EVMC6678L时钟主频配置
本文从两个方面来讲解如何配置6678的CPU:
关于6678芯片时钟初始化可以利用F:\ProgramFiles\ti\ccsv8\ccs_base\emulation\boards\evmc6678l\gel 文件夹下面的GEL文件来进行初始化,在Target Configuration.ccxml下Advanced中右边Initialization script中加载6678的gel文件即可。
- 打开GEL文件,第42行注释文件详细解释了CPU输出频率的计算,以及倍频器与分频器的设置:
// The System PLL governs the device (CorePac) operating speed.
//
// Each board designer defines the CLKIN frequency. On the
// TMDXEVM6678L,LE,LXE EVMs, the CLKIN frequency defined to 100MHz. The
// values for PLL1_M(39) and PLL1_D(1) defined below are pre-set
// to provide a 1000MHz operating frequency on the EVMs.
//
// Other board designs using different CLKIN frequencies and/or
// applications that requiring other operating frequecies, the PLL can
// be configured by adjusting PLL1_M and PLL1_D per the
// following formula:
//
// Target Frequency (MHz) =
// input_clock (MHz) * [(PLL1_M + 1)]/ (2 * (PLL1_D + 1) )
//
// Table 2-13, "C66x DSP System PLL Configuration" in the device data sheet,
// http://focus.ti.com/lit/ds/symlink/tms320c6678.pdf provides the suggested
// values for PLL1_M and PLL1_D for various input clocks and desired
// operating frequencies.
//
// Please note that there might be multiple PLL1_M and PLL1_D
// values for the same Input clock and Desired Device Speed as long as the
// multipliers and dividers are in the acceptable range.
//
// More details on the PLL including the limitations on acceptable ranges
// for multipliers and dividers are in the PLL's user guide at
// http://www.ti.com/lit/sprugv2
//
// The table provides some sample values of PLL1_M and PLL1_D:
//
// Please select PLL1_M values such that 0 < PLL1_M <= 64
// +--------------------+---------------+--------+--------+
// | (CLK)Desired | (CLKIN) Input | | |
// | Device Speed (MHz) | Clock (MHz) | PLL1_M | PLL1_D |
// +--------------------+---------------+--------+--------+
// | 1000 | 100 | 19 | 0 |
// | 1000 | 100 (EVM) | 39 | 1 |
// | 1250 | 100 | 24 | 0 |
// | 1000 | 50 | 39 | 1 |
// | 1000 | 156.25 | 63 | 4 |
// +--------------------+---------------+--------+--------+
//
// +--------------------+---------------+--------+--------+
// | PA PLL VCO | (CLKIN) Input | | |
// | Rate (MHz) | Clock (MHz) | PLL1_M | PLL1_D |
// +--------------------+---------------+--------+--------+
// | 1050 | 100.00 (EVM) | 20 | 0 |
// | 1044 | 122.88 | 31 | 1 |
// | 1050 | 122.88 | 204 | 11 |
// | 1050 | 156.25 | 335 | 24 |
// +--------------------+---------------+--------+--------+
//
// +--------------------+---------------+--------+--------+
// | DDR3 PLL VCO | (CLKIN) Input | | |
// | Rate (MHz) | Clock (MHz) | PLL1_M | PLL1_D |
// +--------------------+---------------+--------+--------+
// | 1333 | 66.667 (EVM) | 19 | 0 |
// | 1066 | 66.667 | 31 | 1 |
// | 800 | 66.667 | 11 | 0 |
// +--------------------+---------------+--------+--------+从注释文件中可知,CPU的频率 = 输入时钟频率 * [(PLL1_M + 1)] / (2 * (PLL1_D + 1) ),例如当输入时钟频率(Input Clock)为100Mhz时,若设置PLL1_M为24,PLL1_D为0,则得到的输出时钟频率为1250MHZ。定位文件到第857行,
这里的Init_PLL函数为配置CPU时钟频率的入口函数,入口参数为倍频值,分频值,默认GEL文件中在第101行定义的为39,1:
#define PLL1_M 39
#define PLL1_D 1
