FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:宏块解码(Decode)部分-帧间宏块(Inter)
=====================================================
H.264源代码分析文章列表:
【编码 - x264】
x264源代码简单分析:概述
x264源代码简单分析:x264命令行工具(x264.exe)
x264源代码简单分析:编码器主干部分-1
x264源代码简单分析:编码器主干部分-2
x264源代码简单分析:x264_slice_write()
x264源代码简单分析:滤波(Filter)部分
x264源代码简单分析:宏块分析(Analysis)部分-帧内宏块(Intra)
x264源代码简单分析:宏块分析(Analysis)部分-帧间宏块(Inter)
x264源代码简单分析:宏块编码(Encode)部分
x264源代码简单分析:熵编码(Entropy Encoding)部分
FFmpeg与libx264接口源代码简单分析
【解码 - libavcodec H.264 解码器】
FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:概述
FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:解析器(Parser)部分
FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:解码器主干部分
FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:熵解码(EntropyDecoding)部分
FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:宏块解码(Decode)部分-帧内宏块(Intra)
FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:宏块解码(Decode)部分-帧间宏块(Inter)
FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:环路滤波(Loop Filter)部分
=====================================================
本文分析FFmpeg的H.264解码器的宏块解码(Decode)部分。FFmpeg的H.264解码器调用decode_slice()函数完成了解码工作。这些解码工作可以大体上分为3个步骤:熵解码,宏块解码以及环路滤波。本文分析这3个步骤中的第2个步骤:宏块解码。上一篇文章已经记录了帧内预测宏块(Intra)的宏块解码,本文继续上一篇文章的内容,记录帧间预测宏块(Inter)的宏块解码。
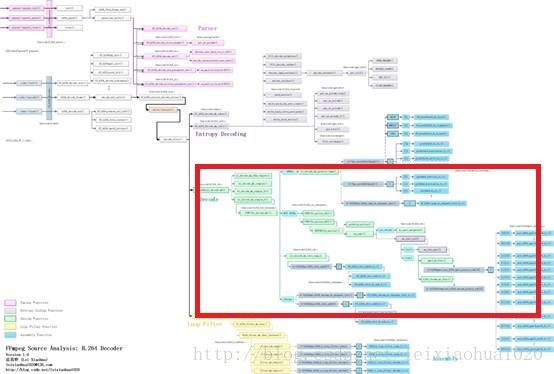
函数调用关系图
宏块解码(Decode)部分的源代码在整个H.264解码器中的位置如下图所示。hl_decode_mb_simple_8()的定义是无法在源代码中直接找到的,这是因为它实际代码的函数名称是使用宏的方式写的。hl_decode_mb_simple_8()的源代码实际上就是FUNC(hl_decode_mb)()函数的源代码。
从函数调用图中可以看出,FUNC(hl_decode_mb)()根据宏块类型的不同作不同的处理:如果帧内预测宏块(INTRA),就会调用hl_decode_mb_predict_luma()进行帧内预测;如果是帧间预测宏块(INTER),就会调用FUNC(hl_motion_422)()或者FUNC(hl_motion_420)()进行四分之一像素运动补偿。
经过帧内预测或者帧间预测步骤之后,就得到了预测数据。随后FUNC(hl_decode_mb)()会调用hl_decode_mb_idct_luma()等几个函数对残差数据进行DCT反变换工作,并将变换后的数据叠加到预测数据上,形成解码后的图像数据。
由于帧内预测宏块和帧间预测宏块的解码工作都比较复杂,因此分成两篇文章记录这两部分的源代码。上篇文章已经记录了帧内预测宏块的解码,本文继续记录帧间预测宏块的解码。
下面首先回顾一下decode_slice()函数。
decode_slice()
decode_slice()用于解码H.264的Slice。该函数完成了“熵解码”、“宏块解码”、“环路滤波”的功能。它的定义位于libavcodec\h264_slice.c,如下所示。//解码slice
//三个主要步骤:
//1.熵解码(CAVLC/CABAC)
//2.宏块解码
//3.环路滤波
//此外还包含了错误隐藏代码
static int decode_slice(struct AVCodecContext *avctx, void *arg)
{
H264Context *h = *(void **)arg;
int lf_x_start = h->mb_x;
h->mb_skip_run = -1;
av_assert0(h->block_offset[15] == (4 * ((scan8[15] - scan8[0]) & 7) << h->pixel_shift) + 4 * h->linesize * ((scan8[15] - scan8[0]) >> 3));
h->is_complex = FRAME_MBAFF(h) || h->picture_structure != PICT_FRAME ||
avctx->codec_id != AV_CODEC_ID_H264 ||
(CONFIG_GRAY && (h->flags & CODEC_FLAG_GRAY));
if (!(h->avctx->active_thread_type & FF_THREAD_SLICE) && h->picture_structure == PICT_FRAME && h->er.error_status_table) {
const int start_i = av_clip(h->resync_mb_x + h->resync_mb_y * h->mb_width, 0, h->mb_num - 1);
if (start_i) {
int prev_status = h->er.error_status_table[h->er.mb_index2xy[start_i - 1]];
prev_status &= ~ VP_START;
if (prev_status != (ER_MV_END | ER_DC_END | ER_AC_END))
h->er.error_occurred = 1;
}
}
//CABAC情况
if (h->pps.cabac) {
/* realign */
align_get_bits(&h->gb);
/* init cabac */
//初始化CABAC解码器
ff_init_cabac_decoder(&h->cabac,
h->gb.buffer + get_bits_count(&h->gb) / 8,
(get_bits_left(&h->gb) + 7) / 8);
ff_h264_init_cabac_states(h);
//循环处理每个宏块
for (;;) {
// START_TIMER
//解码CABAC数据
int ret = ff_h264_decode_mb_cabac(h);
int eos;
// STOP_TIMER("decode_mb_cabac")
//解码宏块
if (ret >= 0)
ff_h264_hl_decode_mb(h);
// FIXME optimal? or let mb_decode decode 16x32 ?
//宏块级帧场自适应。很少接触
if (ret >= 0 && FRAME_MBAFF(h)) {
h->mb_y++;
ret = ff_h264_decode_mb_cabac(h);
//解码宏块
if (ret >= 0)
ff_h264_hl_decode_mb(h);
h->mb_y--;
}
eos = get_cabac_terminate(&h->cabac);
if ((h->workaround_bugs & FF_BUG_TRUNCATED) &&
h->cabac.bytestream > h->cabac.bytestream_end + 2) {
//错误隐藏
er_add_slice(h, h->resync_mb_x, h->resync_mb_y, h->mb_x - 1,
h->mb_y, ER_MB_END);
if (h->mb_x >= lf_x_start)
loop_filter(h, lf_x_start, h->mb_x + 1);
return 0;
}
if (h->cabac.bytestream > h->cabac.bytestream_end + 2 )
av_log(h->avctx, AV_LOG_DEBUG, "bytestream overread %"PTRDIFF_SPECIFIER"\n", h->cabac.bytestream_end - h->cabac.bytestream);
if (ret < 0 || h->cabac.bytestream > h->cabac.bytestream_end + 4) {
av_log(h->avctx, AV_LOG_ERROR,
"error while decoding MB %d %d, bytestream %"PTRDIFF_SPECIFIER"\n",
h->mb_x, h->mb_y,
h->cabac.bytestream_end - h->cabac.bytestream);
er_add_slice(h, h->resync_mb_x, h->resync_mb_y, h->mb_x,
h->mb_y, ER_MB_ERROR);
return AVERROR_INVALIDDATA;
}
//mb_x自增
//如果自增后超过了一行的mb个数
if (++h->mb_x >= h->mb_width) {
//环路滤波
loop_filter(h, lf_x_start, h->mb_x);
h->mb_x = lf_x_start = 0;
decode_finish_row(h);
//mb_y自增(处理下一行)
++h->mb_y;
//宏块级帧场自适应,暂不考虑
if (FIELD_OR_MBAFF_PICTURE(h)) {
++h->mb_y;
if (FRAME_MBAFF(h) && h->mb_y < h->mb_height)
predict_field_decoding_flag(h);
}
}
//如果mb_y超过了mb的行数
if (eos || h->mb_y >= h->mb_height) {
tprintf(h->avctx, "slice end %d %d\n",
get_bits_count(&h->gb), h->gb.size_in_bits);
er_add_slice(h, h->resync_mb_x, h->resync_mb_y, h->mb_x - 1,
h->mb_y, ER_MB_END);
if (h->mb_x > lf_x_start)
loop_filter(h, lf_x_start, h->mb_x);
return 0;
}
}
} else {
//CAVLC情况
//循环处理每个宏块
for (;;) {
//解码宏块的CAVLC
int ret = ff_h264_decode_mb_cavlc(h);
//解码宏块
if (ret >= 0)
ff_h264_hl_decode_mb(h);
// FIXME optimal? or let mb_decode decode 16x32 ?
if (ret >= 0 && FRAME_MBAFF(h)) {
h->mb_y++;
ret = ff_h264_decode_mb_cavlc(h);
if (ret >= 0)
ff_h264_hl_decode_mb(h);
h->mb_y--;
}
if (ret < 0) {
av_log(h->avctx, AV_LOG_ERROR,
"error while decoding MB %d %d\n", h->mb_x, h->mb_y);
er_add_slice(h, h->resync_mb_x, h->resync_mb_y, h->mb_x,
h->mb_y, ER_MB_ERROR);
return ret;
}
if (++h->mb_x >= h->mb_width) {
//环路滤波
loop_filter(h, lf_x_start, h->mb_x);
h->mb_x = lf_x_start = 0;
decode_finish_row(h);
++h->mb_y;
if (FIELD_OR_MBAFF_PICTURE(h)) {
++h->mb_y;
if (FRAME_MBAFF(h) && h->mb_y < h->mb_height)
predict_field_decoding_flag(h);
}
if (h->mb_y >= h->mb_height) {
tprintf(h->avctx, "slice end %d %d\n",
get_bits_count(&h->gb), h->gb.size_in_bits);
if ( get_bits_left(&h->gb) == 0
|| get_bits_left(&h->gb) > 0 && !(h->avctx->err_recognition & AV_EF_AGGRESSIVE)) {
//错误隐藏
er_add_slice(h, h->resync_mb_x, h->resync_mb_y,
h->mb_x - 1, h->mb_y, ER_MB_END);
return 0;
} else {
er_add_slice(h, h->resync_mb_x, h->resync_mb_y,
h->mb_x, h->mb_y, ER_MB_END);
return AVERROR_INVALIDDATA;
}
}
}
if (get_bits_left(&h->gb) <= 0 && h->mb_skip_run <= 0) {
tprintf(h->avctx, "slice end %d %d\n",
get_bits_count(&h->gb), h->gb.size_in_bits);
if (get_bits_left(&h->gb) == 0) {
er_add_slice(h, h->resync_mb_x, h->resync_mb_y,
h->mb_x - 1, h->mb_y, ER_MB_END);
if (h->mb_x > lf_x_start)
loop_filter(h, lf_x_start, h->mb_x);
return 0;
} else {
er_add_slice(h, h->resync_mb_x, h->resync_mb_y, h->mb_x,
h->mb_y, ER_MB_ERROR);
return AVERROR_INVALIDDATA;
}
}
}
}
}
decode_slice()的流程如下所示:
(1)判断H.264码流是CABAC编码还是CAVLC编码,进入不同的处理循环。
(2)如果是CABAC编码,首先调用ff_init_cabac_decoder()初始化CABAC解码器。然后进入一个循环,依次对每个宏块进行以下处理:
a)调用ff_h264_decode_mb_cabac()进行CABAC熵解码
可以看出,宏块解码函数是ff_h264_hl_decode_mb()。下面看一下这个函数。b)调用ff_h264_hl_decode_mb()进行宏块解码c)解码一行宏块之后调用loop_filter()进行环路滤波d)此外还有可能调用er_add_slice()进行错误隐藏处理(3)如果是CABAC编码,直接进入一个循环,依次对每个宏块进行以下处理:a)调用ff_h264_decode_mb_cavlc()进行CAVLC熵解码b)调用ff_h264_hl_decode_mb()进行宏块解码c)解码一行宏块之后调用loop_filter()进行环路滤波d)此外还有可能调用er_add_slice()进行错误隐藏处理
ff_h264_hl_decode_mb()
ff_h264_hl_decode_mb()完成了宏块解码的工作。“宏块解码”就是根据前一步骤“熵解码”得到的宏块类型、运动矢量、参考帧、DCT残差数据等信息恢复图像数据的过程。该函数的定义位于libavcodec\h264_mb.c,如下所示。//解码宏块
void ff_h264_hl_decode_mb(H264Context *h)
{
//宏块序号 mb_xy = mb_x + mb_y*mb_stride
const int mb_xy = h->mb_xy;
//宏块类型
const int mb_type = h->cur_pic.mb_type[mb_xy];
//比较少见,PCM类型
int is_complex = CONFIG_SMALL || h->is_complex ||
IS_INTRA_PCM(mb_type) || h->qscale == 0;
//YUV444
if (CHROMA444(h)) {
if (is_complex || h->pixel_shift)
hl_decode_mb_444_complex(h);
else
hl_decode_mb_444_simple_8(h);
} else if (is_complex) {
hl_decode_mb_complex(h); //PCM类型?
} else if (h->pixel_shift) {
hl_decode_mb_simple_16(h); //色彩深度为16
} else
hl_decode_mb_simple_8(h); //色彩深度为8
}
可以看出ff_h264_hl_decode_mb()的定义很简单:通过系统的参数(例如颜色位深是不是8bit,YUV采样格式是不是4:4:4等)判断该调用哪一个函数作为解码函数。由于最普遍的情况是解码8bit的YUV420P格式的H.264数据,因此一般情况下会调用hl_decode_mb_simple_8()。这里有一点需要注意:如果我们直接查找hl_decode_mb_simple_8()的定义,会发现这个函数是找不到的。这个函数的定义实际上就是FUNC(hl_decode_mb)()函数。FUNC(hl_decode_mb)()函数名称中的宏“FUNC()”展开后就是hl_decode_mb_simple_8()。下面看一下FUNC(hl_decode_mb)()函数。
FUNC(hl_decode_mb)()
FUNC(hl_decode_mb)()的定义位于libavcodec\h264_mb_template.c。下面看一下FUNC(hl_decode_mb)()函数的定义。//hl是什么意思?high level?
