corresponding file in
* /data/dalvik-cache and open it, possibly creating or updating
* it first if system permissions allow. Don't pass in the name of
* a file in /data/dalvik-cache, as the named file is expected to be
* in its original (pre-dexopt) state.
*
* @param fileName
* the filename of the DEX file
*
* @throws IOException
* if an I/O error occurs, such as the file not being found or
* access rights missing for opening it
*/
public DexFile(String fileName) throws IOException {
mCookie = openDexFile(fileName, null, 0);
mFileName = fileName;
guard.open("close");
//System.out.println("DEX FILE cookie is " + mCookie + " fileName=" + fileName);
}
/**
* Opens a DEX file from a given filename, using a specified file
* to hold the optimized data.
*
* @param sourceName
* Jar or APK file with "classes.dex".
* @param outputName
* File that will hold the optimized form of the DEX data.
* @param flags
* Enable optional features.
*/
private DexFile(String sourceName, String outputName, int flags) throws IOException {
if (outputName != null) {
try {
String parent = new File(outputName).getParent();
if (Libcore.os.getuid() != Libcore.os.stat(parent).st_uid) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Optimized data directory " + parent
+ " is not owned by the current user. Shared storage cannot protect"
+ " your application from code injection attacks.");
}
} catch (ErrnoException ignored) {
// assume we'll fail with a more contextual error later
}
}
mCookie = openDexFile(sourceName, outputName, flags);
mFileName = sourceName;
guard.open("close");
//System.out.println("DEX FILE cookie is " + mCookie + " sourceName=" + sourceName + " outputName=" + outputName);
}
/**
* Open a DEX file, specifying the file in which the optimized DEX
* data should be written. If the optimized form exists and appears
* to be current, it will be used; if not, the VM will attempt to
* regenerate it.
*
* This is intended for use by applications that wish to download
* and execute DEX files outside the usual application installation
* mechanism. This function should not be called directly by an
* application; instead, use a class loader such as
* dalvik.system.DexClassLoader.
*
* @param sourcePathName
* Jar or APK file with "classes.dex". (May expand this to include
* "raw DEX" in the future.)
* @param outputPathName
* File that will hold the optimized form of the DEX data.
* @param flags
* Enable optional features. (Currently none defined.)
* @return
* A new or previously-opened DexFile.
* @throws IOException
* If unable to open the source or output file.
*/
static public DexFile loadDex(String sourcePathName, String outputPathName,
int flags) throws IOException {
/*
* TODO: we may want to cache previously-opened DexFile objects.
* The cache would be synchronized with close(). This would help
* us avoid mapping the same DEX more than once when an app
* decided to open it multiple times. In practice this may not
* be a real issue.
*/
return new DexFile(sourcePathName, outputPathName, flags);
}
/**
* Gets the name of the (already opened) DEX file.
*
* @return the file name
*/
public String getName() {
return mFileName;
}
@Override public String toString() {
return getName();
}
/**
* Closes the DEX file.
*
* This may not be able to release any resources. If classes from this
* DEX file are still resident, the DEX file can't be unmapped.
*
* @throws IOException
* if an I/O error occurs during closing the file, which
* normally should not happen
*/
public void close() throws IOException {
if (mCookie != 0) {
guard.close();
closeDexFile(mCookie);
mCookie = 0;
}
}
/**
* Loads a class. Returns the class on success, or a {@code null} reference
* on failure.
*
* If you are not calling this from a class loader, this is most likely not
* going to do what you want. Use {@link Class#forName(String)} instead.
*
* The method does not throw {@link ClassNotFoundException} if the class
* isn't found because it isn't reasonable to throw exceptions wildly every
* time a class is not found in the first DEX file we look at.
*
* @param name
* the class name, which should look like "java/lang/String"
*
* @param loader
* the class loader that tries to load the class (in most cases
* the caller of the method
*
* @return the {@link Class} object representing the class, or {@code null}
* if the class cannot be loaded
*/
public Class loadClass(String name, ClassLoader loader) {
String slashName = name.replace('.', '/');
return loadClassBinaryName(slashName, loader, null);
}
/**
* See {@link #loadClass(String, ClassLoader)}.
*
* This takes a "binary" class name to better match ClassLoader semantics.