#define DDR3_BASE_ADDRESS 0x80000000打开Init_PLL(int pll_mult, int pll_div )函数:
hotmenu Init_PLL(int pll_mult, int pll_div )
{
int i, TEMP;
/* Default dividers */
unsigned int div2=3, div5=5, div8=64;
int dsp_freq;
int dsp_freM,dsp_freD;
GEL_TextOut ( "Main PLL (PLL1) Setup ... \n");
/*Unlock Boot Config*/
KICK0 = 0x83E70B13;
KICK1 = 0x95A4F1E0;
// Only core0 can set PLL
if (DNUM == 0)
{
/* 1. Wait for Stabilization time (min 100 us) *
* The below loop is good enough for the Gel file to get minimum of *
* 100 micro seconds, this should be appropriately modified for port *
* to a C function *
* Minimum delay in GEL can be 1 milli seconds, so program to 1ms=1000us, *
* more than required, but should be Okay */
Delay_milli_seconds(1);
/* 2. Check the status of BYPASS bit in SECCTL register, *
* execute following steps if *
* BYPASS == 1 (if bypass enabled), if BYPASS==0 then Jump to Step 3 */
TEMP = PLL1_SECCTL & 0x00800000; /* Check the Bit 23 value */
if (TEMP != 0) /* PLL BYPASS is enabled, we assume if not in Bypass ENSAT = 1 */
{
GEL_TextOut ( "PLL in Bypass ... \n");
/* 2a. Usage Note 9: For optimal PLL operation, the ENSAT bit in the PLL control *
* registers for the Main PLL, DDR3 PLL, and PA PLL should be set to 1. *
* The PLL initialization sequence in the boot ROM sets this bit to 0 and *
* could lead to non-optimal PLL operation. Software can set the bit to the *
* optimal value of 1 after boot *
* Ref: http://www.ti.com/lit/er/sprz334b/sprz334b.pdf *
* |31...7 |6 |5 4 |3...0 | *
* |Reserved |ENSAT |Reserved |BWADJ[11:8]| */
MAINPLLCTL1 = MAINPLLCTL1 | 0x00000040;
/* 2b. Clear PLLEN bit */
PLL1_PLLCTL &= ~(1 << 0);
/* 2c. Clear PLLENSRC bit */
PLL1_PLLCTL &= ~(1 << 5);
/* 2d. Wait for 4 RefClks *
* Assuming slowest Ref clock of 25MHz, min: 160 ns delay */
Delay_milli_seconds(1);
/* 2e. Bypass needed to perform PWRDN cycle for C6670 and C6678 *
* Needed on all devices when in NOBOOT, I2C or SPI boot modes *
* Ref: Figure 4-2 of http://www.ti.com/lit/ug/sprugv2a/sprugv2a.pdf *
* PLL Secondary Control Register (SECCTL) Layout *
* |31...24 |23 |22...19 |18...0 | *
* |Reserved |BYPASS |OUTPUT DIVIDE |Reserved | */
PLL1_SECCTL |= 0x00800000; /* Set the Bit 23 */
/* 2f. Advisory 8: Multiple PLLs May Not Lock After Power-on Reset Issue *
* In order to ensure proper PLL startup, the PLL power_down pin needs to be *
* toggled. This is accomplished by toggling the PLLPWRDN bit in the PLLCTL *
* register. This needs to be done before the main PLL initialization *
* sequence *
* Ref: Figure 4-1 of http://www.ti.com/lit/ug/sprugv2a/sprugv2a.pdf *
* PLL Control Register (PLLCTL) Layout *
* |31...4 |3 |2 |1 |0 | *
* |Reserved |PLLRST |Reserved |PLLPWRDN |Reserved | */
PLL1_PLLCTL |= 0x00000002; /*Power Down the PLL */
/* 2g. Stay in a loop such that the bit is set for 5 �s (minimum) and *
* then clear the bit. */
Delay_milli_seconds(1); /* This is more than required delay */
/* 2h. Power up the PLL */
PLL1_PLLCTL &= ~(0x00000002);
}
else
{
/* 3. Enable BYPASS in the PLL controller */
GEL_TextOut ( "PLL not in Bypass, Enable BYPASS in the PLL Controller... \n");