/*
* 注释:雷霄骅
* [email protected]
* http://blog.csdn.net/leixiaohua1020
*
* 宏块解码
* 帧内宏块:帧内预测->残差DCT反变换
* 帧间宏块:帧间预测(运动补偿)->残差DCT反变换
*
*/
static av_noinline void FUNC(hl_decode_mb)(H264Context *h)
{
//序号:x(行)和y(列)
const int mb_x = h->mb_x;
const int mb_y = h->mb_y;
//宏块序号 mb_xy = mb_x + mb_y*mb_stride
const int mb_xy = h->mb_xy;
//宏块类型
const int mb_type = h->cur_pic.mb_type[mb_xy];
//这三个变量存储最后处理完成的像素值
uint8_t *dest_y, *dest_cb, *dest_cr;
int linesize, uvlinesize /*dct_offset*/;
int i, j;
int *block_offset = &h->block_offset[0];
const int transform_bypass = !SIMPLE && (h->qscale == 0 && h->sps.transform_bypass);
/* is_h264 should always be true if SVQ3 is disabled. */
const int is_h264 = !CONFIG_SVQ3_DECODER || SIMPLE || h->avctx->codec_id == AV_CODEC_ID_H264;
void (*idct_add)(uint8_t *dst, int16_t *block, int stride);
const int block_h = 16 >> h->chroma_y_shift;
const int chroma422 = CHROMA422(h);
//存储Y,U,V像素的位置:dest_y,dest_cb,dest_cr
//分别对应AVFrame的data[0],data[1],data[2]
dest_y = h->cur_pic.f.data[0] + ((mb_x << PIXEL_SHIFT) + mb_y * h->linesize) * 16;
dest_cb = h->cur_pic.f.data[1] + (mb_x << PIXEL_SHIFT) * 8 + mb_y * h->uvlinesize * block_h;
dest_cr = h->cur_pic.f.data[2] + (mb_x << PIXEL_SHIFT) * 8 + mb_y * h->uvlinesize * block_h;
h->vdsp.prefetch(dest_y + (h->mb_x & 3) * 4 * h->linesize + (64 << PIXEL_SHIFT), h->linesize, 4);
h->vdsp.prefetch(dest_cb + (h->mb_x & 7) * h->uvlinesize + (64 << PIXEL_SHIFT), dest_cr - dest_cb, 2);
h->list_counts[mb_xy] = h->list_count;
//系统中包含了
//#define SIMPLE 1
//不会执行?
if (!SIMPLE && MB_FIELD(h)) {
linesize = h->mb_linesize = h->linesize * 2;
uvlinesize = h->mb_uvlinesize = h->uvlinesize * 2;
block_offset = &h->block_offset[48];
if (mb_y & 1) { // FIXME move out of this function?
dest_y -= h->linesize * 15;
dest_cb -= h->uvlinesize * (block_h - 1);
dest_cr -= h->uvlinesize * (block_h - 1);
}
if (FRAME_MBAFF(h)) {
int list;
for (list = 0; list < h->list_count; list++) {
if (!USES_LIST(mb_type, list))
continue;
if (IS_16X16(mb_type)) {
int8_t *ref = &h->ref_cache[list][scan8[0]];
fill_rectangle(ref, 4, 4, 8, (16 + *ref) ^ (h->mb_y & 1), 1);
} else {
for (i = 0; i < 16; i += 4) {
int ref = h->ref_cache[list][scan8[i]];
if (ref >= 0)
fill_rectangle(&h->ref_cache[list][scan8[i]], 2, 2,
8, (16 + ref) ^ (h->mb_y & 1), 1);
}
}
}
}
} else {
linesize = h->mb_linesize = h->linesize;
uvlinesize = h->mb_uvlinesize = h->uvlinesize;
// dct_offset = s->linesize * 16;
}
//系统中包含了
//#define SIMPLE 1
//不会执行?
if (!SIMPLE && IS_INTRA_PCM(mb_type)) {
const int bit_depth = h->sps.bit_depth_luma;
if (PIXEL_SHIFT) {
int j;
GetBitContext gb;
init_get_bits(&gb, h->intra_pcm_ptr,
ff_h264_mb_sizes[h->sps.chroma_format_idc] * bit_depth);
for (i = 0; i < 16; i++) {
uint16_t *tmp_y = (uint16_t *)(dest_y + i * linesize);
for (j = 0; j < 16; j++)
tmp_y[j] = get_bits(&gb, bit_depth);
}
if (SIMPLE || !CONFIG_GRAY || !(h->flags & CODEC_FLAG_GRAY)) {
if (!h->sps.chroma_format_idc) {
for (i = 0; i < block_h; i++) {
uint16_t *tmp_cb = (uint16_t *)(dest_cb + i * uvlinesize);
uint16_t *tmp_cr = (uint16_t *)(dest_cr + i * uvlinesize);
for (j = 0; j < 8; j++) {
tmp_cb[j] = tmp_cr[j] = 1 << (bit_depth - 1);
}
}
} else {
for (i = 0; i < block_h; i++) {
uint16_t *tmp_cb = (uint16_t *)(dest_cb + i * uvlinesize);
for (j = 0; j < 8; j++)
tmp_cb[j] = get_bits(&gb, bit_depth);
}
for (i = 0; i < block_h; i++) {
uint16_t *tmp_cr = (uint16_t *)(dest_cr + i * uvlinesize);
for (j = 0; j < 8; j++)
tmp_cr[j] = get_bits(&gb, bit_depth);
}
}
}
} else {
for (i = 0; i < 16; i++)
memcpy(dest_y + i * linesize, h->intra_pcm_ptr + i * 16, 16);
if (SIMPLE || !CONFIG_GRAY || !(h->flags & CODEC_FLAG_GRAY)) {
if (!h->sps.chroma_format_idc) {
for (i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
memset(dest_cb + i * uvlinesize, 1 << (bit_depth - 1), 8);
memset(dest_cr + i * uvlinesize, 1 << (bit_depth - 1), 8);
}
} else {
const uint8_t *src_cb = h->intra_pcm_ptr + 256;
const uint8_t *src_cr = h->intra_pcm_ptr + 256 + block_h * 8;
for (i = 0; i < block_h; i++) {
memcpy(dest_cb + i * uvlinesize, src_cb + i * 8, 8);
memcpy(dest_cr + i * uvlinesize, src_cr + i * 8, 8);
}
}
}
}
} else {
//Intra类型
//Intra4x4或者Intra16x16
if (IS_INTRA(mb_type)) {
if (h->deblocking_filter)
xchg_mb_border(h, dest_y, dest_cb, dest_cr, linesize,
uvlinesize, 1, 0, SIMPLE, PIXEL_SHIFT);
if (SIMPLE || !CONFIG_GRAY || !(h->flags & CODEC_FLAG_GRAY)) {
h->hpc.pred8x8[h->chroma_pred_mode](dest_cb, uvlinesize);
h->hpc.pred8x8[h->chroma_pred_mode](dest_cr, uvlinesize);
}
//帧内预测-亮度
hl_decode_mb_predict_luma(h, mb_type, is_h264, SIMPLE,
transform_bypass, PIXEL_SHIFT,
block_offset, linesize, dest_y, 0);
if (h->deblocking_filter)
xchg_mb_border(h, dest_y, dest_cb, dest_cr, linesize,
uvlinesize, 0, 0, SIMPLE, PIXEL_SHIFT);
} else if (is_h264) {
//Inter类型
//运动补偿
if (chroma422) {
FUNC(hl_motion_422)(h, dest_y, dest_cb, dest_cr,
h->qpel_put, h->h264chroma.put_h264_chroma_pixels_tab,
h->qpel_avg, h->h264chroma.avg_h264_chroma_pixels_tab,
h->h264dsp.weight_h264_pixels_tab,
h->h264dsp.biweight_h264_pixels_tab);
} else {
//“*_put”处理单向预测,“*_avg”处理双向预测,“weight”处理加权预测
//h->qpel_put[16]包含了单向预测的四分之一像素运动补偿所有样点处理的函数
//两个像素之间横向的点(内插点和原始的点)有4个,纵向的点有4个,组合起来一共16个
//h->qpel_avg[16]情况也类似
FUNC(hl_motion_420)(h, dest_y, dest_cb, dest_cr,
h->qpel_put, h->h264chroma.put_h264_chroma_pixels_tab,
h->qpel_avg, h->h264chroma.avg_h264_chroma_pixels_tab,
h->h264dsp.weight_h264_pixels_tab,
h->h264dsp.biweight_h264_pixels_tab);
}
}
//亮度的IDCT
hl_decode_mb_idct_luma(h, mb_type, is_h264, SIMPLE, transform_bypass,
PIXEL_SHIFT, block_offset, linesize, dest_y, 0);
//色度的IDCT(没有写在一个单独的函数中)
if ((SIMPLE || !CONFIG_GRAY || !(h->flags & CODEC_FLAG_GRAY)) &&
(h->cbp & 0x30)) {
uint8_t *dest[2] = { dest_cb, dest_cr };
//transform_bypass=0,不考虑
if (transform_bypass) {
if (IS_INTRA(mb_type) && h->sps.profile_idc == 244 &&
(h->chroma_pred_mode == VERT_PRED8x8 ||
h->chroma_pred_mode == HOR_PRED8x8)) {
h->hpc.pred8x8_add[h->chroma_pred_mode](dest[0],
block_offset + 16,
h->mb + (16 * 16 * 1 << PIXEL_SHIFT),
uvlinesize);
h->hpc.pred8x8_add[h->chroma_pred_mode](dest[1],
block_offset + 32,
h->mb + (16 * 16 * 2 << PIXEL_SHIFT),
uvlinesize);
} else {
idct_add = h->h264dsp.h264_add_pixels4_clear;
for (j = 1; j < 3; j++) {
for (i = j * 16; i < j * 16 + 4; i++)
if (h->non_zero_count_cache[scan8[i]] ||
dctcoef_get(h->mb, PIXEL_SHIFT, i * 16))
idct_add(dest[j - 1] + block_offset[i],
h->mb + (i * 16 << PIXEL_SHIFT),
uvlinesize);
if (chroma422) {
for (i = j * 16 + 4; i < j * 16 + 8; i++)
if (h->non_zero_count_cache[scan8[i + 4]] ||
dctcoef_get(h->mb, PIXEL_SHIFT, i * 16))
idct_add(dest[j - 1] + block_offset[i + 4],
h->mb + (i * 16 << PIXEL_SHIFT),
uvlinesize);
}
}
}
} else {
if (is_h264) {
int qp[2];
if (chroma422) {
qp[0] = h->chroma_qp[0] + 3;
qp[1] = h->chroma_qp[1] + 3;
} else {
qp[0] = h->chroma_qp[0];
qp[1] = h->chroma_qp[1];
}
//色度的IDCT
//直流分量的hadamard变换
if (h->non_zero_count_cache[scan8[CHROMA_DC_BLOCK_INDEX + 0]])
h->h264dsp.h264_chroma_dc_dequant_idct(h->mb + (16 * 16 * 1 << PIXEL_SHIFT),
h->dequant4_coeff[IS_INTRA(mb_type) ? 1 : 4][qp[0]][0]);
if (h->non_zero_count_cache[scan8[CHROMA_DC_BLOCK_INDEX + 1]])
h->h264dsp.h264_chroma_dc_dequant_idct(h->mb + (16 * 16 * 2 << PIXEL_SHIFT),
h->dequant4_coeff[IS_INTRA(mb_type) ? 2 : 5][qp[1]][0]);
//IDCT
//最后的“8”代表内部循环处理8次(U,V各4次)
h->h264dsp.h264_idct_add8(dest, block_offset,
h->mb, uvlinesize,
h->non_zero_count_cache);
} else if (CONFIG_SVQ3_DECODER) {
h->h264dsp.h264_chroma_dc_dequant_idct(h->mb + 16 * 16 * 1,
h->dequant4_coeff[IS_INTRA(mb_type) ? 1 : 4][h->chroma_qp[0]][0]);
h->h264dsp.h264_chroma_dc_dequant_idct(h->mb + 16 * 16 * 2,
h->dequant4_coeff[IS_INTRA(mb_type) ? 2 : 5][h->chroma_qp[1]][0]);
for (j = 1; j < 3; j++) {
for (i = j * 16; i < j * 16 + 4; i++)
if (h->non_zero_count_cache[scan8[i]] || h->mb[i * 16]) {
uint8_t *const ptr = dest[j - 1] + block_offset[i];
ff_svq3_add_idct_c(ptr, h->mb + i * 16,
uvlinesize,
ff_h264_chroma_qp[0][h->qscale + 12] - 12, 2);
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
下面简单梳理一下FUNC(hl_decode_mb)的流程(在这里只考虑亮度分量的解码,色度分量的解码过程是类似的):
(1)预测
a)如果是帧内预测宏块(Intra),调用hl_decode_mb_predict_luma()进行帧内预测,得到预测数据。b)如果不是帧内预测宏块(Inter),调用FUNC(hl_motion_420)()或者FUNC(hl_motion_422)()进行帧间预测(即运动补偿),得到预测数据。
(2)残差叠加
a)调用hl_decode_mb_idct_luma()对DCT残差数据进行DCT反变换,获得残差像素数据并且叠加到之前得到的预测数据上,得到最后的图像数据。
PS:该流程中有一个重要的贯穿始终的内存指针dest_y,其指向的内存中存储了解码后的亮度数据。
本文将会分析上述流程中的帧间预测部分(帧内预测部分已经在上一篇文章中完成)的源代码。下面先简单记录一下运动补偿相关的知识。
运动补偿小知识
在看具体的运动补偿代码之前,先简单回顾一下《H.264标准》中有关运动估计的知识。
1/4像素运动估计
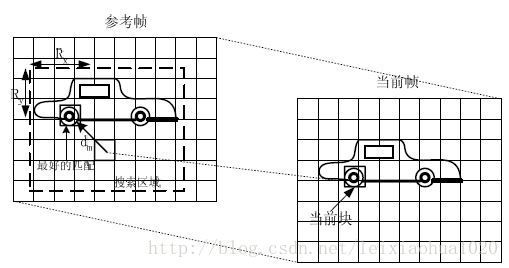
运动估计的理论基础就是活动图像邻近帧中的景物存在着一定的相关性。因此在压缩编码中不需要传递每一帧的所有信息,而只需要传递帧与帧之间差值就可以了(可以想象,如果画面背景是静止的,那么只需要传递很少的数据)。在视频编码的运动估计步骤中,会查找与当前宏块或者子宏块“长得像”的宏块作为“匹配块”,然后编码传输匹配块的位置(运动矢量,参考帧)和当前宏块与匹配块之间的微小差别(残差数据)。例如下图中,当前宏块中一个“车轮”在参考帧中找到了形状同样为一个“轮子”的匹配块。
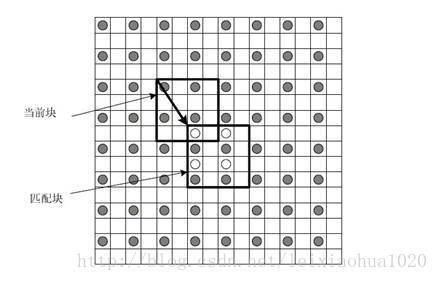
最早视频编码标准中都是以整像素的方式进行运动估计的。这样处理的好处是计算简单,坏处是不够精确。随着硬件技术的进步,比较新的视频编码标准(例如MPEG2)中使用1/2像素精度的方式进行运动估计。这样做计算相对复杂,但是计算也相对准确。1/2像素精度运动估计如下图所示。