*
* @hide
*/
public Class loadClassBinaryName(String name, ClassLoader loader, List suppressed) {
return defineClass(name, loader, mCookie, suppressed);
}
private static Class defineClass(String name, ClassLoader loader, long cookie,
List suppressed) {
Class result = null;
try {
result = defineClassNative(name, loader, cookie);
} catch (NoClassDefFoundError e) {
if (suppressed != null) {
suppressed.add(e);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
if (suppressed != null) {
suppressed.add(e);
}
}
return result;
}
/**
* Enumerate the names of the classes in this DEX file.
*
* @return an enumeration of names of classes contained in the DEX file, in
* the usual internal form (like "java/lang/String").
*/
public Enumeration entries() {
return new DFEnum(this);
}
/*
* Helper class.
*/
private class DFEnum implements Enumeration<String> {
private int mIndex;
private String[] mNameList;
DFEnum(DexFile df) {
mIndex = 0;
mNameList = getClassNameList(mCookie);
}
public boolean hasMoreElements() {
return (mIndex < mNameList.length);
}
public String nextElement() {
return mNameList[mIndex++];
}
}
/**
* Called when the class is finalized. Makes sure the DEX file is closed.
*
* @throws IOException
* if an I/O error occurs during closing the file, which
* normally should not happen
*/
@Override protected void finalize() throws Throwable {
try {
if (guard != null) {
guard.warnIfOpen();
}
close();
} finally {
super.finalize();
}
}
/*
* Open a DEX file. The value returned is a magic VM cookie. On
* failure, an IOException is thrown.
*/
private static long openDexFile(String sourceName, String outputName, int flags) throws IOException {
// Use absolute paths to enable the use of relative paths when testing on host.
return openDexFileNative(new File(sourceName).getAbsolutePath(),
(outputName == null) ? null : new File(outputName).getAbsolutePath(),
flags);
}
private static native void closeDexFile(long cookie);
private static native Class defineClassNative(String name, ClassLoader loader, long cookie)
throws ClassNotFoundException, NoClassDefFoundError;
private static native String[] getClassNameList(long cookie);
/*
* Open a DEX file. The value returned is a magic VM cookie. On
* failure, an IOException is thrown.
*/
private static native long openDexFileNative(String sourceName, String outputName, int flags);
/**
* Returns true if the VM believes that the apk/jar file is out of date
* and should be passed through "dexopt" again.
*
* @param fileName the absolute path to the apk/jar file to examine.
* @return true if dexopt should be called on the file, false otherwise.
* @throws java.io.FileNotFoundException if fileName is not readable,
* not a file, or not present.
* @throws java.io.IOException if fileName is not a valid apk/jar file or
* if problems occur while parsing it.
* @throws java.lang.NullPointerException if fileName is null.
* @throws dalvik.system.StaleDexCacheError if the optimized dex file
* is stale but exists on a read-only partition.
*/
public static native boolean isDexOptNeeded(String fileName)
throws FileNotFoundException, IOException;
/**
* See {@link #isDexOptNeededInternal(String, String, String, boolean)}.
*
* @hide
*/
public static final byte UP_TO_DATE = 0;
/**
* See {@link #isDexOptNeededInternal(String, String, String, boolean)}.
*
* @hide
*/
public static final byte PATCHOAT_NEEDED = 1;
/**
* See {@link #isDexOptNeededInternal(String, String, String, boolean)}.
*
* @hide
*/
public static final byte DEXOPT_NEEDED = 2;
/**
* Returns UP_TO_DATE if the VM believes that the apk/jar file
* is up to date, PATCHOAT_NEEDED if it believes that the file is up
* to date but it must be relocated to match the base address offset,
* and DEXOPT_NEEDED if it believes that it is out of date and should
* be passed through "dexopt" again.
*
* @param fileName the absolute path to the apk/jar file to examine.
* @return DEXOPT_NEEDED if dexopt should be called on the file,
* PATCHOAT_NEEDED if we need to run "patchoat" on it and
* UP_TO_DATE otherwise.
* @throws java.io.FileNotFoundException if fileName is not readable,
* not a file, or not present.
* @throws java.io.IOException if fileName is not a valid apk/jar file or
* if problems occur while parsing it.
