IEEE 2030.5智能逆变器实施指南(4)
4 General CSIP Requirements CSIP的一般要求
This section provides general requirements3 related to implementing all grid support DER utility interactions. The related IEEE 2030.5 specific requirements can be found in Section 5.
本节提供与实现所有网格支持DER实用程序交互有关的一般要求。 有关IEEE 2030.5的特定要求,请参见第5节。
4.1 Security Requirements安全需求
IEEE 2030.5 security requirements are covered in section 5.2.1. Although outside the scope of CSIP, security SHOULD be used in all non-IEEE 2030.5 interactions between the Aggregators, site hosts, GFEMS, and DERs and other entities receiving or transmitting DER related communications. Security includes data in motion (e.g. encryption of communications), data at rest, the authentication of clients and services, as well as the authorization of all requests. The composition of any Aggregator or DER access to utility servers is managed via contractual relationships. As such, the specific permissible actions across different utility servers may be different. See utility handbooks or programs/contracts for further cyber security requirements.
第5.2.1节介绍了IEEE 2030.5安全要求。 尽管不在CSIP的范围之内,但安全性应在聚合器,站点主机,GFEMS和DER以及其他接收或传输DER相关通信的实体之间的所有非IEEE 2030.5交互中使用。 安全性包括移动中的数据(例如通信的加密),静态数据,客户端和服务的身份验证以及所有请求的授权。 任何聚合器或对公用程序服务器的DER访问的组成都是通过合同关系进行管理的。 这样,跨不同实用程序服务器的特定允许操作可能会有所不同。 有关进一步的网络安全要求,请参见实用程序手册或程序/合同。
4.2 Registration and Identification of DERs DER的注册和识别
The registration of DER Clients is utility specific and is assumed to be outside the scope of CSIP. The registration process may result in the delivery of a globally unique identifier (GUID) associated with a particular DER. The GUID provides a shared name between the utility and the other party to ensure that operations and data are routed appropriately. The GUID is used to guarantee its authenticity and uniqueness within the scope of a single utility’s CSIP server. For DER Clients that have an IEEE 2030.5 certificate, the GUID SHALL be derived from this certificate (see section 5.2.1.2). Implementers SHALL refer to each utility’s Interconnection Handbook for requirements related to the creation, use or management of this identifier.
DER客户的注册是特定于实用程序的,并且被认为不在CSIP范围内。 注册过程可能导致传递与特定DER相关的全局唯一标识符(GUID)。 GUID在实用程序和另一方之间提供了一个共享名称,以确保适当地路由操作和数据。 GUID用于在单个公用程序的CSIP服务器范围内保证其真实性和唯一性。 对于具有IEEE 2030.5证书的DER客户端,GUID应从该证书派生(请参阅5.2.1.2节)。 实施者应参考每个实用程序的《互连手册》,以了解与该标识符的创建,使用或管理有关的要求。
4.3 Group Management组管理
Effective utility management of DERs requires that their location from an electrical system perspective be known. As a result, a special management function is required to align DERs operated by Aggregators to the utility system topology or other utility defined grouping. In certain cases, settings or commands can be sent to the entire system under a specific Aggregator’s control. In other cases, the settings or commands will be targeted to limited numbers of DERs due to differences in needs across the utilities distribution system. For the purposes of this specification, DERs can be assigned to a minimum of one group and a maximum of 15 groups.
有效的DER实用程序管理要求从电气系统角度了解其位置。 结果,需要特殊的管理功能来将聚合器操作的DER与公用事业系统拓扑或其他公用事业定义的分组对齐。 在某些情况下,设置或命令可以在特定的聚合器的控制下发送到整个系统。 在其他情况下,由于整个公用事业分配系统之间的需求差异,设置或命令将仅针对有限数量的DER。 出于本规范的目的,可以将DER分配到最少一组,最多15组。
Although topological grouping is expected to be the primary use case, any type of grouping is allowed. A group consisting of DERs from a specific vendor or a group of DERs enrolled on a special program can be implemented. Each utility will apply the grouping levels as it sees fit to meet its own operational needs. For example, distribution transformer-level grouping is likely to be a future rather than a near term requirement. Likewise, other utilities may want to apply these group constructs in support of other distribution system network models.