《H.264标准》中对运动估计的精度要求又有了提升,变成了1/4像素精度。因此H.264编码器对系统性能要求又有了更高的要求。在H.264编码和解码的过程中,需要将画面中的像素进行插值——简单地说就是把原先的1个像素点拓展成4x4一共16个点。下图显示了H.264编码和解码过程中像素插值情况。可以看出原先的G点的右下方通过插值的方式产生了a、b、c、d等一共16个点(具体的方法后文论叙述)。
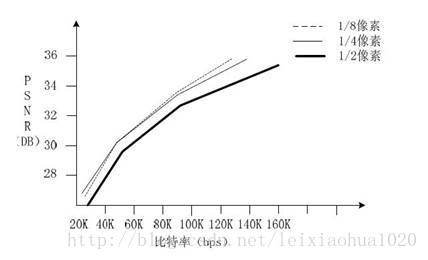
一些实验证明,1/4像素精度基本上达到了运动估计性能提升的极限。更高精度的运动估计并不能更明显的提升性能,却会导致计算复杂度的显著提升。因此现存主流的编解码标准在运动估计方面都采用了1/4精度。曾经有人压缩对比过1/2、1/4、1/8精度的运动估计下编码的视频质量,如下图所示。
从图中可以看出:1/4精度相比于1/2精度来说有显著的提升,但是1/8精度实际上和1/4精度是差不多的。
宏块划分
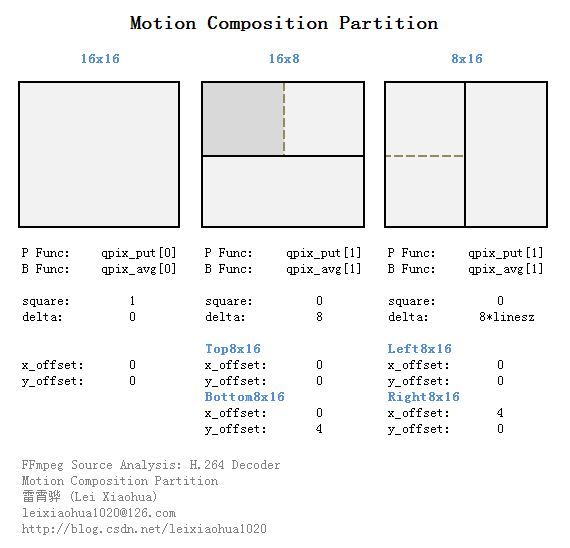
《H.264标准》中规定,每个16x16的宏块可以划分为16x16,16x8,8x16,8x8四种类型。而如果宏块划分为8x8类型的时候,每个8x8宏块又可以划分为8x8,8x4,4x8,4x4四种小块。它们之间的关系下图所示。上图中这些子宏块都包含了自己的运动矢量和参考帧序号,并且根据这两个信息获得最终的预测数据。总体说来,大的子宏块适合平坦区域,而小的子宏块适合多细节区域。例如下面这张图是一张没有进行运动补偿的残差帧的宏块分割方式图,可以看出平坦区域使用了较大的16x16分割方式,而细节区域使用了相对较小的宏块分割方式。
单向预测与双向预测
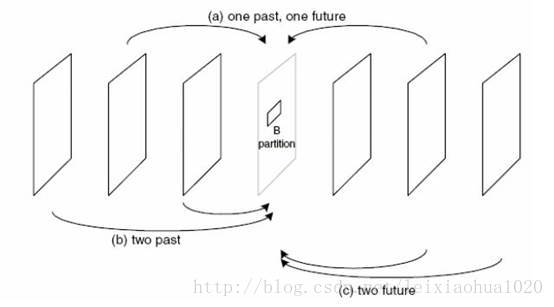
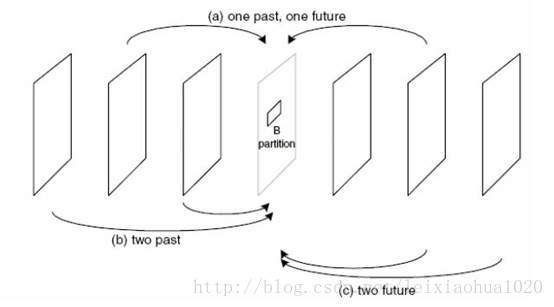
在运动估计的过程中,不仅仅只可以选择一个图像作为参考帧(P帧),而且还可以选择两张图片作为参考帧(B帧)。使用一张图像作为参考帧称为单向预测,而使用两张图像作为参考帧称为双向预测。使用单向预测的时候,直接将参考帧上的匹配块的数据“搬移下来”作后续的处理(“赋值”),而使用双向预测的时候,需要首先将两个参考帧上的匹配块的数据求平均值(“求平均”),然后再做后续处理。毫无疑问双向预测可以得到更好的压缩效果,但是也会使码流变得复杂一些。双向预测的示意图如下所示。
记录完这些基础概念之后,就可以看一下帧间预测函数FUNC(hl_motion_420)()了。FUNC(hl_motion_420)()
FUNC(hl_motion_420)()用于对YUV420P格式的H.264码流进行帧间预测,根据运动矢量和参考帧获得帧间预测的结果。如果直接查找“FUNC(hl_motion_420)()”的定义是无法找到的,该函数的定义实际上就是MCFUNC(hl_motion)的定义。
MCFUNC(hl_motion)
MCFUNC(hl_motion)的定义位于libavcodec\h264_mc_template.c,如下所示。//运动补偿
//“*_put”处理单向预测,“*_avg”处理双向预测,“weight”处理加权预测
static void MCFUNC(hl_motion)(H264Context *h, uint8_t *dest_y,
uint8_t *dest_cb, uint8_t *dest_cr,
qpel_mc_func(*qpix_put)[16],
h264_chroma_mc_func(*chroma_put),
qpel_mc_func(*qpix_avg)[16],
h264_chroma_mc_func(*chroma_avg),
h264_weight_func *weight_op,
h264_biweight_func *weight_avg)
{
const int mb_xy = h->mb_xy;
const int mb_type = h->cur_pic.mb_type[mb_xy];
av_assert2(IS_INTER(mb_type));
if (HAVE_THREADS && (h->avctx->active_thread_type & FF_THREAD_FRAME))
await_references(h);
prefetch_motion(h, 0, PIXEL_SHIFT, CHROMA_IDC);
if (IS_16X16(mb_type)) {
/*
* 16x16 宏块
*
* +--------+--------+
* | |
* | |
* | |
* + + +
* | |
* | |
* | |
* +--------+--------+
*
*/
//第3个参数square标志了该块是否为方形
//第5个参数delta用于配合square,运动补偿必须以“方形”为单位处理。
//当宏块不是“方形”的时候,需要进行2次运动补偿,这时候需要知道第二个方形与起始点dest_y之间的偏移值
//几种运动补偿函数:适用于不同大小的方块:
//qpix_put[0],qpix_avg[0]一次处理16x16个像素
//qpix_put[1],qpix_avg[1]一次处理8x8个像素
//qpix_put[2],qpix_avg[2]一次处理4x4个像素
//16x16块使用qpix_put[0],qpix_avg[0]
//
//IS_DIR()通过宏块类型判断本宏块是否使用list0和list1(使用list1的话需要进行双向预测)
//
mc_part(h, 0, 1, 16, 0, dest_y, dest_cb, dest_cr, 0, 0,
qpix_put[0], chroma_put[0], qpix_avg[0], chroma_avg[0],
weight_op, weight_avg,
IS_DIR(mb_type, 0, 0), IS_DIR(mb_type, 0, 1));
} else if (IS_16X8(mb_type)) {
/*
* 16x8 宏块划分
*
* +--------+--------+
* | | |
* | | |
* | | |
* +--------+--------+
*
*/
//第2个参数n用于h->mv_cache[list][scan8[n]]中的“n”,该值决定了运动补偿过程中使用哪一个MV
/*
* mv_cache如下所示
* 图中数字为scan8[n]中的n
* |
* --+--------------------
* | x x x x x x x x
* | x x x x 0 1 4 5
* | x x x x 2 3 6 7
* | x x x x 8 9 12 13
* | x x x x 10 11 14 15
*/
//
//dest_cr后面第1个参数x_offset代表了子宏块x偏移值
//dest_cr后面第2个参数y_offset代表了子宏块y偏移值(为什么是4而不是8?以YUV420P中的色度为基本单位?)
//总而言之,x_offset,y_offset决定了子宏块的位置(左上角像素点位置)
//而square,delta,和qpix_put[x]中的“x”决定的子宏块的大小(相当于确定了子宏块右下角像素的位置)
//上面几个值联合决定了子宏块位置和大小信息
//上16x8
//已经分割为子宏块的运动补偿
mc_part(h, 0, 0, 8, 8 << PIXEL_SHIFT, dest_y, dest_cb, dest_cr, 0, 0,
qpix_put[1], chroma_put[0], qpix_avg[1], chroma_avg[0],
weight_op, weight_avg,
IS_DIR(mb_type, 0, 0), IS_DIR(mb_type, 0, 1));
//下16x8
//已经分割为子宏块的运动补偿
mc_part(h, 8, 0, 8, 8 << PIXEL_SHIFT, dest_y, dest_cb, dest_cr, 0, 4,
qpix_put[1], chroma_put[0], qpix_avg[1], chroma_avg[0],
weight_op, weight_avg,
IS_DIR(mb_type, 1, 0), IS_DIR(mb_type, 1, 1));
} else if (IS_8X16(mb_type)) {
/*
* 8x16 宏块划分
*
* +--------+
* | |
* | |
* | |
* +--------+
* | |
* | |
* | |
* +--------+
*
*/
//左8x16
mc_part(h, 0, 0, 16, 8 * h->mb_linesize, dest_y, dest_cb, dest_cr, 0, 0,
qpix_put[1], chroma_put[1], qpix_avg[1], chroma_avg[1],
&weight_op[1], &weight_avg[1],
IS_DIR(mb_type, 0, 0), IS_DIR(mb_type, 0, 1));
//右8x16
mc_part(h, 4, 0, 16, 8 * h->mb_linesize, dest_y, dest_cb, dest_cr, 4, 0,
qpix_put[1], chroma_put[1], qpix_avg[1], chroma_avg[1],
&weight_op[1], &weight_avg[1],
IS_DIR(mb_type, 1, 0), IS_DIR(mb_type, 1, 1));
} else {
/*
* 16x16 宏块被划分为4个8x8子块
*
* +--------+--------+
* | | |
* | 0 | 1 |
* | | |
* +--------+--------+
* | | |
* | 2 | 3 |
* | | |
* +--------+--------+
*
*/
int i;
av_assert2(IS_8X8(mb_type));
//循环处理4个8x8宏块
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
const int sub_mb_type = h->sub_mb_type[i];
const int n = 4 * i;
int x_offset = (i & 1) << 2;
int y_offset = (i & 2) << 1;
//每个8x8的块可以再次划分为:8x8,8x4,4x8,4x4
if (IS_SUB_8X8(sub_mb_type)) {
/*
* 8x8(等同于没划分)
* +----+----+
* | |
* + + +
* | |
* +----+----+
*
*/
//“qpix_put[1]”说明运动补偿的时候一次处理8x8个像素
mc_part(h, n, 1, 8, 0, dest_y, dest_cb, dest_cr,
x_offset, y_offset,
qpix_put[1], chroma_put[1], qpix_avg[1], chroma_avg[1],
&weight_op[1], &weight_avg[1],
IS_DIR(sub_mb_type, 0, 0), IS_DIR(sub_mb_type, 0, 1));
} else if (IS_SUB_8X4(sub_mb_type)) {
/*
* 8x4
* +----+----+
* | |
* +----+----+
* | |
* +----+----+
*
*/
//“qpix_put[2]”说明运动补偿的时候一次处理4x4个像素
mc_part(h, n, 0, 4, 4 << PIXEL_SHIFT, dest_y, dest_cb, dest_cr,
x_offset, y_offset,
qpix_put[2], chroma_put[1], qpix_avg[2], chroma_avg[1],
&weight_op[1], &weight_avg[1],
IS_DIR(sub_mb_type, 0, 0), IS_DIR(sub_mb_type, 0, 1));
mc_part(h, n + 2, 0, 4, 4 << PIXEL_SHIFT,
dest_y, dest_cb, dest_cr, x_offset, y_offset + 2,
qpix_put[2], chroma_put[1], qpix_avg[2], chroma_avg[1],
&weight_op[1], &weight_avg[1],
IS_DIR(sub_mb_type, 0, 0), IS_DIR(sub_mb_type, 0, 1));
} else if (IS_SUB_4X8(sub_mb_type)) {
/*
* 4x8
* +----+----+
* | | |
* + + +
* | | |
* +----+----+
*
*/
mc_part(h, n, 0, 8, 4 * h->mb_linesize,
dest_y, dest_cb, dest_cr, x_offset, y_offset,
qpix_put[2], chroma_put[2], qpix_avg[2], chroma_avg[2],
&weight_op[2], &weight_avg[2],
IS_DIR(sub_mb_type, 0, 0), IS_DIR(sub_mb_type, 0, 1));
mc_part(h, n + 1, 0, 8, 4 * h->mb_linesize,
dest_y, dest_cb, dest_cr, x_offset + 2, y_offset,
qpix_put[2], chroma_put[2], qpix_avg[2], chroma_avg[2],
&weight_op[2], &weight_avg[2],
IS_DIR(sub_mb_type, 0, 0), IS_DIR(sub_mb_type, 0, 1));
} else {
/*
* 4x4
* +----+----+
* | | |
* +----+----+
* | | |
* +----+----+
*
*/
int j;
av_assert2(IS_SUB_4X4(sub_mb_type));
for (j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
int sub_x_offset = x_offset + 2 * (j & 1);
int sub_y_offset = y_offset + (j & 2);
mc_part(h, n + j, 1, 4, 0,
dest_y, dest_cb, dest_cr, sub_x_offset, sub_y_offset,
qpix_put[2], chroma_put[2], qpix_avg[2], chroma_avg[2],
&weight_op[2], &weight_avg[2],
IS_DIR(sub_mb_type, 0, 0), IS_DIR(sub_mb_type, 0, 1));
}
}
}
}
prefetch_motion(h, 1, PIXEL_SHIFT, CHROMA_IDC);
}
从源代码可以看出,MCFUNC(hl_motion)根据子宏块的划分类型的不同,传递不同的参数调用mc_part()函数。
(1)如果子宏块划分为16x16(等同于没有划分),直接调用mc_part()并且传递如下参数:a)单向预测汇编函数集:qpix_put[0] (qpix_put[0]中的函数进行16x16块的四分之一像素运动补偿)。b)双向预测汇编函数集:qpix_avg[0]。c)square设置为1,delta设置为0。d)x_offset和y_offset都设置为0。(2)如果子宏块划分为16x8,分两次调用mc_part()并且传递如下参数:a)单向预测汇编函数集:qpix_put[1] (qpix_put[1]中的函数进行8x8块的四分之一像素运动补偿)。b)双向预测汇编函数集:qpix_avg[1]。c)square设置为0,delta设置为8。其中第1次调用mc_part()的时候x_offset和y_offset都设置为0,第2次调用mc_part()的时候x_offset设置为0,y_offset设置为4。(3)如果子宏块划分为8x16,分两次调用mc_part()并且传递如下参数:a)单向预测汇编函数集:qpix_put[1] (qpix_put[1]中的函数进行8x8块的四分之一像素运动补偿)。b)双向预测汇编函数集:qpix_avg[1]。c)square设置为0,delta设置为8 * h->mb_linesize。其中第1次调用mc_part()的时候x_offset和y_offset都设置为0,第2次调用mc_part()的时候x_offset设置为4,y_offset设置为0。(4)如果子宏块划分为8x8,说明此时每个8x8子宏块还可以继续划分为8x8,8x8,4x8,4x4几种类型,此时根据上述的规则,分成4次分别对这些小块做类似的处理。
下面简单分析一下上文提到的几个变量。
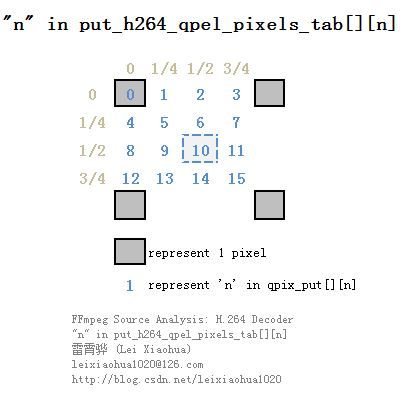
qpix_put[4][16]实际上指向了H264QpelContext的put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[4][16],其中存储了所有单向预测方块的四分之一像素运动补偿函数。其中:
qpix_put[0]存储的是16x16方块的运动补偿函数;其中每种方块包含了16个运动补偿函数,这些函数按照顺序分别代表了四分之一像素运动补偿不同的位置(从左到右,从上到下),如下图所示。
qpix_put[1]存储的是8x8方块的运动补偿函数;
qpix_put[2]存储的是4x4方块的运动补偿函数;
qpix_put[3]存储的是2x2方块的运动补偿函数;
从图中可以看出,qpix_put[X][0]不涉及像素内插;qpix_put[X][2],qpix_put[X][8],qpix_put[X][10]只涉及到了半像素内插;而其它函数则涉及到了1/4像素内插。
qpix_avg[4][16]
qpix_avg[4][16]中包含的函数qpix_put[4][16]结构是一样的,由于“_avg”系列函数用于双向预测,而“_put”系列函数用于单向预测,所以qpix_avg系列函数用于“求平均”,而qpix_put系列函数用于“赋值”。
square和delta
在FFmpeg H.264解码器中,四分之一像素运动补偿实际上只能按照“方块”的方式处理的(16x16,8x8,4x4)。因此对于不是“方块”形状的子宏块(例如16x8、8x16),需要把它们分成2个“方块”之后,一步一步进行处理。解码器中使用square记录子宏块是否为方形,使用delta记录不是方形的子宏块中“方块”之间的位置。例如处理16x8的子宏块的预测的时候的过程如下所示。从图中可以看出,解码器实际上调用了2次8x8方块的运动补偿函数。
x_offset和y_offset
FFmpeg H.264解码器使用x_offset和y_offset记录子宏块的位置信息(实际上记录的是子宏块左上角点的坐标)。在这里需要注意,x_offset和y_offset并不是以亮度整像素为单位记录该信息的,而是用色度像素为单位记录该信息的,因此在计算亮度块的位置的时候要把这两个值乘以2(这个地方目前没有完全弄明白,暂且这么认为吧)。
下面画一个示意图简单总结一下不同宏块划分下上文几个变量的取值情况。
记录完上面几个变量之后,就该看一下MCFUNC(hl_motion)()中调用的函数mc_part()了。
mc_part()
mc_part()用于判断已经分块后的子宏块是否使用了加权预测。该函数的定义位于libavcodec\h264_mc_template.c,如下所示。//已经分割(part)为子宏块的运动补偿
static void mc_part(H264Context *h, int n, int square,
int height, int delta,
uint8_t *dest_y, uint8_t *dest_cb,
uint8_t *dest_cr,
int x_offset, int y_offset,
qpel_mc_func *qpix_put,
h264_chroma_mc_func chroma_put,
qpel_mc_func *qpix_avg,
h264_chroma_mc_func chroma_avg,
h264_weight_func *weight_op,
h264_biweight_func *weight_avg,
int list0, int list1)
{
//是否使用加权预测?
