Springboot学习笔记(五)——数据库事务处理
在互联网数据库的使用中,对于电商和金融网站可能面对高并发场景。因为存在高并发,数据库的数据将在一个多事务的场景下运行,在没有采取一定的手段的情况下就会造成数据的不一致。与此同时,网站也会面临巨大的性能压力。面对这样的高并发场景,数据库的事务机制是至关重要的,它能够帮助我们在一定的程度上保证数据的一致性,并且有效提高系统性能,避免系统宕机。
springboot配置数据库信息
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_boot_chapter06?serverTimezone=UTC
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=root
#spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
#最大等待连接数,设0为没有限制
spring.datasource.tomcat.max-idle=10
#最大等待毫秒数,单位ms,超过时间会出错误信息
spring.datasource.tomcat.max-wait=10000
#数据库连接池初始化连接数
spring.datasource.tomcat.initial-size=5
#日志配置
#logging.level.root=debug
#logging.level.org.springframework=debug
#logging.level.org.org.mybatis=debug
logging.file=mylog.log
#mybatis映射文件通配
mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:com/springboot/chapter06/mapper/*.xml
#mybatis扫描别名包,和注解@Alias联用
mybatis.type-aliases-package=com.springboot.chapter06.pojo
#配置typeHandler的扫描包
mybatis.type-handlers-package=com.springboot.chapter06.typehandler
#1 读未提交
#2 读已提交
#3 可重复读
#4 串行化
#Tomcat数据源默认隔离级别
spring.datasource.tomcat.default-transaction-isolation=2
#bcp2数据库连接池默认隔离级别
#spring.datasource.dbcp2.default-transaction-isolation=2
JDBC的数据库事务
package com.springboot.chapter06.service.impl;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import com.springboot.chapter06.enumeration.SexEnum;
import com.springboot.chapter06.pojo.User;
import com.springboot.chapter06.service.JdbcService;
@Service
public class JdbcServiceImpl implements JdbcService {
@Autowired
private DataSource dataSource = null;
@Override
public int insertUser(String user_name,Integer sex,String note) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
User user = new User();
user.setUser_name(user_name);
user.setSex(SexEnum.getSexEnumById(sex));
user.setNote(note);
Connection conn = null;
int result = 0;
try {
conn = dataSource.getConnection();
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement("insert into t_user (user_name,sex,note) values (?,?,?)");
ps.setString(1, user.getUser_name());
ps.setInt(2, user.getSex().getId());
ps.setString(3, user.getNote());
result = ps.executeUpdate();
conn.commit();
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
if(conn!=null) {
try {
conn.rollback();
} catch (SQLException e1) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
if(conn!=null&&!conn.isClosed()) {
conn.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return result;
}
}
在上述代码中,业务代码只有PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement("insert into t_user (user_name,sex,note) values (?,?,?)"); ps.setString(1, user.getUser_name()); ps.setInt(2, user.getSex().getId()); ps.setString(3, user.getNote()); result = ps.executeUpdate();这一部份,其他都是有关JDBC代码的功能,有数据库连接的获取和关闭以及事务的提交和回滚、大量的try…catch语句。所以代码的优化是显而易见的。在spring中,可以用AOP把公共的代码抽取出来,单独实现。除了有业务逻辑的部分也只是执行sql那一步骤,其他步骤都是比较固定的。按照aop的设计思想,就可以吧除执行sql这步之外的步骤抽取出来单独实现。
Spring声明式事务的使用
- spring声明式数据库事务约定
对于声明式事务,是通过@Transactional进行标注的。这个注解可以用在类或方法上,当标注在类上时,代表这个类所有public非静态的方法都将启用事务功能。在@Transaction中,还允许配置许多的属性,如事务的隔离级别、传播行为、异常类型等。这些配置内容,实在springioc容器在加载时就会将这些配置信息解析出来,然后把这些信息存到事务定义器(TransactionDefinition的接口实现类)里,并且记录哪些类或者方法需要启动事务功能,采取什么策略去执行事务。在这个过程中,只需要给事务的类或方法标注@Tranctional和配置其属性就可以。
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.READ_COMMITTED,timeout = 1)
public User getUser(Integer id) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return this.userDao.getUser(id);
}
- @Tranactional的配置项
package org.springframework.transaction.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.Documented;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Inherited;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import org.springframework.core.annotation.AliasFor;
import org.springframework.transaction.TransactionDefinition;
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
@Documented
public @interface Transactional {