尽管拓扑分组有望成为主要用例,但允许使用任何类型的分组。 可以实现由特定供应商提供的DER组成的组,或在特殊程序中注册的DER组成的组。 每个公用事业公司都将根据自己的需要来应用分组级别。 例如,配电变压器级分组可能是未来的需求,而不是近期的需求。 同样,其他实用程序可能希望应用这些组构造来支持其他分发系统网络模型。
Group membership may change over the life of the inverter being interconnected to the utility’s system. These changes can be the result of system configuration or changes in segmentation or equipment. Aggregators and DER Clients SHALL support IEEE 2030.5 based grouping and full lifecycle management of group relationships as defined within Section 5.2.3 and within each utility’s Interconnection Handbook or program/contract requirements.
组成员资格可能会在与公用事业系统互连的逆变器的使用寿命内发生变化。 这些更改可能是系统配置或分段或设备更改的结果。 聚合器和DER客户端应支持基于IEEE 2030.5的分组和组关系的完整生命周期管理,如5.2.3节以及每个公用事业公司的《互连手册》或计划/合同要求所定义。
Finally, a key concept of grouping is that DER can exist in multiple groups to support utility management at differing levels of the system. In all cases, the utility is responsible for maintaining these groups over time and to deliver any changes to groups to the impacted DERs.
最后,分组的关键概念是DER可以存在于多个组中,以支持不同系统级别的公用事业管理。 在所有情况下,该实用程序都负责随着时间的推移维护这些组,并将对组的任何更改交付给受影响的DER。
1. System – refers to the utility service territory in total. All inverters are assigned to this group. It is expected that an inverter’s membership will never change.
2. Sub-transmission – refers to a section of a utility’s service territory where the transmission grid is managed directly by the utility
3. Substation – refers to the substation from which the inverter is electrically connected. Note that this group assignment can change as the electric system topology changes.
4. Feeder– refers to the feeder that the inverter is attached to. Note that this group assignment can change as the electric system topology changes.
5. Segment – refers to a section of a distribution feeder/circuit that cannot be further isolated or 250 modified via switching or other sectionalizing device.
6. Service Transformer – refers to the collection of service points that are electrically connected to a single service transformer.
7. Service Point – refers to the point of common coupling between the utility and a 3rd party facility where one or more smart inverters are present.
8. Non-Topology- refers to a DER that has been placed in a group based on utility system needs
1.系统–指公用事业服务区域。所有逆变器都分配给该组。期望逆变器的成员资格不会改变。
2.子传输–指公用事业的服务区域中由公用事业直接管理传输网格的部分
3.变电站–指与变频器电气连接的变电站。注意,该组分配可以随着电气系统拓扑的变化而变化。
4.馈线–指变频器所连接的馈线。注意,该组分配可以随着电气系统拓扑的变化而变化。
5.段-指配电馈线/电路的一部分,无法通过开关或其他分段装置进一步隔离或修改250。
6.服务变压器–是指电气连接到单个服务变压器的服务点的集合。
7.服务点–指公用事业与存在一个或多个智能逆变器的第三方设施之间的公共耦合点。
8.非拓扑-是指根据公用事业系统的需要放在一个组中的DER
4.4 DER Control Events and Settings DER控制事件和设置
4.4.1 Definition and Usage定义和用法
Before listing the requirements, some terms that are used in this guide need to be defined and explained.
在列出要求之前,需要定义和解释本指南中使用的一些术语。
• A DER control is a generic term for a grid control function (e.g. fixed power factor or connect/disconnect).
• A DERControl is an IEEE 2030.5 control event that contains a start time, a duration, and a control parameter value. An example of a DERControl resource is the fixed power factor control event DERControl:opModFixedPF.