if ((h->use_weight == 2 && list0 && list1 &&
(h->implicit_weight[h->ref_cache[0][scan8[n]]][h->ref_cache[1][scan8[n]]][h->mb_y & 1] != 32)) ||
h->use_weight == 1)
mc_part_weighted(h, n, square, height, delta, dest_y, dest_cb, dest_cr,
x_offset, y_offset, qpix_put, chroma_put,
weight_op[0], weight_op[1], weight_avg[0],
weight_avg[1], list0, list1, PIXEL_SHIFT, CHROMA_IDC);//加权版
else
mc_part_std(h, n, square, height, delta, dest_y, dest_cb, dest_cr,
x_offset, y_offset, qpix_put, chroma_put, qpix_avg,
chroma_avg, list0, list1, PIXEL_SHIFT, CHROMA_IDC);//标准版
}
从源代码可以看出,mc_part()逻辑非常简单,基本上原封不动的把函数参数传递给了它调用的函数:判断H.264码流是否使用了加权预测,如果使用了的话,就调用加权预测的函数mc_part_weighted(),否则就使用标准的函数mc_part_std()。下面看一下标准的函数mc_part_std()。
mc_part_std()
mc_part_std()函数用于判断已经分块的子宏块是单向预测还是双向预测。该函数的定义位于libavcodec\h264_mb.c,如下所示。//已经分割为子宏块的运动补偿-标准版(区别于加权版)
static av_always_inline void mc_part_std(H264Context *h, int n, int square,
int height, int delta,
uint8_t *dest_y, uint8_t *dest_cb,
uint8_t *dest_cr,
int x_offset, int y_offset,
qpel_mc_func *qpix_put,
h264_chroma_mc_func chroma_put,
qpel_mc_func *qpix_avg,
h264_chroma_mc_func chroma_avg,
int list0, int list1,
int pixel_shift, int chroma_idc)
{
qpel_mc_func *qpix_op = qpix_put;
h264_chroma_mc_func chroma_op = chroma_put;
//x_offset,y_offset只有在有子宏块划分的情况下不为0
//16x16宏块的话,为0
//亮度的x_offset,y_offset都要乘以2
dest_y += (2 * x_offset << pixel_shift) + 2 * y_offset * h->mb_linesize;
if (chroma_idc == 3 /* yuv444 */) {
dest_cb += (2 * x_offset << pixel_shift) + 2 * y_offset * h->mb_linesize;
dest_cr += (2 * x_offset << pixel_shift) + 2 * y_offset * h->mb_linesize;
} else if (chroma_idc == 2 /* yuv422 */) {
dest_cb += (x_offset << pixel_shift) + 2 * y_offset * h->mb_uvlinesize;
dest_cr += (x_offset << pixel_shift) + 2 * y_offset * h->mb_uvlinesize;
} else { /* yuv420 */
//色度的x_offset,y_offset
dest_cb += (x_offset << pixel_shift) + y_offset * h->mb_uvlinesize;
dest_cr += (x_offset << pixel_shift) + y_offset * h->mb_uvlinesize;
}
//注意x_offset,y_offset取值(以YUV420P中色度为基准?所以乘以8)
x_offset += 8 * h->mb_x;
y_offset += 8 * (h->mb_y >> MB_FIELD(h));
//如果使用List0
//P宏块
if (list0) {
H264Picture *ref = &h->ref_list[0][h->ref_cache[0][scan8[n]]];
//真正的运动补偿
mc_dir_part(h, ref, n, square, height, delta, 0,
dest_y, dest_cb, dest_cr, x_offset, y_offset,
qpix_op, chroma_op, pixel_shift, chroma_idc);
//注意:“_put”变成“_avg”
qpix_op = qpix_avg;
chroma_op = chroma_avg;
}
//如果使用List1
//B宏块
if (list1) {
H264Picture *ref = &h->ref_list[1][h->ref_cache[1][scan8[n]]];
mc_dir_part(h, ref, n, square, height, delta, 1,
dest_y, dest_cb, dest_cr, x_offset, y_offset,
qpix_op, chroma_op, pixel_shift, chroma_idc);
}
}
从源代码可以看出,mc_part_std()首先计算了几个关键的用于确定子宏块位置的参数,然后根据预测类型的不同(单向预测或者双向预测),把不同的函数指针传递给mc_dir_part():如果仅仅使用了list0(单向预测),则只传递qpix_put();如果使用了list0和list1(双向预测),则调用两次mc_dir_part(),第一次传递qpix_put(),第二次传递qpix_avg()。
mc_part_std()中赋值了3个重要的变量(只考虑亮度):
(1)dest_y:指向子宏块亮度数据指针。这个值是通过x_offset和y_offset计算得来的。在这里需要注意一点:x_offset和y_offset是以色度为基本单位的,所以在计算亮度相关的变量的时候需要乘以2。
(2)x_offset:传入的x_offset本来是子宏块相对于整个宏块位置的横坐标,在这里加上8 * h->mb_x之后,变成了子宏块相对于整个图像的位置的横坐标(以色度为基本单位)。
(3)y_offset:传入的y_offset本来是子宏块相对于整个宏块位置的纵坐标,在这里加上8 * h->mb_y之后,变成了子宏块相对于整个图像的位置的纵坐标(以色度为基本单位)。
下面看一下真正完成运动补偿功能的函数mc_dir_part()。
mc_dir_part()
mc_dir_part()完成了子宏块的运动补偿。该函数的定义位于libavcodec\h264_mb.c,如下所示。//真正的运动补偿
static av_always_inline void mc_dir_part(H264Context *h, H264Picture *pic,
int n, int square, int height,
int delta, int list,
uint8_t *dest_y, uint8_t *dest_cb,
uint8_t *dest_cr,
int src_x_offset, int src_y_offset,
qpel_mc_func *qpix_op,
h264_chroma_mc_func chroma_op,
int pixel_shift, int chroma_idc)
{
//运动补偿块在图像中的横坐标x和纵坐标y
//基本单位是1/4像素
//src_x_offset,src_y_offset是以色度(而非亮度)为基本单位的,所以基本单位是2px
/*
* 注意scan8[]数组
* mv_cache如下所示
* 图中数字为scan8[n]中的n
* |
* --+--------------------
* | x x x x x x x x
* | x x x x 0 1 4 5
* | x x x x 2 3 6 7
* | x x x x 8 9 12 13
* | x x x x 10 11 14 15
*/
const int mx = h->mv_cache[list][scan8[n]][0] + src_x_offset * 8;
int my = h->mv_cache[list][scan8[n]][1] + src_y_offset * 8;
//
//luma_xy为运动补偿系数的序号
//决定了调用的运动补偿函数
//在系统找到了整像素点的运动补偿块之后,需要调用四分之一运动补偿模块对像素点进行内插等处理
//
//运动补偿函数集(16个函数)的列表(“qpel8”代表处理8个像素):
//[0]: put_h264_qpel8_mc00_8_c()
//[1]: put_h264_qpel8_mc10_8_c()
//[2]: put_h264_qpel8_mc20_8_c()
//[3]: put_h264_qpel8_mc30_8_c()
//注:4个一循环--------------------
//[4]: put_h264_qpel8_mc01_8_c()
//[5]: put_h264_qpel8_mc11_8_c()
//[6]: put_h264_qpel8_mc21_8_c()
//...
//[16]: put_h264_qpel8_mc33_8_c()
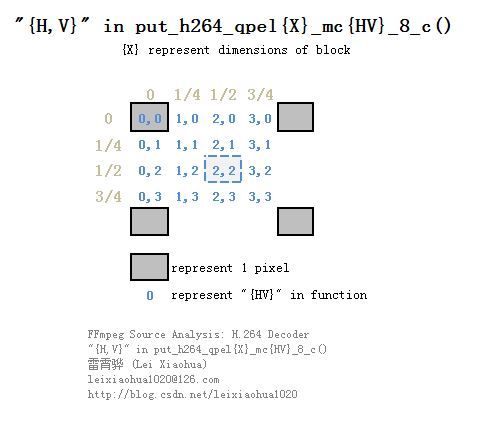
//函数名称中mc{ab}命名规则?
//纵向为垂直,横向为水平{ab}中{a}代表水平,{b}代表垂直
//{a,b}与像素内插点之间的关系如下表所示
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// | |原始像素(0) | 1/4内插点 | 1/2内插点 | 3/4内插点 | 原始像素(1)
//-+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// | 原始像素(0) | 0,0 | 1,0 | 2,0 | 3,0 |
// | 1/4内插点 | 0,1 | 1,1 | 2,1 | 3,1 |
// | 1/2内插点 | 0,2 | 1,2 | 2,2 | 3,2 |
// | 3/4内插点 | 0,3 | 1,3 | 2,3 | 3,3 |
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// | 原始像素(0+1行) |
//取出mx和my的后2位(代表了小于整像素点的mv,因为mx,my基本单位是1/4像素)
const int luma_xy = (mx & 3) + ((my & 3) << 2);
//offset计算:mx,my都除以4(四分之一像素运动补偿),变成整像素
ptrdiff_t offset = ((mx >> 2) << pixel_shift) + (my >> 2) * h->mb_linesize;
//源src_y
//AVFrame的data[0]+整像素偏移值
uint8_t *src_y = pic->f.data[0] + offset;
uint8_t *src_cb, *src_cr;
int extra_width = 0;
int extra_height = 0;
int emu = 0;
//mx,my都除以4,变成整像素
const int full_mx = mx >> 2;
const int full_my = my >> 2;
const int pic_width = 16 * h->mb_width;
const int pic_height = 16 * h->mb_height >> MB_FIELD(h);
int ysh;
if (mx & 7)
extra_width -= 3;
if (my & 7)
extra_height -= 3;
//在图像边界处的处理
if (full_mx < 0 - extra_width ||
full_my < 0 - extra_height ||
full_mx + 16 /*FIXME*/ > pic_width + extra_width ||
full_my + 16 /*FIXME*/ > pic_height + extra_height) {
h->vdsp.emulated_edge_mc(h->edge_emu_buffer,
src_y - (2 << pixel_shift) - 2 * h->mb_linesize,
h->mb_linesize, h->mb_linesize,
16 + 5, 16 + 5 /*FIXME*/, full_mx - 2,
full_my - 2, pic_width, pic_height);
src_y = h->edge_emu_buffer + (2 << pixel_shift) + 2 * h->mb_linesize;
emu = 1;
}
//汇编函数:实际的运动补偿函数-亮度
//注意只能以正方形的形式处理(16x16,8x8,4x4)
//src_y是输入的整像素点的图像块
//dest_y是输出的经过四分之一运动补偿之后的图像块(经过内插处理)
qpix_op[luma_xy](dest_y, src_y, h->mb_linesize); // FIXME try variable height perhaps?
//square标记了宏块是否为方形
//如果不是方形,说明是一个包含两个正方形的长方形(16x8,8x16,8x4,4x8),这时候还需要处理另外一块
//delta标记了另外一块“方形”的起始点与dest_y之间的偏移值(例如16x8中,delta取值为8)
/*
* 例如对于16x8 宏块划分,就分别进行2次8x8的运动补偿,如下所示。
*
* 8 8
* +--------+--------+ +--------+ +--------+
* | | | | | |
* 8 | | | = | | + | |
* | | | | | |
* +--------+--------+ +--------+ +--------+
*
*/
if (!square)
qpix_op[luma_xy](dest_y + delta, src_y + delta, h->mb_linesize);
if (CONFIG_GRAY && h->flags & CODEC_FLAG_GRAY)
return;
//如果是YUV444的话,按照亮度的方法,再处理2遍,然后返回
if (chroma_idc == 3 /* yuv444 */) {
src_cb = pic->f.data[1] + offset;
if (emu) {
h->vdsp.emulated_edge_mc(h->edge_emu_buffer,
src_cb - (2 << pixel_shift) - 2 * h->mb_linesize,
h->mb_linesize, h->mb_linesize,
16 + 5, 16 + 5 /*FIXME*/,
full_mx - 2, full_my - 2,
pic_width, pic_height);
src_cb = h->edge_emu_buffer + (2 << pixel_shift) + 2 * h->mb_linesize;
}
qpix_op[luma_xy](dest_cb, src_cb, h->mb_linesize); // FIXME try variable height perhaps?
if (!square)
qpix_op[luma_xy](dest_cb + delta, src_cb + delta, h->mb_linesize);
src_cr = pic->f.data[2] + offset;
if (emu) {
h->vdsp.emulated_edge_mc(h->edge_emu_buffer,
src_cr - (2 << pixel_shift) - 2 * h->mb_linesize,
h->mb_linesize, h->mb_linesize,
16 + 5, 16 + 5 /*FIXME*/,
full_mx - 2, full_my - 2,
pic_width, pic_height);
src_cr = h->edge_emu_buffer + (2 << pixel_shift) + 2 * h->mb_linesize;
}
qpix_op[luma_xy](dest_cr, src_cr, h->mb_linesize); // FIXME try variable height perhaps?
