sql server语法(基础整理)
sql server身份验证
系统内置的数据库用户有 dbo,guest..
创建新的登录账户
use master
go
exec sp_addlogin 'xiaozhang','1234' --xiaowang是账户,1234是密码删除登录账户的方法
use master
go
--删除登录账户
exec sp_droplogin 'xiaozhang'登录账户删除后,该账户创建的数据库用户还在,并不会一同删除
添加/删除数据库用户
--创建数据库用户
use TestManageDB
go
exec sp_grantdbaccess 'xiaozhang','xiaozhang03'
--删除数据库用户
use TestManageDB
go
exec sp_dropuser 'xiaozhang03'给数据库用户授权 (grant 权限 on 表名 to 数据库用户)
注意:这里是将数据库中的数据表的权限给数据库用户
use SchoolDB
go
--为数据库用户分配权限(查询,修改,输入)
grant select,update,insert on UserInfo to xiaozhang03
--分配权限(创建数据表)
grant create table to xiaozhang03收回数据库用户的权限(remove 权限 on 表面 to 数据库用户)
revoke select,update,insert on SchoolDB to xiaozhang03给单个数据库用户授权非常麻烦,可以定义一个角色,给该角色授权,再将角色赋给特定用户。
角色 db_owner 数据库的拥有者,可以对数据库和其对象进行所有管理工作。其他的角色还有很多,就不一一记录了
赋予/删除数据库用户角色
--赋予数据库用户固定角色
exec sp_addrolemember '数据库角色名称','数据库用户名'
--删除角色成员
exec sp_droprolemember '数据库角色名称','数据库用户名'即执行以下代码就可以获得/删除SchoolDB的所有权限了
use SchoolDB
go
--赋予角色
exec sp_addrolemember 'db_owner','xiaozhang02'
--删除角色
exec sp_droprolemember 'db_owner','xiaozhang02'变量的分类
局部变量:(过程中使用)
- 局部变量必须以标记@为前缀,如@age
- 局部变量的使用也是先声明(declare),再赋值
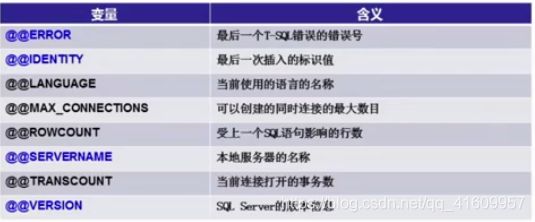
全局变量:(任何时候都可使用)
例
--print 数据库输出
print '服务器名称:'+@@servername --服务器名称:LAPTOP-AF8MEEAE
print '服务器版本信息:'+@@version --服务器版本信息...
print @@error --最后一条执行错误的SQL语句错误号局部变量定义与赋值
--局部变量定义的语法
declare @变量名 数据类型
--赋值方法
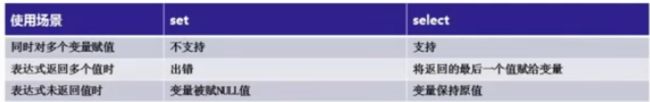
set @变量名=值 或 select @变量名=值 --使用select赋值要确保筛选出的记录只有一条set和select赋值比较
declare @stuId int,@stuName nvarchar(20)
--多个变量赋值
set @stuId='1001',@stuName='小章' --不允许这样赋值
select @stuId='1001,@stuName='小章' --允许
--表达式返回多个值
set @stuId=(select *from Students)--不允许
select @stuId=stuId from Students --得到最后一个值
--表达式未返回值时
set @stuId=(select *from Students where 1<0) --@stuId被赋NULL值
select @stuId=stuId from Students where 1<0 --@stuId保持原值select可以用于查询赋值,语法和select查询语句一样。set用于单个赋值
例子:编写T-SQL查询刘德华及其学号相邻的学员?