• A DefaultDERControl is an IEEE 2030.5 control resource that is in effect if there are no active DERControls for that resource. For example, the DefaultDERControl:opModFixedPF resource is in effect when there are no DERControl:opModFixedPF events active.
•DER控制是电网控制功能的通用术语(例如,固定功率因数或连接/断开连接)。
•DERControl是IEEE 2030.5控制事件,其中包含开始时间,持续时间和控制参数值。 DERControl资源的示例是固定功率因数控制事件DERControl:opModFixedPF。
•DefaultDERControl是IEEE 2030.5控制资源,如果该资源没有活动的DERControl,则该资源有效。 例如,当没有活动的DERControl:opModFixedPF事件时,DefaultDERControl:opModFixedPF资源有效。
For most DER controls, there are two ways to issue the control: using DERControl events or using DefaultDERControls.
对于大多数DER控件,有两种发布控件的方法:使用DERControl事件或使用DefaultDERControls。
When the start time and duration of the control is known, the typical way to issue the control is to create a DERControl event for the control. Like any IEEE 2030.5 event, DERControl events can be scheduled, superseded, cancelled, etc. If configured, the utility DER server can receive the event status responses (e.g. received, started, completed, superseded, etc.) of the DERControl from each DER.
知道控件的开始时间和持续时间后,发布控件的典型方法是为控件创建DERControl事件。像任何IEEE 2030.5事件一样,可以调度,取代,取消等DERControl事件。如果进行了配置,则实用程序DER服务器可以从每个DER接收DERControl的事件状态响应(例如,接收,启动,完成,取代等)
When the DER control is intended to be used to modify a setting (i.e. start time is “now” and the duration is indefinite), the most natural way to issue the control is to create or update the DefaultDERControl. The DefaultDERControl will be in effect until it is changed or a DERControl event occurs. In many use cases, the utility server may simply use DefaultDERControls and never issue a DERControl event for the controls. One limitation of using DefaultDERControls is there are no status responses associated with DefaultDERControls.
当打算使用DER控件修改设置时(即开始时间为“现在”且持续时间不确定),发出该控件的最自然的方法是创建或更新DefaultDERControl。 DefaultDERControl将一直有效,直到对其进行更改或发生DERControl事件。在许多使用情况下,实用程序服务器可能只使用DefaultDERControls而从不为控件发出DERControl事件。使用DefaultDERControls的限制之一是没有与DefaultDERControls相关的状态响应。
If status responses for modification of settings are needed, the utility server can use DERControl events. To accomplish this, the start time of the DERControl is “now”, and the duration is set to a very large, effectively infinite, number. To change the DERControl setting, a new DERControl is issued to supersede or cancel the existing DERControl.
如果需要状态响应以更改设置,则实用程序服务器可以使用DERControl事件。为此,DERControl的开始时间为“现在”,持续时间设置为非常大的,实际上是无限的数字。要更改DERControl设置,将发出新的DERControl来取代或取消现有的DERControl。
4.4.2 Requirements需求
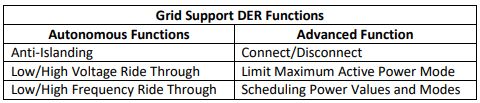
All DERs and related communications will support the Autonomous and Advanced functionality and controls as shown below.
所有DER和相关通信将支持“自治和高级”功能和控件,如下所示。
| 电网支持的DER功能 | |
|---|---|
| 自治功能 | 高级功能 |
| 防孤岛 | 连接/断开 |
| 低压/高压穿越 | 限制最大有功功率模式 |
| 低频/高频穿越 | 调度功率值及模式 |
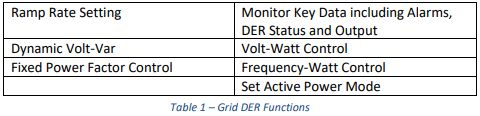
| 斜坡率设定 | 监视关键数据,包括报警,DER状态和输出 |
| 动态V-Var | V-W控制 |
| 固定功率因数控制 | 频率-瓦特控制 |
| 设置有功功率模式 | |
Default settings or modes for Autonomous Functions, including which are activated and deactivated at deployment, will be specified in the applicable interconnection tariff and/or the utility’s Interconnection Handbook. Autonomous functions’ default settings SHALL be changeable via IEEE 2030.5 DefaultDERControl communications. Modifications to default settings SHALL occur immediately upon receipt and have an indefinite duration.