if (!square)
qpix_op[luma_xy](dest_cr + delta, src_cr + delta, h->mb_linesize);
return;
}
ysh = 3 - (chroma_idc == 2 /* yuv422 */);
if (chroma_idc == 1 /* yuv420 */ && MB_FIELD(h)) {
// chroma offset when predicting from a field of opposite parity
my += 2 * ((h->mb_y & 1) - (pic->reference - 1));
emu |= (my >> 3) < 0 || (my >> 3) + 8 >= (pic_height >> 1);
}
//色度UV的运动补偿
//mx,my除以8。色度运动补偿为1/8像素
//AVFrame的data[1]和data[2]
src_cb = pic->f.data[1] + ((mx >> 3) << pixel_shift) +
(my >> ysh) * h->mb_uvlinesize;
src_cr = pic->f.data[2] + ((mx >> 3) << pixel_shift) +
(my >> ysh) * h->mb_uvlinesize;
if (emu) {
h->vdsp.emulated_edge_mc(h->edge_emu_buffer, src_cb,
h->mb_uvlinesize, h->mb_uvlinesize,
9, 8 * chroma_idc + 1, (mx >> 3), (my >> ysh),
pic_width >> 1, pic_height >> (chroma_idc == 1 /* yuv420 */));
src_cb = h->edge_emu_buffer;
}
chroma_op(dest_cb, src_cb, h->mb_uvlinesize,
height >> (chroma_idc == 1 /* yuv420 */),
mx & 7, (my << (chroma_idc == 2 /* yuv422 */)) & 7);
if (emu) {
h->vdsp.emulated_edge_mc(h->edge_emu_buffer, src_cr,
h->mb_uvlinesize, h->mb_uvlinesize,
9, 8 * chroma_idc + 1, (mx >> 3), (my >> ysh),
pic_width >> 1, pic_height >> (chroma_idc == 1 /* yuv420 */));
src_cr = h->edge_emu_buffer;
}
chroma_op(dest_cr, src_cr, h->mb_uvlinesize, height >> (chroma_idc == 1 /* yuv420 */),
mx & 7, (my << (chroma_idc == 2 /* yuv422 */)) & 7);
}
通过源代码,简单梳理一下mc_dir_part()的流程(只考虑亮度,色度的流程类似):
(1)计算mx和my。mx和my是当前宏块的匹配块的位置坐标。需要注意的是该坐标是以1/4像素(而不是整像素)为基本单位的。总而言之,首先找到当前宏块的匹配块的整像素位置,然后在该位置的基础上进行四分之一像素的内插,并将结果输出出来。
(2)计算offset。offset是当前宏块的匹配块相对于图像的整像素偏移量,由mx、my计算而来。
(3)计算luma_xy。luma_xy决定了当前宏块的匹配块采用的四分之一像素运动补偿的方式,由mx、my计算而来。
(4)调用运动补偿汇编函数qpix_op[luma_xy]()完成运动补偿。在这里需要注意,如果子宏块不是正方形的(square取0),则还会调用1次qpix_op[luma_xy]()完成另外一个方块的运动补偿。
前文中曾经提过,由于H.264解码器中只提供了正方形块的四分之一像素运动补偿函数,所以如果子宏块不是正方形的(例如16x8,8x16),就需要先将子宏块划分为正方形的方块,然后再进行两次运动补偿(两个正方形方块之间的位置关系用delta变量记录)。例如16x8的宏块,就会划分成两个8x8的方块,调用两次相同的运动补偿函数,如下图所示。
下面具体看一下完成四分之一运动补偿的汇编函数qpix_op[luma_xy]()。这个函数在单向预测(使用List0)的时候属于H264QpelContext中的put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[4][16]函数集,在双向预测(使用List0和List1)的时候属于H264QpelContext中的avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab [4][16]函数集。下文主要分析单向预测时候的函数。双向预测时候的函数和单向预测是类似的,只是把单向预测时候的“赋值”改成了“取平均值”。
首先看一下四分之一运动补偿的汇编函数的初始化函数ff_h264qpel_init()。ff_h264qpel_init()
ff_h264qpel_init()用于初始化四分之一像素运动补偿相关的函数,该函数的定义位于libavcodec\h264qpel.c,如下所示。//四分之一像素(Quarterpel)补偿
av_cold void ff_h264qpel_init(H264QpelContext *c, int bit_depth)
{
#undef FUNCC
#define FUNCC(f, depth) f ## _ ## depth ## _c
//这样用宏定义写的函数在FFmpeg的H.264解码器中很常见
#define dspfunc2(PFX, IDX, NUM, depth) \
c->PFX ## _pixels_tab[IDX][ 0] = FUNCC(PFX ## NUM ## _mc00, depth); \
c->PFX ## _pixels_tab[IDX][ 1] = FUNCC(PFX ## NUM ## _mc10, depth); \
c->PFX ## _pixels_tab[IDX][ 2] = FUNCC(PFX ## NUM ## _mc20, depth); \
c->PFX ## _pixels_tab[IDX][ 3] = FUNCC(PFX ## NUM ## _mc30, depth); \
c->PFX ## _pixels_tab[IDX][ 4] = FUNCC(PFX ## NUM ## _mc01, depth); \
c->PFX ## _pixels_tab[IDX][ 5] = FUNCC(PFX ## NUM ## _mc11, depth); \
c->PFX ## _pixels_tab[IDX][ 6] = FUNCC(PFX ## NUM ## _mc21, depth); \
c->PFX ## _pixels_tab[IDX][ 7] = FUNCC(PFX ## NUM ## _mc31, depth); \
c->PFX ## _pixels_tab[IDX][ 8] = FUNCC(PFX ## NUM ## _mc02, depth); \
c->PFX ## _pixels_tab[IDX][ 9] = FUNCC(PFX ## NUM ## _mc12, depth); \
c->PFX ## _pixels_tab[IDX][10] = FUNCC(PFX ## NUM ## _mc22, depth); \
c->PFX ## _pixels_tab[IDX][11] = FUNCC(PFX ## NUM ## _mc32, depth); \
c->PFX ## _pixels_tab[IDX][12] = FUNCC(PFX ## NUM ## _mc03, depth); \
c->PFX ## _pixels_tab[IDX][13] = FUNCC(PFX ## NUM ## _mc13, depth); \
c->PFX ## _pixels_tab[IDX][14] = FUNCC(PFX ## NUM ## _mc23, depth); \
c->PFX ## _pixels_tab[IDX][15] = FUNCC(PFX ## NUM ## _mc33, depth)
#define SET_QPEL(depth) \
dspfunc2(put_h264_qpel, 0, 16, depth); \
dspfunc2(put_h264_qpel, 1, 8, depth); \
dspfunc2(put_h264_qpel, 2, 4, depth); \
dspfunc2(put_h264_qpel, 3, 2, depth); \
dspfunc2(avg_h264_qpel, 0, 16, depth); \
dspfunc2(avg_h264_qpel, 1, 8, depth); \
dspfunc2(avg_h264_qpel, 2, 4, depth)
switch (bit_depth) {
default:
SET_QPEL(8);
break;
case 9:
SET_QPEL(9);
break;
case 10:
SET_QPEL(10);
break;
case 12:
SET_QPEL(12);
break;
case 14:
SET_QPEL(14);
break;
}
//如果支持汇编
if (ARCH_AARCH64)
ff_h264qpel_init_aarch64(c, bit_depth);
if (ARCH_ARM)
ff_h264qpel_init_arm(c, bit_depth);
if (ARCH_PPC)
ff_h264qpel_init_ppc(c, bit_depth);
if (ARCH_X86)
ff_h264qpel_init_x86(c, bit_depth);
}
从源代码中可以看出,ff_h264qpel_init()通过SET_QPEL(8)初始化四分之像素运动补偿C语言版本的函数。在函数的末尾,系统会检查的配置,如果支持汇编优化的话,还会调用类似于ff_h264qpel_init_x86()这类的函数初始化经过汇编优化之后的四分之一像素运动补偿的函数。
下面展开“SET_QPEL(8)”看一下里面具体的内容。
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[0][ 0] = put_h264_qpel16_mc00_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[0][ 1] = put_h264_qpel16_mc10_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[0][ 2] = put_h264_qpel16_mc20_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[0][ 3] = put_h264_qpel16_mc30_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[0][ 4] = put_h264_qpel16_mc01_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[0][ 5] = put_h264_qpel16_mc11_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[0][ 6] = put_h264_qpel16_mc21_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[0][ 7] = put_h264_qpel16_mc31_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[0][ 8] = put_h264_qpel16_mc02_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[0][ 9] = put_h264_qpel16_mc12_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[0][10] = put_h264_qpel16_mc22_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[0][11] = put_h264_qpel16_mc32_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[0][12] = put_h264_qpel16_mc03_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[0][13] = put_h264_qpel16_mc13_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[0][14] = put_h264_qpel16_mc23_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[0][15] = put_h264_qpel16_mc33_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[1][ 0] = put_h264_qpel8_mc00_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[1][ 1] = put_h264_qpel8_mc10_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[1][ 2] = put_h264_qpel8_mc20_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[1][ 3] = put_h264_qpel8_mc30_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[1][ 4] = put_h264_qpel8_mc01_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[1][ 5] = put_h264_qpel8_mc11_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[1][ 6] = put_h264_qpel8_mc21_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[1][ 7] = put_h264_qpel8_mc31_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[1][ 8] = put_h264_qpel8_mc02_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[1][ 9] = put_h264_qpel8_mc12_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[1][10] = put_h264_qpel8_mc22_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[1][11] = put_h264_qpel8_mc32_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[1][12] = put_h264_qpel8_mc03_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[1][13] = put_h264_qpel8_mc13_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[1][14] = put_h264_qpel8_mc23_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[1][15] = put_h264_qpel8_mc33_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[2][ 0] = put_h264_qpel4_mc00_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[2][ 1] = put_h264_qpel4_mc10_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[2][ 2] = put_h264_qpel4_mc20_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[2][ 3] = put_h264_qpel4_mc30_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[2][ 4] = put_h264_qpel4_mc01_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[2][ 5] = put_h264_qpel4_mc11_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[2][ 6] = put_h264_qpel4_mc21_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[2][ 7] = put_h264_qpel4_mc31_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[2][ 8] = put_h264_qpel4_mc02_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[2][ 9] = put_h264_qpel4_mc12_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[2][10] = put_h264_qpel4_mc22_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[2][11] = put_h264_qpel4_mc32_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[2][12] = put_h264_qpel4_mc03_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[2][13] = put_h264_qpel4_mc13_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[2][14] = put_h264_qpel4_mc23_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[2][15] = put_h264_qpel4_mc33_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[3][ 0] = put_h264_qpel2_mc00_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[3][ 1] = put_h264_qpel2_mc10_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[3][ 2] = put_h264_qpel2_mc20_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[3][ 3] = put_h264_qpel2_mc30_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[3][ 4] = put_h264_qpel2_mc01_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[3][ 5] = put_h264_qpel2_mc11_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[3][ 6] = put_h264_qpel2_mc21_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[3][ 7] = put_h264_qpel2_mc31_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[3][ 8] = put_h264_qpel2_mc02_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[3][ 9] = put_h264_qpel2_mc12_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[3][10] = put_h264_qpel2_mc22_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[3][11] = put_h264_qpel2_mc32_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[3][12] = put_h264_qpel2_mc03_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[3][13] = put_h264_qpel2_mc13_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[3][14] = put_h264_qpel2_mc23_8_c;
c->put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[3][15] = put_h264_qpel2_mc33_8_c;
c->avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[0][ 0] = avg_h264_qpel16_mc00_8_c;
c->avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[0][ 1] = avg_h264_qpel16_mc10_8_c;
c->avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[0][ 2] = avg_h264_qpel16_mc20_8_c;
c->avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[0][ 3] = avg_h264_qpel16_mc30_8_c;
c->avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[0][ 4] = avg_h264_qpel16_mc01_8_c;
c->avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[0][ 5] = avg_h264_qpel16_mc11_8_c;
c->avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[0][ 6] = avg_h264_qpel16_mc21_8_c;
c->avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[0][ 7] = avg_h264_qpel16_mc31_8_c;
c->avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[0][ 8] = avg_h264_qpel16_mc02_8_c;
c->avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[0][ 9] = avg_h264_qpel16_mc12_8_c;
c->avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[0][10] = avg_h264_qpel16_mc22_8_c;
c->avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[0][11] = avg_h264_qpel16_mc32_8_c;
c->avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[0][12] = avg_h264_qpel16_mc03_8_c;
c->avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[0][13] = avg_h264_qpel16_mc13_8_c;
c->avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[0][14] = avg_h264_qpel16_mc23_8_c;
c->avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[0][15] = avg_h264_qpel16_mc33_8_c;
c->avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[1][ 0] = avg_h264_qpel8_mc00_8_c;
c->avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[1][ 1] = avg_h264_qpel8_mc10_8_c;
c->avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[1][ 2] = avg_h264_qpel8_mc20_8_c;
c->avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[1][ 3] = avg_h264_qpel8_mc30_8_c;
c->avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[1][ 4] = avg_h264_qpel8_mc01_8_c;
c->avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[1][ 5] = avg_h264_qpel8_mc11_8_c;
c->avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[1][ 6] = avg_h264_qpel8_mc21_8_c;
c->avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[1][ 7] = avg_h264_qpel8_mc31_8_c;
c->avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[1][ 8] = avg_h264_qpel8_mc02_8_c;
c->avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[1][ 9] = avg_h264_qpel8_mc12_8_c;
c->avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[1][10] = avg_h264_qpel8_mc22_8_c;
c->avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[1][11] = avg_h264_qpel8_mc32_8_c;
c->avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[1][12] = avg_h264_qpel8_mc03_8_c;
c->avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[1][13] = avg_h264_qpel8_mc13_8_c;
c->avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[1][14] = avg_h264_qpel8_mc23_8_c;
c->avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[1][15] = avg_h264_qpel8_mc33_8_c;
c->avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[2][ 0] = avg_h264_qpel4_mc00_8_c;
c->avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[2][ 1] = avg_h264_qpel4_mc10_8_c;
c->avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[2][ 2] = avg_h264_qpel4_mc20_8_c;
c->avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[2][ 3] = avg_h264_qpel4_mc30_8_c;
c->avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[2][ 4] = avg_h264_qpel4_mc01_8_c;
c->avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[2][ 5] = avg_h264_qpel4_mc11_8_c;
c->avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[2][ 6] = avg_h264_qpel4_mc21_8_c;
c->avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[2][ 7] = avg_h264_qpel4_mc31_8_c;
c->avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[2][ 8] = avg_h264_qpel4_mc02_8_c;
c->avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[2][ 9] = avg_h264_qpel4_mc12_8_c;
c->avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[2][10] = avg_h264_qpel4_mc22_8_c;
c->avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[2][11] = avg_h264_qpel4_mc32_8_c;
c->avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[2][12] = avg_h264_qpel4_mc03_8_c;
c->avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[2][13] = avg_h264_qpel4_mc13_8_c;
c->avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[2][14] = avg_h264_qpel4_mc23_8_c;
c->avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[2][15] = avg_h264_qpel4_mc33_8_c
从SET_QPEL(8)宏定义展开的结果可以看出,该部分代码对H264QpelContext中的函数指针数组put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab和avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab进行了赋值。其中put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab中保存了单向预测(使用List0)时候用到的函数,而avg_h264_qpel_pixels_tab中保存了双向预测(使用List0和List1)时候用到的函数。现在以put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab为例,叙述一下数组的规则:
(1)put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[x][y]中的“x”存储了该函数处理的图像方块的大小。规则如下:研究完put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[][]的规则之后,可以再看一下赋值的C语言函数的命名规则。可以看出这些函数都统一命名为put_h264_qpel{X}_mc{HV}_8_c()的形式。其中“X”代表了C语言函数处理的图像方块的大小;而“HV”则代表了该函数处理的内插点的位置。“HV”中的“H”代表了横坐标,“V”则代表了纵坐标,“H,V”与像素内插点之间的关系如下图所示。[0]:处理16x16的图像数据[1]:处理8x8的图像数据[2]:处理4x4的图像数据[3]:处理2x2的图像数据(2)put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab[x][y]中的“y”存储了该函数进行1/4像素内插的位置。以一个2x2的图像块为例,假设左上角的点坐标为(0,0),那么x轴方向可以进行像素内插的点为0,1/4,1/2,3/4;y轴方向可以进行像素内插的点同样也是0,1/4,1/2,3/4,因此这些x、y组合起来一共包含了16个点。在put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab中为这16个点分别提供了内插函数,它们内插的点和它们在put_h264_qpel_pixels_tab中的位置(对应“y”)关系如下图所示。
至此四分之一像素运动补偿汇编函数的初始化函数ff_h264qpel_init()就基本上分析完毕了。下面可以看一下C语言版本的四分之一像素运动补偿函数的源代码。由于1/4像素内插比较复杂,其中还用到了整像素赋值函数以及1/2像素线性内插函数,所以需要从简到难一步一步的看这些源代码。打算按照顺序一步一步分析这些源代码:
(1)pel_template.c(展开“DEF_PEL(put, op_put)”宏):整像素赋值(用于整像素的单向预测)
(2)pel_template.c(展开“DEF_PEL(avg, op_avg)”宏):整像素求平均(写这个为了举一个双向预测的例子)
(3)hpel_template.c((展开“DEF_HPEL(put, op_put)”宏):1/2像素线性内插
(4)h264qpel_template.c(展开“H264_LOWPASS(put_, op_put, op2_put)”宏):半像素内插(注意不是1/2像素线性内插,而是需要滤波的)
(5)h264qpel_template.c(展开“H264_MC(put_, 8)”宏):1/4像素运动补偿
pel_template.c-put-(整像素精度-单向预测)
pel_template.c中的函数用于整像素运动估计。该C语言文件位于libavcodec\pel_template.c(貌似它不仅仅用于H.264解码器,而且用于libavcodec中其它的编解码器),它的内容如下所示。/*
* This file is part of FFmpeg.
*
* FFmpeg is free software; you can redistribute it and/or
* modify it under the terms of the GNU Lesser General Public
* License as published by the Free Software Foundation; either
* version 2.1 of the License, or (at your option) any later version.
*
* FFmpeg is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
* but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
* MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU
* Lesser General Public License for more details.