/* 3a. Clear PLLEN bit (bypass enabled in PLL controlelr mux) */
PLL1_PLLCTL &= ~(1 << 0);
/* 3b. Clear PLLENSRC bit (enable PLLEN to control PLL controller mux) */
PLL1_PLLCTL &= ~(1 << 5);
/* 3c. Wait for 4 RefClks (to make sure the PLL controller *
* mux switches properly to the bypass) *
* Assuming slowest Ref clock of 25MHz, min: 160 ns delay */
Delay_milli_seconds(1);
}
/* Wait for PLL Reset assertion Time (min: 50 us) *
* Minimum delay in GEL can be 1 milli seconds, so program to 1ms=1000us, *
* more than required, but should be Okay */
//Delay_milli_seconds(1);
/* 4, 5, 6 and 7 are done here: *
* Program the necessary multipliers/dividers and BW adjustments */
prog_pll1_values(pll_mult, pll_div, 1);
/* 8. Set PLL dividers if needed */
/* part of 8, go stat bit needs to be zero here *
* Read the GOSTAT bit in PLLSTAT to make sure the bit returns to 0 to *
* indicate that the GO operation has completed */
/* wait for the GOSTAT, but don't trap if lock is never read */
for (i = 0; i < 1000; i++)
{
if ( (PLL1_STAT & 0x00000001) == 0 ) {
break;
}
}
if ( i == 1000 ) {
GEL_TextOut ( "Error while waiting for GOSTAT bit returning to 0 ... \n");
return(-1);
}
/* part of 8, Set PLL dividers if needed */
PLL1_DIV2 = (0x8000) | (div2 - 1);
PLL1_DIV5 = (0x8000) | (div5 - 1);
PLL1_DIV8 = (0x8000) | (div8 - 1);
/* part of 8, Program ALNCTLn */
/* Set bit 1, 4 and 7 */
PLL1_ALNCTL |= ( (1 << 1) | (1 << 4) | (1 << 7));
/* part of 8, Set GOSET bit in PLLCMD to initiate the GO operation to change the divide *
* values and align the SYSCLKs as programmed */
PLL1_CMD |= 0x00000001;
/* part of 8, Read the GOSTAT bit in PLLSTAT to make sure the bit returns to 0 to *
* indicate that the GO operation has completed */
/* wait for the GOSTAT, but don't trap if lock is never read */
for (i = 0; i < 1000; i++)
{
if ( (PLL1_STAT & 0x00000001) == 0 ) {
break;
}
}
if ( i == 1000 ) {
GEL_TextOut ( "Error while waiting for GOSTAT bit returning to 0 ... \n");
return(-1);
}
/* 9. Place PLL in Reset, In PLLCTL, write PLLRST = 1 (PLL is reset) */
PLL1_PLLCTL |= 0x00000008;
/* 10. Wait for the PLL Reset duration time (min: 7us ) */
Delay_milli_seconds(1);
/* 11. In PLLCTL, write PLLRST = 0 to bring PLL out of reset */
PLL1_PLLCTL &= ~(0x00000008);
/*
* 12. PLL Lock Delay needs to be 500 RefClk periods * (PLLD + 1)
* i.e., Wait for at least 500 * CLKIN cycles * (PLLD + 1) (PLL lock time)
* Using 2000 25ns RefClk periods per DM
* Wait for PLL to lock min 50 micro seconds
*
* */
Delay_milli_seconds(1);
/* 13. In SECCTL, write BYPASS = 0 to enable PLL mux to switch to PLL mode */
PLL1_SECCTL &= ~(0x00800000); /* Release Bypass */
/* 14. Set the PLLEN */
PLL1_PLLCTL |= (1 << 0);
/* 15. The PLL and PLL Controller are now initialized in PLL mode - Complete */
// Compute the real dsp freq (*100)
dsp_freq = (((REF_CLOCK_KHZ/10) * ((pll_mult+1)/2))/(pll_div+1));
// Displayed frequency setup
// dsp freq in MHz
dsp_freM = dsp_freq / 100;
// dsp freq first decimal if freq expressed in MHz
dsp_freD = ((dsp_freq - dsp_freM * 100) + 5) / 10;
// Add roundup unit to MHz displayed and reajust decimal value if necessary...