自治功能的默认设置或模式,包括在部署时激活和停用的默认设置或模式,将在适用的互连资费和/或公用事业的互连手册中指定。自治功能的默认设置应可以通过IEEE 2030.5 DefaultDERControl通信进行更改。对默认设置的修改应在收到后立即进行,并且持续时间不确定。
Scheduling Autonomous and Advanced Power Values and Modes SHALL be controllable via IEEE 2030.5 DERControl events. As opposed to modification of default settings, these events allow the server to schedule operations for single or groups of DERs at a future point in time for a specific duration. Through events, the utility can send one or more operations as a sequence to the DERs for processing and implementation. In this way, the utility can schedule and sequence DER control events.
可以通过IEEE 2030.5 DERControl事件控制自主和高级功率值和模式的调度。与修改默认设置相反,这些事件允许服务器在将来的某个时间点为特定持续时间安排单个或一组DER的操作。通过事件,实用程序可以将一个或多个操作作为顺序发送到DER,以进行处理和实现。这样,该实用程序可以调度和控制DER控制事件的顺序。
Aggregators and DER Clients SHALL be responsible for assuring that all operations received from the utility are processed in the appropriate time sequence as specified by the utility.
聚合器和DER客户端应负责确保从实用程序接收到的所有操作均按照实用程序指定的适当时间顺序进行处理。
An Aggregator acting for its DERs and DER Clients SHALL be able to store at least 24 scheduled DER control events for each DER.
代理其DER和DER客户端的聚合器应能够为每个DER存储至少24个调度的DER控制事件。
In the absence of scheduled controls, DERs SHALL revert to a default control setting specified by interconnection tariffs, the utility Interconnection Handbook or as specified by the last 304 DefaultDERControl.
在没有计划的控制的情况下,DER将还原为由互连费率,实用程序《互连手册》或最后304个DefaultDERControl指定的默认控制设置。
Should there be a loss of communications, DERs SHALL complete any scheduled event and then revert to default settings or other settings as determined by the site host or tariffs/contracts.
如果通信中断,DER将完成所有计划的事件,然后恢复为默认设置或站点主机或资费/合同确定的其他设置。
4.4.3 Prioritization优先次序
When commanded in a manner where two or more operations are in conflict, the interpreting system SHALL operate against the control operation which has the highest priority subject to the systems capability, contracts and self-protection requirements.
当以两种或两种以上操作发生冲突的方式命令系统时,应根据系统能力,合同和自我保护的要求,对具有最高优先级的控制操作进行操作。
In setting up commands for groups of DERs, it is expected that commands for lower level groups will typically have precedence over higher level groups (i.e. commands at the System level are trumped by commands at a more local level Feeder). In this manner, multiple needs can be managed. For example, a system level group operation might call for a voltage-watt mode of operation with a set of curve parameters at the same time as several circuits might require a voltage-watt mode with a different set of curve parameters.
在为DER组设置命令时,预计用于较低级别组的命令通常优先于较高级别的组(即系统级别的命令被本地级别更高的Feeder的命令所取代)。 以这种方式,可以管理多个需求。 例如,系统级组操作可能会要求同时具有一组曲线参数的电压瓦特模式,因为几个电路可能需要具有一组曲线参数的电压-瓦特模式。
The utility will avoid creating situations where there can be conflicting commands of the same priority. If avoidance of conflicting commands is not possible, the more recently received command SHOULD have precedence over the older command. In either case, it SHALL be the responsibility of the Aggregator or DER Client to decide how to handle two simultaneous controls.