*
* You should have received a copy of the GNU Lesser General Public
* License along with FFmpeg; if not, write to the Free Software
* Foundation, Inc., 51 Franklin Street, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA
*/
#include
#include
#include "libavutil/intreadwrite.h"
#include "pixels.h"
#include "rnd_avg.h"
#include "bit_depth_template.c"
#define DEF_PEL(OPNAME, OP) \
static inline void FUNCC(OPNAME ## _pixels2)(uint8_t *block, \
const uint8_t *pixels, \
ptrdiff_t line_size, \
int h) \
{ \
int i; \
for (i = 0; i < h; i++) { \
OP(*((pixel2 *) block), AV_RN2P(pixels)); \
pixels += line_size; \
block += line_size; \
} \
} \
\
static inline void FUNCC(OPNAME ## _pixels4)(uint8_t *block, \
const uint8_t *pixels, \
ptrdiff_t line_size, \
int h) \
{ \
int i; \
for (i = 0; i < h; i++) { \
OP(*((pixel4 *) block), AV_RN4P(pixels)); \
pixels += line_size; \
block += line_size; \
} \
} \
\
static inline void FUNCC(OPNAME ## _pixels8)(uint8_t *block, \
const uint8_t *pixels, \
ptrdiff_t line_size, \
int h) \
{ \
int i; \
for (i = 0; i < h; i++) { \
OP(*((pixel4 *) block), AV_RN4P(pixels)); \
OP(*((pixel4 *) (block + 4 * sizeof(pixel))), \
AV_RN4P(pixels + 4 * sizeof(pixel))); \
pixels += line_size; \
block += line_size; \
} \
} \
\
CALL_2X_PIXELS(FUNCC(OPNAME ## _pixels16), \
FUNCC(OPNAME ## _pixels8), \
8 * sizeof(pixel))
//注意
//双向预测会使用op_avg这个宏
//求出a,b的平均值
#define op_avg(a, b) a = rnd_avg_pixel4(a, b)
//单向预测会使用这个宏
//把b赋值给a
#define op_put(a, b) a = b
//双向预测
DEF_PEL(avg, op_avg)
//单向预测
DEF_PEL(put, op_put)
#undef op_avg
#undef op_put
pel_template.c源代码中包含了一个名称为“DEF_PEL(OPNAME, OP)”的宏,通过给该宏传递不同的参数,可以定义不同的函数。在文件的末尾有两句代码分别用于初始化单向预测的函数和双向预测的函数,如下所示。
//双向预测
DEF_PEL(avg, op_avg)
//单向预测
DEF_PEL(put, op_put)可以看出,在初始化单向预测的时候,传递给DEF_PEL()宏了一个“op_put”,在初始化双向预测的时候,传递给DEF_PEL()宏了一个“op_avg”。而“op_put”和“op_avg”分别又是两个宏定义,如下所示。
//注意
//双向预测会使用op_avg这个宏
//求出a,b的平均值
#define op_avg(a, b) a = rnd_avg_pixel4(a, b)
//单向预测会使用这个宏
//把b赋值给a
#define op_put(a, b) a = b下面展开“DEF_PEL(put, op_put)”宏看一下其中的函数,如下所示。
//================================================================
/*
* pel_template.c (pixel,整像素)
* DEF_PEL(OPNAME, OP)取值为DEF_PEL(put, op_put)的情况
*
* 源代码注释和处理:雷霄骅
* [email protected]
* http://blog.csdn.net/leixiaohua1020
*
* 这个文件中存储了直接拷贝像素(不进行内插)的方法
* 不同的函数处理的水平像素个数不同
*
* 拷贝像素put用于单向预测(P宏块)
*/
//================================================================
//函数参数含义如下
//pixels:源
//block:目标
//line_size:图像一行像素的大小
//h:处理的行数(纵向)
//命名:“pixelsX”中的“X”代表水平方向像素数
//赋值2个像素(横向)
static inline void put_pixels2_8_c(uint8_t *block,
const uint8_t *pixels,
ptrdiff_t line_size,
int h)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < h; i++) {
//直接赋值。uint16_t占用2Byte,存储2个像素
*((uint16_t *) block) = (((const union unaligned_16 *) (pixels))->l);
pixels += line_size;
block += line_size;
}
}
//赋值4个像素(横向)
static inline void put_pixels4_8_c(uint8_t *block,
const uint8_t *pixels,
ptrdiff_t line_size,
int h)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < h; i++) {
//直接赋值。uint32_t占用4Byte,存储4个像素
*((uint32_t *) block) = (((const union unaligned_32 *) (pixels))->l);
pixels += line_size;
block += line_size;
}
}
//赋值8个像素(横向)
static inline void put_pixels8_8_c(uint8_t *block,
const uint8_t *pixels,
ptrdiff_t line_size,
int h)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < h; i++) {
//直接赋值。2个uint32_t。
//uint32_t占用4Byte,存储4个像素
//在这里一共处理8个像素
*((uint32_t *) block) = (((const union unaligned_32 *) (pixels))->l);
*((uint32_t *) (block + 4 * sizeof(uint8_t))) = (((const union unaligned_32 *) (pixels + 4 * sizeof(uint8_t)))->l);
pixels += line_size;
block += line_size;
}
}
//赋值16个像素(横向)
static void put_pixels16_8_c(uint8_t *block, const uint8_t *pixels,
ptrdiff_t line_size, int h)
{
//2次赋值8个像素
put_pixels8_8_c(block, pixels, line_size, h);
put_pixels8_8_c(block + 8 * sizeof(uint8_t), pixels + 8 * sizeof(uint8_t), line_size, h);
}
源代码中注释比较多,在这里就不一一解释这几个函数的功能了。可以看出put_pixels2_8_c(),put_pixels4_8_c(),put_pixels8_8_c(),put_pixels16_8_c()这些函数都用于将pixels中像素的值赋值给block(block为输出),它们唯一的不同在于一次性横向处理的像素数目不同。
pel_template.c-avg-(整像素精度-双向预测)
在看完单向预测函数代码之后,作为对比看一下双向预测函数的代码。前文已经提过,使用单向预测的时候,直接将参考帧上的匹配块的数据“搬移下来”作后续的处理(“赋值”),而使用双向预测的时候,需要首先将两个参考帧上的匹配块的数据求平均值(“求平均”),然后再做后续处理。双向预测的示意图如下所示。正是因为双向预测需要求平均,因此双向预测的函数里面核心的概念就是“求平均”。在这里如果我们展开pel_template.c 中的“DEF_PEL(avg, op_avg)”宏,就可以查看整像素精度下双向预测有关的函数,如下所示。
//================================================================
/*
* pel_template.c (pixel,整像素)
* DEF_PEL(OPNAME, OP)取值为DEF_PEL(avg, op_avg)的情况
* 源代码注释和处理:雷霄骅
* [email protected]
* http://blog.csdn.net/leixiaohua1020
*
* 这个文件中存储了直接求平均值(不进行内插)的方法
* 不同的函数处理的水平像素个数不同
*
* 求平均值avg用于双向预测(B宏块)
*/
//================================================================
//函数参数含义如下
//pixels:源
//block:目标
//line_size:图像一行像素的大小
//h:处理的行数(纵向)
//求输入和输出的平均值,2个像素(横向)
static inline void avg_pixels2_8_c(uint8_t *block,
const uint8_t *pixels,
ptrdiff_t line_size,
int h)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < h; i++) {
//pixels和block求平均
//注意rnd_avg32()函数是分别求4个像素(32bit,划分为4个8bit)的平均值
//例如:
//unsigned int x1=0x02030405;
//unsigned int x2=0x08070403;
//unsigned int y=0;
//y=rnd_avg32(x1,x2);
//
//则y=0x05050404
//
*((uint16_t *) block) = rnd_avg32(*((uint16_t *) block), (((const union unaligned_16 *) (pixels))->l));
pixels += line_size;
block += line_size;
}
}
//求输入和输出的平均值,4个像素(横向)
static inline void avg_pixels4_8_c(uint8_t *block,
const uint8_t *pixels,
ptrdiff_t line_size,
int h)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < h; i++) {
*((uint32_t *) block) = rnd_avg32(*((uint32_t *) block), (((const union unaligned_32 *) (pixels))->l));
pixels += line_size;
block += line_size;
}
}
//求输入和输出的平均值,8个像素(横向)
static inline void avg_pixels8_8_c(uint8_t *block,
const uint8_t *pixels,
ptrdiff_t line_size,
int h)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < h; i++) {
*((uint32_t *) block) = rnd_avg32(*((uint32_t *) block), (((const union unaligned_32 *) (pixels))->l));
*((uint32_t *) (block + 4 * sizeof(uint8_t))) = rnd_avg32(*((uint32_t *) (block + 4 * sizeof(uint8_t))), (((const union unaligned_32 *) (pixels + 4 * sizeof(uint8_t)))->l));
pixels += line_size;
block += line_size;
}
}
//求输入和输出的平均值,16个像素(横向)
static void avg_pixels16_8_c(uint8_t *block, const uint8_t *pixels,
ptrdiff_t line_size, int h)
{
avg_pixels8_8_c(block, pixels, line_size, h);
avg_pixels8_8_c(block + 8 * sizeof(uint8_t), pixels + 8 * sizeof(uint8_t), line_size, h);
}
从源代码中可以看出,avg_pixels2_8_c(),avg_pixels4_8_c(),avg_pixels8_8_c(),avg_pixels16_8_c()几个函数都是首先求pixels和block的平均值,然后将结果赋值给block(block为输出)。其中用到了一个关键的函数rnd_avg32(x1, x2),该函数可以一次性求出两块输入数据中4个像素(32bit)分别求平均之后的结果。例如x1=0x02030405,x2=0x08070403,而y=rnd_avg32(x1,x2),那么y=0x05050404。
hpel_template.c-put-(1/2像素精度(线性)-单向预测)
hpel_template.c中的函数用于1/2像素线性内插。该文件的格式和pel_template.c是一模一样的,在这里不再重复叙述。1/2像素线性内插在早期的视频编码标准中使用比较广泛(例如MPEG2中就使用了这种内插方法)。该方法的计算公式比较简单,之间将相邻的两个像素点的像素值求平均就可以了。假设两个相邻像素点的像素值为a和b,内插点的像素值为c,那么内插公式为:
c=round((a+b)/2)
下面看一下hpel_template.c中的“DEF_HPEL(put, op_put)”宏展开的结果,如下所示。//================================================================
/*
* hpel_template.c(half-pixel)
* DEF_HPEL(OPNAME, OP)取值为DEF_HPEL(put, op_put)的情况
*
* 源代码注释和处理:雷霄骅
* [email protected]
* http://blog.csdn.net/leixiaohua1020
*
* 这个文件中存储了求1/2像素点的方法(此处通过线性内插,与H.264半像素内插(需要滤波)不同)
* 不同的函数处理的水平像素个数不同
*/
//================================================================
//函数参数含义如下
//src1:源1
//src_stride1:源1一行像素的大小
//src2:源2
//src_stride2:源2一行像素的大小
//dst:目标
//dst_stride1:处理后一行像素的大小
//h:处理的行数(纵向)
//求src1和src2的平均值存入dst
//“pixelsX”中的“X”代表水平方向像素数
//处理8个像素(横向)
/*
* [示例]
* 2 3 4 5 2 3 4 5
* ==> 5 5 4 4 5 5 4 4
* 8 7 4 3 8 7 4 3
*/
static inline void put_pixels8_l2_8(uint8_t *dst,
const uint8_t *src1,
const uint8_t *src2,
int dst_stride,
int src_stride1,
int src_stride2,
int h)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < h; i++) {
//取出4个像素(32bit),存入uint32_t(32bit)
uint32_t a, b;
a = (((const union unaligned_32 *) (&src1[i * src_stride1]))->l);
b = (((const union unaligned_32 *) (&src2[i * src_stride2]))->l);
//求平均,注意rnd_avg32()函数是分别求4个像素(32bit,划分为4个8bit)的平均值
//例如:
//unsigned int x1=0x02030405;
//unsigned int x2=0x08070403;
//unsigned int y=0;
//y=rnd_avg32(x1,x2);
//
//则y=0x05050404
//
*((uint32_t *) &dst[i * dst_stride]) = rnd_avg32(a, b);
//换4个像素,再来一次
a = (((const union unaligned_32 *) (&src1[i * src_stride1 + 4 * sizeof(uint8_t)]))->l);
b = (((const union unaligned_32 *) (&src2[i * src_stride2 + 4 * sizeof(uint8_t)]))->l);
*((uint32_t *) &dst[i * dst_stride + 4 * sizeof(uint8_t)]) = rnd_avg32(a, b);
}
}
//处理4个像素(横向)
/*
* [示例]
* 2 3 4 5
* ==> 5 5 4 4
* 8 7 4 3
*/
//求src1和src2的平均值存入dst
static inline void put_pixels4_l2_8(uint8_t *dst,
const uint8_t *src1,
const uint8_t *src2,
int dst_stride,
int src_stride1,
int src_stride2,
int h)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < h; i++) {
//取出4个像素(32bit),存入uint32_t(32bit)
uint32_t a, b;
a = (((const union unaligned_32 *) (&src1[i * src_stride1]))->l);
b = (((const union unaligned_32 *) (&src2[i * src_stride2]))->l);
//求平均
*((uint32_t *) &dst[i * dst_stride]) = rnd_avg32(a, b);
}
}
//处理2个像素(横向)
static inline void put_pixels2_l2_8(uint8_t *dst,
const uint8_t *src1,
const uint8_t *src2,
int dst_stride,
int src_stride1,
int src_stride2,
int h)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < h; i++) {
uint32_t a, b;
a = (((const union unaligned_16 *) (&src1[i * src_stride1]))->l);
b = (((const union unaligned_16 *) (&src2[i * src_stride2]))->l);
*((uint16_t *) &dst[i * dst_stride]) = rnd_avg32(a, b);
}
}
//处理16个像素(横向)
//分成2次,每次8个像素
static inline void put_pixels16_l2_8(uint8_t *dst,
const uint8_t *src1,
const uint8_t *src2,
int dst_stride,
int src_stride1,
int src_stride2,
int h)
{
put_pixels8_l2_8(dst, src1, src2, dst_stride,
src_stride1, src_stride2, h);
put_pixels8_l2_8(dst + 8 * sizeof(uint8_t),
src1 + 8 * sizeof(uint8_t),
src2 + 8 * sizeof(uint8_t),
dst_stride, src_stride1,
src_stride2, h);
}
源代码中注释比较充分,不再详细分析每个函数。可以看出put_pixels8_l2_8(),put_pixels4_l2_8(),put_pixels2_l2_8(),put_pixels16_l2_8()几个函数都是将输入的src1和src2中的像素值线性插值(取平均值)之后,赋值给dst。它们之间的不同在于一次性横向处理的像素数目不同。
h264qpel_template.c-put-(1/4像素精度-单向预测)
h264qpel_template.c中的函数用于1/4像素内插。该文件的格式和pel_template.c也是类似的,在这里不再重复叙述。1/4像素线性内插是在H.264标准中提出来的一种新型的内插方法,计算方法要比传统的1/2像素线性内插复杂很多。1/4像素内插一般分成两步:
(1)半像素内插。这一步通过6抽头滤波器获得5个半像素点。
(2)线性内插。这一步通过简单的线性内插获得剩余的1/4像素点。
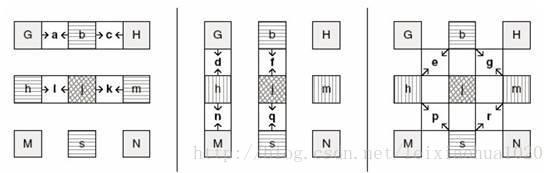
1/4像素内插的示意图如下图所示。半像素内插点为b、m、h、s、j五个点。半像素内插方法是对整像素点进行6 抽头滤波得出,滤波器的权重为(1/32, -5/32, 5/8, 5/8, -5/32, 1/32)。例如b的计算公式为:
b=round( (E - 5F + 20G + 20H - 5I + J ) / 32)
剩下几个半像素点的计算关系如下:m:由B、D、H、N、S、U计算
h:由A、C、G、M、R、T计算
s:由K、L、M、N、P、Q计算
j:由cc、dd、h、m、ee、ff计算。需要注意j点的运算量比较大,因为cc、dd、ee、ff都需要通过半像素内插方法进行计算。