//通过bean name指定事务管理器
@AliasFor("transactionManager")
String value() default "";
//同value属性
@AliasFor("value")
String transactionManager() default "";
//指定传播行为(默认required)
Propagation propagation() default Propagation.REQUIRED;
//指定隔离级别(默认default)
Isolation isolation() default Isolation.DEFAULT;
//指定超时时间(单位秒)
int timeout() default TransactionDefinition.TIMEOUT_DEFAULT;
//是否只读事务
boolean readOnly() default false;
//方法在发生指定异常时回滚,默认是所有异常都回滚
Class[] rollbackFor() default {};
//方法在发生指定异常名称时回滚,默认是所有异常都回滚
String[] rollbackForClassName() default {};
//方法在发生指定异常时不回滚,默认是所有异常都回滚
Class[] noRollbackFor() default {};
//方法在发生指定异常名称时不回滚,默认是所有异常都回滚
String[] noRollbackForClassName() default {};
}
- spring事务管理器
在spring中,事务管理器的顶层接口为PlatformTransactionManager。在引入其他框架时,还会有其他事务的管理器类,比如hibernate,spring包会提供HibernateTransactionManager与之对应给我们使用,这里用的是mybatis框架,最常用的事务管理器是DatasourceTransactionManager,他也是实现了接口PlatformTransactionManager,这个接口提供了getTransaction方法、commit方法和rollback方法。
在springboot中,当依赖了mybatis-sping-boot-starter之后,它会自动创建一个DatasourceTransactionManager对象,作为事务管理器,如果依赖于spring-boot-starter-data-jpa,则他会自动创建JpaTransactionManager对象作为事务管理器,所以一般不需要自己创建事务管理器而是直接使用他们即可 - 测试数据库事务
用户pojo
package com.springboot.chapter06.pojo;
import org.apache.ibatis.type.Alias;
import com.springboot.chapter06.enumeration.SexEnum;
@Alias(value = "user")
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String user_name;
private SexEnum sex; //枚举
private String note;
//get和set方法
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User [id=" + id + ", userName=" + user_name + ", sex=" + sex + ", note=" + note + "]";
}
}
性别枚举实现
package com.springboot.chapter06.enumeration;
public enum SexEnum {
MAIL(1,"男"),
FEMAIL(2,"女");
private int id;
private String name;
private SexEnum(int id, String name) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public static SexEnum getSexEnumById(int id) {
for (SexEnum sex : SexEnum.values()) {
if(sex.getId()==id) {
return sex;
}
}
return null;
}
}
枚举类型转换
package com.springboot.chapter06.typehandler;
import java.sql.CallableStatement;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import org.apache.ibatis.type.BaseTypeHandler;
import org.apache.ibatis.type.JdbcType;
import org.apache.ibatis.type.MappedJdbcTypes;
import org.apache.ibatis.type.MappedTypes;
import com.springboot.chapter06.enumeration.SexEnum;
//声明jdbcType为整型
@MappedJdbcTypes(JdbcType.INTEGER)
//声明javatype为SexEnum
@MappedTypes(value = SexEnum.class)
public class SexTypeHandler extends BaseTypeHandler {
@Override
public void setNonNullParameter(PreparedStatement ps, int i, SexEnum sex, JdbcType jdbcType)
throws SQLException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
ps.setInt(i, sex.getId());
}
@Override
public SexEnum getNullableResult(ResultSet rs, String columnName) throws SQLException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int sex = rs.getInt(columnName);
if(sex!=1&&sex!=2) {
return null;
}
return SexEnum.getSexEnumById(sex);
}
@Override
public SexEnum getNullableResult(ResultSet rs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int sex = rs.getInt(columnIndex);
if(sex!=1&&sex!=2) {
return null;
}
return SexEnum.getSexEnumById(sex);
}
@Override
public SexEnum getNullableResult(CallableStatement cs, int columnIndex) throws SQLException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int sex = cs.getInt(columnIndex);
if(sex!=1&&sex!=2) {
return null;
}
return SexEnum.getSexEnumById(sex);
}
}
mybatis接口
package com.springboot.chapter06.dao;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import com.springboot.chapter06.pojo.User;
@Repository
public interface UserDao {
public User getUser(Integer id);
public int insertUser(User user);
}
用户映射
insert into t_user (user_name,sex,note) values (#{user_name},#{sex},#{note})
用户服务接口和实现类
package com.springboot.chapter06.service;
import com.springboot.chapter06.pojo.User;