use SchoolDB
go
--声明学号变量
declare @stuId int,@stuName varchar(20)
--查询刘德华的信息
set @stuName='刘德华'
select stuNo,stuName,sex from Students
where stuName=@stuName
--查询刘德华的学号
select @stuId=stuNo from Students where stuName=@stuName--select赋值要确保记录只有一条
--查询与刘德华学号相邻的学员
select stuNo,stuName,sex from Students
where stuNo=(@stuId+1)or (stuNo=@stuId-1)数据类型转换convert/cast
convert(要转换的数据类型,表达式,样式)//样式可以省略,一般用于日期转字符,浮点转字符,不同样式使数据显示格式不同
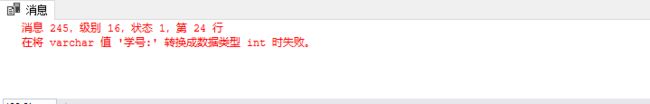
例,输出姓名为刘德华的学生的学号
declare @id int
select @id=stuNo from Students where stuName='刘德华'
print'学号:'+@id这里因为变量@id是int型,而‘学号’是字符型,字符串和数值无法直接+连接,需要我们手动转换成成同一类型
转换为字符类型后
declare @id int
select @id=stuNo from Students where stuName='刘德华'
print '学号:'+convert(nvarchar(20),@id)cast(表达式 as 数据类型) case无法指定转换的样式
下面一个例子 比较两种转换方法
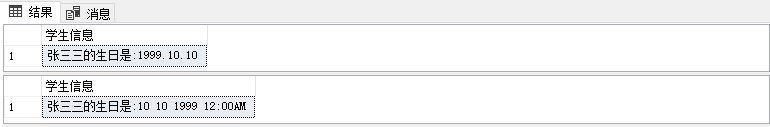
use SchoolDB
go
select stuName+'的生日是:'+convert(nvarchar(100),birthday,102) as 学生信息 from Students where stuNo='1001'
select stuName+'的生日是:'+cast(birthday as nvarchar(100))as 学生信息 from Students where stuNo='1001'
这里convert转换设置了样式102,使得数据样式不同与默认的了
练习:查询学号为1001的学生的年龄
declare @birthday datetime,@days int,@age int
--查询出生日期
select @birthday=birthday from Students where stuNo=1001
print @birthday
--计算天数
set @days=DATEDIFF(day,@birthday,getdate())--datediff函数返回两个日期间的时间,day表示天数
print @days
--计算年纪
set @age=floor(@days/365)--floor函数返回小于或等于数值表达式的最大正数 即天数/365获取周岁
print '1001号学员年纪:'+convert(nvarchar(20),@age)输出
简写
declare @birthday datetime
select @birthday=birthday from Students where stuNo=1001
select floor(datediff(day,@birthday,getdate())/365)as 年龄 from Students where stuNo=1001IF-ELSE语句
IF(条件)
begin
语句1
语句2
...
end
else
begin
语句1
语句2
...
endelse是可选部分,一条可不加,begin end
例子:
WHILE语句
while(条件)
begin
语句1
语句2
...
end
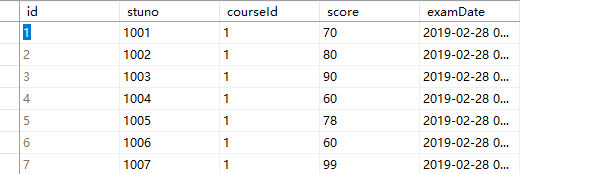
--break表示跳出循环,多条语句才需要begin-end语句块练习:将成绩小于60的学生课程分数改为60
数据表如下
declare @id int,@score int
while(1=1)
begin
select top 1 @id=id,@score=score from results where score<60
if(@score<60)
--update results set score=score+1 where id=@id
update Results set score=60 where id=@id
if((select count(*) from Results where score<60)=0)
break
endCASE-END
CASE
WHEN 条件1 THEN 结果1
WHEN 条件2 THEN 结果2
...