在获得半像素点之后,就可以通过简单的线性内插获得1/4像素内插点了。1/4像素内插的方式如下图所示。例如图中a点的计算公式如下:
A=round( (G+b)/2 )
在这里有一点需要注意:位于4个角的e、g、p、r四个点并不是通过j点计算计算的,而是通过b、h、s、m四个半像素点计算的。有关1/4像素内插的知识暂时记录到这里。下面看一下相关的源代码。
半像素内插函数
h264qpel_template.c中包含了两类函数:半像素内插函数和1/4运动补偿函数。其中后者调用了前者完成了半像素内插的工作。下面首先看一下半像素内插相关的源代码。“H264_LOWPASS(put_, op_put, op2_put)”宏完成了半像素内插函数的初始化工作,该宏展开后的代码如下所示。//================================================================
/*
* h264qpel_template.c (quarter-pixel)
* H264_LOWPASS(OPNAME, OP, OP2)取值为H264_LOWPASS(put_, op_put, op2_put)的情况
*
* 源代码注释和处理:雷霄骅
* [email protected]
* http://blog.csdn.net/leixiaohua1020
*
* 这个文件中存储了:
* (1)H.264 1/4像素内插(包括半像素内插)的方法
* (2)1/4像素运动补偿的方法
*
* 处理的数据为一个方形的阵列,不同的函数处理的方形的大小不同
*/
//================================================================
//半像素内插
//H.264半像素内插,使用6抽头的滤波器
//H.264标准中的计算方法是b = ( A+ 5B + 20C + 20D + 5E + F )/32
//“qpelX”中的“X”代表一个方向(水平或垂直)上处理的像素数
//“v”代表水平滤波器(horizontal),“h”代表垂直滤波器(vertical),“hv”代表“水平+垂直”滤波器
//函数参数含义如下
//p_dst:处理后数据
//p_src:输入的数据
//dstStride:处理后图像一行像素的大小
//srcStride:输入图像一行像素的大小
/*
* [水平半像素内插]
*
*
*
* A B C X D E F
*
*
*
* 什么时候用到?(P1,P2,P3,P4代表相邻的4个像素)
*
* P1 X P2
*
*
*
* P3 P4
*/
//处理2x2个像素---水平滤波器(horizontal)
static __attribute__((unused)) void put_h264_qpel2_h_lowpass_8(uint8_t *p_dst
, const uint8_t *p_src, int dstStride, int srcStride){
//循环2次
const int h=2;
int i;
uint8_t *dst = (uint8_t*)p_dst;
const uint8_t *src = (const uint8_t*)p_src;
//一般不右移
dstStride >>= sizeof(uint8_t)-1;
srcStride >>= sizeof(uint8_t)-1;
for(i=0; i>5);
dst[1] = av_clip_uint8_c((((src[1]+src[2])*20 - (src[0 ]+src[3])*5 + (
src[-1]+src[4])) + 16)>>5);
dst+=dstStride;
src+=srcStride;
}
}
//垂直滤波器(vertical)
//滤波器的加权系数和水平滤波器是一样的
/*
* [垂直半像素内插]
*
* A
*
* B
*
* C
* X
* D
*
* E
*
* F
*
*
* 什么时候用到?(P1,P2,P3,P4代表相邻的4个像素)
*
* P1 P2
*
* X
*
* P3 P4
*/
//处理2x2个像素---垂直滤波器(vertical)
static __attribute__((unused)) void put_h264_qpel2_v_lowpass_8(uint8_t *_dst,
const uint8_t *_src, int dstStride, int srcStride){
//循环2次
const int w=2;
int i;
uint8_t *dst = (uint8_t*)_dst;
const uint8_t *src = (const uint8_t*)_src;
dstStride >>= sizeof(uint8_t)-1;
srcStride >>= sizeof(uint8_t)-1;
for(i=0; i>5);
dst[1*dstStride] = av_clip_uint8_c((((src1+src2)*20 - (src0+src3)*5 +
(srcA+src4)) + 16)>>5);
dst++;
src++;
}
}
/*
* [水平垂直半像素内插]
* 先水平内插5个点,每个点都如下处理:
*
* A B C Y1 D E F
*
*
* 然后在这5个点的基础上垂直内插1个点
*
* Y1
*
* Y1
*
* Y3
* X
* Y4
*
* Y5
*
* Y6
*
*
* 什么时候用到?(P1,P2,P3,P4代表相邻的4个像素)
*
* P1 P2
*
* X
*
* P3 P4
*/
//处理2x2个像素---水平滤波器(horizontal)+垂直滤波器(vertical)
static __attribute__((unused)) void put_h264_qpel2_hv_lowpass_8(uint8_t *_dst
, int16_t *tmp, const uint8_t *_src, int dstStride, int tmpStride, int
srcStride){
const int h=2;
const int w=2;
const int pad = (8 == 10) ? (-10 * ((1<<8)-1)) : 0;
int i;
uint8_t *dst = (uint8_t*)_dst;
const uint8_t *src = (const uint8_t*)_src;
dstStride >>= sizeof(uint8_t)-1;
srcStride >>= sizeof(uint8_t)-1;
src -= 2*srcStride;
//水平滤波-注意多处理了5个点
for(i=0; i>10);
dst[1*dstStride] = av_clip_uint8_c((((tmp1+tmp2)*20 - (tmp0+tmp3)*5 +
(tmpA+tmp4)) + 512)>>10);
dst++;
tmp++;
}
}
//处理4x4个像素---水平滤波器(horizontal)
static void put_h264_qpel4_h_lowpass_8(uint8_t *_dst, const uint8_t *_src,
int dstStride, int srcStride){
//和上面的函数一样,只是h取值变成4
const int h=4;
int i;
uint8_t *dst = (uint8_t*)_dst;
const uint8_t *src = (const uint8_t*)_src;
dstStride >>= sizeof(uint8_t)-1;
srcStride >>= sizeof(uint8_t)-1;
for(i=0; i>5);
dst[1] = av_clip_uint8_c((((src[1]+src[2])*20 - (src[0 ]+src[3])*5 + (
src[-1]+src[4])) + 16)>>5);
dst[2] = av_clip_uint8_c((((src[2]+src[3])*20 - (src[1 ]+src[4])*5 + (
src[0 ]+src[5])) + 16)>>5);
dst[3] = av_clip_uint8_c((((src[3]+src[4])*20 - (src[2 ]+src[5])*5 + (
src[1 ]+src[6])) + 16)>>5);
dst+=dstStride;
src+=srcStride;
}
}
//处理4x4个像素---垂直滤波器(vertical)
static void put_h264_qpel4_v_lowpass_8(uint8_t *_dst, const uint8_t *_src,
int dstStride, int srcStride){
//和上面的函数一样,只是w取值变成4
const int w=4;
int i;
uint8_t *dst = (uint8_t*)_dst;
const uint8_t *src = (const uint8_t*)_src;
dstStride >>= sizeof(uint8_t)-1;
srcStride >>= sizeof(uint8_t)-1;
for(i=0; i>5);
dst[1*dstStride] = av_clip_uint8_c((((src1+src2)*20 - (src0+src3)*5 +
(srcA+src4)) + 16)>>5);
dst[2*dstStride] = av_clip_uint8_c((((src2+src3)*20 - (src1+src4)*5 +
(src0+src5)) + 16)>>5);
dst[3*dstStride] = av_clip_uint8_c((((src3+src4)*20 - (src2+src5)*5 +
(src1+src6)) + 16)>>5);
dst++;
src++;
}
}
//处理4x4个像素---水平滤波器(horizontal)+垂直滤波器(vertical)
static void put_h264_qpel4_hv_lowpass_8(uint8_t *_dst, int16_t *tmp, const
uint8_t *_src, int dstStride, int tmpStride, int srcStride){
//和上面的函数一样,只是w,h取值变成4
const int h=4;
const int w=4;
const int pad = (8 == 10) ? (-10 * ((1<<8)-1)) : 0;
int i;
uint8_t *dst = (uint8_t*)_dst;
const uint8_t *src = (const uint8_t*)_src;
dstStride >>= sizeof(uint8_t)-1;
srcStride >>= sizeof(uint8_t)-1;
src -= 2*srcStride;
for(i=0; i>10);
dst[1*dstStride] = av_clip_uint8_c((((tmp1+tmp2)*20 - (tmp0+tmp3)*5 +
(tmpA+tmp4)) + 512)>>10);
dst[2*dstStride] = av_clip_uint8_c((((tmp2+tmp3)*20 - (tmp1+tmp4)*5 +
(tmp0+tmp5)) + 512)>>10);
dst[3*dstStride] = av_clip_uint8_c((((tmp3+tmp4)*20 - (tmp2+tmp5)*5 +
(tmp1+tmp6)) + 512)>>10);
dst++;
tmp++;
}
}
//处理8x8个像素---水平滤波器(horizontal)
static void put_h264_qpel8_h_lowpass_8(uint8_t *_dst, const uint8_t *_src,
int dstStride, int srcStride){
//和上面的函数一样,只是h取值变成8
const int h=8;
int i;
uint8_t *dst = (uint8_t*)_dst;
const uint8_t *src = (const uint8_t*)_src;
dstStride >>= sizeof(uint8_t)-1;
srcStride >>= sizeof(uint8_t)-1;
for(i=0; i>5);
dst[1] = av_clip_uint8_c((((src[1]+src[2])*20 - (src[0 ]+src[3])*5 + (
src[-1]+src[4 ])) + 16)>>5);
dst[2] = av_clip_uint8_c((((src[2]+src[3])*20 - (src[1 ]+src[4])*5 + (
src[0 ]+src[5 ])) + 16)>>5);
dst[3] = av_clip_uint8_c((((src[3]+src[4])*20 - (src[2 ]+src[5])*5 + (
src[1 ]+src[6 ])) + 16)>>5);
dst[4] = av_clip_uint8_c((((src[4]+src[5])*20 - (src[3 ]+src[6])*5 + (
src[2 ]+src[7 ])) + 16)>>5);
dst[5] = av_clip_uint8_c((((src[5]+src[6])*20 - (src[4 ]+src[7])*5 + (
src[3 ]+src[8 ])) + 16)>>5);
dst[6] = av_clip_uint8_c((((src[6]+src[7])*20 - (src[5 ]+src[8])*5 + (
src[4 ]+src[9 ])) + 16)>>5);
dst[7] = av_clip_uint8_c((((src[7]+src[8])*20 - (src[6 ]+src[9])*5 + (
src[5 ]+src[10])) + 16)>>5);
dst+=dstStride;
src+=srcStride;
}
}
//处理8x8个像素---垂直滤波器(vertical)
static void put_h264_qpel8_v_lowpass_8(uint8_t *_dst, const uint8_t *_src,
int dstStride, int srcStride){
//和上面的函数一样,只是w取值变成8
const int w=8;
int i;
uint8_t *dst = (uint8_t*)_dst;
const uint8_t *src = (const uint8_t*)_src;
dstStride >>= sizeof(uint8_t)-1;
srcStride >>= sizeof(uint8_t)-1;
for(i=0; i>5);
dst[1*dstStride] = av_clip_uint8_c((((src1+src2)*20 - (src0+src3)*5 +
(srcA+src4)) + 16)>>5);
dst[2*dstStride] = av_clip_uint8_c((((src2+src3)*20 - (src1+src4)*5 +
(src0+src5)) + 16)>>5);
dst[3*dstStride] = av_clip_uint8_c((((src3+src4)*20 - (src2+src5)*5 +
(src1+src6)) + 16)>>5);
dst[4*dstStride] = av_clip_uint8_c((((src4+src5)*20 - (src3+src6)*5 +
(src2+src7)) + 16)>>5);
dst[5*dstStride] = av_clip_uint8_c((((src5+src6)*20 - (src4+src7)*5 +
(src3+src8)) + 16)>>5);
dst[6*dstStride] = av_clip_uint8_c((((src6+src7)*20 - (src5+src8)*5 +
(src4+src9)) + 16)>>5);
dst[7*dstStride] = av_clip_uint8_c((((src7+src8)*20 - (src6+src9)*5 +
(src5+src10)) + 16)>>5);
dst++;
src++;
}
}
//处理8x8个像素---水平滤波器(horizontal)+垂直滤波器(vertical)
static void put_h264_qpel8_hv_lowpass_8(uint8_t *_dst, int16_t *tmp, const
uint8_t *_src, int dstStride, int tmpStride, int srcStride){
const int h=8;
const int w=8;
const int pad = (8 == 10) ? (-10 * ((1<<8)-1)) : 0;
int i;
uint8_t *dst = (uint8_t*)_dst;
const uint8_t *src = (const uint8_t*)_src;
dstStride >>= sizeof(uint8_t)-1;
srcStride >>= sizeof(uint8_t)-1;
src -= 2*srcStride;
for(i=0; i>10);
dst[1*dstStride] = av_clip_uint8_c((((tmp1+tmp2)*20 - (tmp0+tmp3)*5 +
(tmpA+tmp4)) + 512)>>10);
dst[2*dstStride] = av_clip_uint8_c((((tmp2+tmp3)*20 - (tmp1+tmp4)*5 +
(tmp0+tmp5)) + 512)>>10);
dst[3*dstStride] = av_clip_uint8_c((((tmp3+tmp4)*20 - (tmp2+tmp5)*5 +
(tmp1+tmp6)) + 512)>>10);
dst[4*dstStride] = av_clip_uint8_c((((tmp4+tmp5)*20 - (tmp3+tmp6)*5 +
(tmp2+tmp7)) + 512)>>10);
dst[5*dstStride] = av_clip_uint8_c((((tmp5+tmp6)*20 - (tmp4+tmp7)*5 +
(tmp3+tmp8)) + 512)>>10);
dst[6*dstStride] = av_clip_uint8_c((((tmp6+tmp7)*20 - (tmp5+tmp8)*5 +
(tmp4+tmp9)) + 512)>>10);
dst[7*dstStride] = av_clip_uint8_c((((tmp7+tmp8)*20 - (tmp6+tmp9)*5 +
(tmp5+tmp10)) + 512)>>10);
dst++;
tmp++;
}
}
//处理16x16个像素---水平滤波器(horizontal)
static void put_h264_qpel16_v_lowpass_8(uint8_t *dst, const uint8_t *src, int
dstStride, int srcStride){
//分解为4个8x8处理
put_h264_qpel8_v_lowpass_8(dst , src ,
dstStride, srcStride);
put_h264_qpel8_v_lowpass_8(dst+8*sizeof(uint8_t), src+8*sizeof(uint8_t),
dstStride, srcStride);
src += 8*srcStride;
dst += 8*dstStride;
put_h264_qpel8_v_lowpass_8(dst , src ,
dstStride, srcStride);
put_h264_qpel8_v_lowpass_8(dst+8*sizeof(uint8_t), src+8*sizeof(uint8_t),
dstStride, srcStride);
}
//处理16x16个像素---垂直滤波器(vertical)
static void put_h264_qpel16_h_lowpass_8(uint8_t *dst, const uint8_t *src, int
dstStride, int srcStride){
//分解为4个8x8处理
put_h264_qpel8_h_lowpass_8(dst , src ,
dstStride, srcStride);
put_h264_qpel8_h_lowpass_8(dst+8*sizeof(uint8_t), src+8*sizeof(uint8_t),
dstStride, srcStride);
src += 8*srcStride;
dst += 8*dstStride;
put_h264_qpel8_h_lowpass_8(dst , src ,
dstStride, srcStride);
put_h264_qpel8_h_lowpass_8(dst+8*sizeof(uint8_t), src+8*sizeof(uint8_t),
dstStride, srcStride);
}
//处理16x16个像素---水平滤波器(horizontal)+垂直滤波器(vertical)
static void put_h264_qpel16_hv_lowpass_8(uint8_t *dst, int16_t *tmp, const
uint8_t *src, int dstStride, int tmpStride, int srcStride){
//分解为4个8x8处理
put_h264_qpel8_hv_lowpass_8(dst , tmp ,
src , dstStride, tmpStride, srcStride);
put_h264_qpel8_hv_lowpass_8(dst+8*sizeof(uint8_t), tmp+8, src+8*sizeof(
uint8_t), dstStride, tmpStride, srcStride);
src += 8*srcStride;
dst += 8*dstStride;
put_h264_qpel8_hv_lowpass_8(dst , tmp ,
src , dstStride, tmpStride, srcStride);
put_h264_qpel8_hv_lowpass_8(dst+8*sizeof(uint8_t), tmp+8, src+8*sizeof(
uint8_t), dstStride, tmpStride, srcStride);
}
源代码中已经对这些函数做了比较详细的注释,在这里不再重复叙述。这些半像素内插函数都实现了半像素内插公式:
b=round( (E - 5F + 20G + 20H - 5I + J ) / 32)
这些函数的名称都是“put_h264_qpel{X}_{Y}_lowpass_8()”的形式。其中“X”代表了处理的图像方块的大小:
2:2x2图像块“Y”代表了滤波的方向:
4:4x4图像块
8:8x8图像块
16:16x16图像块
h:水平半像素滤波
v:垂直半像素滤波
hv:水平+垂直半像素滤波(计算相对复杂)
看完前面这些内插函数之后,就可以研究最重要的1/4像素运动补偿函数了。
1/4像素运动补偿函数
1/4像素运动补偿是《H.264标准中》规定的运动补偿方法。将h264qpel_template.c中有一系列宏用于初始化1/4运动补偿函数,如下所示。H264_MC(put_, 2) //2x2块
H264_MC(put_, 4) //4x4块
H264_MC(put_, 8) //8x8块
H264_MC(put_, 16) //16x16块//===================================================================================
//1/4运动补偿(mc, motion composition)函数
//
//mc{ab}命名规则?