* @throws java.lang.NullPointerException if fileName is null.
* @throws dalvik.system.StaleDexCacheError if the optimized dex file
* is stale but exists on a read-only partition.
*
* @hide
*/
public static native byte isDexOptNeededInternal(String fileName, String pkgname,
String instructionSet, boolean defer)
throws FileNotFoundException, IOException;
}
附录六:【Lollipop 5.1.1_r6】DexPathList源码
/*
* Copyright (C) 2011 The Android Open Source Project
*
* Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
* you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
* You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*/
package dalvik.system;
import android.system.ErrnoException;
import android.system.StructStat;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.zip.ZipFile;
import libcore.io.IoUtils;
import libcore.io.Libcore;
import static android.system.OsConstants.*;
/**
* A pair of lists of entries, associated with a {@code ClassLoader}.
* One of the lists is a dex/resource path — typically referred
* to as a "class path" — list, and the other names directories
* containing native code libraries. Class path entries may be any of:
* a {@code .jar} or {@code .zip} file containing an optional
* top-level {@code classes.dex} file as well as arbitrary resources,
* or a plain {@code .dex} file (with no possibility of associated
* resources).
*
* This class also contains methods to use these lists to look up
* classes and resources.
*/
/*package*/ final class DexPathList {
private static final String DEX_SUFFIX = ".dex";
/** class definition context */
private final ClassLoader definingContext;
/**
* List of dex/resource (class path) elements.
* Should be called pathElements, but the Facebook app uses reflection
* to modify 'dexElements' (http://b/7726934).
*/
private final Element[] dexElements;
/** List of native library directories. */
private final File[] nativeLibraryDirectories;
/**
* Exceptions thrown during creation of the dexElements list.
*/
private final IOException[] dexElementsSuppressedExceptions;
/**
* Constructs an instance.
*
* @param definingContext the context in which any as-yet unresolved
* classes should be defined
* @param dexPath list of dex/resource path elements, separated by
* {@code File.pathSeparator}
* @param libraryPath list of native library directory path elements,
* separated by {@code File.pathSeparator}
* @param optimizedDirectory directory where optimized {@code .dex} files
* should be found and written to, or {@code null} to use the default
* system directory for same
*/
public DexPathList(ClassLoader definingContext, String dexPath,
String libraryPath, File optimizedDirectory) {
if (definingContext == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("definingContext == null");
}
if (dexPath == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("dexPath == null");
}
if (optimizedDirectory != null) {
if (!optimizedDirectory.exists()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"optimizedDirectory doesn't exist: "
+ optimizedDirectory);
}
if (!(optimizedDirectory.canRead()
&& optimizedDirectory.canWrite())) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"optimizedDirectory not readable/writable: "
+ optimizedDirectory);
}
}
this.definingContext = definingContext;
ArrayList suppressedExceptions = new ArrayList();
this.dexElements = makeDexElements(splitDexPath(dexPath), optimizedDirectory,
suppressedExceptions);
if (suppressedExceptions.size() > 0) {
this.dexElementsSuppressedExceptions =
suppressedExceptions.toArray(new IOException[suppressedExceptions.size()]);
} else {
dexElementsSuppressedExceptions = null;
}
this.nativeLibraryDirectories = splitLibraryPath(libraryPath);
}
@Override public String toString() {
return "DexPathList[" + Arrays.toString(dexElements) +
",nativeLibraryDirectories=" + Arrays.toString(nativeLibraryDirectories) + "]";
}
/**
* For BaseDexClassLoader.getLdLibraryPath.
*/
public File[] getNativeLibraryDirectories() {
return nativeLibraryDirectories;
}
/**
* Splits the given dex path string into elements using the path
* separator, pruning out any elements that do not refer to existing
* and readable files. (That is, directories are not included in the
* result.)
*/
private static ArrayList splitDexPath(String path) {
return splitPaths(path, null, false);
}
/**
* Splits the given library directory path string into elements
* using the path separator ({@code File.pathSeparator}, which
* defaults to {@code ":"} on Android, appending on the elements
* from the system library path, and pruning out any elements that
* do not refer to existing and readable directories.
