MyBatis源码的学习(6)---二级缓存默认是关闭的?
以前,没有看源码,一直印象中记得二级缓存是关闭的。最近看了源码才发现,原来二级缓存总开关默认是开了,只是使用时需要加一定条件的。
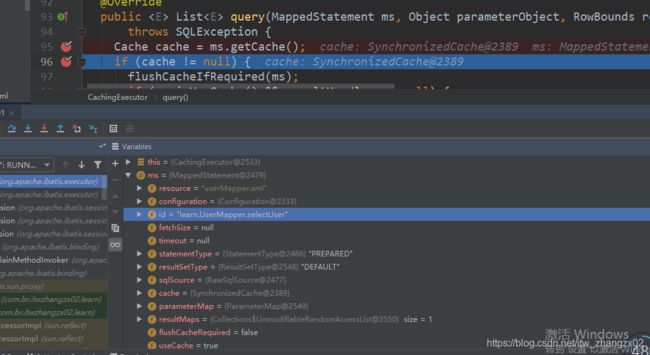
先说结论,要想某个Mapper.xml使用到二级缓存,只需要在cacheEnabled默认是true,二级缓存是在使用CachingExecutor执行器进行查询时,使用的。如果我们把总配置文件的cacheEnabled改为false后,就不会用到CachingExecutor执行器了,也就是二级缓存失效了。但是,不管总开关是什么值,我们创建二级缓存对象时,是根据Mapper.xml文件中是否有
另外,只有sql语句类型是“SELECT”的时候,使用二级缓存里拿值,其他操作,刷新缓存里的值。一个二级缓存Cache对象创建之后放入到configuration对象的缓存列表中的caches中,是作为一个MappedStatement对象的成员变量的。而一个MappedStatement对象代表的是一个mapper.xml中的某一个sql语句(四种类型:增删改查)。
具体的创建对象的方法:
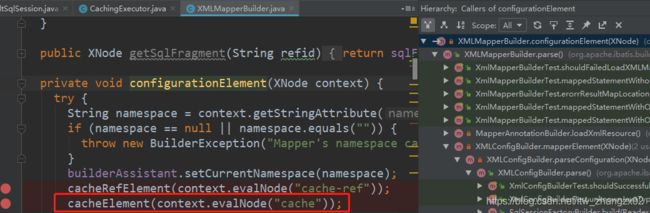
private void cacheElement(XNode context) {
if (context != null) {
String type = context.getStringAttribute("type", "PERPETUAL");
Class typeClass = typeAliasRegistry.resolveAlias(type);
String eviction = context.getStringAttribute("eviction", "LRU");
Class evictionClass = typeAliasRegistry.resolveAlias(eviction);
Long flushInterval = context.getLongAttribute("flushInterval");
Integer size = context.getIntAttribute("size");
boolean readWrite = !context.getBooleanAttribute("readOnly", false);
boolean blocking = context.getBooleanAttribute("blocking", false);
Properties props = context.getChildrenAsProperties();
//关键代码,创建CACHE
builderAssistant.useNewCache(typeClass, evictionClass, flushInterval, size, readWrite, blocking, props);
}
}public Cache useNewCache(Class typeClass,
Class evictionClass,
Long flushInterval,
Integer size,
boolean readWrite,
boolean blocking,
Properties props) {
Cache cache = new CacheBuilder(currentNamespace)
.implementation(valueOrDefault(typeClass, PerpetualCache.class))
.addDecorator(valueOrDefault(evictionClass, LruCache.class))
.clearInterval(flushInterval)
.size(size)
.readWrite(readWrite)
.blocking(blocking)
.properties(props)
.build();
configuration.addCache(cache);
currentCache = cache;
return cache;
}builderAssistant对象来自MapperBuilderAssistant 类,这个类是构建一个Mapper文件时新new的,也就是每一个Mapper.xml文件会对应
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, resource, configuration.getSqlFragments());一个MapperBuilderAssistant 对象,这个对象个属性 CurrentNameSpace,里面存放当前Mapper.xml的命名空间。
private XMLMapperBuilder(XPathParser parser, Configuration configuration, String resource, Map sqlFragments) {
super(configuration);
this.builderAssistant = new MapperBuilderAssistant(configuration, resource);
this.parser = parser;
this.sqlFragments = sqlFragments;
this.resource = resource;
} 从上面代码看的出来,就是一个MapperBuilderAssistant 对象对应了一个Mapper.xml文件。
参数:resource的值类似:
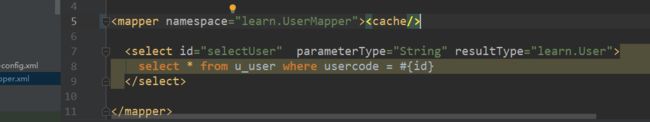
我们的二级缓存的级别是Mapper.xml级别,也就是namespace级别的。每一个namespace都有一个二级缓存,前提是加了标签cacheEnabled参数作为条件。
//下面方法,来自XMLMapperBuilder类,用于构建一个一个Mapper。一个Mapper.xml文件抽象后的对象
//key就是我们的namespace。
//所以说,二级缓存是namespace级别的。
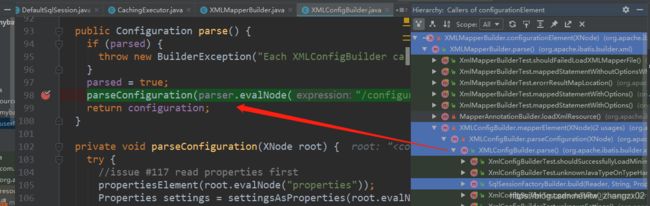
private void configurationElement(XNode context) {
try {
String namespace = context.getStringAttribute("namespace");
if (namespace == null || namespace.equals("")) {
throw new BuilderException("Mapper's namespace cannot be empty");
}
builderAssistant.setCurrentNamespace(namespace);
cacheRefElement(context.evalNode("cache-ref"));
cacheElement(context.evalNode("cache"));
parameterMapElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/parameterMap"));
resultMapElements(context.evalNodes("/mapper/resultMap"));
sqlElement(context.evalNodes("/mapper/sql"));
buildStatementFromContext(context.evalNodes("select|insert|update|delete"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing Mapper XML. The XML location is '" + resource + "'. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}另外,由于二级缓存的级别是namespace维度的,所以说如果不同Mapper.xml中对同一条数据的不同操作,会造成脏数据。
举例:执行数据顺序如下
1)AMapper.xml中执行查询操作id=10的人员数据。(假设这个namespace中只有查询,即从不刷新二级缓存)
2)BMapper.xml中对id=10的人员数据进行update操作。(执行update,将name修改,要记得提交事务)
3)AMapper.xml中执行查询操作id=10的人员数据。(查询的是缓存中的值,实际name数据库中已修改了)。
另外,还有涉及到关联查询,修改等操作,不同的namespace等都可能引起脏读,所以实际使用中,一般都是建议使用MyBatis的二级缓存,而是使用redis等外部缓存。
为了提高性能,建议将总配置文件中的改为fasle,这样我们执行器可以不用CachingExecutor,能够提高点效率,同时每个Mapper文件中不要由cache标签。缓存数据可以用专门的缓存工具来做。
最后,结论。二级缓存的开启与否,默认是看Mapper文件中是否加了
另外,二级缓存啥时候放入进去,是需要提交事务才可以的。关键代码可以查看
TransactionalCache这个类,它的commit()方法。
通过装饰的设计模式,最终查询出来的数据,会经历序列化,然后放到最基础的cache:PerpetualCache。另外,二级缓存时,value值里的对象,必须是实现了序列化接口。