该实用程序将避免出现可能存在相同优先级的命令冲突的情况。 如果不能避免冲突的命令,则较新接收的命令应优先于较旧的命令。 无论哪种情况,聚合器或DER客户端都有责任决定如何处理两个同时的控件。
4.5 Communication Interactions通信交互
For Aggregator communications, notifications and call backs (subscription/notification) SHALL be used to limit system polling to the greatest extent practical.
对于聚合器通信,应使用通知和回调(订阅/通知)来最大程度地限制系统轮询。
To simplify communication requirements for Direct DER Communications scenarios, unless specified otherwise in utility Interconnection Handbooks or programs/contracts, all communications SHALL be initiated by the DER Client (i.e., client-side initiation). This model of communication eliminates the need for unsophisticated parties to make changes in networking security based on the needs of CSIP. In Direct DER communication scenarios, the client system SHALL initiate communications with the utility according to pre-defined polling and posting intervals to ensure the DER has up to date settings and the utility understands the operational state of the DER. Unless specified in each utility’s Interconnection Handbook or programs/contracts, default polling and posting rates SHALL be as follows:
为了简化直接DER通信场景的通信要求,除非在实用程序互连手册或程序/合同中另有规定,否则所有通信都应由DER客户端启动(即客户端启动)。 这种通信模型消除了对复杂各方的需求,可以根据CSIP的需要对网络安全进行更改。 在直接DER通信场景中,客户端系统应根据预定义的轮询和发布间隔启动与实用程序的通信,以确保DER具有最新设置,并且实用程序了解DER的操作状态。 除非每个公用事业公司的《互连手册》或程序/合同中都有规定,否则默认的轮询和发布费率应如下所示:
• Polling of DERControls and DefaultDERControls (Direct DER Communication)– every 10 minutes
• Posting monitoring information (Direct and Aggregator Mediated Communications)– every 5 minutes
•轮询DERControl和DefaultDERControls(直接DER通信)–每10分钟
•发布监控信息(直接和聚合介导的通信)-每5分钟
For DERs with an external SMCU, the SMCU SHALL transfer the DER control to the DER within 10 minutes of receiving the control from the server.
对于具有外部SMCU的DER,SMCU应在从服务器接收到控制的10分钟内将DER控件转移到DER。
For DERs with a GFEMS, the GFEMS SHALL transfer the DER control to the DERs within 10 minutes of receiving the control from the server.
对于具有GFEMS的DER,GFEMS应当在从服务器接收到DER的10分钟内将DER控件转移到DER。
For DERs mediated by Aggregators, the Aggregator SHALL transfer the DER control to the DERs within 15 minutes of receiving the control from the server.
对于由聚合器中介的DER,聚合器应在从服务器接收到控制的15分钟内将DER控件转移到DER。
4.6 Reporting DER Data上报DER数据
4.6.1 Monitor Data监控数据
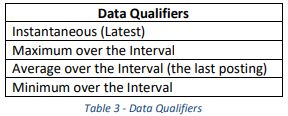
Aggregators acting for its DERs and DER Clients SHALL have the capability to report the monitoring data in Table 2. Aggregators acting for its DERs and DER Clients SHALL have the capability to include the data qualifiers in Table 3. All measurement SHALL include a date-time stamp. Unless otherwise specified in each utility’s Interconnection Handbook or programs/contracts, Aggregators acting for its DERs and DER Clients SHALL report the monitoring data in Table 2 and MAY include the data qualifiers in Table 3.
代表其DER和DER客户的聚合器应具有报告表2中的监视数据的能力。代表其DER和DER客户的聚合器应具有在表3中包括数据限定符的能力。所有度量应包括日期时间戳。 除非每个公用事业公司的互连手册或程序/合同中另有规定,否则代表其DER和DER客户的聚合商应在表2中报告监控数据,并且可以在表3中包括数据限定符。
| 监控数据 |
|---|
| 有功功率 |
| 无功功率 |
| 频率 |
| 各相电压 |
| 数据限定 |
|---|
| 实时值(最新) |
| 间隔内的最大值 |
| 间隔内的平均值(最后发布) |
| 间隔内的最小值 |
Note that some DERs may be capable of only reporting instantaneous measurements and cannot report minimum, maximum, or average values. For those situations where the DERs cannot provide Monitoring Data, the Aggregator acting for its DERs and DER Clients SHALL not send the data.