*/
private static File[] splitLibraryPath(String path) {
// Native libraries may exist in both the system and
// application library paths, and we use this search order:
//
// 1. this class loader's library path for application libraries
// 2. the VM's library path from the system property for system libraries
//
// This order was reversed prior to Gingerbread; see http://b/2933456.
ArrayList result = splitPaths(path, System.getProperty("java.library.path"), true);
return result.toArray(new File[result.size()]);
}
/**
* Splits the given path strings into file elements using the path
* separator, combining the results and filtering out elements
* that don't exist, aren't readable, or aren't either a regular
* file or a directory (as specified). Either string may be empty
* or {@code null}, in which case it is ignored. If both strings
* are empty or {@code null}, or all elements get pruned out, then
* this returns a zero-element list.
*/
private static ArrayList splitPaths(String path1, String path2,
boolean wantDirectories) {
ArrayList result = new ArrayList();
splitAndAdd(path1, wantDirectories, result);
splitAndAdd(path2, wantDirectories, result);
return result;
}
/**
* Helper for {@link #splitPaths}, which does the actual splitting
* and filtering and adding to a result.
*/
private static void splitAndAdd(String searchPath, boolean directoriesOnly,
ArrayList resultList) {
if (searchPath == null) {
return;
}
for (String path : searchPath.split(":")) {
try {
StructStat sb = Libcore.os.stat(path);
if (!directoriesOnly || S_ISDIR(sb.st_mode)) {
resultList.add(new File(path));
}
} catch (ErrnoException ignored) {
}
}
}
/**
* Makes an array of dex/resource path elements, one per element of
* the given array.
*/
private static Element[] makeDexElements(ArrayList files, File optimizedDirectory,
ArrayList suppressedExceptions) {
ArrayList elements = new ArrayList();
/*
* Open all files and load the (direct or contained) dex files
* up front.
*/
for (File file : files) {
File zip = null;
DexFile dex = null;
String name = file.getName();
if (file.isDirectory()) {
// We support directories for looking up resources.
// This is only useful for running libcore tests.
elements.add(new Element(file, true, null, null));
} else if (file.isFile()){
if (name.endsWith(DEX_SUFFIX)) {
// Raw dex file (not inside a zip/jar).
try {
dex = loadDexFile(file, optimizedDirectory);
} catch (IOException ex) {
System.logE("Unable to load dex file: " + file, ex);
}
} else {
zip = file;
try {
dex = loadDexFile(file, optimizedDirectory);
} catch (IOException suppressed) {
/*
* IOException might get thrown "legitimately" by the DexFile constructor if
* the zip file turns out to be resource-only (that is, no classes.dex file
* in it).
* Let dex == null and hang on to the exception to add to the tea-leaves for
* when findClass returns null.
*/
suppressedExceptions.add(suppressed);
}
}
} else {
System.logW("ClassLoader referenced unknown path: " + file);
}
if ((zip != null) || (dex != null)) {
elements.add(new Element(file, false, zip, dex));
}
}
return elements.toArray(new Element[elements.size()]);
}
/**
* Constructs a {@code DexFile} instance, as appropriate depending
* on whether {@code optimizedDirectory} is {@code null}.
*/
private static DexFile loadDexFile(File file, File optimizedDirectory)
throws IOException {
if (optimizedDirectory == null) {
return new DexFile(file);
} else {
String optimizedPath = optimizedPathFor(file, optimizedDirectory);
return DexFile.loadDex(file.getPath(), optimizedPath, 0);
}
}
/**
* Converts a dex/jar file path and an output directory to an
* output file path for an associated optimized dex file.
*/
private static String optimizedPathFor(File path,
File optimizedDirectory) {
/*
* Get the filename component of the path, and replace the
* suffix with ".dex" if that's not already the suffix.
*
* We don't want to use ".odex", because the build system uses
* that for files that are paired with resource-only jar
* files. If the VM can assume that there's no classes.dex in
* the matching jar, it doesn't need to open the jar to check
* for updated dependencies, providing a slight performance
* boost at startup. The use of ".dex" here matches the use on
* files in /data/dalvik-cache.
