基于NVIDIA TX2的串口(UART1_J17)通讯
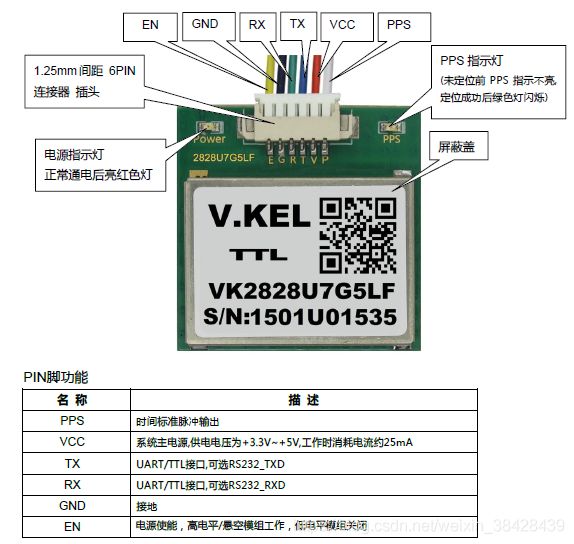
本文所讲述的是基于NVIDIA TX2的串口通讯,通讯的设备为NVIDIA TX2和GPS信号接收芯片模块。如下图所示是该芯片的示意图:
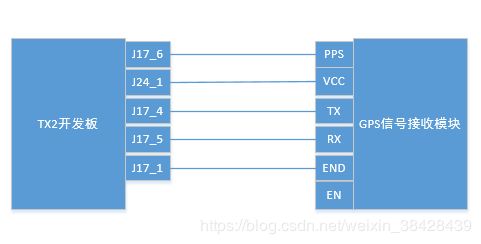
1、首先先画出该GPS信号接收芯片与TX2开发板的连接示意图,如下图所示:
切记,J17_1表示J17模块的1接口,表示接地;因此J17模块的引脚从上往下依次是6-1接口,千万不要接反了!!!
2、接下来就是串口通讯,直接上代码。
2.1采用Linux的可函数进行串口通讯
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "fun.h"
#define TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
int speed_arr[] = { B38400, B19200, B9600, B4800, B2400, B1200, B300, //波特率设计
B38400, B19200, B9600, B4800, B2400, B1200, B300, };
int name_arr[] = {38400, 19200, 9600, 4800, 2400, 1200, 300,
38400, 19200, 9600, 4800, 2400, 1200, 300, };
char *freq[]={ //改变GPS芯片的接受数据模式(可以不用在意)
"B5 62 06 08 06 00 20 4E 01 00 01 00 84 00 B5 62 06 08 00 00 0E 30",
"B5 62 06 08 06 00 10 27 01 00 01 00 4D DD B5 62 06 08 00 00 0E 30",
"B5 62 06 08 06 00 88 13 01 00 01 00 B1 49 B5 62 06 08 00 00 0E 30",
"B5 62 06 08 06 00 B8 0B 01 00 01 00 D9 41 B5 62 06 08 00 00 0E 30",
"B5 62 06 08 06 00 E8 03 01 00 01 00 01 39",
"B5 62 06 08 06 00 C8 00 01 00 01 00 DE 6A B5 62 06 08 00 00 0E 30",
"B5 62 06 08 06 00 64 00 01 00 01 00 7A 12 B5 62 06 08 00 00 0E 30",
};
char *GPL[]={ //改变GPS芯片的接受数据模式(可以不用在意)
"B5 62 06 09 0D 00 FF FF 00 00 00 00 00 00 FF FF 00 00 07 1F 9E",
"B5 62 06 3E 24 00 00 00 16 04 00 04 FF 00 00 00 00 00 01 01 03 00 00 00 00 00 05 00 03 00 00 00 00 00 06 08 FF 00 01 00 00 00 A0 D9 B5 62 06 3E 00 00 42 D2",
};
void set_speed(int fd, int speed) //设定波特率的速度
{
int i;
int status;
struct termios Opt;
tcgetattr(fd, &Opt);
for ( i= 0; i < sizeof(speed_arr) / sizeof(int); i++)
{
if (speed == name_arr[i])
{
tcflush(fd, TCIOFLUSH); //刷新缓存
cfsetispeed(&Opt, speed_arr[i]); //设定输入波特率
cfsetospeed(&Opt, speed_arr[i]); //设定输出波特率
status = tcsetattr(fd, TCSANOW, &Opt);
if (status != 0)
perror("tcsetattr fd1");
return;
}
tcflush(fd,TCIOFLUSH);
}
}
int set_Parity(int fd,int databits,int stopbits,int parity) //数据个数和奇偶校验位设置
{
struct termios options;
if ( tcgetattr( fd,&options) != 0)
{
perror("SetupSerial 1");
return(FALSE);
}
options.c_cflag &= ~CSIZE;
switch (databits)
{
case 7:
options.c_cflag |= CS7;
break;
case 8:
options.c_cflag |= CS8;
break;
default:
fprintf(stderr,"Unsupported data size\n");
return (FALSE);
}
switch (parity)
{
case 'n':
case 'N':
options.c_cflag &= ~PARENB; /* Clear parity enable */
options.c_iflag &= ~INPCK; /* Enable parity checking */
break;
case 'o':
case 'O':
options.c_cflag |= (PARODD | PARENB);
options.c_iflag |= INPCK; /* Disnable parity checking */
break;
case 'e':
case 'E':
options.c_cflag |= PARENB; /* Enable parity */
options.c_cflag &= ~PARODD;
options.c_iflag |= INPCK; /* Disnable parity checking */
break;
case 'S':
case 's': /*as no parity*/
options.c_cflag &= ~PARENB;
options.c_cflag &= ~CSTOPB;
break;
default:
fprintf(stderr,"Unsupported parity\n");
return (FALSE);
}
switch (stopbits)
{
case 1:
options.c_cflag &= ~CSTOPB;
break;
case 2:
options.c_cflag |= CSTOPB;
break;
default:
fprintf(stderr,"Unsupported stop bits\n");
return (FALSE);
}
/* Set input parity option */
if (parity != 'n')
options.c_iflag |= INPCK;
options.c_cc[VTIME] = 15; // 1.5 seconds
options.c_cc[VMIN] = 1;
tcflush(fd,TCIFLUSH); /* Update the options and do it NOW */
if (tcsetattr(fd,TCSANOW,&options) != 0)
{
perror("SetupSerial 3");
return (FALSE);
}
return (TRUE);
}
int OpenDev(char *Dev)
{
int fd = open( Dev, O_RDWR ); //| O_NOCTTY | O_NDELAY 打开UART1串口