ELSE 其他结果
END
--ELSE表示CASE中所有WHEN条件均不为TRUE使的返回结果
--如果省略ELSE且when条件都为false时,case语句返回NULL例子:计算学号为1001号学员成绩,90以上为A,80-89为B,70-79为C,剩下的为D
select 学号=id,
总评=case
when score>=90 then 'A'
when score>=80 then 'B'
when score>=70 then 'C'
else 'D'
end
from results输出
注意:从上自下 有一个when条件满足就不去执行下面的when和else了
例题:查询刘德华后面的学员信息
declare @stuId int
select @stuId=stuNo from students where stuName='刘德华'
select *from students where stuNo>@stuId
--子查询
select *from students where stuNo>(select stuNo from students where stuName='刘德华')注:
子查询先执行小括号中的查询内容,再执行外层的父查询。
当子查询和比较运算符联合使用时,子查询返回的值不能多余一个
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
例子 查询 分数大于90的学员姓名和分数
隐式内连接
--分数大于90的学员姓名
select s.stuName as 姓名,r.score as 分数
from students s,results r
where s.stuNo=r.stuNo and r.score> 90 order by s.stuNameinner join显示内连接
--内连接
select s.stuName as 姓名,r.score
from students s
inner join results r
on s.stuNo=r.stuno
where r.score>90查询结果
子查询返回不止一个值时,使用比较运算符会出错,使用In子查询
IN 操作符允许我们在 WHERE 子句中规定多个值
- in后面的子查询可以返回多条记录
- 常用In替换等于(=)的比较子查询
例子 分数大于90的学员姓名(students中字段stuName,stuNo,results表中字段score,stuNo)
select s.stuName
from students s
where s.stuNo in(select stuNo from results where score>80)
--where s.stuNo =(select stuNo from results where score>80) -in 代替了= ,等号只有在1条记录时可用not in 不包含
查询students表中不包含在results里的学生学号,姓名
select s.stuName,stuNo from students s where s.stuNo not in (select stuNo from results)
EXISTS/NOT EXISTS
语法
IF EXISTS(子查询)
语句
- 如果子查询的结果非空,即记录条数大于等于1条,返回TRUE,否则返回false
- exists也可以作为where语句的子查询,但一般都可以用in查询替换
例子 查询成绩,如果有学生低于60,显示本次考试难,没有显示适中
if exists(select s.stuNo from Students s inner join results r on r.stuNo=s.stuNo where r.score<60)
print '本次考试难'
else
print '本次考试适中'if not exists(子查询) 子查询结果为空 返回true
if not exists(select s.stuNo from Students s inner join results r on r.stuNo=s.stuNo where r.score<60)
print '本次考试适中'
else
print '本次考试难'
视图VIEW
创建视图
(create view 视图名 as sql语句)
删除视图
(drop view 视图名)
use SchoolDB
go
--判断视图是否存在,若存在删除该视图
if exists(select *from sysobjects where name='View_Test1')--视图和数据表都被认为是一个对象,都通过sysobjects判断
drop view View_Test1
go
--创建视图
create view View_Test1
as
select s.stuNo,s.stuName,r.score,r.courseId
from Students s
inner join results r on s.stuNo=r.stuNo
go
--查询视图
select *from View_Test1 order by stuName 视图定义中的select语句不能包括下列内容
- 想要在视图中使用order by 排序必须在select语句中使用top子句
- into关键字
- 引用临时表或表变量
综合练习
重新建立数据库,建表,建立视图,查看视图
use master
go
if exists(select * from sysdatabases where name='Test')--查看Test数据库是否已存在
drop database Test
go
create database Test--创建数据库
on primary
( --逻辑文件
name='Test_data',
filename='d:\db\Test_data.mdf',--主数据文件
size=10MB,
filegrowth=1MB
)
log on
(
name='Test_log',
filename='d:\db\Test_data.ldf',--日志文件
size=10MB,
filegrowth=1MB
)
go
----
use Test
go
create table Students--建立数据表
(
stuId int primary key identity(1,1),--自增约束identitiy(初始值,增长值)
stuName nvarchar(100) not null
)
go
create table Course--建立数据表
(
Id int identity(1,1) primary key,
score int not null,
stuId int references Students(stuId)not null--外键约束references 表名(列名)
)
go
----插入数据
insert into Students(stuName) values('小章')
insert into Students(stuName) values('小王')
insert into Course(score,stuId) values(85,1)
insert into Course(score,stuId) values(83,2)
---------------------------------------------------------
--内连接查寻所有学生信息
select *from Students inner join course on students.stuId=course.stuId
--去掉重复的列stuId
select s.*,c.Id,c.score from Students s inner join course c on s.stuId=c.stuId
--创建视图
use Test
go
create view view_test
as select s.*,c.Id,c.score from Students s inner join course c on s.stuId=c.stuId
go
--显示所有数据
select *from view_test
存储过程
存储过程就是预先存储好的sql程序,有点像C#中的方法,保存在sql server中
视图和存储过程的优点:安全且执行速度快
一般sql语句的执行过程
数据传输--->语法检查---》语句优化---》编译---》执行
存储过程和视图的执行过程
传输参数---》语法执行
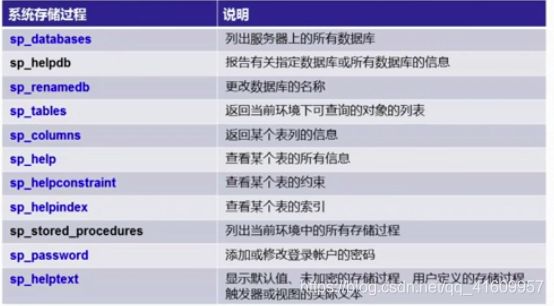
系统存储过程 sp_...