//纵向为垂直,横向为水平{ab}中{a}代表水平,{b}代表垂直
//{a,b}与像素内插点之间的关系如下表所示
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// | |原始像素(0) | 1/4内插点 | 1/2内插点 | 3/4内插点 | 原始像素(1)
//-+-------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// | 原始像素(0) | 0,0 | 1,0 | 2,0 | 3,0 |
// | 1/4内插点 | 0,1 | 1,1 | 2,1 | 3,1 |
// | 1/2内插点 | 0,2 | 1,2 | 2,2 | 3,2 |
// | 3/4内插点 | 0,3 | 1,3 | 2,3 | 3,3 |
//---------------------------------------------------------------------------------
// | 原始像素(0+1行) |
//处理的数据为一个方块
//“qpelX”中的“X”代表方块的大小
//FFmpeg对于亮度提供了16x16,8x8,4x4的块的内插方法,在这里仅列出8x8的情况,其他情况的源代码也是类似的
/*
* qpel16处理的块适用于16x16的块
* +--------+--------+
* | |
* | |
* | |
* + + +
* | |
* | |
* | |
* +--------+--------+
*
* qpel8处理的块适用于16x8,8x16,8x8的块(非正方形需要分成两个正方形处理)
* +--------+
* | |
* | |
* | |
* +--------+
*
* qpel4处理的块适用于8x4,4x8,4x4的块
* +---+
* | |
* +---+
*
*/
//下面的代码为qpel8的情况(处理8x8的块)
//函数参数含义如下
//dst:处理后数据
//src:输入的数据
//stride:输入图像一行像素的大小
//运动矢量正好指向整像素点(0,0)
static void put_h264_qpel8_mc00_8_c(uint8_t *dst, const uint8_t *src, ptrdiff_t stride)
{
//直接赋值
put_pixels8_8_c(dst, src, stride, 8);
}
//运动矢量指向像素点(1/4,0)
/*
* 计算顺序为1,2,3......
* P1,P2,P3,P4代表相邻的4个点
*
* P1 2 1 P2
*
*
*
* P3 P4
*
*/
static void put_h264_qpel8_mc10_8_c(uint8_t *dst, const uint8_t *src, ptrdiff_t stride)
{
//half存储半像素内插的结果
uint8_t half[8*8*sizeof(uint8_t)];
//水平滤波器-处理8个像素
//得到半像素内插后的结果,存入half
put_h264_qpel8_h_lowpass_8(half, src, 8*sizeof(uint8_t), stride);
//然后半像素内插后的结果,再与原始像素线性内插,得到1/4像素内插的结果
put_pixels8_l2_8(dst, src, half, stride, stride, 8*sizeof(uint8_t), 8);
}
//运动矢量指向像素点(1/2,0)
/*
* 计算顺序为1,2,3......
* P1,P2,P3,P4代表相邻的4个点
*
* P1 1 P2
*
*
*
* P3 P4
*
*/
static void put_h264_qpel8_mc20_8_c(uint8_t *dst, const uint8_t *src, ptrdiff_t stride)
{
//水平滤波器-处理8个像素
put_h264_qpel8_h_lowpass_8(dst, src, stride, stride);
//不再进行1/4像素内插
}
//运动矢量指向像素点(3/4,0)
/*
* 计算顺序为1,2,3......
* P1,P2,P3,P4代表相邻的4个点
*
* P1 1 2 P2
*
*
*
* P3 P4
*
*/
static void put_h264_qpel8_mc30_8_c(uint8_t *dst, const uint8_t *src, ptrdiff_t stride)
{
uint8_t half[8*8*sizeof(uint8_t)];
//水平滤波器-处理8个像素
//得到半像素内插后的结果,存入half
put_h264_qpel8_h_lowpass_8(half, src, 8*sizeof(uint8_t), stride);
//然后半像素内插后的结果,再与原始像素的下一个点线性内插,得到3/4像素内插的结果
put_pixels8_l2_8(dst, src+sizeof(uint8_t), half, stride, stride, 8*sizeof(uint8_t), 8);
}
//运动矢量指向像素点(0,1/4)
/*
* 计算顺序为1,2,3......
* P1,P2,P3,P4代表相邻的4个点
*
* P1 P2
* 2
* 1
*
* P3 P4
*
*/
static void put_h264_qpel8_mc01_8_c(uint8_t *dst, const uint8_t *src, ptrdiff_t stride)
{
uint8_t full[8*(8+5)*sizeof(uint8_t)];
uint8_t * const full_mid= full + 8*2*sizeof(uint8_t);
uint8_t half[8*8*sizeof(uint8_t)];
copy_block8_8(full, src - stride*2, 8*sizeof(uint8_t), stride, 8 + 5);
//垂直滤波器-处理8个像素
//得到半像素内插后的结果,存入half
put_h264_qpel8_v_lowpass_8(half, full_mid, 8*sizeof(uint8_t), 8*sizeof(uint8_t));
//然后半像素内插后的结果,再与原始像素线性内插,得到1/4像素内插的结果
put_pixels8_l2_8(dst, full_mid, half, stride, 8*sizeof(uint8_t), 8*sizeof(uint8_t), 8);
}
//运动矢量指向像素点(0,1/2)
/*
* 计算顺序为1,2,3......
* P1,P2,P3,P4代表相邻的4个点
*
* P1 P2
*
* 1
*
* P3 P4
*
*/
static void put_h264_qpel8_mc02_8_c(uint8_t *dst, const uint8_t *src, ptrdiff_t stride)
{
uint8_t full[8*(8+5)*sizeof(uint8_t)];
uint8_t * const full_mid= full + 8*2*sizeof(uint8_t);
copy_block8_8(full, src - stride*2, 8*sizeof(uint8_t), stride, 8 + 5);
//垂直滤波器-处理8个像素
put_h264_qpel8_v_lowpass_8(dst, full_mid, stride, 8*sizeof(uint8_t));
//不再进行1/4像素内插
}
//运动矢量指向像素点(0,3/4)
/*
* 计算顺序为1,2,3......
* P1,P2,P3,P4代表相邻的4个点
*
* P1 P2
*
* 1
* 2
* P3 P4
*
*/
static void put_h264_qpel8_mc03_8_c(uint8_t *dst, const uint8_t *src, ptrdiff_t stride)
{
uint8_t full[8*(8+5)*sizeof(uint8_t)];
uint8_t * const full_mid= full + 8*2*sizeof(uint8_t);
uint8_t half[8*8*sizeof(uint8_t)];
copy_block8_8(full, src - stride*2, 8*sizeof(uint8_t), stride, 8 + 5);
put_h264_qpel8_v_lowpass_8(half, full_mid, 8*sizeof(uint8_t), 8*sizeof(uint8_t));
put_pixels8_l2_8(dst, full_mid+8*sizeof(uint8_t), half, stride, 8*sizeof(uint8_t), 8*sizeof(uint8_t), 8);
}
//运动矢量指向像素点(1/4,1/4)
/*
* 计算顺序为1,2,3......
* P1,P2,P3,P4代表相邻的4个点
*
* P1 1 P2
* 3
* 2
*
* P3 P4
*
*/
static void put_h264_qpel8_mc11_8_c(uint8_t *dst, const uint8_t *src, ptrdiff_t stride)
{
uint8_t full[8*(8+5)*sizeof(uint8_t)];
uint8_t * const full_mid= full + 8*2*sizeof(uint8_t);
uint8_t halfH[8*8*sizeof(uint8_t)];
uint8_t halfV[8*8*sizeof(uint8_t)];
//水平滤波,得到样点1
put_h264_qpel8_h_lowpass_8(halfH, src, 8*sizeof(uint8_t), stride);
copy_block8_8(full, src - stride*2, 8*sizeof(uint8_t), stride, 8 + 5);
//垂直滤波,得到样点2
put_h264_qpel8_v_lowpass_8(halfV, full_mid, 8*sizeof(uint8_t), 8*sizeof(uint8_t));
//线性插值样点1和样点2,得到样点3
put_pixels8_l2_8(dst, halfH, halfV, stride, 8*sizeof(uint8_t), 8*sizeof(uint8_t), 8);
}
//运动矢量指向像素点(3/4,1/4)
/*
* 计算顺序为1,2,3......
* P1,P2,P3,P4代表相邻的4个点
*
* P1 1 P2
* 3
* 2
*
* P3 P4
*
*/
static void put_h264_qpel8_mc31_8_c(uint8_t *dst, const uint8_t *src, ptrdiff_t stride)
{
uint8_t full[8*(8+5)*sizeof(uint8_t)];
uint8_t * const full_mid= full + 8*2*sizeof(uint8_t);
uint8_t halfH[8*8*sizeof(uint8_t)];
uint8_t halfV[8*8*sizeof(uint8_t)];
put_h264_qpel8_h_lowpass_8(halfH, src, 8*sizeof(uint8_t), stride);
copy_block8_8(full, src - stride*2 + sizeof(uint8_t), 8*sizeof(uint8_t), stride, 8 + 5);
put_h264_qpel8_v_lowpass_8(halfV, full_mid, 8*sizeof(uint8_t), 8*sizeof(uint8_t));
put_pixels8_l2_8(dst, halfH, halfV, stride, 8*sizeof(uint8_t), 8*sizeof(uint8_t), 8);
}
static void put_h264_qpel8_mc13_8_c(uint8_t *dst, const uint8_t *src, ptrdiff_t stride)
{
uint8_t full[8*(8+5)*sizeof(uint8_t)];
uint8_t * const full_mid= full + 8*2*sizeof(uint8_t);
uint8_t halfH[8*8*sizeof(uint8_t)];
uint8_t halfV[8*8*sizeof(uint8_t)];
put_h264_qpel8_h_lowpass_8(halfH, src + stride, 8*sizeof(uint8_t), stride);
copy_block8_8(full, src - stride*2, 8*sizeof(uint8_t), stride, 8 + 5);
put_h264_qpel8_v_lowpass_8(halfV, full_mid, 8*sizeof(uint8_t), 8*sizeof(uint8_t));
put_pixels8_l2_8(dst, halfH, halfV, stride, 8*sizeof(uint8_t), 8*sizeof(uint8_t), 8);
}
static void put_h264_qpel8_mc33_8_c(uint8_t *dst, const uint8_t *src, ptrdiff_t stride)
{
uint8_t full[8*(8+5)*sizeof(uint8_t)];
uint8_t * const full_mid= full + 8*2*sizeof(uint8_t);
uint8_t halfH[8*8*sizeof(uint8_t)];
uint8_t halfV[8*8*sizeof(uint8_t)];
put_h264_qpel8_h_lowpass_8(halfH, src + stride, 8*sizeof(uint8_t), stride);
copy_block8_8(full, src - stride*2 + sizeof(uint8_t), 8*sizeof(uint8_t), stride, 8 + 5);
put_h264_qpel8_v_lowpass_8(halfV, full_mid, 8*sizeof(uint8_t), 8*sizeof(uint8_t));
put_pixels8_l2_8(dst, halfH, halfV, stride, 8*sizeof(uint8_t), 8*sizeof(uint8_t), 8);
}
//============================================================
//下面的函数处理的几个点必须要位于正中间的“水平+垂直”滤波点(对应[1/2,1/2]点,计算量较大)的支持
/*
* 计算“X”所示的点
*
* P1 P2
* X
* X X X
* X
* P3 P4
*
*/
//============================================================
//运动矢量指向像素点(1/2,1/2)
/*
* 计算顺序为1,2,3......
* P1,P2,P3,P4代表相邻的4个点
*
* P1 P2
*
* 1
*
* P3 P4
*
*/
static void put_h264_qpel8_mc22_8_c(uint8_t *dst, const uint8_t *src, ptrdiff_t stride)
{
int16_t tmp[8*(8+5)*sizeof(uint8_t)];
put_h264_qpel8_hv_lowpass_8(dst, tmp, src, stride, 8*sizeof(uint8_t), stride);
}
//运动矢量指向像素点(1/2,1/4)
/*
* 计算顺序为1,2,3......
* P1,P2,P3,P4代表相邻的4个点
*
* P1 1 P2
* 3
* 2
*
* P3 P4
*
*/
static void put_h264_qpel8_mc21_8_c(uint8_t *dst, const uint8_t *src, ptrdiff_t stride)
{
int16_t tmp[8*(8+5)*sizeof(uint8_t)];
uint8_t halfH[8*8*sizeof(uint8_t)];
uint8_t halfHV[8*8*sizeof(uint8_t)];
//水平滤波,得到样点1
put_h264_qpel8_h_lowpass_8(halfH, src, 8*sizeof(uint8_t), stride);
//水平+垂直滤波,得到样点2
put_h264_qpel8_hv_lowpass_8(halfHV, tmp, src, 8*sizeof(uint8_t), 8*sizeof(uint8_t), stride);
//线性插值样点1和样点2,得到样点3
put_pixels8_l2_8(dst, halfH, halfHV, stride, 8*sizeof(uint8_t), 8*sizeof(uint8_t), 8);
}
static void put_h264_qpel8_mc23_8_c(uint8_t *dst, const uint8_t *src, ptrdiff_t stride)
{
int16_t tmp[8*(8+5)*sizeof(uint8_t)];
uint8_t halfH[8*8*sizeof(uint8_t)];
uint8_t halfHV[8*8*sizeof(uint8_t)];
put_h264_qpel8_h_lowpass_8(halfH, src + stride, 8*sizeof(uint8_t), stride);
put_h264_qpel8_hv_lowpass_8(halfHV, tmp, src, 8*sizeof(uint8_t), 8*sizeof(uint8_t), stride);
put_pixels8_l2_8(dst, halfH, halfHV, stride, 8*sizeof(uint8_t), 8*sizeof(uint8_t), 8);
}
//运动矢量指向像素点(1/4,1/2)
/*
* 计算顺序为1,2,3......
* P1,P2,P3,P4代表相邻的4个点
*
* P1 P2
*
* 1 3 2
*
* P3 P4
*
*/
static void put_h264_qpel8_mc12_8_c(uint8_t *dst, const uint8_t *src, ptrdiff_t stride)
{
uint8_t full[8*(8+5)*sizeof(uint8_t)];
uint8_t * const full_mid= full + 8*2*sizeof(uint8_t);
int16_t tmp[8*(8+5)*sizeof(uint8_t)];
uint8_t halfV[8*8*sizeof(uint8_t)];
uint8_t halfHV[8*8*sizeof(uint8_t)];
copy_block8_8(full, src - stride*2, 8*sizeof(uint8_t), stride, 8 + 5);
//垂直滤波,得到样点1
put_h264_qpel8_v_lowpass_8(halfV, full_mid, 8*sizeof(uint8_t), 8*sizeof(uint8_t));
//水平+垂直滤波,得到样点2
put_h264_qpel8_hv_lowpass_8(halfHV, tmp, src, 8*sizeof(uint8_t), 8*sizeof(uint8_t), stride);
//线性插值样点1和样点2,得到样点3
put_pixels8_l2_8(dst, halfV, halfHV, stride, 8*sizeof(uint8_t), 8*sizeof(uint8_t), 8);
}
static void put_h264_qpel8_mc32_8_c(uint8_t *dst, const uint8_t *src, ptrdiff_t stride)
{
uint8_t full[8*(8+5)*sizeof(uint8_t)];
uint8_t * const full_mid= full + 8*2*sizeof(uint8_t);
int16_t tmp[8*(8+5)*sizeof(uint8_t)];
uint8_t halfV[8*8*sizeof(uint8_t)];
uint8_t halfHV[8*8*sizeof(uint8_t)];
copy_block8_8(full, src - stride*2 + sizeof(uint8_t), 8*sizeof(uint8_t), stride, 8 + 5);
put_h264_qpel8_v_lowpass_8(halfV, full_mid, 8*sizeof(uint8_t), 8*sizeof(uint8_t));
put_h264_qpel8_hv_lowpass_8(halfHV, tmp, src, 8*sizeof(uint8_t), 8*sizeof(uint8_t), stride);
put_pixels8_l2_8(dst, halfV, halfHV, stride, 8*sizeof(uint8_t), 8*sizeof(uint8_t), 8);
}
该部分源代码已经做了比较充分的注释,不再详细叙述。这些函数的名称都是“put_h264_qpel{X}_mc{HV}_8_c()”的形式,其中“X”代表了处理的图像方块的的大小,而“HV”则代表了1/4像素内插点的位置。其中{H,V}取值和内插点的位置关系如下图所示。
至此FFmpeg H.264解码器四分之一像素运动补偿部分的代码就分析完毕了。在运动补偿完成之后就得到了预测数据。在随后解码器会调用DCT反变换模块将DCT残差数据变换为像素残差数据,并叠加到预测数据上,完成解码。
hl_decode_mb_idct_luma()
和帧内预测宏块类似,帧间预测宏块的DCT反变换同样是经过hl_decode_mb_idct_luma()函数。由于在上一篇文章《FFmpeg的H.264解码器源代码简单分析:宏块解码(Decode)部分-帧内宏块(Intra)》中已经详细分析过这部分代码,在这里不再重复。雷霄骅
[email protected]
http://blog.csdn.net/leixiaohua1020