if (dsp_freD > 9)
{
dsp_freD = dsp_freD - 10;
dsp_freM = dsp_freM + 1;
}
// Print freq info...
GEL_TextOut( "PLL1 Setup for DSP @ %d.%d MHz.\n",,,,, dsp_freM, dsp_freD );
GEL_TextOut( " SYSCLK2 = %f MHz, SYSCLK5 = %f MHz.\n",,,,, ((float)(dsp_freq/100)/div2), ((float)(dsp_freq/100)/div5));
GEL_TextOut( " SYSCLK8 = %f MHz.\n",,,,, ((float)(dsp_freq/100)/div8));
GEL_TextOut( "PLL1 Setup... Done.\n" );
return (0);
}
else
{
GEL_TextOut("DSP core #%d cannot set PLL1.\n",,2,,,DNUM);
return(-1);
}
}在GEL文件中第1229-1233行代码知道F(MHZ) = dsp_freq / 100; dsp_freq = (((REF_CLOCK_KHZ/10) * ((pll_mult+1)/2))/(pll_div+1));其中REF_CLOCK_KHZ定义在第108行中为100000;根据默认传入的参数39,1,通过计算可得频率为1000MHZ。接下来打开prog_pll1_values(pll_mult, pll_div, 1)函数,该函数主要是对PLLM寄存器和MAINPLLCTL0寄存器进行配置。
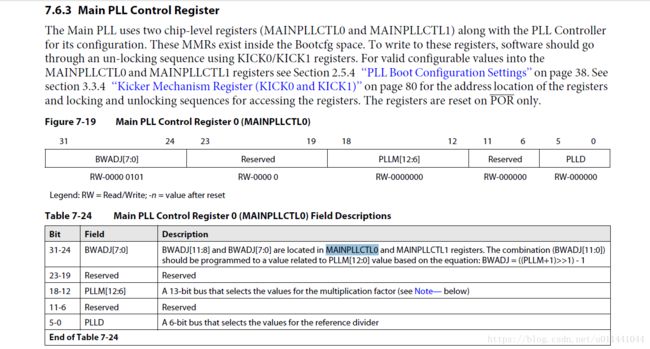
/* Set the PLL Multiplier, Divider, BWADJ *
* The PLLM[5:0] bits of the multiplier are controlled by the PLLM Register *
* inside the PLL Controller and the PLLM[12:6] bits are controlled by the *
* chip-level MAINPLLCTL0 Register. *
* PLL Control Register (PLLM) Layout *
* |31...6 |5...0 | *
* |Reserved |PLLM | *
* *
* Main PLL Control Register (MAINPLLCTL0) *
* |31...24 |23...19 |18...12 | 11...6 |5...0 | *
* |BWADJ[7:0]| Reserved |PLLM[12:6] | Reserved | PLLD | */
/* Set pll multipler (13 bit field) */
PLL1_PLLM = (pll_multiplier & 0x0000003F); /* bits[5:0] */
TEMP = (pll_multiplier & 0x1FC0) >> 6;/* bits[12:6] */
MAINPLLCTL0 &=~(0x0007F000); /*Clear PLLM field */
MAINPLLCTL0 |=((TEMP << 12) & 0x0007F000);
/* Set the BWADJ (12 bit field) *
* BWADJ[11:8] and BWADJ[7:0] are located in MAINPLLCTL0 and MAINPLLCTL1 *
* registers. BWADJ[11:0] should be programmed to a value equal to half of *
* PLLM[12:0] value (round down if PLLM has an odd value) *
* Example: If PLLM = 15, then BWADJ = 7 */
TEMP = ((pll_multiplier + 1) >> 1) - 1; /* Divide the pllm by 2 */
MAINPLLCTL0 &=~(0xFF000000); /* Clear the BWADJ Field */
MAINPLLCTL0 |= ((TEMP << 24) & 0xFF000000);