*/
String fileName = path.getName();
if (!fileName.endsWith(DEX_SUFFIX)) {
int lastDot = fileName.lastIndexOf(".");
if (lastDot < 0) {
fileName += DEX_SUFFIX;
} else {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(lastDot + 4);
sb.append(fileName, 0, lastDot);
sb.append(DEX_SUFFIX);
fileName = sb.toString();
}
}
File result = new File(optimizedDirectory, fileName);
return result.getPath();
}
/**
* Finds the named class in one of the dex files pointed at by
* this instance. This will find the one in the earliest listed
* path element. If the class is found but has not yet been
* defined, then this method will define it in the defining
* context that this instance was constructed with.
*
* @param name of class to find
* @param suppressed exceptions encountered whilst finding the class
* @return the named class or {@code null} if the class is not
* found in any of the dex files
*/
public Class findClass(String name, List suppressed) {
for (Element element : dexElements) {
DexFile dex = element.dexFile;
if (dex != null) {
Class clazz = dex.loadClassBinaryName(name, definingContext, suppressed);
if (clazz != null) {
return clazz;
}
}
}
if (dexElementsSuppressedExceptions != null) {
suppressed.addAll(Arrays.asList(dexElementsSuppressedExceptions));
}
return null;
}
/**
* Finds the named resource in one of the zip/jar files pointed at
* by this instance. This will find the one in the earliest listed
* path element.
*
* @return a URL to the named resource or {@code null} if the
* resource is not found in any of the zip/jar files
*/
public URL findResource(String name) {
for (Element element : dexElements) {
URL url = element.findResource(name);
if (url != null) {
return url;
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* Finds all the resources with the given name, returning an
* enumeration of them. If there are no resources with the given
* name, then this method returns an empty enumeration.
*/
public Enumeration findResources(String name) {
ArrayList result = new ArrayList();
for (Element element : dexElements) {
URL url = element.findResource(name);
if (url != null) {
result.add(url);
}
}
return Collections.enumeration(result);
}
/**
* Finds the named native code library on any of the library
* directories pointed at by this instance. This will find the
* one in the earliest listed directory, ignoring any that are not
* readable regular files.
*
* @return the complete path to the library or {@code null} if no
* library was found
*/
public String findLibrary(String libraryName) {
String fileName = System.mapLibraryName(libraryName);
for (File directory : nativeLibraryDirectories) {
String path = new File(directory, fileName).getPath();
if (IoUtils.canOpenReadOnly(path)) {
return path;
}
}
return null;
}
/**
* Element of the dex/resource file path
*/
/*package*/ static class Element {
private final File file;
private final boolean isDirectory;
private final File zip;
private final DexFile dexFile;
private ZipFile zipFile;
private boolean initialized;
public Element(File file, boolean isDirectory, File zip, DexFile dexFile) {
this.file = file;
this.isDirectory = isDirectory;
this.zip = zip;
this.dexFile = dexFile;
}
@Override public String toString() {
if (isDirectory) {
return "directory \"" + file + "\"";
} else if (zip != null) {
return "zip file \"" + zip + "\"";
} else {
return "dex file \"" + dexFile + "\"";
}
}
public synchronized void maybeInit() {
if (initialized) {
return;
}
initialized = true;
if (isDirectory || zip == null) {
return;
}
try {
zipFile = new ZipFile(zip);
} catch (IOException ioe) {
/*
* Note: ZipException (a subclass of IOException)
* might get thrown by the ZipFile constructor
* (e.g. if the file isn't actually a zip/jar
* file).
*/
System.logE("Unable to open zip file: " + file, ioe);
zipFile = null;
}
}
public URL findResource(String name) {
maybeInit();
// We support directories so we can run tests and/or legacy code
// that uses Class.getResource.
if (isDirectory) {
File resourceFile = new File(file, name);
if (resourceFile.exists()) {
try {
return resourceFile.toURI().toURL();
} catch (MalformedURLException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
}
}
if (zipFile == null || zipFile.getEntry(name) == null) {
/*
* Either this element has no zip/jar file (first
* clause), or the zip/jar file doesn't have an entry
* for the given name (second clause).
*/
return null;
}
try {
/*
* File.toURL() is compliant with RFC 1738 in
* always creating absolute path names. If we
* construct the URL by concatenating strings, we
* might end up with illegal URLs for relative
* names.
*/
return new URL("jar:" + file.toURL() + "!/" + name);
} catch (MalformedURLException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
}
}
}