调用存储过程的语法
EXECUTE 过程名 [参数] EXEC 过程名 [参数】
--调用系统存储过程
exec sp_databases --列出当前系统中数据库
--------
use SchoolDB
go
exec sp_help Students --查看表Students信息
扩展存储过程 xp_...
自定义无参数存储过程
语法
create proc 存储过程名 /create procedure 存储过程名
as
SQL语句
go
无参存储过程的创建
create proc 存储过程名
as
sql语句
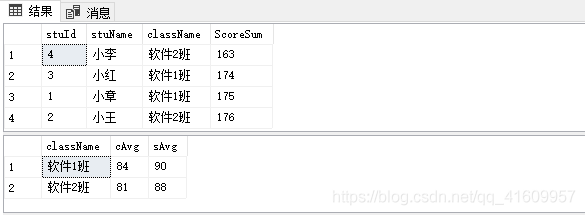
go练习:创建存储过程 查询学号,姓名,班级名称,总成绩,并按总成绩高低排序
统计分析考试成绩,显示班级名称,c平均分,s平均分,按班级分组
use Test
go
if exists(select *from sys.objects where name='usp_Test')--判断存储过程是否存在,存在就删除
drop proc usp_Test
go
--
use Test
go
create proc usp_Test
as
--查询考试成绩
select s.stuId,s.stuName,className,ScoreSum=(c.c_score+c.s_score) from Students s
inner join Course c on s.stuId=c.stuId
inner join Class on class.id=s.classid
order by ScoreSum
--分析考试信息
select class.className,cAvg=avg(c_score),sAvg=avg(s_score)from Class
inner join Students on Students.classId=class.id
inner join course on course.stuId=Students.stuId
group by class.className
go查询存储过程
--执行存储过程
exec usp_Test
带输入参数的存储过程
if exists(select *from sysobjects where name='存储过程名')
print '该存储过程存在'
create proc usp_Test2
参数
as
sql语句
go
例:查询学生学号,姓名,考试成绩,要求能按照自定义参数查寻结果
use Test
go
if exists(select *from sysobjects where name ='usp_Test2')
drop proc usp_Test2
go
--创建带参数的存储过程
create proc usp_Test2
@s_score int,
@c_score int
as
select s.stuId,s.stuName,c_score,s_score from Course c
inner join Students s on s.stuId=c.stuId
where s_score<@s_score or c_score<@c_score
go
--调用存储过程
exec usp_Test2 90,80 --按参数顺序赋值
exec usp_Test2 @c_score=80,@s_score=90--根据参数赋值,顺序可调换如上题,输入参数可以定义默认值
@s_score int =60,
@c_score int=65注:有多个参数时,有默认值的参数放在存储过程的最后面
这样, 调用存储过程的时如果没赋值就会调用默认值
exec usp_Test2 --两个参数都是默认值
exec usp_Test2 @s_score=75 --@c_score为默认值65
exec usp_Test2 @s_score=75,@c_score=70 --没有使用默认值
exec usp_Test2 default,80 --第一个参数为默认值,第二个为80带输出参数的存储过程
要求能按照自定义参数查寻结果,显示学生学号,姓名,考试成绩,并输出不及格人数,缺考人数
use Test
go
if exists(select *from sysobjects where name ='usp_Test2')
drop proc usp_Test2
go
--创建带参数的存储过程
create proc usp_Test2
@noneCount int output,--缺考总人数,输出参数定义需要output
@failCount int output,--不及格总人数
@s_score int =60,
@c_score int=60
as
select s.stuId,s.stuName,c_score,s_score from Course c
inner join Students s on s.stuId=c.stuId
where s_score<@s_score or c_score<@c_score
--查询统计结果
--查询缺考人数
select @noneCount=count(*)from Students where stuId not IN(select Course.stuId from Course )
--查询不及格人数
select @failCount=(select Count(*)from Course inner join Students on Students.stuId=Course.stuId where Course.c_score<@c_score or Course.s_score<@s_score)
go
--调用带输出参数的存储过程
declare @noneCount int,@failCount int--定义输出参数
exec usp_Test2 @noneCount output,@failCount output,60,65
select 缺考人数=@noneCount,不及格人数=@failCount注意:调用带参存储过程的时候需要注意 ,先定义输出参数,调用时output也不能漏掉