MAINPLLCTL1 &=~(0x0000000F); /* Clear the BWADJ field */
MAINPLLCTL1 |= ((TEMP >> 8) & 0x0000000F);
/* Set the pll divider (6 bit field) *
* PLLD[5:0] is located in MAINPLLCTL0 */
MAINPLLCTL0 &= ~(0x0000003F); /* Clear the Field */
MAINPLLCTL0 |= (pll_divider & 0x0000003F);
/* Set the OUTPUT DIVIDE (4 bit field) in SECCTL */
PLL1_SECCTL &= ~(0x00780000); /* Clear the field */
PLL1_SECCTL |= ((odiv << 19) & 0x00780000) ;需要注意的是,倍频器中的PLLM[5:0]是在PLL控制器中的PLL寄存器所控制(PLLM),该寄存器的详细说明文档在KeyStone Architecture Phase-Locked Loop (PLL)手册中:
代码:PLL1_PLLM = (pll_multiplier & 0x0000003F) 表示将倍频值与3F相与,结果存入PLL1_PLLM地址中。
而倍频器中的PLLM[12:6]为是在主PLL寄存器所控制(MAINPLLCTL0),MAINPLLCTL0的说明文档在SPRS691E中列出:
TEMP = (pll_multiplier & 0x1FC0) >> 6;/* bits[12:6] */
MAINPLLCTL0 &=~(0x0007F000); /*Clear PLLM field */
MAINPLLCTL0 |=((TEMP << 12) & 0x0007F000);
将倍频值与0x1FC0相与右移6位放置低6位存储于TEMP中,MAINPLLCTL0 寄存器中值进行取反相与清零处理,将TEMP值进行左移12位移动到PLLM[12:6]处,并于7F000相与,确保该寄存器中其他值位0,因此导致PLLD[5:0]与BWADJ[7:0]全为零。从这里看出应该先配置PLLM,再配置BWADJ,最后配置PLLD;
关于BWADJ配置:
TEMP = ((pll_multiplier + 1) >> 1) - 1; /* Divide the pllm by 2 */
MAINPLLCTL0 &=~(0xFF000000); /* Clear the BWADJ Field */
MAINPLLCTL0 |= ((TEMP << 24) & 0xFF000000);
MAINPLLCTL1 &=~(0x0000000F); /* Clear the BWADJ field */
MAINPLLCTL1 |= ((TEMP >> 8) & 0x0000000F);
BWADJ域由BWADJ[11:8]和BWADJ[7:0]构成,分别位于MAINPLLCTL1和MAINPLLCTL0寄存器中,其中,BWADJ[11:0]寄存器组合值必须设置为PLLM[12:0]值的一半,向下取整,得到TEMP值。BWADJ[7:0]位于MAINPLLCTL0寄存器中的第24-31位,因此需要将TEMP值左移24位并于0xFF000000相与,清空TEMP中其他位,再和MAINPLLCTL0寄存器相或,避免之前设置的PLLM[12:6]被改变。对于MAINPLLCTL1寄存器中的BWADJ[11:8]域,通过手册可知,BWADJ位于MAINPLLCTL1中的第0到第3位。因此需要将TEMP值中BWADJ[11:8]右移8位到低位处再于0xF相与清空TEMP其他位并于原始MAINPLLCTL1寄存器中值相或。
分频器 PLLD[5:0]位于MAINPLLCTL0寄存器中,因此先清空MAINPLLCTL0中PLLD区域,再将分频值pll_divider与0x3F相与并于原始MAINPLLCTL0寄存器相或更新PLLD[5:0]中值。
2. 第二种配置时钟的方法是通过platform_init()函数进行配置;该函数文件位于F:\ProgramFiles\ti\pdk_c667x_2_0_9\packages\ti\platform\evmc6678l\platform_lib\src文件夹下面。
memset(&pllc_hwSetup, 0, sizeof(PllcHwSetup));
/* Setup PLLC hardware parameters */