public interface UserService {
public User getUser(Integer id);
public int insertUser(User user);
}
package com.springboot.chapter06.service.impl;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Isolation;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import com.springboot.chapter06.dao.UserDao;
import com.springboot.chapter06.pojo.User;
import com.springboot.chapter06.service.UserService;
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao = null;
@Override
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.READ_COMMITTED,timeout = 1)
public User getUser(Integer id) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return this.userDao.getUser(id);
}
@Override
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.READ_COMMITTED,timeout = 1)
public int insertUser(User user) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return this.userDao.insertUser(user);
}
}
测试数据库事务
package com.springboot.chapter06.controller;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import com.springboot.chapter06.enumeration.SexEnum;
import com.springboot.chapter06.main.UserBatchService;
import com.springboot.chapter06.pojo.User;
import com.springboot.chapter06.service.UserService;
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService = null;
@Autowired
private UserBatchService userBatchService = null;
@RequestMapping("/getUser")
@ResponseBody
public User getUser(Integer id) {
return this.userService.getUser(id);
}
@RequestMapping("/insertUser")
@ResponseBody
public Map insertUser(String user_name, Integer sex, String note) {
User user = new User();
user.setUser_name(user_name);
user.setSex(SexEnum.getSexEnumById(sex));
user.setNote(note);
int result = this.userService.insertUser(user);
Map map = new HashMap();
map.put("success", result == 1);
return map;
}
}
配置mybatis
#mybatis映射文件通配
mybatis.mapper-locations=classpath:com/springboot/chapter06/mapper/*.xml
#mybatis扫描别名包,和注解@Alias联用
mybatis.type-aliases-package=com.springboot.chapter06.pojo
#配置typeHandler的扫描包
mybatis.type-handlers-package=com.springboot.chapter06.typehandler
springboot启动文件
package com.springboot.chapter06.main;
import javax.annotation.PostConstruct;
import org.mybatis.spring.annotation.MapperScan;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
import org.springframework.transaction.PlatformTransactionManager;
@SpringBootApplication(scanBasePackages = "com.springboot.chapter06")
@MapperScan(
basePackages = "com.springboot.chapter06",
annotationClass = Repository.class
)
public class Chapter06Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Chapter06Application.class, args);
}
//注入事务管理器,由springboot自动生成
@Autowired
PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager = null;
//使用后初始化方法,观察自动生成的事务管理器
@PostConstruct
public void viewTranstractionManager() {
System.out.println(transactionManager.getClass().getName());
}
}
隔离级别
spring事务机制中最重要的两个配置项,即隔离级别和传播行为
数据库事务具有以下4个基本特征:
- 原子性:事务中包含的操作被看作一个整体的业务单元,这个业务单元中的操作要么全部成功,要么全部失败
- 一致性:事务在完成时,必须所有的数据保持在一致状态,在数据库中所有的修改基于事务,保证数据的完整性
- 隔离性:事务允许多个用户对同一个数据进行并发访问,而不破坏数据的正确性 和完整性。同时,并行事务的修改必须与其他并行事务的修改相互独立
- 持久性:事物结束后,所有的数据会固化到一个地方,即使断电重启后也可以提供给应用程序访问
在多个事务同时操作数据的情况下,会引发丢失更新的场景。
第一类丢失更新:一个事物回滚另外一个事务提交而引发的数据不一致的情况
第二类丢失更新:多个事务提交引发的丢失更新
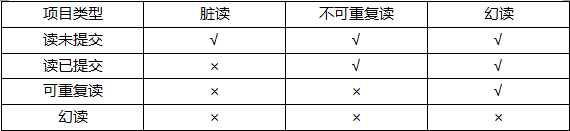
- 读未提交
最低的隔离级别,允许一个事务读取另一个事务未提交的数据,会产生脏读 - 读已提交
一个事物只能读取另一个事务已提交的数据,不能读取未提交的数据,克服了脏读,产生了不可重复读 - 可重复读
克服读已提交中出现的不可重复读的现象,会产生幻读
幻读和可重复读的区别是:幻读不是针对一条数据库记录而言,而是多条记录,例如多条交易笔数就是多条数据库记录统计出来的;而可重复读是针对数据库的单一条记录,例如商品的库存是以一条记录存储的。 - 串行化
数据库的最高隔离级别,他会要求所有的sql都会按照顺序执行,这样就可以克服上述隔离级别出现的各种问题,所以他能够完全保证数据的一致性 - 使用合理的隔离级别
追求更高的隔离级别,能更好的的保证数据的一致性,但是也要付出锁的代价。有了锁,就意味着性能的丢失,而且隔离级别越高,性能就直线下降。所以在选择隔离级别时,要考虑的不单单是数据一致性的问题,还要考虑系统性能的问题。
一般而言,选择隔离级别会以读已提交为主。对于隔离级别,不同的数据库的支持也不一样,Oracle只能支持读已提交和串行化,而MySQL能够支持4种。Oracle默认的隔离级别是读已提交,MySQL的是可重复读。需要根据具体的数据库来决定。使用隔离级别只需要在@Transactional配置即可。