if (-1 == fd)
{
perror("Can't Open Serial Port");
return -1;
}
else
return fd;
}
/*
*@breif main()
*/
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int fd,res;
FILE *fd1;
int count=0,sum=0;
long int length;
int nread;
long int nwrite;
char buff[1024];
char *dev ="/dev/ttyTHS2"; //J17串口模块的设备描述符
char *p=GPL[1];
struct timespec time_out;
fd = OpenDev(dev);
if (fd>0)
set_speed(fd,9600);
else
{
perror("Can't Open Serial Port!");
exit(0);
}
if (set_Parity(fd,8,1,'N')== FALSE)
{
perror("Set Parity Error\n");
exit(1);
}
/*************************************************************************/
if(argc>1) //个人需求的一些设置,不用在意
{
int flag=atoi(argv[1]);
switch(flag)
{
case 1:{
length=strlen(p);
if((nwrite = write(fd,p,length))==length)
{
printf("%s\n %ld\n %ld\n",p,nwrite,length);
printf("write successfully***********\n");
}
else
perror("write error!");
}
break;
case 2:{
p=freq[6];
length=strlen(p);
if((nwrite = write(fd,p,length))==length)
{
printf("%s\n %ld\n %ld\n",p,nwrite,length);
printf("write successfully***********\n");
}
else
perror("write error!");
}
break;
default:printf("please choose 1 or 2\n");break;
}
}
else
printf("you should choose mode\n");
/*****************************************************************/
fd1=fopen("/home/nvidia/gpsdata.txt","w"); //个人需求的一些设置,不用在意
if(fd1 == NULL)
perror("create file fail");
if(res=setvbuf(fd1,NULL,_IONBF,0)!=0)
printf("setvbuf failure\n");
/*******************************************************************/
while(1)
{
while((nread = read(fd,buff,1024))>0) //接收区字符大于1024时输出
{
if((nread>30)&&(nread<90)) //对接收信息的长度进行判断
{
count++;
buff[nread+1]='\0';
clock_gettime(CLOCK_REALTIME, &time_out);
fprintf(fd1,"%ld %ld\n %s\n",
time_out.tv_sec,time_out.tv_nsec,buff); //打印时间
printf("%ld %ld\n",
time_out.tv_sec,time_out.tv_nsec);
analyse(buff);
fflush(stdout);
sum++;
}
else
break;
}
if(count==128) //只接收128次数据就停止
{
printf("totally %d message got\n",sum);
fprintf(fd1,"totally %d message got\n",sum);
fflush(stdout);
sum=0;
count=0;
break;
}
}
close(fd);
fclose(fd1);
printf("just list these datas\n");
exit(0);
} 2.2 采用ros中的函数进行串口通讯,代码如下:
#include
#include
#include //ROS已经内置了的串口包
#include
#include
serial::Serial ser; //声明串口对象
/*
void write_callback(const std_msgs::String::ConstPtr& msg)
{
ROS_INFO_STREAM("Writing to serial port" <data);
ser.write(msg->data); //发送串口数据
}
*/
int main (int argc, char** argv)
{
//初始化节点
ros::init(argc, argv, "uart_ros");
//声明节点句柄
ros::NodeHandle nh;
//订阅主题,并配置回调函数
// ros::Subscriber write_sub = nh.subscribe("write", 1000, write_callback);
//发布主题
ros::Publisher read_pub = nh.advertise("read", 1000);
try
{
//设置串口属性,并打开串口
ser.setPort("/dev/ttyTHS2");
ser.setBaudrate(9600);
serial::Timeout to = serial::Timeout::simpleTimeout(1000);
ser.setTimeout(to);
ser.open();
}
catch (serial::IOException& e)
{
ROS_ERROR_STREAM("Unable to open port ");
return -1;
}
if(ser.isOpen())
{
ROS_INFO_STREAM("Serial Port initialized");
}
else
{
return -1;
}
ros::Rate loop_rate(50);
while(ros::ok())
{
if(ser.available()){
ROS_INFO_STREAM("Reading from serial port");
std_msgs::String result;
result.data = ser.read(ser.available());
ROS_INFO_STREAM("Read:\n " << result.data);
read_pub.publish(result);
}
//处理ROS的信息,比如订阅消息,并调用回调函数
ros::spinOnce();
loop_rate.sleep();
}
}
3.可以看到,ros中的串口通讯非常简单,因为ros的串口通讯已经封装成函数,直接调用就行了,但CMake需要添加相关的依赖库,不用像Linux中那么麻烦需要设置许多参数;本文主要是讲解TX2开发板的串口通讯的大概架构,具体函数的使用不在讲解之内。如果有问题欢迎提问!