pllc_hwSetup.divEnable = (CSL_BitMask32) (PLLC_DIVEN_PLLDIV2 |
PLLC_DIVEN_PLLDIV5 |
PLLC_DIVEN_PLLDIV8) ;
/* Setup PLLC hardware parameters */
pllc_hwSetup.pllM =
(((p_config->pllm) ? p_config->pllm : PLATFORM_PLL1_PLLM_val) - 1);
pllc_hwSetup.preDiv = PLATFORM_PLL_PREDIV_val - 1;
pllc_hwSetup.pllDiv2 = PLATFORM_PLLDIV2_val - 1;
pllc_hwSetup.pllDiv5 = PLATFORM_PLLDIV5_val - 1;
pllc_hwSetup.pllDiv8 = PLATFORM_PLLDIV8_val - 1;
pllc_hwSetup.postDiv = PLATFORM_PLL_POSTDIV_val -1;
/* set Pll */
status = CorePllcHwSetup (&pllc_hwSetup);定位到函数内部第384行可知,这里的倍频系数设置值为pllM = PLATFORM_PLL1_PLLM_val - 1,分频值为preDiv = PLATFORM_PLL_PREDIV_val - 1。打开这两个变量的定义在F:\ProgramFiles\ti\pdk_c667x_2_0_9\packages\ti\platform\evmc6678l\platform_lib\include下的platform_internal.h文件中。
/* Clock rate */
#define PLATFORM_BASE_CLK_RATE_MHZ (100)
/* PREDIV */
#define PLATFORM_PLL_PREDIV_val (1)
/* POSTDIV */
#define PLATFORM_PLL_POSTDIV_val (2)
/* Default PLL PLLM value (100/1*(20/2)) = 1.0GHz) */
#define PLATFORM_PLL1_PLLM_val (25)//25 = 1.2如代码所示,基准频率设置的是100,PLATFORM_PLL_PREDIV_val为1,PLATFORM_PLL1_PLLM_val为25(默认为20);因为这两个变量均减去1,因此实际传入到prog_pll1_values函数中的值为0,24;之后的寄存器配置和第一部分介绍相同。 配置完成后在platform.c文件中的第458行代码platform_get_frequency()函数中计算实际频率值,打开该函数:
static inline uint32_t platform_get_frequency(void)
{
CSL_Status status;
PllcHwSetup hwSetupRead;
uint32_t dsp_freq;
status = CorePllcGetHwSetup (&hwSetupRead);
if (status != CSL_SOK) {
IFPRINT(platform_write("platform_get_info: Hardware setup parameters reading... Failed.\n"));
IFPRINT(platform_write("\tReason: Error setting in hardware validation."\
" [status = 0x%x].\n", status));
platform_errno = PLATFORM_ERRNO_GENERIC;
return (uint32_t)-1;
} else {
/* Compute the real dsp freq (*100) */
dsp_freq = (hwSetupRead.pllM + 1)>> 1;
dsp_freq = (dsp_freq * PLATFORM_BASE_CLK_RATE_MHZ)/(hwSetupRead.preDiv + 1);
}
printf("dsp_freq: %dHZ\n",dsp_freq);
return (dsp_freq);
}从else分支语句中看出频率值 = [100 * (pllM + 1) / 2] / ( preDiv + 1 ) = 100 * ( 24 + 1 ) / 2 / 1 = 1250Hz