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.READ_COMMITTED,timeout = 1)
public User getUser(Integer id) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return this.userDao.getUser(id);
}
在springboot的application.properties中配置默认的隔离级别
#1 读未提交
#2 读已提交
#3 可重复读
#4 串行化
#Tomcat数据源默认隔离级别
spring.datasource.tomcat.default-transaction-isolation=2
#bcp2数据库连接池默认隔离级别
#spring.datasource.dbcp2.default-transaction-isolation=2
传播行为
传播行为是方法之间调用事务采取的策略问题。
在一个批量事务执行的过程中,调用多个交易时,如果有一些交易发生异常,只是回滚那些出现异常的交易,而不是整个批量任务,这样就能够使得那些没有问题的交易可以顺利完成,而有问题的交易则不做任何事情。
在spring中,当一个方法调用另外一个方法时,可以让事务采取不同的策略工作,如新建事务或挂起当前事务等,这就是事务的传播行为。
在spring事务机制中对数据库存在7种传播行为,他是通过枚举类Propagation
package org.springframework.transaction.annotation;
import org.springframework.transaction.TransactionDefinition;
public enum Propagation {
/**
* 需要事务,默认的传播行为,如果当前存在事务,就沿用当前事务,否则新建一个事务运行子方法
*/
REQUIRED(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRED),
/**
* 支持事务,如果当前存在事务,就沿用当前事务,如果不存在,则继续采用无事务的方式运行子方法
*/
SUPPORTS(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_SUPPORTS),
/**
* 必须使用事务,如果当前没有事务,就抛出异常,如果存在当前事务,就沿用当前事务
*/
MANDATORY(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_MANDATORY),
/**
*无论当前事务是否存在,都会创建新事物运行方法,这样新事物就可以拥有新的锁和隔离级别等特性,与当前事务相互独立
*/
REQUIRES_NEW(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_REQUIRES_NEW),
/**
*不支持事务,当前存在事务,将挂起事务,运行方法
*/
NOT_SUPPORTED(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NOT_SUPPORTED),
/**
*不支持事务,如果当前方法存在事务,则抛出异常,否则继续使用无事务机制运行
*/
NEVER(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NEVER),
/**
* 在当前方法调用子方法时,如果子方法发生异常,只回滚子方法执行过的sql,而不回滚当前方法的事务
*/
NESTED(TransactionDefinition.PROPAGATION_NESTED);
private final int value;
Propagation(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
public int value() {
return this.value;
}
}
测试传播行为
批量更新用户
package com.springboot.chapter06.main;
import java.util.List;
import com.springboot.chapter06.pojo.User;
public interface UserBatchService {
public int insertUser1(List userList);
public int insertUser2(List userList);
public int insertUser3(List userList);
}
package com.springboot.chapter06.service.impl;
import java.util.List;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Isolation;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Propagation;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
import com.springboot.chapter06.main.UserBatchService;
import com.springboot.chapter06.pojo.User;
import com.springboot.chapter06.service.UserService;
@Service
public class UserBatchServiceImpl implements UserBatchService {
@Autowired
private UserService userService = null;
@Override
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.READ_COMMITTED,propagation = Propagation.REQUIRED)
public int insertUser1(List userList) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int count = 0;
for (User user : userList) {
count+=this.userService.insertUser(user);
}
return count;
}
@Override
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.READ_COMMITTED,propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
public int insertUser2(List userList) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int count = 0;
for (User user : userList) {
count+=this.userService.insertUser(user);
}
return count;
}
@Override
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.READ_COMMITTED,propagation = Propagation.NESTED)
public int insertUser3(List userList) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int count = 0;
for (User user : userList) {
count+=this.userService.insertUser(user);
}
return count;
}
}
// 测试REQUIRED传播行为
@RequestMapping("/insertUsers1")
@ResponseBody
public Map insertUsers1(String user_name1, Integer sex1, String note1, String user_name2,
Integer sex2, String note2) {
User user1 = new User();
user1.setUser_name(user_name1);
user1.setSex(SexEnum.getSexEnumById(sex1));
user1.setNote(note1);
User user2 = new User();