请注意,某些DER可能仅能够报告瞬时测量值,而不能报告最小值,最大值或平均值。 对于那些DER无法提供监视数据的情况,充当其DER的聚合器和DER客户端将不发送数据。
4.6.2 Status Information状态信息
4.6.2.1 Ratings and Settings额定和设置
Aggregators acting for its DERs and DER Clients SHALL have the capability to report the Nameplate Ratings and Adjusted Settings information shown in Table 4. Nameplate Ratings and Adjusted Settings SHOULD be reported once at start-up and whenever there is a change in value. This information is not expected to change during normal operation. The Nameplate Rating is the value of the item as manufactured. The Adjusted Setting is the modified value of the Nameplate Rating to account site specific deviations, degradations over time, or other factors. Specific requirements related to when Nameplate Ratings and Adjusted Setting must be provided will be found in each utility’s Interconnection Handbook or contracts/programs.
代表其DER和DER客户的聚合器应能够报告表4所示的铭牌额定值和调整后的设置信息。启动时以及每当值发生变化时,均应报告一次铭牌额定值和经调整的设置。 在正常操作期间,预计该信息不会更改。 铭牌等级是所制造产品的价值。 调整后的设置是铭牌额定值的修改后的值,用于说明特定于站点的偏差,随时间推移而退化或其他因素。 每个公用事业部门的《互连手册》或合同/程序中都将找到与何时必须提供铭牌额定值和调整设置有关的特定要求。
| 铭牌额定值和调整设置 |
|---|
| 收到的最大能量传输率 |
| 能量传递的最大速率 |
| 最大视在功率 |
| 输送的最大无功功率 |
| 收到的最大无功功率 |
| 最大有功功率 |
| 最小功率因数位移 |
4.6.2.2 Operational Status Information运行状态信息
Aggregators acting for its DERs and DER Clients SHALL have the capability to report the dynamic Operational Status Information shown in Table 5. The frequency of reporting will be specified in each utility’s Interconnection Handbook or contracts/programs.
代表其DER和DER客户的聚合商应能够报告表5中所示的动态操作状态信息。报告频率将在每个公用事业公司的《互连手册》或合同/程序中指定。
| 运行状态信息 |
|---|
| 工作状态 |
| 连接状态 |
| 告警状态 |
| 运营储能能力 |
4.6.3 Alarms告警
Aggregators acting for its DERs and DER Clients SHALL have the capability to report the alarm data shown in Table 6 as they occur. For each alarm, there is a corresponding “return to normal” message. All alarms and their “return to normal” messages SHALL include a date-time stamp along with the alarm type. The frequency of reporting of alarms will be specified in each utility’s Interconnection Handbook or contracts/programs.
充当其DER和DER客户的聚合器应具有报告表6中显示的警报数据的能力。 对于每个警报,都有一条相应的“恢复正常”消息。 所有警报及其“恢复正常”消息均应包括日期时间戳以及警报类型。 报告警报的频率将在每个公用事业公司的《互连手册》或合同/程序中指定。
| 告警 |
|---|
| 过流 |
| 过压 |
| 欠压 |
| 过频 |
| 欠频 |
| 电压不平衡 |
| 电流不平衡 |
| 本地紧急情况 |
| 远程紧急情况 |
| 低输入功率 |
| 相位旋转 |
By design, low-level equipment health and status information is not part of this interface as the utility does not have maintenance responsibility for these 3rd party operated systems.
通过设计,低级设备运行状况和状态信息不属于该界面,因为该实用程序对这些第三方操作系统不承担维护责任。