user2.setUser_name(user_name2);
user2.setSex(SexEnum.getSexEnumById(sex2));
user2.setNote(note2);
List userList = new ArrayList();
userList.add(user1);
userList.add(user2);
int inserts = this.userBatchService.insertUser1(userList);
Map result = new HashMap();
result.put("success", inserts > 0);
result.put("user", userList);
return result;
}
// 测试REQUIRES_NEW传播行为
@RequestMapping("/insertUsers2")
@ResponseBody
public Map insertUsers2(String user_name1, Integer sex1, String note1, String user_name2,
Integer sex2, String note2) {
User user1 = new User();
user1.setUser_name(user_name1);
user1.setSex(SexEnum.getSexEnumById(sex1));
user1.setNote(note1);
User user2 = new User();
user2.setUser_name(user_name2);
user2.setSex(SexEnum.getSexEnumById(sex2));
user2.setNote(note2);
List userList = new ArrayList();
userList.add(user1);
userList.add(user2);
int inserts = this.userBatchService.insertUser2(userList);
Map result = new HashMap();
result.put("success", inserts > 0);
result.put("user", userList);
return result;
}
// 测试NESTED传播行为
@RequestMapping("/insertUsers3")
@ResponseBody
public Map insertUsers3(String user_name1, Integer sex1, String note1, String user_name2,
Integer sex2, String note2) {
User user1 = new User();
user1.setUser_name(user_name1);
user1.setSex(SexEnum.getSexEnumById(sex1));
user1.setNote(note1);
User user2 = new User();
user2.setUser_name(user_name2);
user2.setSex(SexEnum.getSexEnumById(sex2));
user2.setNote(note2);
List userList = new ArrayList();
userList.add(user1);
userList.add(user2);
int inserts = this.userBatchService.insertUser3(userList);
Map result = new HashMap();
result.put("success", inserts > 0);
result.put("user", userList);
return result;
}
@Transactional自调用失效问题
在上述代码中,使用了一个UserBatchServiceImpl类去调用UserServiceImpl类的方法,那么如果不创建UserBatchServiceImpl类,而只是使用UserServiceImpl类进行批量插入,@Transactional就会失效
package com.springboot.chapter06.service.impl;
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao = null;
@Override
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.READ_COMMITTED,timeout = 1,propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
public int insertUser(User user) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return this.userDao.insertUser(user);
}
@Override
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.READ_COMMITTED,propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
public int insertUsers(List userList) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int count = 0;
for (User user : userList) {
//调用自己类自身的方法,产生自调用问题
count+=insertUser(user);
}
return count;
}
}
spring数据库事务的约定,其实现原理是AOP,而AOP的原理是动态代理,在自调用的过程中,是类自身的调用,而不是代理对象去调用,那么就不会产生AOP,这样spring就不能把代码织入到约定的流程中,就产生了失效的场景。可以使用代理对象执行插入用户,克服自调用问题
package com.springboot.chapter06.service.impl;
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService,ApplicationContextAware {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao = null;
private ApplicationContext applicationContext = null;
//实现生命周期方法,设置IOC容器
@Override
public void setApplicationContext (ApplicationContext applicationContext )throws BeansExecption{
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
@Override
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.READ_COMMITTED,timeout = 1,propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
public int insertUser(User user) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return this.userDao.insertUser(user);
}
@Override
@Transactional(isolation = Isolation.READ_COMMITTED,propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
public int insertUsers(List userList) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int count = 0;
//从IOC容器中取出代理对象
UserService userService = applicationContext.getBean(UserService .class);
for (User user : userList) {
//使用代理对象调用方法插入用户,此时会织入spring数据库事务流程中
count+=userService .insertUser(user);
}
return count;
}
}